💻 keep going
계속 문제를 보다 보니 어떤 부분은 자연스럽게 이해가 되어가고 있다.
💡 예외처리 01
⌨ 모듈
def add(n1, n2):
print("덧셈 연산")
try:
n1 = float(n1)
except :
print("첫 번째 피연산자는 숫자가 아닙니다.")
return # 종료
try:
n2 = float(n2)
except :
print("두 번째 피연산자는 숫자가 아닙니다.")
return
print(f"{n1} + {n2} = {n1 + n2}")
def sub(n1, n2):
print("뺄셈 연산")
try:
n1 = float(n1)
except:
print("첫 번째 피연산자는 숫자가 아닙니다.")
return
try:
n2 = float(n2)
except:
print("두 번째 피연산자는 숫자가 아닙니다.")
return
print(f"{n1} - {n2} = {n1 - n2}")
def mul(n1, n2):
print("곱셈 연산")
try:
n1 = float(n1)
except:
print("첫 번째 피연산자는 숫자가 아닙니다.")
return
try:
n2 = float(n2)
except:
print("두 번째 피연산자는 숫자가 아닙니다.")
return
print(f"{n1} * {n2} = {n1 * n2}")
def div(n1, n2):
print("나눗셈 연산")
try:
n1 = float(n1)
except:
print("첫 번째 피연산자는 숫자가 아닙니다.")
return
try:
n2 = float(n2)
except:
print("두 번째 피연산자는 숫자가 아닙니다.")
return
# if n2 == 0:
# print("0으로 나눌 수 없습니다.")
# return
try :
print(f"{n1} / {n2} = {n1 / n2:.2f}")
except ZeroDivisionError as e : # 0으로 나눌때 에러를 확인할 수 있음
print(e)
print("0으로 나눌 수 없습니다.")
# print(f"{n1} / {n2} = {n1 / n2:.2f}")
def mod(n1, n2):
print("나머지 연산")
try:
n1 = float(n1)
except:
print("첫 번째 피연산자는 숫자가 아닙니다.")
return
try:
n2 = float(n2)
except:
print("두 번째 피연산자는 숫자가 아닙니다.")
return
if n2 == 0:
print("0으로 나눌 수 없습니다.")
return
print(f"{n1} % {n2} = {n1 % n2}")
def flo(n1, n2):
print("몫 연산")
try:
n1 = float(n1)
except:
print("첫 번째 피연산자는 숫자가 아닙니다.")
return
try:
n2 = float(n2)
except:
print("두 번째 피연산자는 숫자가 아닙니다.")
return
if n2 == 0:
print("0으로 나눌 수 없습니다.")
return
print(f"{n1} // {n2} = {n1 // n2}")
def exp(n1, n2):
print("거듭제곱 연산")
try:
n1 = float(n1)
except:
print("첫 번째 피연산자는 숫자가 아닙니다.")
return
try:
n2 = float(n2)
except:
print("두 번째 피연산자는 숫자가 아닙니다.")
return
print(f"{n1} ** {n2} = {int(n1 ** n2)}")문제 :
사용자가 입력한 숫자를 이용해서 산술연산 결과를 출력하는 모듈을 만들되,예상하는 예외에 대한 예외처리 코드를 작성
import calculator as cc
num1 = input("첫 번째 피 연산자 입력 : ")
num2 = input("두 번째 피 연산자 입력 : ")
cc.exp(num1, num2)
cc.add(num1, num2)
cc.sub(num1, num2)
cc.div(num1, num2)
cc.flo(num1, num2)🔥 결과 :
첫 번째 피 연산자 입력 : 10
두 번째 피 연산자 입력 : 3
거듭제곱 연산
10.0 ** 3.0 = 1000
덧셈 연산
10.0 + 3.0 = 13.0
뺄셈 연산
10.0 - 3.0 = 7.0
나눗셈 연산
10.0 / 3.0 = 3.33
몫 연산
10.0 // 3.0 = 3.0💡 예외처리 02
⌨ 모듈
class NotPrimeExcption(Exception):
def __init__(self, n):
super().__init__(f"{n} is not prime number.")
class IsPrimeExcption(Exception):
def __init__(self, n):
super().__init__(f"{n} is prime number.")
def isPrime(number): # 어떤 숫자를 던져줬을때 그 숫자가 소수인지 아닌지
flag = True
for n in range(2, number): # 소수는 자기 자신보다 클 수 없기에 number보다 작아야 함
if number % n == 0:
flag = False
break
if flag == False:
raise NotPrimeExcption(number) # 소수가 아니라면 # 강제로 예외를 발생시킬때 raise
else :
raise IsPrimeExcption(number) # 소수라면문제 :
1부터 1000까지의 소수인 난수 10개를 생성하되, 소수가 아니면 사용자가 예외를 발생하도록 프로그램 만들기
import random
import prime_module as pm
primeNumbers = []
n = 0 # while 루프 10번 반복
while n < 10:
rn = random.randint(2, 1000) # 1은 소수도 아니고 합성수도 아님
if rn not in primeNumbers: # 숫자가 중복되지 말아야 하기 때문에 이조건을 만족하면 아래 실행
try :
pm.isPrime(rn) # pm.isPrime에 rn을 던짐
except pm.NotPrimeExcption as e : # 소수가 아닐때
print(e)
continue # 위로 다시 돌아가
except pm.IsPrimeExcption as e : # 소수 일때
print(e)
primeNumbers.append(rn)
else :
print(f"{rn} is overlap number.")
continue
n += 1
primeNumbers = sorted(primeNumbers)
print(primeNumbers)🔥 결과 :
562 is not prime number.
624 is not prime number.
512 is not prime number.
759 is not prime number.
42 is not prime number.
519 is not prime number.
509 is prime number.
153 is not prime number.
759 is not prime number.
176 is not prime number.
30 is not prime number.
342 is not prime number.
311 is prime number.
232 is not prime number.
509 is overlap number.
851 is not prime number.
285 is not prime number.
930 is not prime number.
250 is not prime number.
908 is not prime number.
877 is prime number.
444 is not prime number.
511 is not prime number.
720 is not prime number.
27 is not prime number.
342 is not prime number.
348 is not prime number.
570 is not prime number.
431 is prime number.
249 is not prime number.
32 is not prime number.
123 is not prime number.
424 is not prime number.
802 is not prime number.
449 is prime number.
147 is not prime number.
60 is not prime number.
926 is not prime number.
491 is prime number.
856 is not prime number.
642 is not prime number.
712 is not prime number.
891 is not prime number.
97 is prime number.
394 is not prime number.
682 is not prime number.
477 is not prime number.
986 is not prime number.
430 is not prime number.
281 is prime number.
488 is not prime number.
709 is prime number.
615 is not prime number.
134 is not prime number.
747 is not prime number.
187 is not prime number.
245 is not prime number.
960 is not prime number.
627 is not prime number.
116 is not prime number.
121 is not prime number.
541 is prime number.
[97, 281, 311, 431, 449, 491, 509, 541, 709, 877]💡 예외처리 03
⌨ 모듈
g1Price = 1200; g2Price = 1000; g3Price = 800; g4Price = 2000; g5Price = 900
def calculator(*gcs): # * <- 몇개의 매개변수가 들어올지 모를 때
gcsDic = {} # 정상적으로 입력된
againCntInput = {} # 미결제 상품들
for idx, gc in enumerate(gcs):
try :
int(gc)
gcsDic[f"g{idx+1}"] = int(gc) # idx가 0부터 시작하는데 상품0 으로 시작하면 어색하니 +1 해준다.
except Exception as e:
againCntInput[f"g{idx+1}"] = gc
print(e)
totalPrice = 0 # 값을 할당해주지 않으면 무작위값을 가질 수 있음
for g in gcsDic.keys():
totalPrice += globals()[f"{g}Price"] * gcsDic[g] # 이건 다시..알아봐야할듯
print("-" * 20)
print(f"총 구매 금액 : {totalPrice:,}원")
print("--------------- 미결제 항목 ---------------")
for g in againCntInput.keys():
print(f"상품 : {g}, \t 구매 개수 : {againCntInput[g]}")
print("-" * 20)문제 :
상품 구매에 따른 "총 구매 금액"을 출력하되, 다음과 같이 개수가 잘 못 입력된 경우 별도로 출력하도록 프로그램 만들기
import calculatorPurchase as cp
g1Cnt = input("goods1 구매 개수 : ")
g2Cnt = input("goods2 구매 개수 : ")
g3Cnt = input("goods3 구매 개수 : ")
g4Cnt = input("goods4 구매 개수 : ")
g5Cnt = input("goods5 구매 개수 : ")
cp.calculator(g1Cnt, g2Cnt, g3Cnt, g4Cnt, g5Cnt)🔥 결과 :
goods1 구매 개수 : 3
goods2 구매 개수 : 2
goods3 구매 개수 :
goods4 구매 개수 :
goods5 구매 개수 : 1
invalid literal for int() with base 10: ' '
invalid literal for int() with base 10: ' '
----------------------------------------
총 구매 금액 : 6,500원
--------------- 미결제 항목 ---------------
상품 : g3, 구매 개수 :
상품 : g4, 구매 개수 :
----------------------------------------💡 예외처리 04
⌨ 모듈
# class(Exception)를 쓰는 이유는 일일이 try~except 해주는것보다 간결하기 때문.
class EmptyDataException(Exception):
def __init__(self, i):
super().__init__(f"{i}부분이 비어있습니다.") # 아래와같이 예외가 발생시 뿌려주는 문구
def checkInputData(n, m, p, a, ph):
if n == "": # n이 비어있다면
raise EmptyDataException("이름")
elif m == "":
raise EmptyDataException("메일")
elif p == "":
raise EmptyDataException("비밀번호")
elif a == "":
raise EmptyDataException("주소")
elif ph == "":
raise EmptyDataException("핸드폰")
class RegistMember():
def __init__(self, n, m, p, a, ph):
self.m_name = n
self.m_mail = m
self.m_password = p
self.m_address = a
self.m_phone = ph
print("Membership complete!!")
def printMemberInfo(self):
print(f"이름 : {self.m_name}")
print(f"메일 : {self.m_mail}")
print(f"비밀번호 : {self.m_password}")
print(f"주소 : {self.m_address}")
print(f"핸드폰 : {self.m_phone}")문제 :
회원가입 프로그램을 만들되, 입력하지 않은 항목이 있는 경우 에러메시지를 출력하는 프로그램 만들기
import mem
m_name = input("이름 입력 :")
m_mail = input("메일 주소 입력 :")
m_pw = input("비밀번호 입력 :")
m_addr = input("주소 입력 :")
m_phone = input("연락처 입력 :")
try :
mem.checkInputData(m_name, m_mail, m_pw, m_addr, m_phone)
newMember = mem.RegistMember(m_name, m_mail, m_pw, m_addr, m_phone)
newMember.printMemberInfo()
except mem.EmptyDataException as e: # 예외발생시 mem의 EmptyDataException 이 잡는다
print(e)🔥 결과 :
이름 입력 :chojiwon
메일 주소 입력 :wlwlwl123@naver.com
비밀번호 입력 :1234
주소 입력 :korea seoul
연락처 입력 :010-1234-5678
Membership complete!!
이름 : chojiwon
메일 : wlwlwl123@naver.com
비밀번호 : 1234
주소 : korea seoul
핸드폰 : 010-1234-5678💡 예외처리 05
⌨ 모듈
import random
class PrivateBank:
def __init__(self, bank, account_name):
self.bank = bank
self.account_name = account_name
while True:
newAccountNo = random.randint(10000, 99999)
if bank.isAccount(newAccountNo): # Bank가 아닌 bank를 사용하는 이유 : 메서드를 사용해야해서 클래스는 같은 파일에 있으면 따로 앞에 Bank. 안 적어도 됌.
# Bank 클래스 isAccounts안에 newAccountNo에 할당받은 번호가 없으면
continue
else:
self.account_no = newAccountNo
break
self.totalMoney = 0
bank.addAccounts(self)
def printBankInfo(self):
print("-" * 40)
print(f"account_name : {self.account_name}")
print(f"account_no : {self.account_no}")
print(f"totalMoney : {self.totalMoney}")
print("-" * 40)
class Bank:
def __init__(self):
self.accounts = {}
def addAccounts(self, privateBank):
self.accounts[privateBank.account_no] = privateBank
def isAccount(self, ano):
return ano in self.accounts
def doDeposit(self, accountNumber, money):
pb = self.accounts[accountNumber] # 개인 통장 찾기
pb.totalMoney = pb.totalMoney + money
def doWithdraw(self, accountNumber, money):
pb = self.accounts[accountNumber]
if pb.totalMoney - money < 0:
raise LackException(pb.totalMoney, money)
else :
pb.totalMoney = pb.totalMoney - money
class LackException(Exception):
def __init__(self, m1, m2): # m1 : 잔고 m2 : 출금하려는 금액
super().__init__(f"잔고 부족!!, 잔액 : {m1}, 출금액 : {m2}")문제 :
은행 계좌 개설 및 입/출금 프로그램을 만들어 보자
import bank
koreaBank = bank.Bank()
new_account_name = input("통장 개설을 위한 예금주 입력 : ")
myAccount = bank.PrivateBank(koreaBank, new_account_name)
myAccount.printBankInfo()
while True:
selectNumber = int(input("1. 입금, \t 2.출금, \t 3.종료"))
if selectNumber == 1 :
m = int(input("입금액 입력 : "))
koreaBank.doDeposit(myAccount.account_no, m)
myAccount.printBankInfo()
elif selectNumber == 2 :
m = int(input("출금액 입력 : "))
try :
koreaBank.doWithdraw(myAccount.account_no, m)
except bank.LackException as e :
print(e)
finally :
myAccount.printBankInfo()
elif selectNumber == 3 :
print("bye~~")
break
else :
print("잘 못 입력하셨습니다.")🔥 결과 :
통장 개설을 위한 예금주 입력 : 조지원
----------------------------------------
account_name : 조지원
account_no : 96119
totalMoney : 0
----------------------------------------
1. 입금, 2.출금, 3.종료1
입금액 입력 : 1000000
----------------------------------------
account_name : 조지원
account_no : 96119
totalMoney : 1000000
----------------------------------------
1. 입금, 2.출금, 3.종료2
출금액 입력 : 300000
----------------------------------------
account_name : 조지원
account_no : 96119
totalMoney : 700000
----------------------------------------
1. 입금, 2.출금, 3.종료3
bye~~💡 텍스트파일 01
⌨ 모듈
import time
def writeDiary(u, f, d):
lt = time.localtime()
timeStr = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %I:%M:%S %p", lt)
filepath = u + f # uri + fileName
with open(filepath, "a") as f:
f.write(f"[{timeStr}] {d}\n")
def readDiary(u, f):
filepath = u + f
datas = []
with open(filepath, "r") as f:
datas = f.readlines()
return datas문제 :
회원 계정별 텍스트 파일을 생성한 후 회원 본인 파일에 "한 줄 일기"를 쓰고 읽는 프로그램을 만들기
import diary
members = {}
uri = "C:/pythonTxt/"
def printMembers():
for m in members.keys(): # 키값이 m에 들어간다
print(f"ID: {m}\t PW : {members[m]}") # 그래서 {m}은 키값인 ID
while True:
selectNum = int(input("1.회원가입\t 2.한 줄 일기쓰기\t 3.일기보기\t 4.종료"))
if selectNum == 1 :
mId = input("input ID :")
mPw = input("input PW :")
members[mId] = mPw # members[mId] : PW
printMembers()
elif selectNum == 2 :
mId = input("input ID :")
mPw = input("input PW :")
if mId in members and members[mId] == mPw :
print("login success!!")
fileName = "myDiary_" + mId + ".txt"
data = input("한줄일기 기록")
diary.writeDiary(uri, fileName, data)
else :
print("login fail!!")
elif selectNum == 3 :
mId = input("input ID :")
mPw = input("input PW :")
if mId in members and members[mId] == mPw:
print("login success!!")
fileName = "myDiary_" + mId + ".txt"
datas = diary.readDiary(uri, fileName)
for d in datas:
print(d, end="")
else:
print("login fail!!")
elif selectNum == 4 :
print("bye")
break🔥 결과 :
1.회원가입 2.한 줄 일기쓰기 3.일기보기 4.종료1
input ID :wlwlwl123
input PW :1234
ID: wlwlwl123 PW : 1234
1.회원가입 2.한 줄 일기쓰기 3.일기보기 4.종료2
input ID :wlwlwl123
input PW :1234
login success!!
한줄일기 기록hello!
1.회원가입 2.한 줄 일기쓰기 3.일기보기 4.종료3
input ID :wlwlwl123
input PW :123
login fail!!
1.회원가입 2.한 줄 일기쓰기 3.일기보기 4.종료3
input ID :wlwlwl123
input PW :1234
login success!!
[2023-05-22 02:08:11 AM] hello!
1.회원가입 2.한 줄 일기쓰기 3.일기보기 4.종료4
bye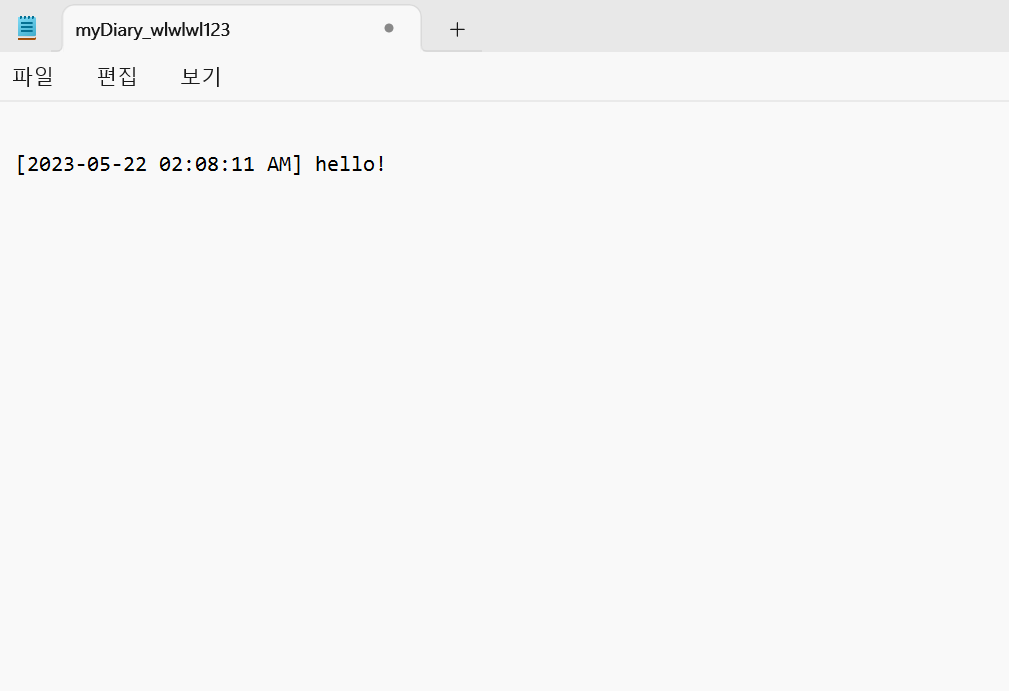
💡 텍스트파일 02
문제 :
텍스트 파일에 수입과 지출을 기록하는 가계부를 만들기
import time
def getTime():
lt = time.localtime()
st = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
return st
while True:
selectNumber = int(input("1.입금\t 2.출금 \t 3.종료"))
if selectNumber == 1 :
money = int(input("입금액 입력 : "))
with open("C:/pythonTxt/bank/money.txt", "r") as f:
m = f.read()
with open("C:/pythonTxt/bank/money.txt", "w") as f:
f.write(str(int(m) + money))
memo = input("입금 내역 입력 : ")
with open("C:/pythonTxt/bank/poketMoney.txt", "a") as f:
f.write("-------------------------------\n")
f.write(f"{getTime()} \n")
f.write(f"[입금] {memo} : {'{:,}'.format(money)}원 \n")
f.write(f"[잔액] : {'{:,}'.format(int(m) + money)}원 \n")
print("입금 완료!!")
print(f"기존 잔액 : {m}")
print(f"입금 후 잔액 : {int(m) + money}")
elif selectNumber == 2 :
money = int(input("출금액 입력 : "))
with open("C:/pythonTxt/bank/money.txt", "r") as f:
m = f.read()
with open("C:/pythonTxt/bank/money.txt", "w") as f:
f.write(str(int(m) - money))
memo = input("출금 내역 입력 : ")
with open("C:/pythonTxt/bank/poketMoney.txt", "a") as f:
f.write("-------------------------------\n")
f.write(f"{getTime()} \n")
f.write(f"[출금] {memo} : {'{:,}'.format(money)}원 \n") # '{:,}'.format(money) : 1000단위 콤마
f.write(f"[잔액] : {'{:,}'.format(int(m) - money)}원 \n")
print("출금 완료!!")
print(f"기존 잔액 : {m}")
print(f"출금 후 잔액 : {int(m) - money}")
elif selectNumber ==3 :
print("bye")
break
else :
print("다시 입력하세요!!")🔥 결과 :
1.입금 2.출금 3.종료1
입금액 입력 : 3000000
입금 내역 입력 : 월급
입금 완료!!
기존 잔액 : 0
입금 후 잔액 : 3000000
1.입금 2.출금 3.종료2
출금액 입력 : 1000000
출금 내역 입력 : 구매1
출금 완료!!
기존 잔액 : 3000000
출금 후 잔액 : 2000000
1.입금 2.출금 3.종료2
출금액 입력 : 100000
출금 내역 입력 : 구매2
출금 완료!!
기존 잔액 : 2000000
출금 후 잔액 : 1900000
1.입금 2.출금 3.종료1
입금액 입력 : 500000
입금 내역 입력 : 용돈
입금 완료!!
기존 잔액 : 1900000
입금 후 잔액 : 2400000
1.입금 2.출금 3.종료3
bye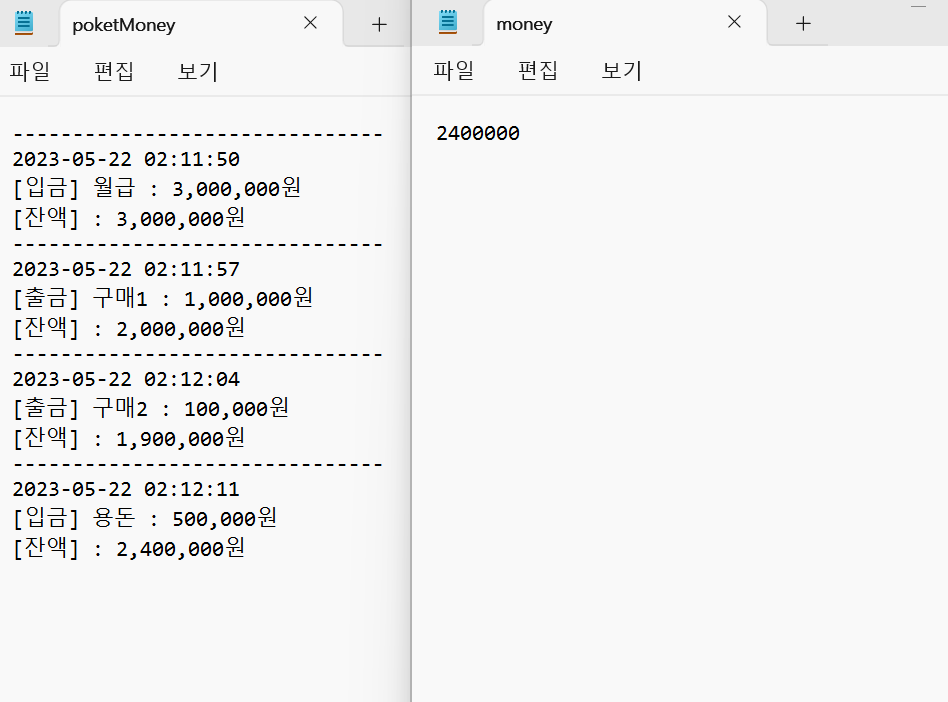
💡 텍스트파일 03
문제 :
사용자가 입력한 숫자의 약수를 텍스트 파일에 기록하기
# 약수
'''
inputNumber = int(input("0보다 큰 정수 입력 : "))
divisor = []
for number in range(1, inputNumber + 1):
if inputNumber % number == 0: # 약수
divisor.append(number)
if len(divisor) > 0: # divisor 리스트안에 정보가 있다면
try :
with open("C:/pythonTxt/divisor.txt", "a") as f:
f.write(f"{inputNumber}의 약수 :")
f.write(f"{divisor}\n")
except Exception as e :
print(e)
else :
print("divisor write complete!!")
print(divisor)
'''
# 소수
inputNumber = int(input("0보다 큰 정수 입력 : "))
prime = []
for number in range(2, inputNumber + 1):
flag = True
for n in range(2, number):
if number % n == 0 :
flag = False
break
if flag : # flag가 True라면
prime.append(number)
if len(prime) > 0:
try :
with open("C:/pythonTxt/prime.txt", "a") as f :
f.write(f"{inputNumber}까지의 소수 : ")
f.write(f"{prime} \n")
except Exception as e :
print(e)
else :
print("prime write complete!!")
print(prime)🔥 결과 :
0보다 큰 정수 입력 : 10
prime write complete!!
[2, 3, 5, 7]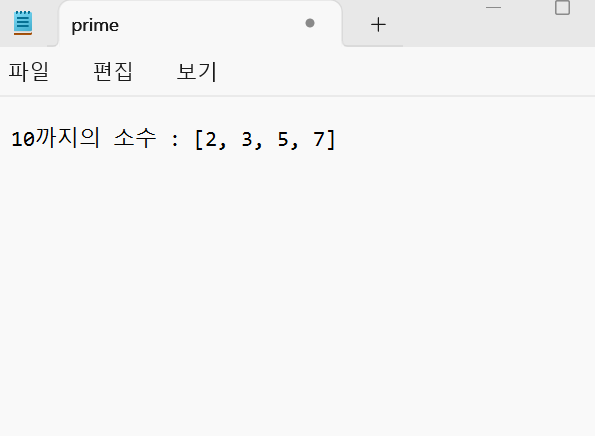
💡 텍스트파일 04
문제 :
# 수 두개의 공약수
num1 = int(input("1보다 큰 정수 입력 : "))
num2 = int(input("1보다 큰 정수 입력 : "))
common = []
for i in range(1, num1 +1):
if num1 % i == 0 and num2 % i == 0:
common.append(i)
if len(common) > 0:
try :
with open("C:/pythonTxt/common.txt", "a") as f :
f.write(f"{num1} 과 {num2}의 공약수 : ")
f.write(f"{common} \n")
except Exception as e :
print(e)
else :
print("common factor write complete!! ")
print(common)🔥 결과 :
1보다 큰 정수 입력 : 20
1보다 큰 정수 입력 : 30
common factor write complete!!
[1, 2, 5, 10]문제 :
# 수 두개의 최대 공약수
num1 = int(input("1보다 큰 정수 입력 : "))
num2 = int(input("1보다 큰 정수 입력 : "))
maxComNum = 0
for i in range(1, num1 +1):
if num1 % i == 0 and num2 % i == 0:
maxComNum = i
try :
with open("C:/pythonTxt/maxComNum.txt", "a") as f :
f.write(f"{num1} 과 {num2}의 최대공약수 : {maxComNum}\n")
except Exception as e :
print(e)
else :
print("maxComNumwrite complete!! ")
print(maxComNum)🔥 결과 :
1보다 큰 정수 입력 : 30
1보다 큰 정수 입력 : 40
maxComNumwrite complete!!
10💡 텍스트파일 05
문제 :
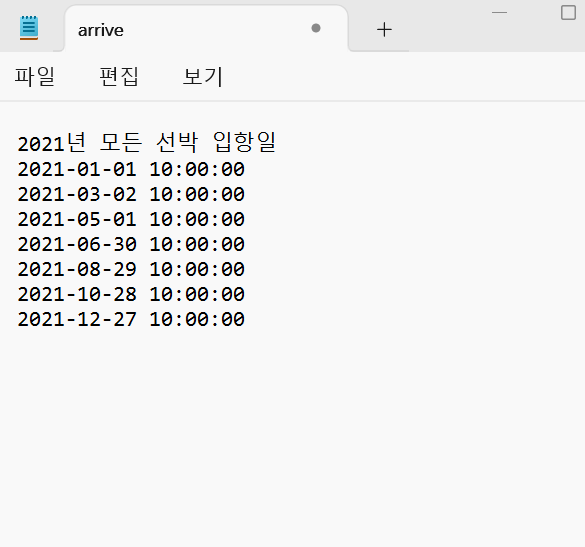
섬마을에 과일, 생선, 야채를 판매하는 배가 다음 주기로 입항한다고 할 떄, 모든 배가 입항하는 날짜를 텍스트 파일에 기록하기
첫 입항일은 2021년 1월 1일 오전 10시
과일 선박 : 3일 / 생선 선박 : 4일 / 야채 선박 : 5일
ship1 = 3
ship2 = 4
ship3 = 5
maxDay = 0 # maxDay : 최대 공약수
# 두개 먼저 구하고 그 값을 남은것과 계산
for i in range(1, ship1 +1):
if ship1 % i == 0 and ship2 % i == 0:
maxDay = i
minDay = (ship1 * ship2) // maxDay # minDay : 최소 공배수
newDay = minDay
for i in range(1, newDay +1):
if newDay % i == 0 and ship3 % i == 0:
maxDay = i
minDay = (newDay * ship3) // maxDay
print(f"minDay : {minDay}") # 60일 마다
print(f"maxDay : {maxDay}") # 의미없음
from datetime import datetime
from datetime import timedelta
n = 1
baseTime = datetime(2021, 1, 1, 10, 0, 0) # 기준일을 정할 수 있음
with open("C:/pythonTxt/arrive.txt", "a") as f:
f.write(f"2021년 모든 선박 입항일\n")
f.write(f"{baseTime}\n")
nextTime = baseTime + timedelta(days=minDay)
while True:
with open("C:/pythonTxt/arrive.txt", "a") as f:
f.write(f"{nextTime}\n")
nextTime = nextTime + timedelta(days=minDay)
try :
if nextTime.year > 2021:
break
except Exception as e :
print(e)
else :
print("완료")
print(nextTime)🔥 결과 :
minDay : 60
maxDay : 1
완료
2021-05-01 10:00:00
완료
2021-06-30 10:00:00
완료
2021-08-29 10:00:00
완료
2021-10-28 10:00:00
완료
2021-12-27 10:00:00