금일은 지난 시간에 이어 Java 의 생산자 소비자 문제를 해결하기 위한 멀티스레드 자료 구조인 BlockingQueue 에 대해 알아보는 시간입니다. 말 그대로 스레드를 차단 할 수 있는 큐를 말합니다.
목차
- BlockingQueue
예제
BlockingQueue 는 인터페이스 이며 스레드 관점에서 보면 큐가 특정 조건이 만족될 때까지 스레드의 작업을 blocking 한다.
Queue 를 상속받으며 데이터 추가, 획득 메서드가 존재한다.
- add(), offer(), put(), offer(timeout)
- take(), poll(timeout), remove(..)
해당 구현체로는 다음과 같다.
- ArrayBlockingQueue : 배열 기반으로 구현되어 있고, 버퍼의 크기가 고정되어 있다.
- LinkedBlockingQueue : 링크 기반으로 구현되어 있고, 버퍼의 크기를 고정할 수도, 또는 무한하게 사용할 수
도 있다. - BlockingDeque : 동시성 자료 구조에 용이
수정된 put, take method
private BlockingQueue<String> queue;
public BoundedQueueV6_1(int max) {
this.queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(max);
}
@Override
public void put(String data) {
try {
queue.put(data);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Override
public String take() {
try {
return queue.take();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
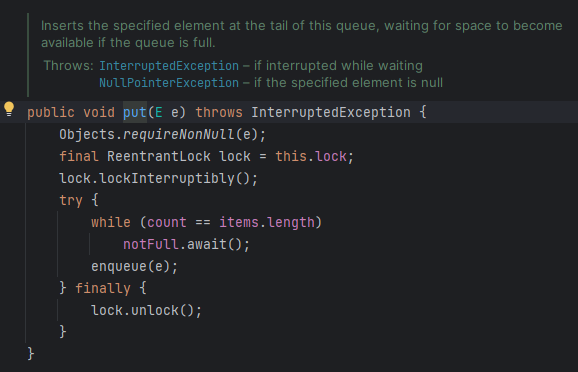
}put() 메서드에 들어가 ArrayBlockkingQueue 의 구현체를 보면 다양한 함수의 기능을 확인 가능합니다.
차이점으로는 lock.lock() 대신에
lock.lockInterruptibly() 을 사용한 점과, 내부 자료 구조의 차이 정도이다
기능 설명
큐가 가득 찼을 때 생각할 수 있는 선택지는 4가지가 있다.
- 예외를 던진다. 예외를 받아서 처리한다.
- 대기하지 않는다. 즉시 false 를 반환한다.
- 대기한다.
- 특정 시간 만큼만 대기한다.
해당 문제를 해결하기 위해 BlockingQueue 는 다양한 메서드를 제공한다.
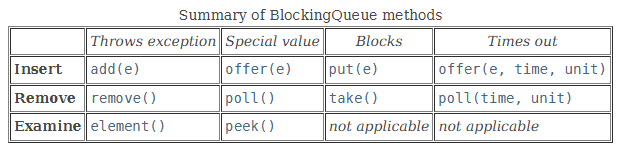
Throws Exception - 대기시 예외
- add(e): 지정된 요소를 큐에 추가하며, 큐가 가득 차면 IllegalStateException 예외를 던진다.
- remove(): 큐에서 요소를 제거하며 반환한다. 큐가 비어 있으면 NoSuchElementException 예외를 던진
다. - element(): 큐의 머리 요소를 반환하지만, 요소를 큐에서 제거하지 않는다. 큐가 비어 있으면
NoSuchElementException 예외를 던진다.
Special Value - 대기시 즉시 반환
- offer(e): 지정된 요소를 큐에 추가하려고 시도하며, 큐가 가득 차면 false 를 반환한다.
- poll(): 큐에서 요소를 제거하고 반환한다. 큐가 비어 있으면 null 을 반환한다.
- peek(): 큐의 머리 요소를 반환하지만, 요소를 큐에서 제거하지 않는다. 큐가 비어 있으면 null 을 반환한다.
Blocks - 대기
- put(e): 지정된 요소를 큐에 추가할 때까지 대기한다. 큐가 가득 차면 공간이 생길 때까지 대기한다.
- take(): 큐에서 요소를 제거하고 반환한다. 큐가 비어 있으면 요소가 준비될 때까지 대기한다.
- Examine (관찰): 해당 사항 없음.
Times Out - 시간 대기
- offer(e, time, unit): 지정된 요소를 큐에 추가하려고 시도하며, 지정된 시간 동안 큐가 비워지기를 기다리다가
시간이 초과되면 false 를 반환한다. - poll(time, unit): 큐에서 요소를 제거하고 반환한다. 큐에 요소가 없다면 지정된 시간 동안 요소가 준비되기를
기다리다가 시간이 초과되면 null 을 반환한다. - Examine (관찰): 해당 사항 없음.
해당 Method 들은 인터럽트를 제공한다
Method 예제
- offer(), poll()
@Override
public void put(String data) {
try {
// 대기 시간 설정 가능
boolean result = queue.offer(data, 1, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS);
log("저장 시도 결과 = " + result);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Override
public String take() {
try {
// 대기 시간 설정 가능
return queue.poll(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
버퍼가 가득차거나 데이터가 없다면 해당 시간 동안 기다리고 없다면 null 을 반환하게 된다.
- add(), remove()
public BoundedQueueV6_4(int max) {
this.queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(max);
}
@Override
public void put(String data) {
queue.add(data); // java.lang.IllegalStateException: Queue full
}
@Override
public String take() {
return queue.remove(); // java.util.NoSuchElementException
}
해당 method 는 대기 발생시 예외를 발생시킨다.
해당 생산자의 호출은 main method 이며 max 는 capacity 를 의미한다.
BlockingQueue 인터페이스를 바로 상속 받아도 아무 문제가 없다.