출처 : https://pozafly.github.io/javascript/event-loop-and-async/
들어가며
JavaScript를 하다 보면 async/await, Promise, setTimeout 등에서 예상치 못한 로그 순서를 마주하게 됩니다. 이번 글에서는 이벤트 루프, 콜 스택, 마이크로태스크, 콜백 큐를 중심으로 JavaScript의 비동기 실행 원리를 파헤쳐 보겠습니다.
async 함수는 언제 비동기일까?
async function asyncFunc() {
console.log("1. Start");
const data = await longRunningAsyncOperation(); // 논블로킹
console.log("3. End");
}
console.log("0. Before asyncFunc call");
asyncFunc();
console.log("2. After asyncFunc call");이 코드에서 로그 순서는 어떻게 될까요?
0. Before asyncFunc call
1. Start
2. After asyncFunc call
3. End포인트
asyncFunc()을 호출하면 바로 실행되며, 내부 코드도 await 전까지는 동기적으로 실행됨.
await을 만나면 해당 줄 이후는 마이크로태스크 큐에 등록되고, 나중에 실행된다.
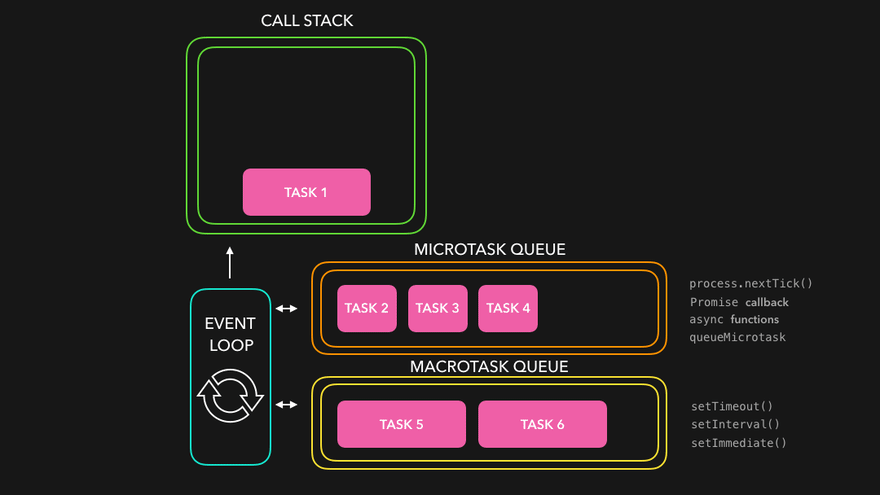
JavaScript 이벤트 루프 구조
JavaScript는 싱글 스레드 언어지만 비동기처럼 작동하는 이유는 이벤트 루프(Event Loop) 덕분입니다.
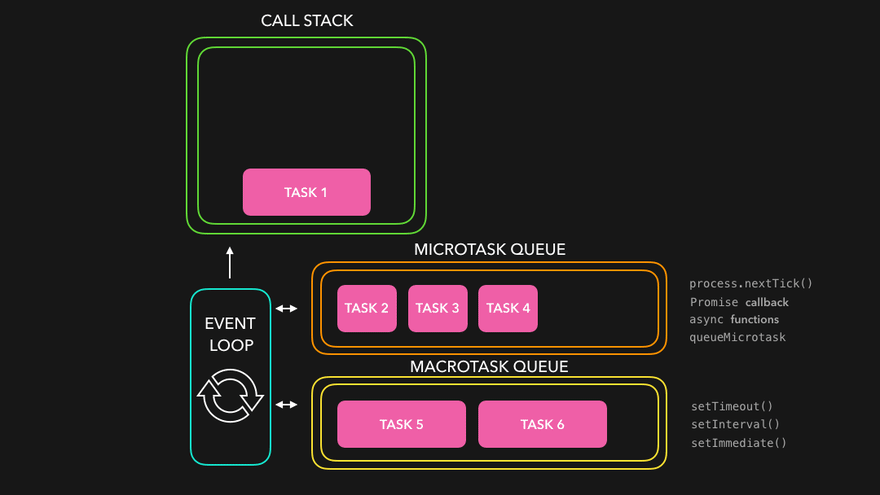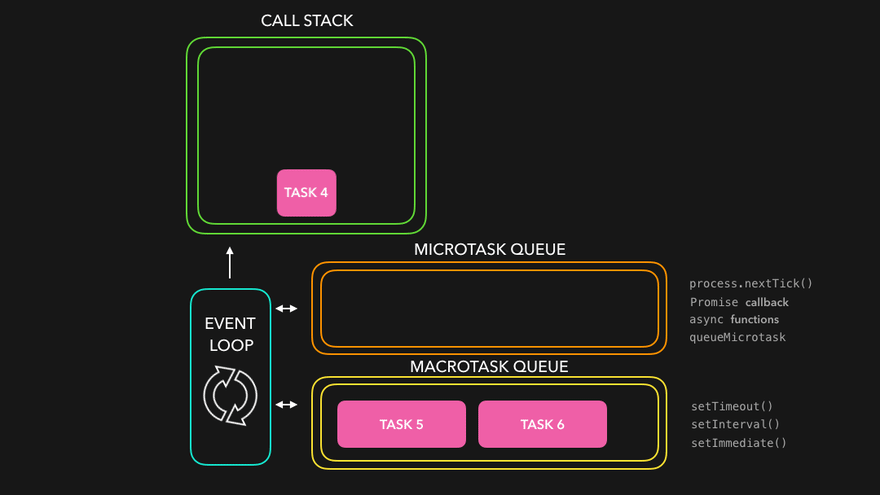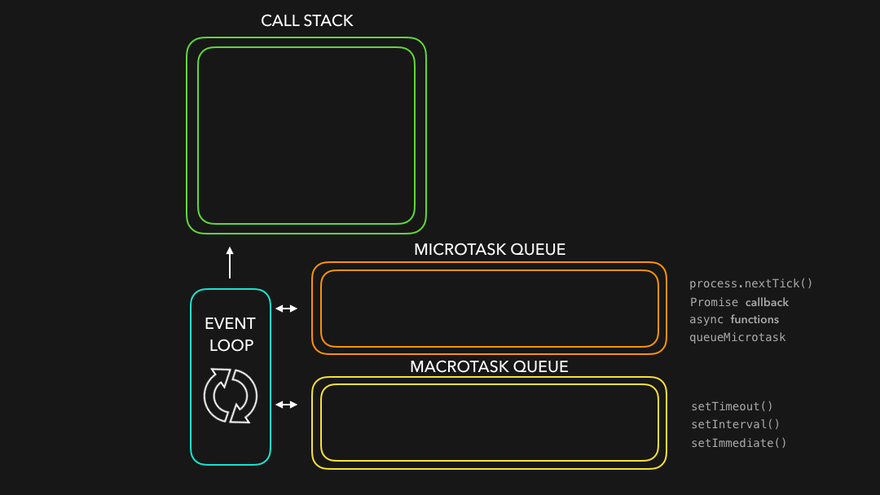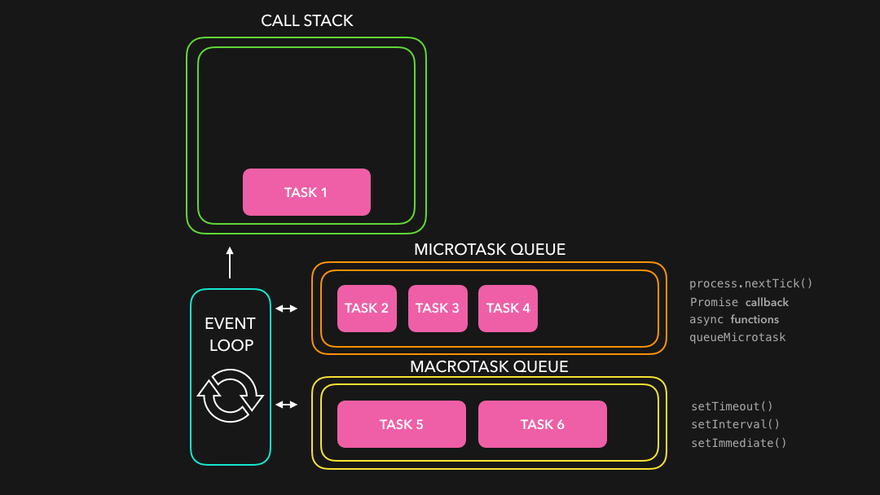
구성 요소
Call Stack : 실행 중인 함수들이 쌓이는 곳
Microtask Queue : Promise.then(), async/await, queueMicrotask() 등
Task Queue : (Callback Queue) setTimeout, setInterval, DOM 이벤트 등
Event Loop : 콜 스택이 비면 큐에서 작업을 꺼내 실행
실행 흐름 예제
console.log("1");
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("2 - setTimeout");
}, 0);
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log("3 - Promise");
});
console.log("4");실행 순서
1
4
3 - Promise
2 - setTimeout1, 4는 동기 코드이니까 즉시 실행됩니다.
Promise.then()은 마이크로태스크 큐 → 콜 스택이 비자마자 실행됩니다.
setTimeout()은 콜백 큐 → 마이크로태스크가 끝난 뒤 실행됩니다.
예제
async function run() {
console.log("1");
await Promise.resolve("result");
console.log("2");
}
run();
console.log("3");console.log("3");
console.log("3");console.log("3");console.log("3");console.log("3");console.log("3");
console.log("3");console.log("3");console.log("3");console.log("3");console.log("3");
console.log("3");console.log("3");console.log("3");console.log("3");console.log("3");
console.log("3");console.log("3");console.log("3");console.log("3");console.log("3");
console.log("3");console.log("3");console.log("3");console.log("3");console.log("3");
console.log("3");console.log("3");console.log("3");console.log("3");console.log("3");
console.log("3");console.log("3"); // 3이지만 오래걸리는 동기작업 이라고 생각실행 순서
1
3 (반복 출력)
2
console.log("2")는 await 이후라 마이크로태스크 큐에 들어감모든 동기 작업이 끝난 후 실행됨 (절대 끼어들지 않음!)
비유로 이해하는 구조
브라우저
├── Web API (setTimeout, fetch 등)
├── JavaScript Engine
│ ├── Call Stack
│ ├── Callback Queue
│ ├── Microtask Queue
│ └── Event Loop예를 들면
Web API = 무대 뒤 작업자들 (실제로 오래걸리는 일 작업중인 곳)
JS 엔진 = 무대 감독 (어떤 장면이 올라갈지 선택, 결정함)
Call Stack = 현재 무대 위 배우 (현재 작업중인 곳)
Microtask/Callback Queue = 대기 중인 장면들 (대기중인 작업)
Event Loop = 무대가 비었는지 확인하는 스태프 (다음 장면을 바로 올리는 스태프)
실전 예제: 순서 맞춰보세요!
console.log("A");
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("B - setTimeout");
}, 0);
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log("C - Promise");
});
(async () => {
console.log("D - async start");
await Promise.resolve();
console.log("E - after await");
})();
console.log("F");순서 해설
A
D - async start
F
C - Promise
E - after await
B - setTimeoutA, D, F는 동기
Promise.then() → 마이크로태스크 큐 C
await 이후 → 마이크로태스크 큐 E
setTimeout() → 콜백 큐 B
정리
async 함수 await 전까지는 동기적으로 실행된다. await 이후 코드는 마이크로태스크 큐에 등록된다. 마이크로태스크 큐 Promise.then, await, 우선순위 높음 콜백 큐 (Task Queue) setTimeout, DOM 이벤트 등 이벤트 루프 콜 스택이 비면 큐에서 작업을 꺼내 실행한다.