String 클래스
-
문자열 = 문자의 나열
-
캐릭터 배열로 다뤄도 됨
-
자바는 스트링 클래스에서 다룸~
-
뭐가 다르냐면 문자열 배열에 메서드 기능을 추가한 것!
String = char[] + 메서드(기능) //문자배열에 관련된 기능을 추가해둔것
-
스트링 클래스 - 내용 변경 x (read only)
스트링 클래스의 주요 메서드
1. charAt(int index) = 문자열에서 해당 위치(인덱스)에 있는 문자를 반환
ex) String str = “abcde”;
char ch = str.charAt(3); => d 반환2. int length() = 문자열의 길이를 반환한다.
ex) str.length() = 53. String substring(int from, int to) = 문자열에서 해당범위의 문자열을 반환한다.(to는 포함 안 됨)
4. boolean equals(Object obj) = 문자열의 내용이 같은지 확인, (==불가) 같으면 트루 다르면 폴스
5. char[] toCharArray() = 스트링을 캐릭터로 바꿀때
* 문자열의 길이는 () 괄호 써주기! 배열은 안써도 되고!!

-
str.length() // 문자열의 길이
-
charAt(i) // 문자열 중 인덱스 번호 하나를 꺼내는 것, 하나씩 쪼개면 문자(열)이 아닌 문자로 받아야함
// 그래서 차형으로 받고, 하나식 쪼개자~
-
문자열 비교는 == 사용할 수 없고, .equals("") 사용!
예제문제를 풀어보자 ~
ex1.
입력받은 문자열 분석하기!
문자열을 입력 : abcdeabcdABCD123%%AB
A - 4 개나옴 (대소문자구분없이)
B - 4
C - 3
D - 3
E - 1
없는거는 안나오게!
나의 풀이
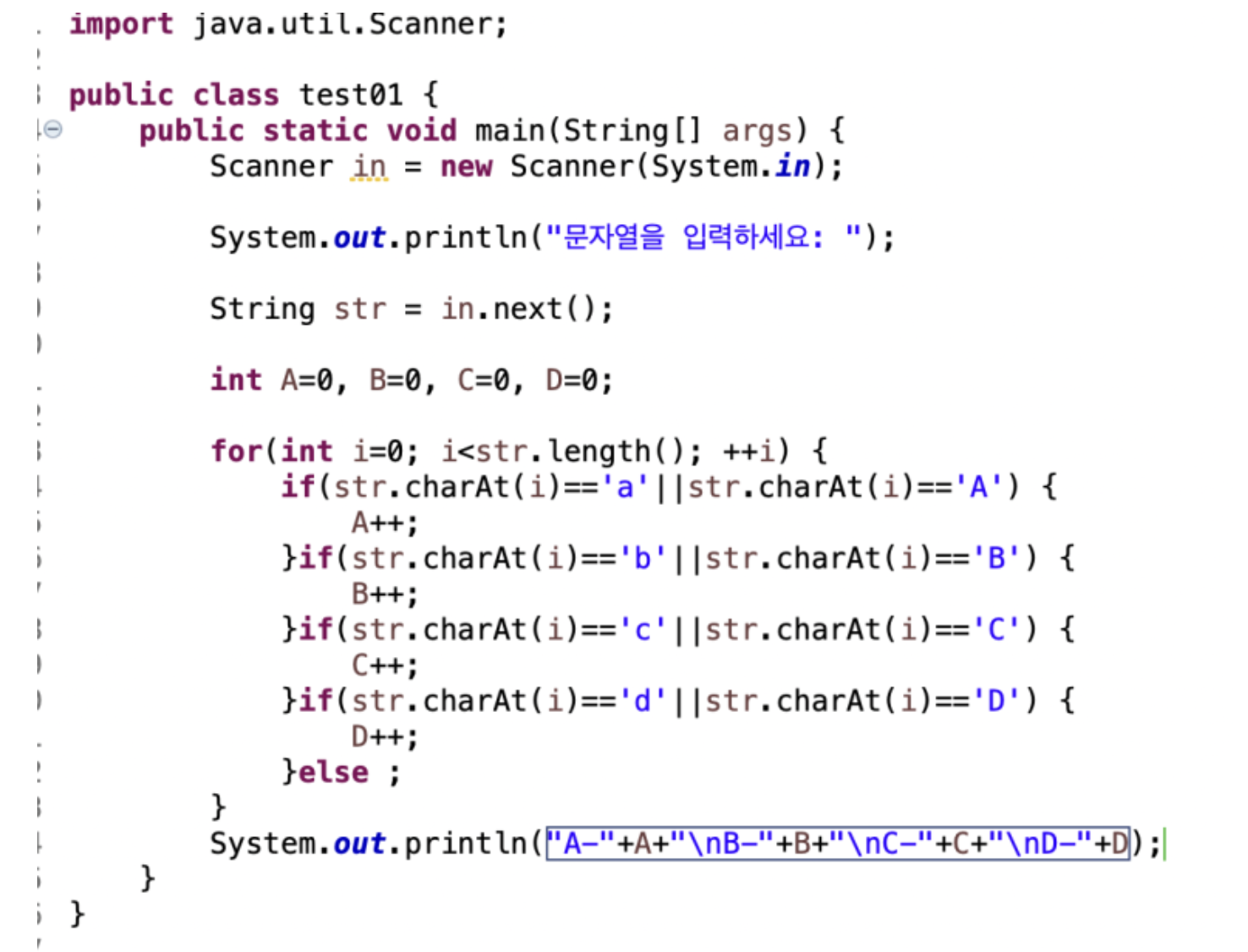
-
단순하고 복잡,,^^
-
근데 오류가 있음, 나는 E까지 하라고 이해했는데 ~ 문제에서 생략한것이지 a~z까지 다 표현하래@@
-
같은 방식으로 26개를 해도 되겠지만, 시간낭비. 아래는 간단한 형식으로 풀이
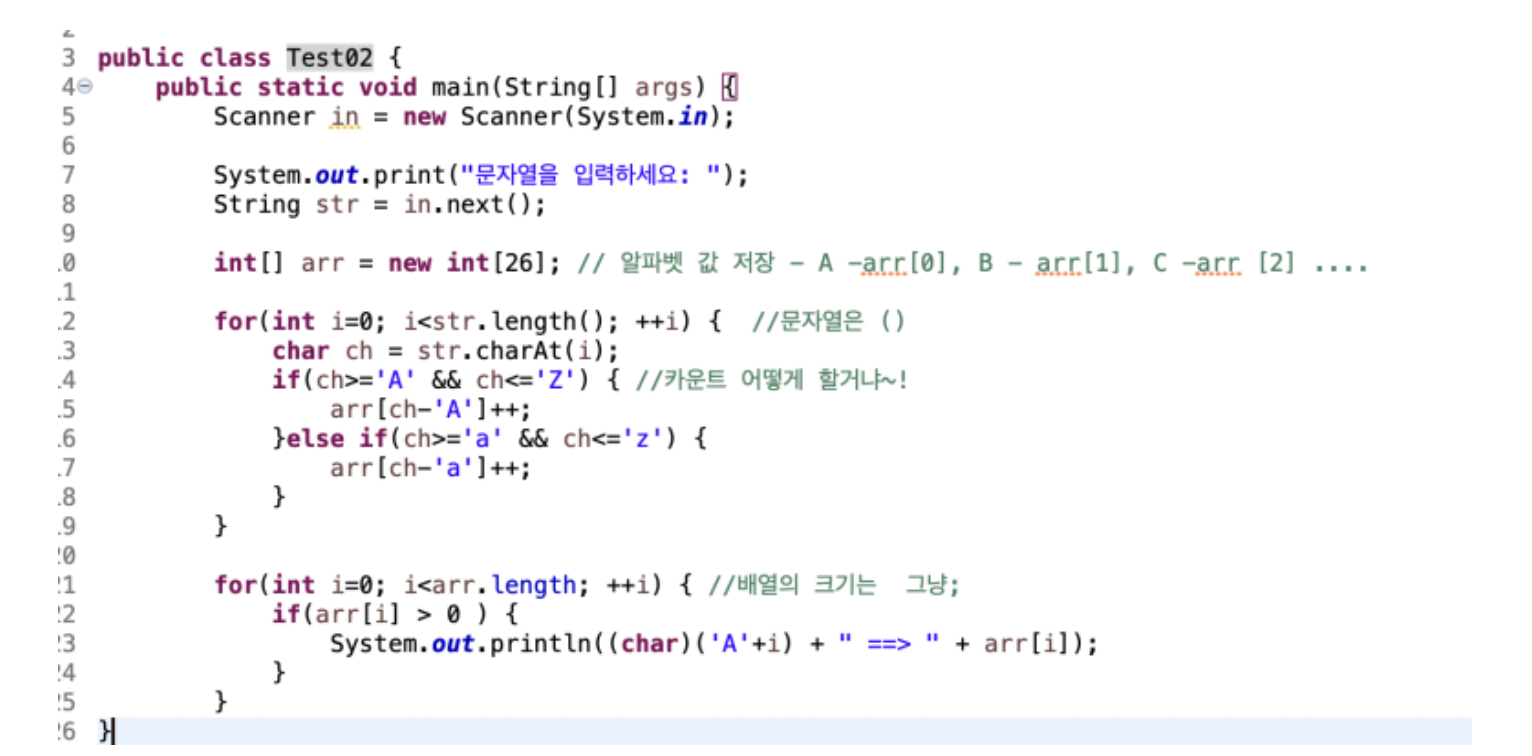
-
알파벳을 담을 방을 준비, 알파벳이 26개니까 배열로 생성
-
0번방을 A , 1번방을 B, (...) 26번방을 Z로 가정하고
-
대문자 소문자를 구분해서, charAt으로 뽑아낸 그 문자를!
-
arr[ch-'A']++; 해줌 // 무슨 뜻이냐면 ~ 예를들어 입력된 ch = A라면 a-a를 뺀 0번방이 ++가 된다.
-
마찬가지로 ch가 B라면, b-a를 뺀 값 1, 1번방이 ++가 된다, 그 문자를 알아내어 해당 되는 숫자 방을 ++해줌
-
다음으로 출력시 'A'+i 방을 문자로 나타내기 위해 캐릭터형으로 형변환해주고~ 각 배열의 방 숫자를 출력해!
*** C(67)의 경우 ch = 67 - 'A(65)' = a[2] : ++;
ex2.
10진수의 수를 입력하면 2진수로 나타내는 프로그램
10진수 수를 입력 : 10
10의 2진수는 : 101010
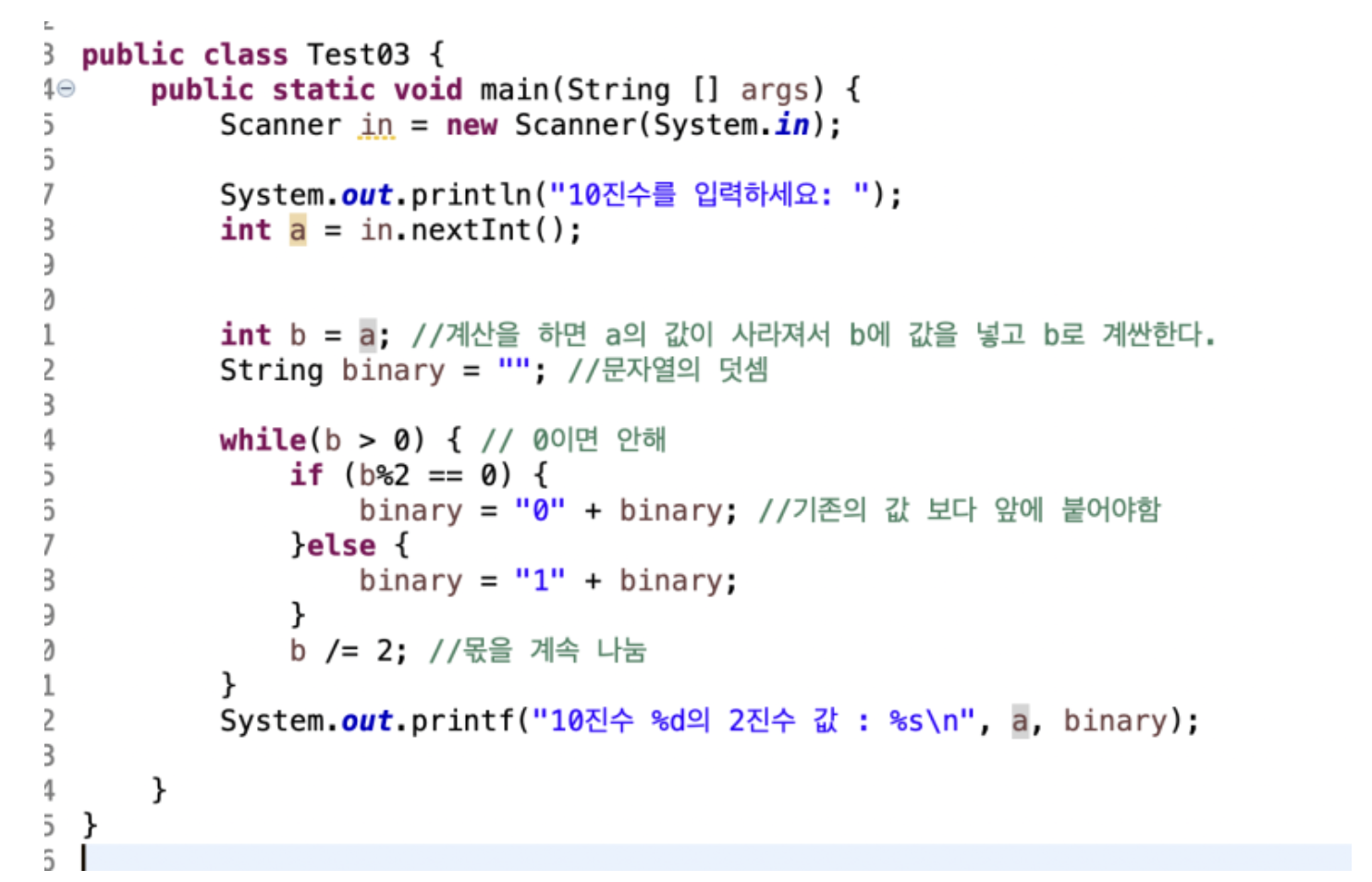
-
계산하면 값이 바뀌니 같은 값을 두개로 저장해 두고,
-
문자열의 덧셈을 하기위해 "" 공백을 만들어줌 ,
-
입력된 값이 0보다 클때를 가정해서, 계속 2로 나눠줌 , 그럴때 나머지가 0이면 공백앞에 0 을 붙여주고,
-
나머지가 0이아니면 1을 붙여준다, 0 -> 10 -> 010-> 이런식으로 계속 앞에 붙어 나가면 2진수 찾기 가능
ex3.
2진수를 10진수로!
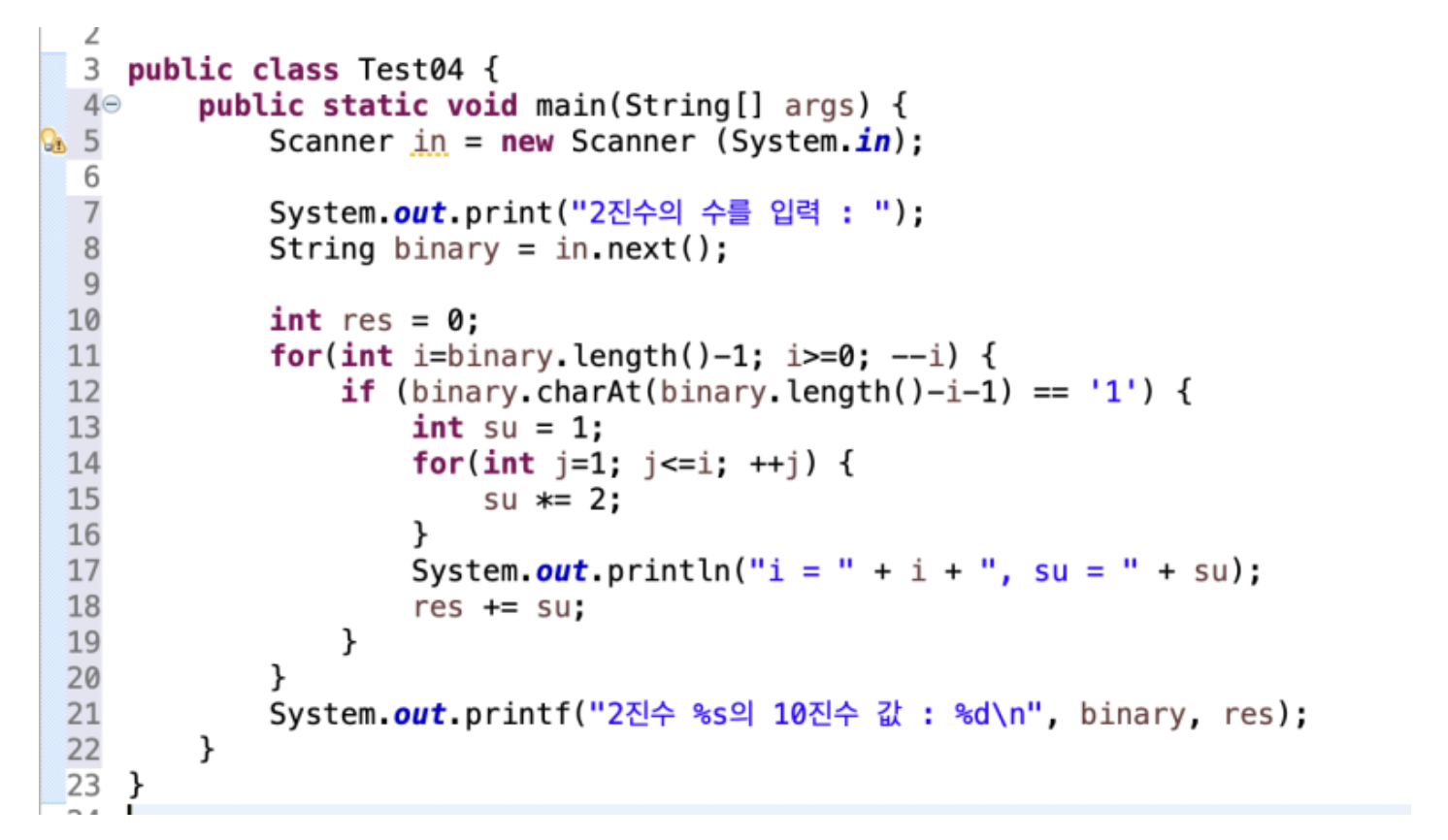
-
시작을 맨 뒤에서부터! str의 렌스-1 !! ~ 0까지 오자, (난 ㅇ런생각 왜못하는거야 ㅠ 슬픔)
-
숫자를 하나하나 뽑아내면서, // charAt(str.length()-i-1) // 이게 오른쪽 끝에서부터 올라오는 방식
-
그 끝이 1이면? 숫자는 1이되고 , 2씩 곱해줘!!

- 살짝 다르게 풀이! 시작점을 다르게 ~ 방식은 같은듯 나중에 한번 풀어봅시다!
++ 시간날 때 풀어봐, 아마도 안풀겠지만.^^

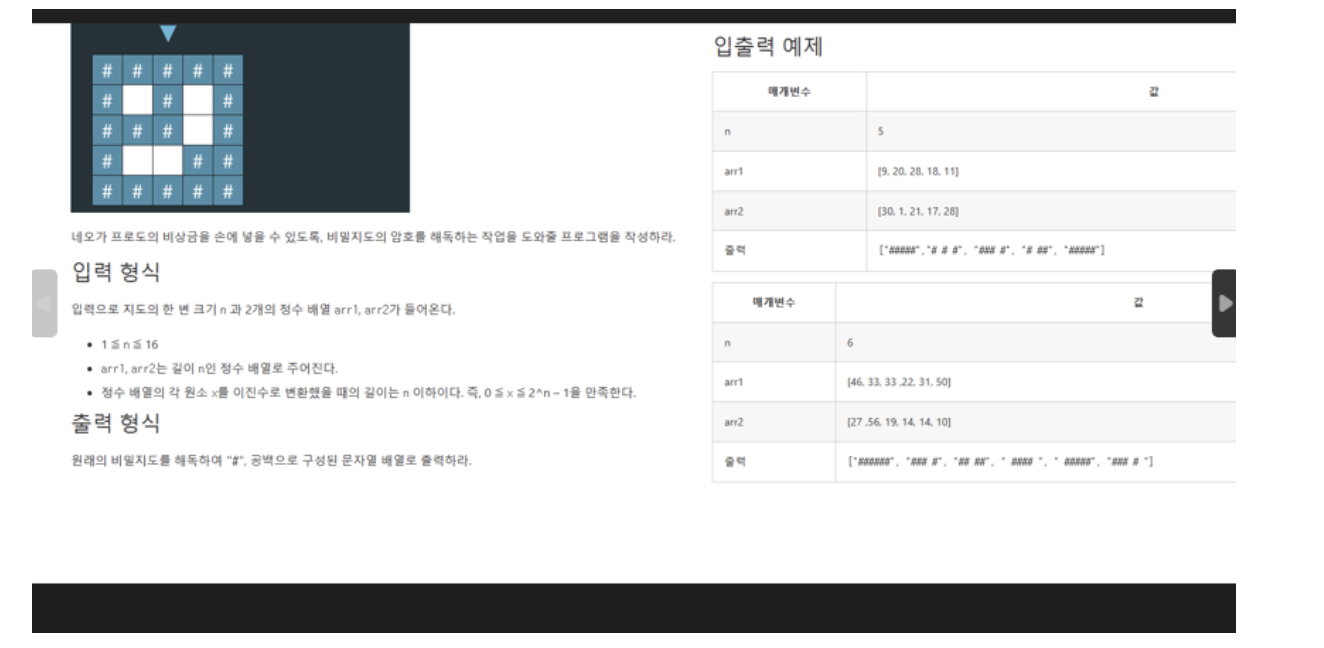
풀이
import java.util.*;
public class Exam_05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("지도의 크기를 입력 : ");
int n = in.nextInt();
//입력받을 최대값을 구하기 위해...
int max = 1;
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i) {
max *= 2;
} //자바에서는 제곱값이없음
max--; //0부터 계산을 하기 때문에
int arr1[] = new int[n];
int arr2[] = new int[n];
//초기값 입력
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i) {
do {
System.out.printf("지도 1의 %d번째 수 : ", i+1);
arr1[i] = in.nextInt();
}while(arr1[i]<0 || arr1[i]>max);
}
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i) {
do {
System.out.printf("지도 2의 %d번째 수 : ", i+1);
arr2[i] = in.nextInt();
}while(arr2[i]<0 || arr2[i]>max);
}
//계산하기
String[] res = new String[n]; //
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i) {
res[i] = "";
//첫번째 입력값을 2진수로...
String binary1 = "";
int su = arr1[i];
for(int j=0; j<n; ++j) {
if (su%2 == 0) {
binary1 = "0" + binary1;
}else {
binary1 = "1" + binary1;
}
su /= 2;
}
//두번째 입력값을 2진수로...
String binary2 = "";
int su2 = arr2[i];
for(int j=0; j<n; ++j) {
if (su2%2 == 0) {
binary2 = "0" + binary2;
}else {
binary2 = "1" + binary2;
}
su2 /= 2;
}
System.out.println(binary1 + " , " + binary2);
//입력된 첫번째수와 두번째수를 비교
for(int j=0; j<n; ++j) {
if (binary1.charAt(j) =='0' && binary2.charAt(j) == '0') {
res[i] += " ";
}else {
res[i] += "#";
}
}
}
//최종 결과 출력
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i) {
System.out.println(res[i]);
}
}
}
}
- 이차원배열로 풀이
import java.util.*;
public class Exam_06052 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("지도의 크기를 입력 : ");
int n = in.nextInt();
//입력받을 최대값을 구하기 위해...
int max = 1;
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i) {
max *= 2;
}
max--; //0부터 계산을 하기 때문에
int arr1[][] = new int[n][n];
int arr2[][] = new int[n][n];
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i) {
int su;
do {
System.out.printf("지도 1의 %d번째 수 : ", i+1);
su = in.nextInt();
}while(su<0 || su>max);
for(int j=0; j<n; ++j) {
if (su%2 == 0) arr1[i][n-j-1] = 0;
else arr1[i][n-j-1] = 1;
su /= 2;
}
}
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i) {
int su;
do {
System.out.printf("지도 2의 %d번째 수 : ", i+1);
su = in.nextInt();
}while(su<0 || su>max);
for(int j=0; j<n; ++j) {
if (su%2 == 0) arr2[i][n-j-1] = 0;
else arr2[i][n-j-1] = 1;
su /= 2;
}
}
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i) {
for(int j=0; j<n; ++j) {
if (arr1[i][j] == 0 && arr2[i][j] == 0) System.out.print(" ");
else System.out.print("#");
}
System.out.println();
}
/*
int arr1[] = new int[n];
int arr2[] = new int[n];
//초기값 입력
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i) {
do {
System.out.printf("지도 1의 %d번째 수 : ", i+1);
arr1[i] = in.nextInt();
}while(arr1[i]<0 || arr1[i]>max);
}
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i) {
do {
System.out.printf("지도 2의 %d번째 수 : ", i+1);
arr2[i] = in.nextInt();
}while(arr2[i]<0 || arr2[i]>max);
}
//계산하기
String[] res = new String[n];
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i) {
res[i] = "";
//첫번째 입력값을 2진수로...
String binary1 = "";
int su = arr1[i];
for(int j=0; j<n; ++j) {
if (su%2 == 0) {
binary1 = "0" + binary1;
}else {
binary1 = "1" + binary1;
}
su /= 2;
}
//두번째 입력값을 2진수로...
String binary2 = "";
int su2 = arr2[i];
for(int j=0; j<n; ++j) {
if (su2%2 == 0) {
binary2 = "0" + binary2;
}else {
binary2 = "1" + binary2;
}
su2 /= 2;
}
System.out.println(binary1 + " , " + binary2);
//입력된 첫번째수와 두번째수를 비교
for(int j=0; j<n; ++j) {
if (binary1.charAt(j) =='0' && binary2.charAt(j) == '0') {
res[i] += " ";
}else {
res[i] += "#";
}
}
}
//최종 결과 출력
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i) {
System.out.print(res[i]);
}
*/
}
}
++ 카카오 문제
다트게임

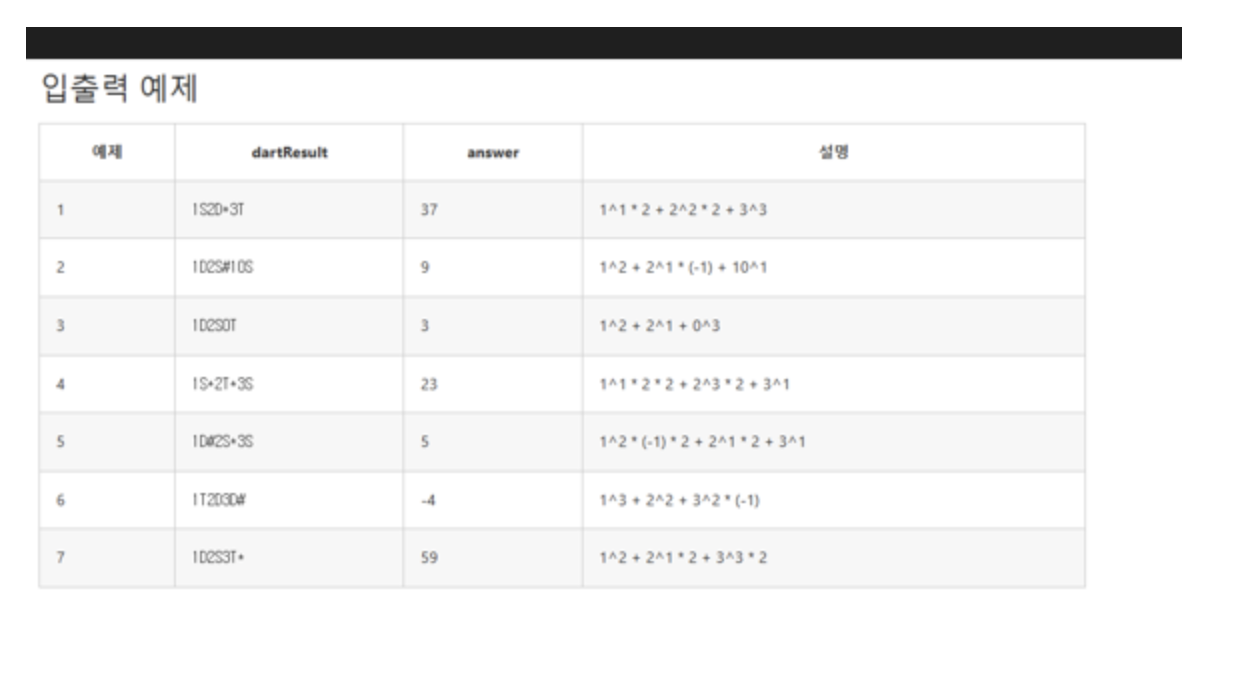
해설~
import java.util.*;
public class Exam_07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("다트 결과를 입력 : ");
String dart = in.next();
int res = 0; //전체 누적값
int a = 0; //현시점 계산값
int i = 0; //위치
int t = 0; //바로 전 계산값
while(i<dart.length()) {
char ch = dart.charAt(i);
if (ch>='0' && ch<='9') {
if (ch == '1' && dart.charAt(i+1) == '0') {
i++;
a = 10;
}else {
a = ch - 48;
}
i++;
}else if (ch=='S' || ch=='D' || ch=='T') {
switch(ch) {
//case 'S' : a = a*1; break;
case 'D' : a = a*a; break;
case 'T' : a = aaa; break;
}
i++;
if (i < dart.length()) {
if (dart.charAt(i)=='*' || dart.charAt(i)=='#') {
ch = dart.charAt(i);
switch(ch) {
case '' : res += (t + a) 2 - t; break;
//기존 누적값에서 바로전 계산값을 빼고, 바로전계산값과 현재 계산값을 * 2
//해서 누적을 시켜준다
case '#' : res -= a; break;
}
i++;
}else {
res += a;
}
}else {
res += a;
}
t = a;
}
}
System.out.println("결과 : " + res);
}
}
카카오 안가겠습니다!(못)
