
💻 keep going
확실히 문제풀이를 할 때는 개념을 배우는 것보다 훨씬 어려운 것 같다.
💡 조건문 01
시속 50km 이하 -> 안전속도 준수!!
시속 50km 초과 -> 안전속도 위반!! 과태료 50,000원 부과 대상!!
speed = int(input("속도 입력 : "))
limitSpeed = 50
if speed <= limitSpeed :
print("안전속도 준수!!")
elif speed > limitSpeed :
print("안전속도 위반!! 과태료 50,000원 부과 대상!!")문자 길이 50 이하 -> SMS발송(50원 부과)
문자 길이 50 초과 -> MMS발송(100원 부과)
message = input("메세지 입력 : ")
lenMessage = len(message)
msgPrice = 50
if lenMessage <= 50 :
msgPrice = 50
print("SMS 발송!!")
if lenMessage > 50 : # 양자택일이니까 지우고 else : 도 가능!
msgPrice = 100
print("MMS발송!!")
print("메세지 길이 : {}".format(lenMessage))
print("메세지 발송 요금 : {}원".format(msgPrice))💡 조건문 02
국어, 영어, 수학, 과학, 국사 점수를 입력하면 총점을 비롯한 각종 데이터 출력 프로그램 만들기
# 편차 : 점수 - 평균점수
korAvg = 85; engAvg = 82; matAvg = 89; sciAvg = 75; hisAvg = 94
totalAvg = korAvg + engAvg + matAvg + sciAvg + hisAvg
avgAvg = int((totalAvg) / 5)
korScore = int(input("국어 점수 : "))
engScore = int(input("영어 점수 : "))
matScore = int(input("수학 점수 : "))
sciScore = int(input("과학 점수 : "))
hisScore = int(input("국사 점수 : "))
totalScore = korScore + engScore + matScore + sciScore + hisScore
avgScore = int(totalScore / 5) # 나누면 실수가 나올 수 있기에 int사용
korGap = korScore - korAvg
engGap = engScore - engAvg
matGap = matScore - matAvg
sciGap = sciScore - sciAvg
hisGap = hisScore - hisAvg
totalGap = totalScore - totalAvg
avgGap = avgScore - avgAvg
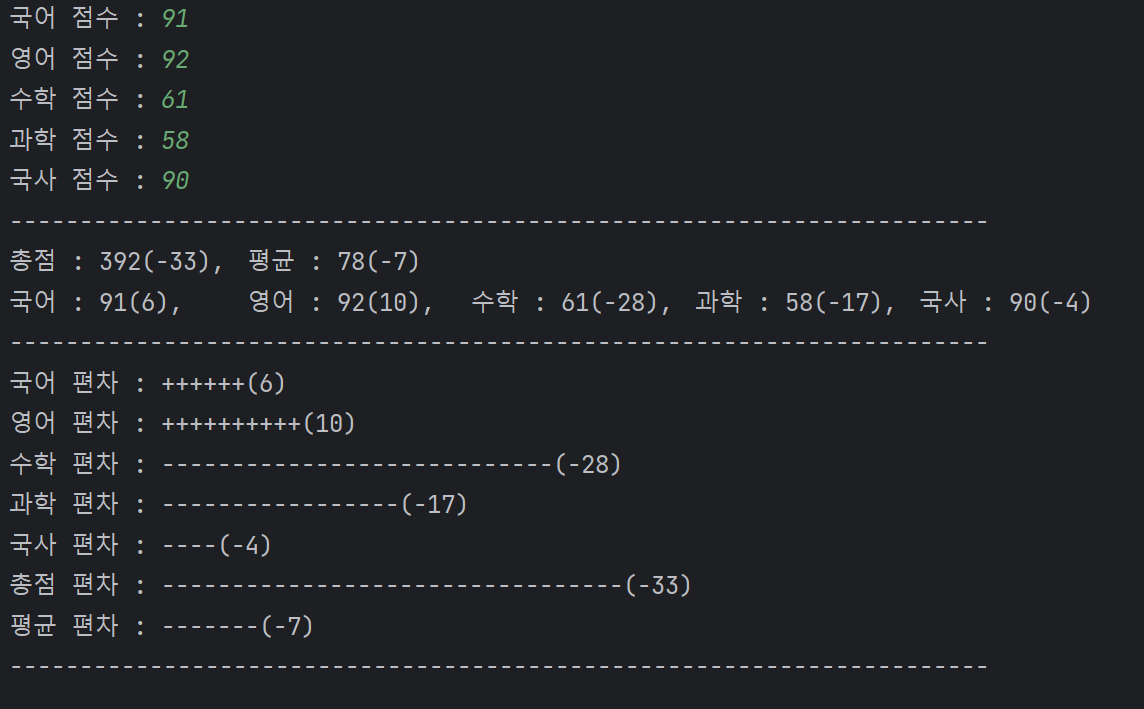
print("-" * 70)
print("총점 : {}({}),\t 평균 : {}({})".format(totalScore, totalGap, avgScore, avgGap))
print("국어 : {}({}),\t 영어 : {}({}),\t 수학 : {}({}),\t 과학 : {}({}),\t \
국사 : {}({})".format(korScore, korGap, engScore, engGap, matScore, matGap, sciScore, sciGap, hisScore, hisGap))
print("-" * 70)
str = "+" if korGap > 0 else "-"
print("국어 편차 : {}({})".format(str * abs(korGap), korGap)) # abs를 사용하여 절대값을 씌운뒤 사용해야한다.
str = "+" if engGap > 0 else "-"
print("영어 편차 : {}({})".format(str * abs(engGap), engGap))
str = "+" if matGap > 0 else "-"
print("수학 편차 : {}({})".format(str * abs(matGap), matGap))
str = "+" if sciGap > 0 else "-"
print("과학 편차 : {}({})".format(str * abs(sciGap), sciGap))
str = "+" if hisGap > 0 else "-"
print("국사 편차 : {}({})".format(str * abs(hisGap), hisGap))
str = "+" if totalGap > 0 else "-"
print("총점 편차 : {}({})".format(str * abs(totalGap), totalGap))
str = "+" if avgGap > 0 else "-"
print("평균 편차 : {}({})".format(str * abs(avgGap), avgGap))
print("-" * 70)🔥 결과 :
💡 조건문 03
난수를 이용해서 홀 / 짝 게임 만들기
import random
comNum = random.randint (1,2) # 홀,짝 2가지 조건이기 때문에 (1,2)
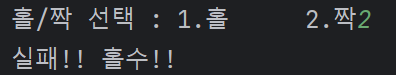
userSelect = int(input("홀/짝 선택 : 1.홀 \t 2.짝"))
if comNum == 1 and userSelect == 1 :
print("빙고!! 홀수!!")
elif comNum == 2 and userSelect == 2 :
print("빙고!! 짝수!!")
elif comNum == 1 and userSelect == 2 :
print("실패!! 홀수!!")
elif comNum == 2 and userSelect == 1 :
print("실패!! 짝수!!")📝
random.randint(1,2): 1 ~ 2 범위 안에서 랜덤으로 뽑아줌
🔥 결과:
난수를 이용해서 가위,바위,보 게임 만들기 : 변형해서 만들어 봄
import random
# comNum = random.randint (1,3) 숫자 보다는 str을 주는게 좋을듯?
comNum = random.choice(["가위", "바위", "보"])
userNum = input("가위, 바위, 보 선택 : ")
if userNum == "가위" and comNum == "보" :
print("컴퓨터 : {}, 유저 : {}".format(comNum, userNum))
print("컴퓨터 : 패, 유저 : 승")
elif userNum == "바위" and comNum == "가위" :
print("컴퓨터 : {}, 유저 : {}".format(comNum, userNum))
print("컴퓨터 : 패, 유저 : 승")
elif userNum == "보" and comNum == "바위" :
print("컴퓨터 : {}, 유저 : {}".format(comNum, userNum))
print("컴퓨터 : 패, 유저 : 승")
elif userNum == "가위" and comNum == "가위" :
print("컴퓨터 : {}, 유저 : {}".format(comNum, userNum))
print("비겼습니다.")
elif userNum == "바위" and comNum == "바위" :
print("컴퓨터 : {}, 유저 : {}".format(comNum, userNum))
print("비겼습니다.")
elif userNum == "보" and comNum == "보" :
print("컴퓨터 : {}, 유저 : {}".format(comNum, userNum))
print("비겼습니다.")
elif userNum == "가위" and comNum == "바위" :
print("컴퓨터 : {}, 유저 : {}".format(comNum, userNum))
print("컴퓨터 : 승, 유저 : 패")
elif userNum == "바위" and comNum == "보" :
print("컴퓨터 : {}, 유저 : {}".format(comNum, userNum))
print("컴퓨터 : 승, 유저 : 패")
elif userNum == "보" and comNum == "가위" :
print("컴퓨터 : {}, 유저 : {}".format(comNum, userNum))
print("컴퓨터 : 승, 유저 : 패")
else :
print("잘 못 입력하셨습니다.")
🔥 결과 :

간단 버전
import random
comNum = random.choice(["가위", "바위", "보"])
userNum = input("가위, 바위, 보 선택 : ")
print("컴퓨터 : {}, 유저 : {}".format(comNum, userNum), "\n") # 내려쓰기 할때 ""안에 \n 작성
if (comNum == "가위" and userNum == "바위") or \
(comNum == "바위" and userNum == "보") or \
(comNum == "보" and userNum == "가위") :
print("이겼습니다.")
elif comNum == userNum :
print("비겼습니다.")
elif (comNum == "바위" and userNum == "가위") or \
(comNum == "보" and userNum == "바위") or \
(comNum == "가위" and userNum == "보") :
print("졌습니다.")
else :
print("잘 못 입력하셨습니다.")🔥 결과 :

💡 조건문 04
요금표를 참고해서 상수도 요금 계산기 만들기
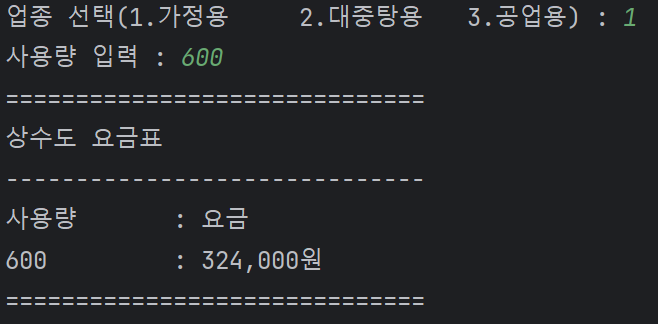
choose = int(input("업종 선택(1.가정용\t 2.대중탕용\t 3.공업용) : "))
price = int(input("사용량 입력 : "))
if choose == 1 :
cost = price * 540
if choose == 2 :
if price <= 50 :
cost = price * 820
elif 50 < price <= 300 : # price > 50 and price <= 300
cost = price * 1920
elif price > 300 :
cost = price * 2400
if choose == 3 :
if price <= 500 :
cost = price * 240
elif price > 500 :
cost = price * 470
print("=" * 30)
print("상수도 요금표")
print("-" * 30)
print("사용량\t\t: 요금 ")
print("{}\t\t : {:,}원".format(price, cost))
print("=" * 30)🔥 결과 :
💡 조건문 05
미세먼지 비상저감조치로 차량 운행제한 프로그램 만들기
# 미세먼지 측정 수치가 150이하면 차량 5부제 실시
# 미세먼지 측정 수치가 150을 초과하면 차량 2부제 실시
# 차량 2부제를 실시하더라도 영업용차량은 5부제 실시
# 미세먼지 수치, 차량종류, 차량번호를 입력하면 운행 가능 여부 출력
import datetime
today = datetime.datetime.today()
day = today.day
limitDust = 150
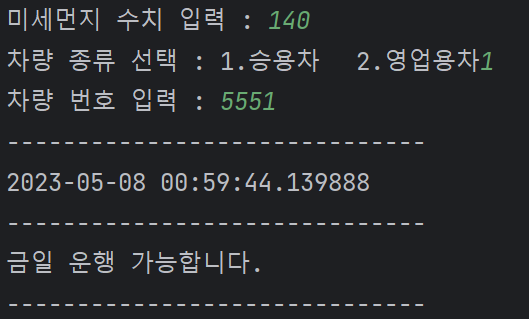
dustNum = int(input("미세먼지 수치 입력 : "))
carType = int(input("차량 종류 선택 : 1.승용차\t 2.영업용차"))
carNum = int(input("차량 번호 입력 : "))
print("-" * 30)
print(today)
print("-" * 30)
if dustNum > limitDust and carType == 1 :
if (day % 2) == (carNum % 2) :
print("\"차량 2부제 적용\"")
print("차량 2부제로 금일 운행제한 대상 차량입니다.")
else :
print("금일 운행 가능합니다.")
if dustNum > limitDust and carType == 2 :
if (day % 5) == (carNum % 5):
print("\"차량 5부제 적용\"")
print("차량 5부제로 금일 운행제한 대상 차량입니다.")
else:
print("금일 운행 가능합니다.")
if dustNum <= limitDust and carType == 1 :
if (day % 5) == (carNum % 5):
print("\"차량 5부제 적용\"")
print("차량 5부제로 금일 운행제한 대상 차량입니다.")
else:
print("금일 운행 가능합니다.")
print("-" * 30)📝
- import datetime 입력
datetime.datetime.today(): 시스템상 오늘 날짜와 현재 시간 나옴.today.day: 오늘이 며칠인지 알려준다.
🔥 결과 :
💡 조건문 06
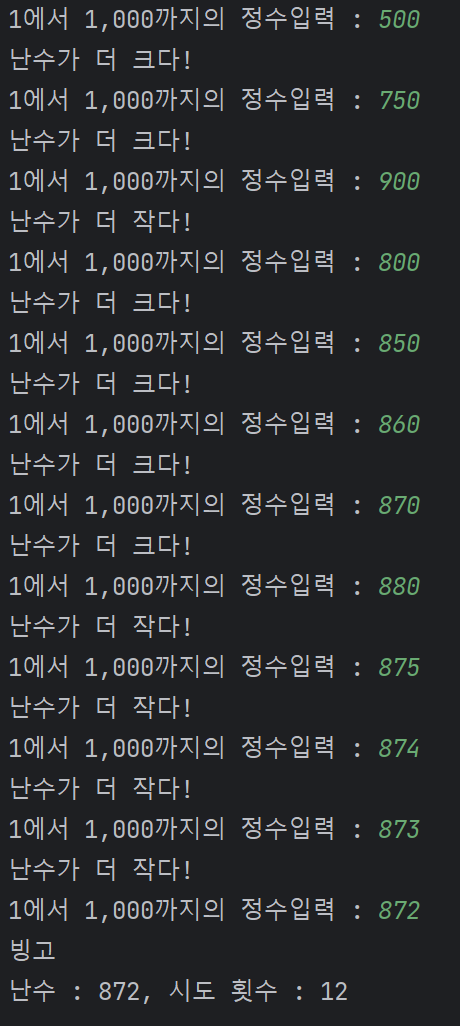
pc에서 난수를 발생하면 사용자가 맞추는 게임 만들기
# pc가 난수(1~1000)를 발생하면 사용자가 숫자를 입력
# 사용자가 난수를 맞추면 게임이 종료
# 만약, 못 맞추게 되면 난수와 사용자 숫자의 크고 작음을 출력한 후 사용자한테 기회를 줌
# 최종적으로 사용자가 시도한 횟수를 출력
# 반복문 사용해야함 !
import random
rNum = random.randint(1, 1000)
tryCount = 0 # 시도한 횟수
gameFlag = True # while반복문을 통해 계속 물어봐야 하기에 True써야함
while gameFlag :
tryCount += 1
pNum = int(input("1에서 1,000까지의 정수입력 : "))
if rNum == pNum :
print("빙고")
gameFlag = False # 빠져나옴 : 게임종료
else :
if rNum > pNum :
print("난수가 더 크다!")
else :
print("난수가 더 작다!")
print("난수 : {}, 시도 횟수 : {}".format(rNum, tryCount))
if not insideTem.isdigit() :
print("숫자로 입력해주세요.")📝 만약 insideTem 이 숫자가 아니면 (False) print 한다
🔥 결과 :
실내온도를 입력하면 스마트에어컨 상태가 자동으로 설정되는 프로그램 만들기
insideTem = input("실내온도 입력 : ")
if not insideTem.isdigit() : # else 대신 이걸쓰자
print("숫자로 입력해주세요.")
else:
if int(insideTem) <= 18 :
print("에어컨 : OFF!!")
elif 18 < int(insideTem) <= 22 :
print("에어컨 : 매우 약!!")
elif 22 < int(insideTem) <= 24 :
print("에어컨 : 약!!")
elif 24 < int(insideTem) <= 26 :
print("에어컨 : 중!!")
elif 26 < int(insideTem) <= 28 :
print("에어컨 : 강!!")
elif 28 < int(insideTem) :
print("에어컨 : 매우 강!!")🔥 결과 :

💡 반복문 01
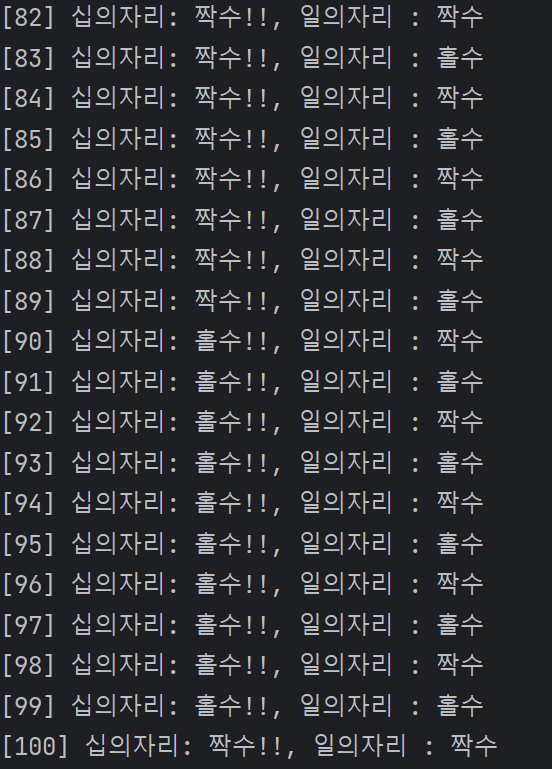
1부터 100까지 정수 중 십의자리와 일의자리에 대해 각각 홀/짝수를 구분하는 프로그램
# 횟수가 딱 정해져있기 때문에 -> for문이 좋음
for i in range(1, 101) :
if i <= 9 :
if i % 2 == 0 : # 짝수
print("[{}] : 짝수!".format(i))
else :
print("[{}] : 홀수!".format(i))
else :
num10 = i // 10 # 10의자리 구하기 // : 몫
num1 = i % 10 # 1의자리 구하기 % : 나머지
result10 = () # 결과를 넣어주기 위해
if num10 % 2 == 0 :
result10 = "짝수"
else :
result10 = "홀수"
result1 = () # {}, " ", () 가능.
if num1 % 2 == 0 :
result1 = "짝수"
else:
result1 = "홀수"
print("[{}] 십의자리: {}!!, 일의자리 : {}".format(i, result10, result1))📝 for i in range(1, 100) : 👉
:을 꼭 해줘야 함 / 100까지 하고 싶으면 101
result1 = () 👈 이렇게 주면 데이터를 넣을 수 있음 <{}, " ", ()> 가능.
if num1 % 2 == 0 :
result1 = "짝수"
else:
result1 = "홀수"🔥 결과 :
위에 결과는 생략
💡 반복문 02
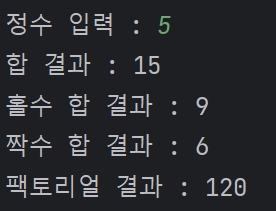
1부터 사용자가 입력한 정수까지의 합, 홀수의합, 짝수의 합 그리고 팩토리얼을 출력하는 프로그램을 만들기
fNum = int(input("정수 입력 : "))
addSum = 0
for i in range(1, (fNum + 1)) : # fNum 까지 원하면 fNum + 1 값을 줘야함
addSum += i
addSumFormat = format(addSum, ",") # addsum 값을 천단위로 끊어줄 때
print("합 결과 : {}".format(addSumFormat))
oddSum = 0 # odd : 홀수
for i in range(1, (fNum + 1)) :
if i % 2 != 0 : # 홀수 구할때
oddSum += i
oddSumFormat = format(oddSum, ",")
print("홀수 합 결과 : {}".format(oddSumFormat))
evenSum = 0 # even : 짝수
for i in range(1, (fNum + 1)) :
if i % 2 == 0 : # 짝수 구할때
evenSum += i
evenSumFormat = format(evenSum, ",")
print("짝수 합 결과 : {}".format(evenSumFormat))
facSum = 1
for i in range(1, (fNum + 1)) :
facSum *= i
facSumFormat = format(facSum, ",")
print("팩토리얼 결과 : {}".format(facSumFormat))📝 fNum 까지 원하면 fNum + 1 값을 줘야함 👉
for i in range(1, (fNum + 1)) :
📝 addsum 값을 천단위로 끊어줄 때 👉
addSumFormat = format(addSum, ",")
📝
반복문 홀수 구할 때 👉if i % 2 != 0 :
반복문 짝수 구할 때 👉if i % 2 == 0 :
🔥 결과 :
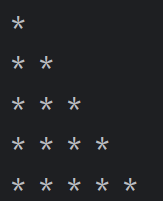
💡 반복문 03
for i in range(1, 6, 1) :
for j in range(i) : # i 가 2이면 2가 들어오고 별이 2개 찍힘(반복)
print("*", end = " ")
print()🔥 결과 :
for i1 in range(1, 6) : # 반복횟수 : 5번 반복하겠다.
for i2 in range(6 - i1 - 1) : # 공생 생성 단계
print(" ", end = " ") # 공백 생성 단계
for i3 in range(i1) :
print("*", end = " ")
print()🔥 결과 :

for i in range(5, 0, -1) :
# 두번째 자리 의미 : 2번째 자리에 있는 수가 되기 바로 전까지 값을 냄
for j in range(i) :
print("*", end = " ")
print()🔥 결과 :

for i in range(1, 6) : # 행을 나타내는
for j in range(1, 6) : # 열에 출력되는
if j == i : # 행 번호와 열 번호가 같다면 * 출력
print("*", end = " ")
else :
print(" ", end = " ")
print()🔥 결과 :

💡 반복문 04
버스 정류장에서 학교까지 가는 버스 A, B, C 운행정보를 통해
2대 이상의 버스가 정차하는 시간대 출력하는 프로그램 만들기
# 버스 A, B 운행 정보
# 오전 6시 첫차 : 오후 23시 운행 종료
# 버스 A : 15분 간격 운행
# 버스 B : 13분 간격 운행
# 버스 C 운행 정보
# 6시 20분 첫차 : 오후 22시 운행 종료
# 버스C : 8분 간격 운행
busA = 15
busB = 13
busC = 8
totalMin = 60 * 17 # 오전6시 ~ 오후 23시 총합 분 계산
for i in range(totalMin + 1) : # 1 작은거 까지 나오기때문에 +1 해줘야 함
if i < 20 or i > (totalMin - 60) : # 6시부터 출발 ~ 22시 마감만 떼어내기 위해서
if i % busA == 0 and i % busB == 0 :
print("busA 와 busB 동시 정차!!", end = " ")
hour = 6 + i // 60 # 6시부터 출발해서 +6에 몫이 시간이기 때문에
min = i % 60
print("{} : {}".format(hour, min))
else:
if i % busA == 0 and i % busB == 0 :
print("busA 와 busB 동시 정차!!", end = " ")
hour = 6 + i // 60
min = i % 60
print("{} : {}".format(hour, min))
elif i % busA == 0 and i % busC == 0 :
print("busA 와 busC 동시 정차!!", end=" ")
hour = 6 + i // 60
min = i % 60
print("{} : {}".format(hour, min))
elif i % busB == 0 and i % busC == 0:
print("busB 와 busC 동시 정차!!", end=" ")
hour = 6 + i // 60
min = i % 60
print("{} : {}".format(hour, min))🔥 결과 :
값을 다시 내야함.
💡 반복문 05
톱니가 각각 n1개와 n2개의 톱니바퀴가 서로 맞물려 회전할 때,
회전을 시작한 후 처음 맞물린 톱니가 최초로 다시 만나게 될 때까지의 톱니의 수와 각각의 바퀴 회전수를 출력해보자 (단, n2는 n1보다 크다)
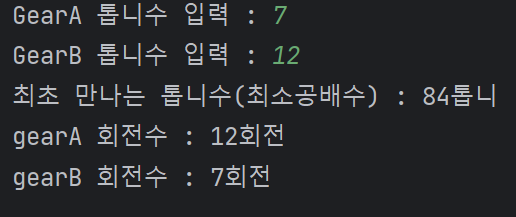
gearACnt = int(input("GearA 톱니수 입력 : "))
gearBCnt = int(input("GearB 톱니수 입력 : "))
gearA = 0
gearB = 0
leastNum = 0 # 다시 만날때 -> 최소공배수
flag = True # while 문을 사용하기위해 필요함!
while flag : # 최소공배수 구할 때까지 사용해야하기 때문에 while
if gearA != 0 :
if gearA != leastNum :
gearA += gearACnt
else :
flag = False # 멈춘다
else :
gearA += gearACnt
if gearB != 0 and gearB % gearACnt == 0 :
leastNum = gearB
else :
gearB += gearBCnt
print("최초 만나는 톱니수(최소공배수) : {}톱니".format(leastNum))
print("gearA 회전수 : {}회전".format(int(leastNum / gearACnt)))
print("gearB 회전수 : {}회전".format(int(leastNum / gearBCnt)))🔥 결과 :
💡 반복문 06
윤년 계산기 만들기
# 연도가 4로 나누어떨어지고 100으로 나누어 떨어지지 않으면 윤년
# 또는 연도가 400으로 나누어떨어지면 윤년
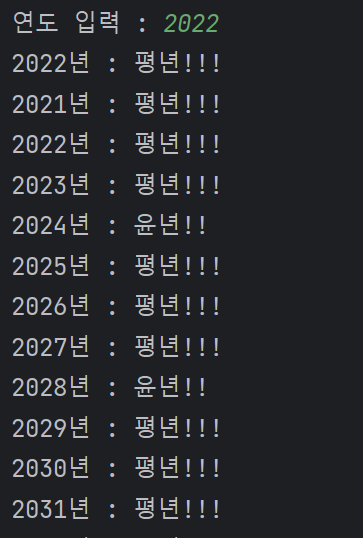
year = int(input("연도 입력 : "))
if (year % 4 == 0 and year % 100 != 0) or (year % 400 == 0 ) :
print("{}년 : 윤년!!".format(year))
else :
print("{}년 : 평년!!!".format(year))
for year in range(2021, (2021 + 101)) :
if (year % 4 == 0 and year % 100 != 0) or (year % 400 == 0):
print("{}년 : 윤년!!".format(year))
else:
print("{}년 : 평년!!!".format(year))🔥 결과 :
이하 생략.
⚡Check
✔ if 와 elif 차이점 : if 문은 단순히 하나의 조건을 검사하고, 조건이 참(True)이면 해당 조건에 대한 코드 블록을 실행한다.
elif 문은`"else if"의 약자로, 이전의 "if"문이 거짓(False)일 때 다음 조건을 검사하고, 조건이 참이면 해당 조건에 대한 코드 블록을 실행한다.
✔ Ctrl + Shift + ↑ / ↓ : 현재 커서 위치의 줄을 위/아래로 이동
✔ .format문 쓸때 {}안에 :,이게 좋다!
✔ 절대값 = abs()
