✅ TIL
지금까지 React를 사용해 웹 애플리케이션을 개발했다.
컴포넌트를 생성하고, 어떠한 사용자 이벤트를 통해 해당 컴포넌트 또는 다른 컴포넌트에 변화를 줄 수 있었다.
물론 이것만으로도 충분히 프로젝트를 진행할 수 있다. 그런데 왜 Redux라는 별도의 개념을 또 알아야 할까?
React에서는 상태와 속성(props)을 이용한 컴포넌트 단위 개발 아키텍처를 배웠다면,
Redux에서는 컴포넌트와 상태를 분리하는 패턴을 배운다.
이번 챕터에서는 Redux가 무엇인지, 왜 생겨났는지, 구조는 어떤지에 대해 알아볼 것이다.
또한 참고할 사항으로는 Redux는 React의 관련 라이브러리,
혹은 하위 라이브러리라는 대표적인 오해가 있는데, 전혀 그렇지 않다는 것이다.
Redux는 React 없이도 사용할 수 있는 상태 관리 라이브러리임을 알아두자.
Redux
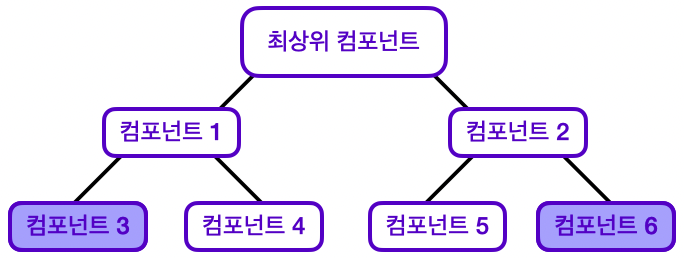
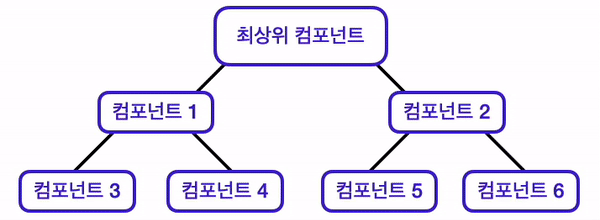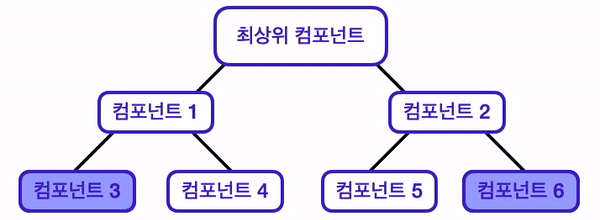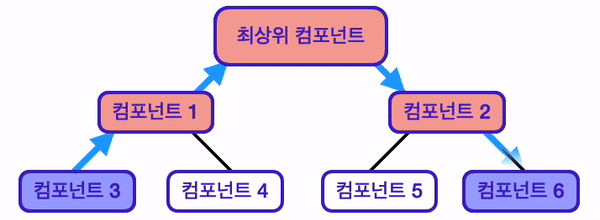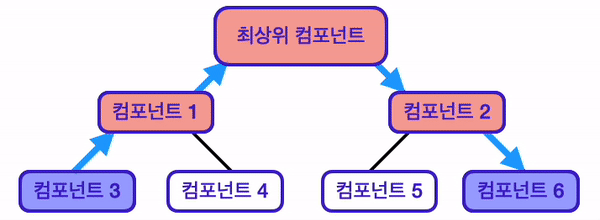
위 사진과 같은 구조의 React 애플리케이션이 있다고 생각해 보자.
이 애플리케이션은 컴포넌트3, 컴포넌트6에서만 사용되는 상태가 있다.
그렇다면 이 상태를 어느 컴포넌트에 위치시켜야 할까?
기존에 배운 React의 데이터 흐름에 따르면, 최상위 컴포넌트에 위치시키는 것이 적절하다.
하지만 이런 상태 배치는 다음과 같은 이유로 다소 비효율적이라고 느껴질 수 있다.
- 해당 상태를 직접 사용하지 않는 최상위 컴포넌트, 컴포넌트1, 컴포넌트2도 상태 데이터를 가짐
- 상태 끌어올리기, Props 내려주기를 여러 번 거쳐야 함
- 애플리케이션이 복잡해질수록 데이터 흐름도 복잡해짐
- 컴포넌트 구조가 바뀐다면, 지금의 데이터 흐름을 완전히 바꿔야 할 수도 있음
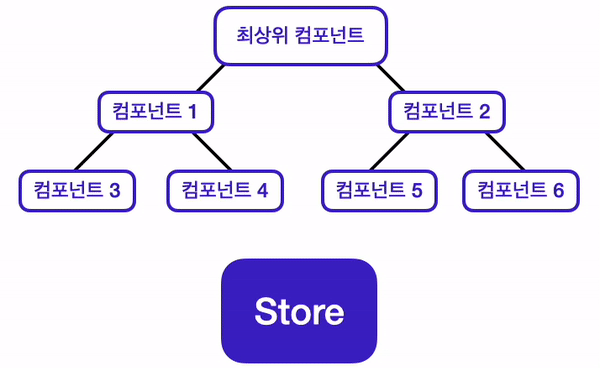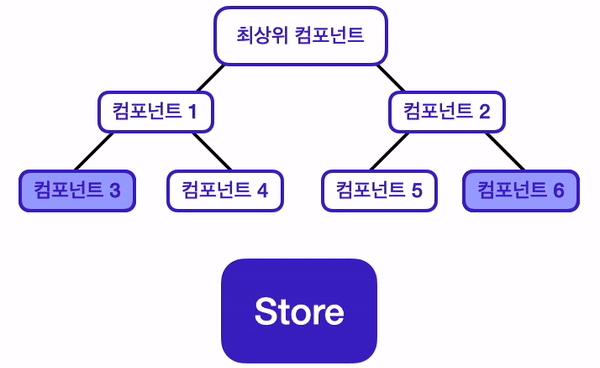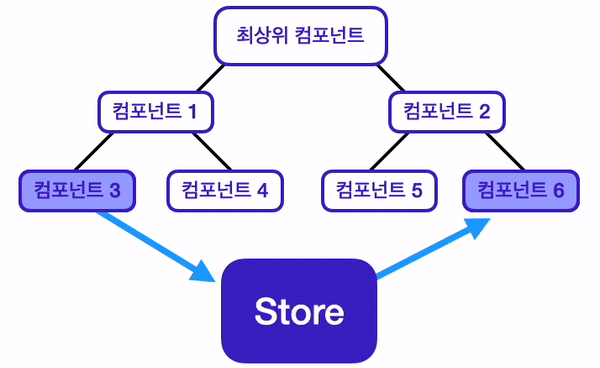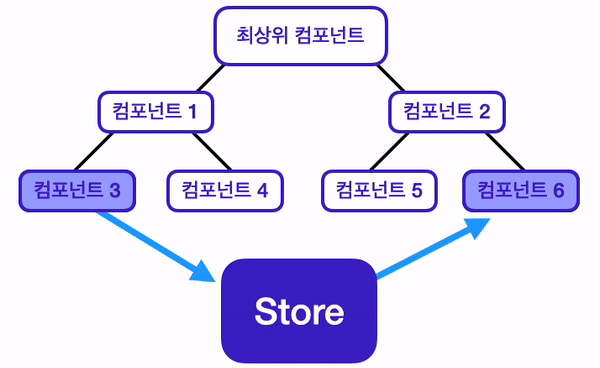
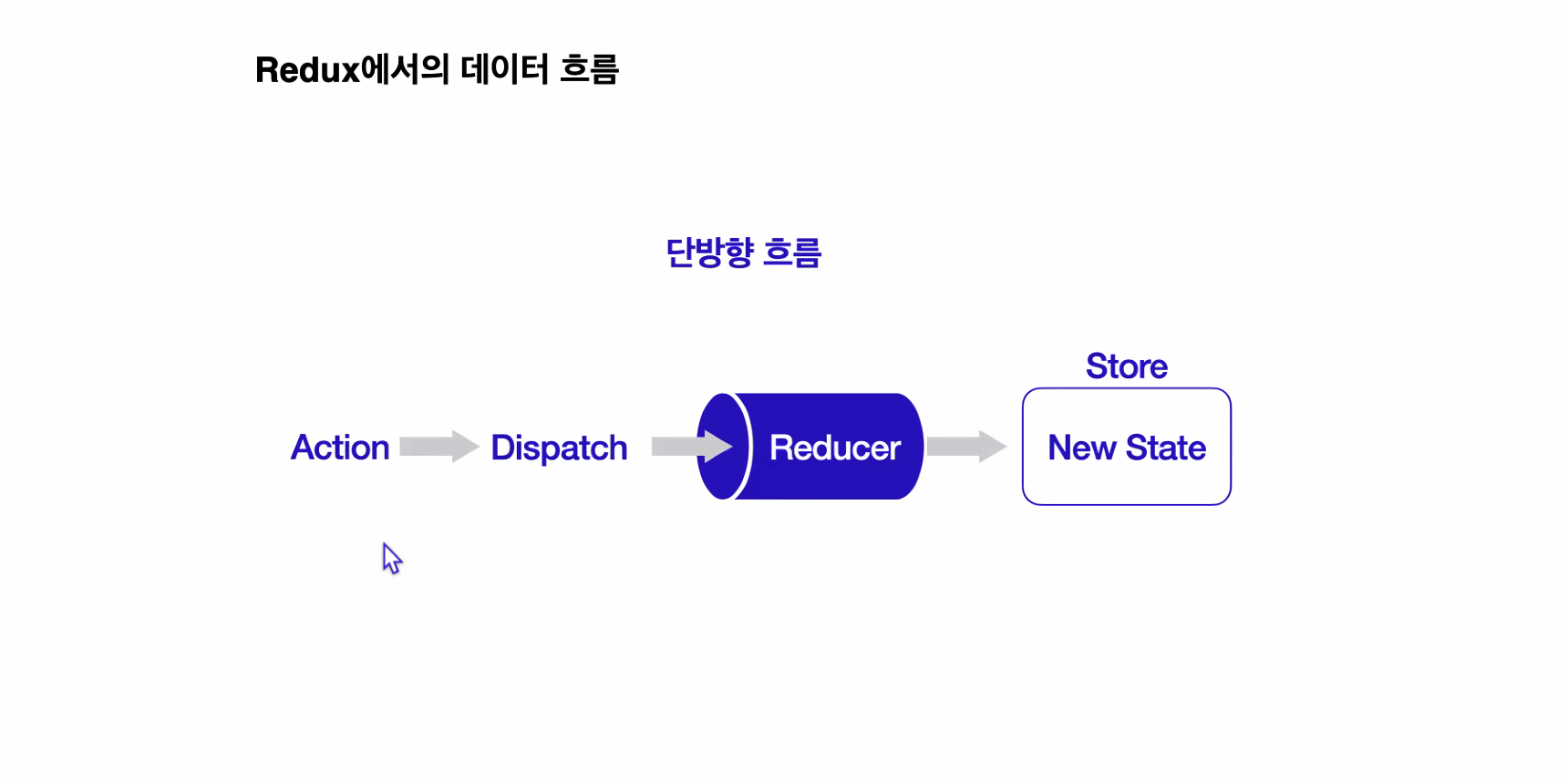
이번 챕터에서 배울 상태 관리 라이브러리인 Redux는, 전역 상태를 관리할 수 있는 저장소인 Store를 제공함으로써 이 문제들을 해결해 준다. 기존 React에서의 데이터 흐름과, Redux를 사용했을 때의 데이터 흐름을 비교해 보면, Redux를 사용했을 때의 데이터 흐름이 보다 더 깔끔해지는 것을 알 수 있다.
Redux의 구조
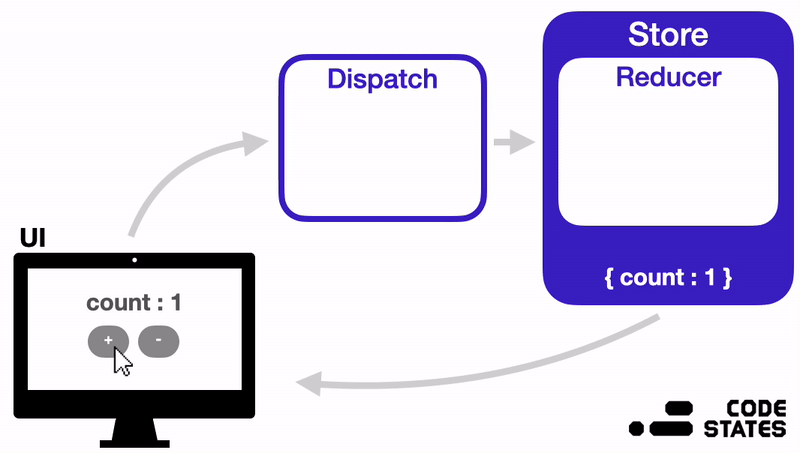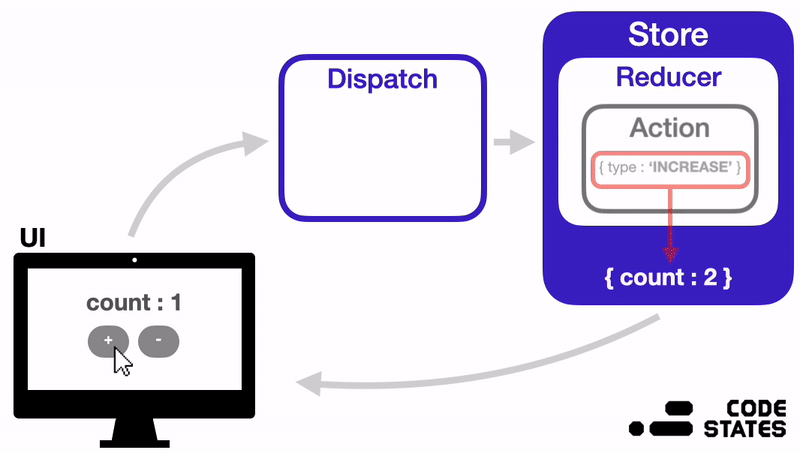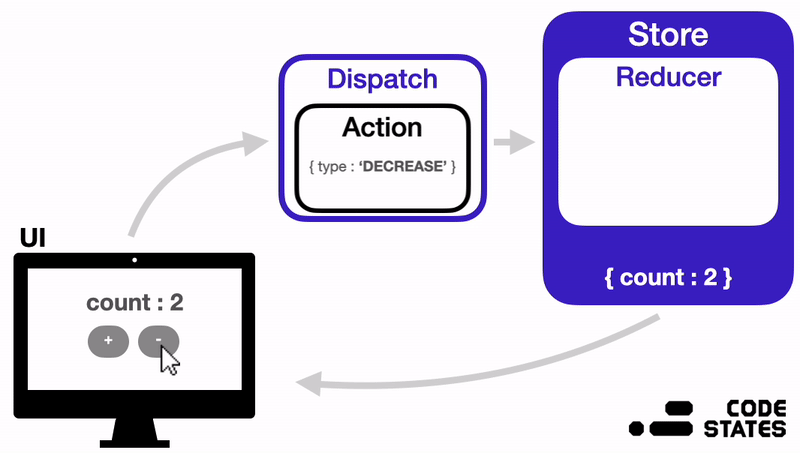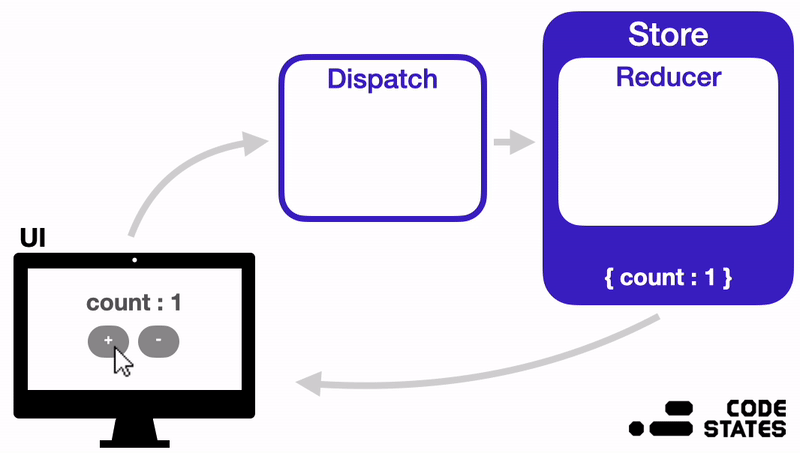
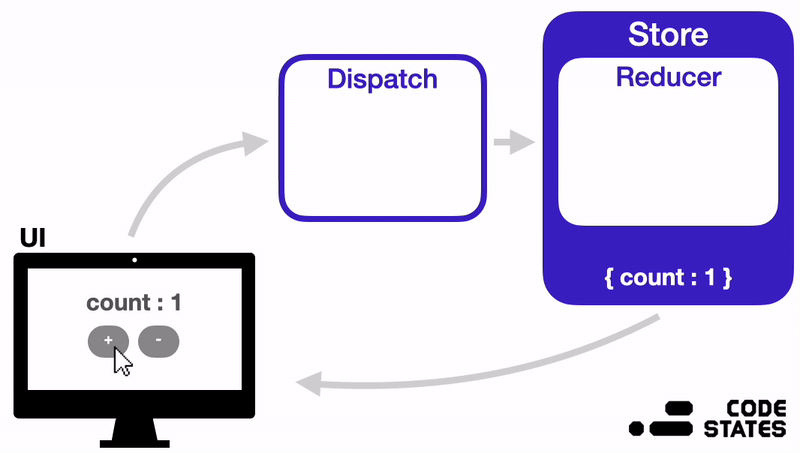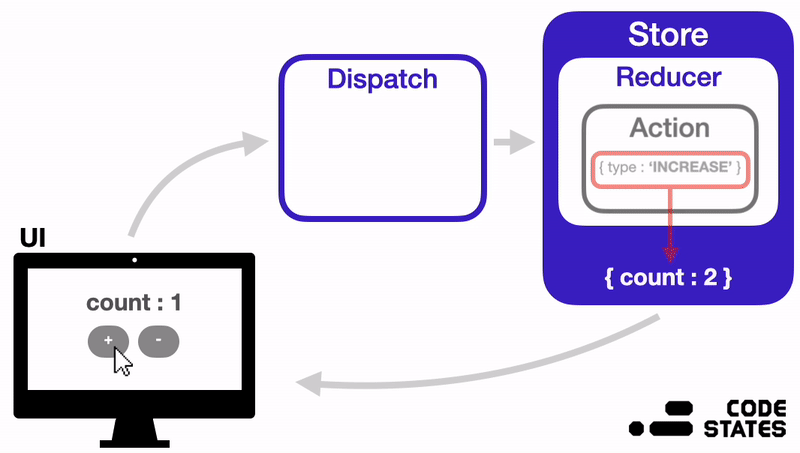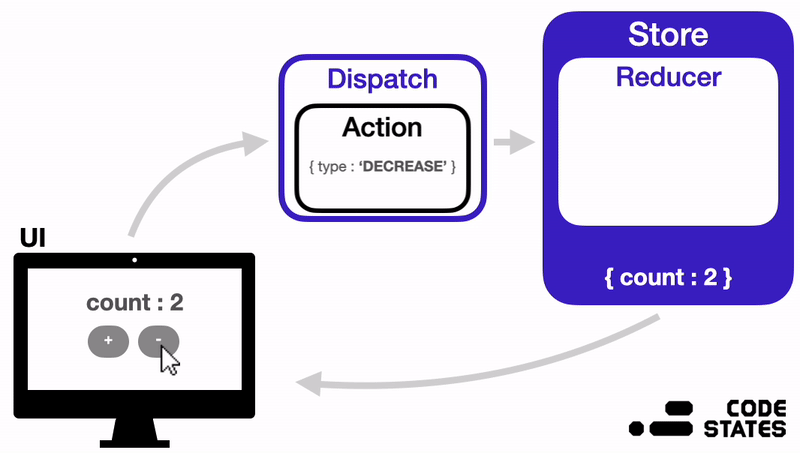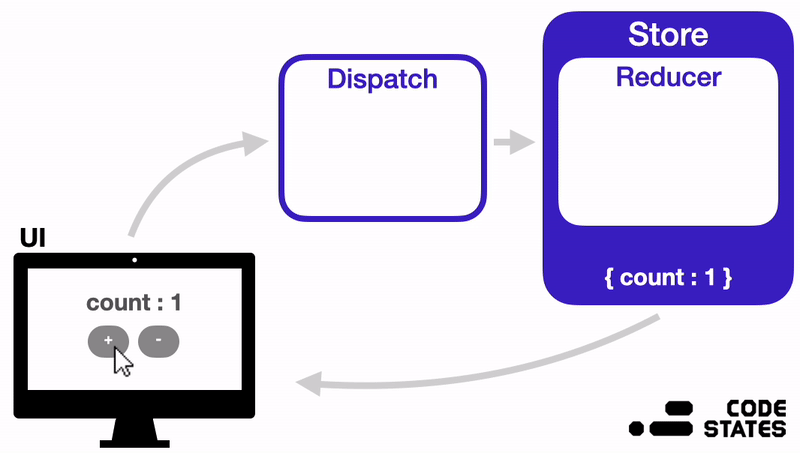
지금부터는 Redux의 구조는 어떻게 되어있는지, 각 부분이 어떤 역할을 하면서 작동하는지 알아보겠다.
위 이미지를 참고하면서 Redux의 구성요소와 작동방식을 이해해 보자.
Redux는 다음과 같은 순서로 상태를 관리한다.
- 상태가 변경되어야 하는 이벤트가 발생하면, 변경될 상태에 대한 정보가 담긴 Action 객체가 생성된다.
- 이 Action 객체는 Dispatch 함수의 인자로 전달된다.
- Dispatch 함수는 Action 객체를 Reducer 함수로 전달해 준다.
- Reducer 함수는 Action 객체의 값을 확인하고, 그 값에 따라 전역 상태 저장소 Store의 상태를 변경한다.
- 상태가 변경되면, React는 화면을 다시 렌더링 한다.
✨ 즉, Redux에서는 Action → Dispatch → Reducer → Store 순서로 데이터가 단방향으로 흐르게 된다.
아래에서 Redux의 각각의 개념들을 코드 예시를 통해 좀 더 구체적으로 살펴보고, 단계별로 구현해 보자.
Store
Store는 상태가 관리되는 오직 하나뿐인 저장소의 역할을 한다. Redux 앱의 state가 저장되어 있는 공간이다.
아래 코드와 같이 createStore 메서드를 활용해 Reducer를 연결해서 Store를 생성할 수 있다.
import { createStore } from 'redux';
const store = createStore(rootReducer);Redux를 사용하기 위해서는 redux와 react-redux를 설치해야합니다.
- DEPENDENCIES
redux, react-redux가 설치되어 있는 것을 확인하실 수 있습니다.
- index.js
안내한 순서에 따라 index.js를 완성해주세요!
1. import { Provider } from 'react-redux';
react-redux에서 Provider를 불러와야 합니다.
- Provider는 store를 손쉽게 사용할 수 있게 하는 컴포넌트입니다.
해당 컴포넌트를 불러온다음에, Store를 사용할 컴포넌트를 감싸준 후
Provider 컴포넌트의 props로 store를 설정해주면 됩니다.
2. import { legacy_createStore as createStore } from 'redux';
redux에서 createStore를 불러와야 합니다.
3. 전역 상태 저장소 store를 사용하기 위해서는 App 컴포넌트를
Provider로 감싸준 후 props로 변수 store를 전달해주여야 합니다.
주석을 해제해주세요.
4. 변수 store에 createStore 메서드를 통해 store를 만들어 줍니다.
그리고, createStore에 인자로 Reducer 함수를 전달해주어야 합니다.
(지금 단계에서는 임시의 함수 reducer를 전달해주겠습니다.)
5. 여기까지가 전역 변수 저장소를 설정하는 방법이였습니다.
브라우저 창에 오류메세지가 나타나지 않는다면 잘 적용된겁니다.👏// ✅ 구현한 코드 - index.js
import React from 'react';
import { createRoot } from 'react-dom/client';
import App from './App';
// 1
import { Provider } from 'react-redux';
// 2
import { legacy_createStore as createStore } from 'redux';
const rootElement = document.getElementById('root');
const root = createRoot(rootElement);
const reducer = () => {};
// 4
const store = createStore(reducer);
root.render(
// 3
<Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>
);Reducer
Reducer는 Dispatch에게서 전달받은 Action 객체의 type 값에 따라서 상태를 변경시키는 함수이다.
이때, Reducer는 순수함수여야 한다.
외부 요인으로 인해 기대한 값이 아닌 엉뚱한 값으로 상태가 변경되는 일이 없어야 하기 때문이다.
const count = 1
// Reducer를 생성할 때에는 초기 상태를 인자로 요구합니다.
const counterReducer = (state = count, action) => {
// Action 객체의 type 값에 따라 분기하는 switch 조건문입니다.
switch (action.type) {
// action === 'INCREASE'일 경우
case 'INCREASE':
return state + 1
// action === 'DECREASE'일 경우
case 'DECREASE':
return state - 1
// action === 'SET_NUMBER'일 경우
case 'SET_NUMBER':
return action.payload
// 해당 되는 경우가 없을 땐 기존 상태를 그대로 리턴
default:
return state;
}
}
// Reducer가 리턴하는 값이 새로운 상태가 됩니다.
만약 여러 개의 Reducer를 사용하는 경우, combineReducers 메서드를 사용해서 하나의 Reducer로 합쳐줄 수 있다.
import { combineReducers } from 'redux';
const rootReducer = combineReducers({
counterReducer,
anyReducer,
...
});이번에는 Reducer 함수를 완성해봅시다!
Reducer함수 첫번째 인자에는 기존 state가 들어오게 됩니다.
첫번째 인자에는 default value를 꼭 설정해주셔야 합니다!
그렇지 않을 경우 undefined가 할당되기 때문에 그로 인한 오류가 발생할 수 있습니다.
(https://redux.js.org/tutorials/fundamentals/part-3-state-actions-reducers#creating-the-root-reducer)
두번째 인자에는 action 객체가 들어오게 됩니다.
action 객체에서 정의한 type에 따라 새로운 state를 리턴합니다.
새로운 state는 전역 변수 저장소 Store에 저장되게 됩니다.
- index.js
안내한 순서에 따라 index.js를 완성해주세요!
1. 유어클래스에 있는 Reducer 예제를 복사해 임의 함수 reducer를
대체해주세요.
2. 가져온 conterReducer를 createStore에 다시 넣어주세요.
3. 주석을 해제해주세요.
4. 예제를 잘 불러오셨다면 정상적으로 화면이 나오는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다!// ✅ 구현한 코드 - index.js
import React from 'react';
import { createRoot } from 'react-dom/client';
import App from './App';
import { Provider } from 'react-redux';
import { legacy_createStore as createStore } from 'redux';
const rootElement = document.getElementById('root');
const root = createRoot(rootElement);
const count = 1;
// 1
// Reducer를 생성할 때에는 초기 상태를 인자로 요구합니다.
const counterReducer = (state = count, action) => {
// Action 객체의 type 값에 따라 분기하는 switch 조건문입니다.
switch (action.type) {
//action === 'INCREASE'일 경우
case 'INCREASE':
return state + 1;
// action === 'DECREASE'일 경우
case 'DECREASE':
return state - 1;
// action === 'SET_NUMBER'일 경우
case 'SET_NUMBER':
return action.payload;
// 해당 되는 경우가 없을 땐 기존 상태를 그대로 리턴
default:
return state;
}
};
// 2
const store = createStore(counterReducer);
root.render(
// 3
<Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>
);Action
Action은 말 그대로 어떤 액션을 취할 것인지 정의해 놓은 객체로, 다음과 같은 형식으로 구성된다.
// payload가 필요 없는 경우
{ type: 'INCREASE' }
// payload가 필요한 경우
{ type: 'SET_NUMBER', payload: 5 }
여기서 type 은 필수로 지정을 해 주어야 한다.
해당 Action 객체가 어떤 동작을 하는지 명시해 주는 역할을 하기 때문이며, 대문자와 Snake Case로 작성한다.
여기에 필요에 따라 payload를 작성해 구체적인 값을 전달한다.
보통 Action을 직접 작성하기보다는 Action 객체를 생성하는 함수를 만들어 사용하는 경우가 많다.
이러한 함수를 액션 생성자(Action Creator)라고도 한다.
// payload가 필요 없는 경우
const increase = () => {
return {
type: 'INCREASE'
}
}
// payload가 필요한 경우
const setNumber = (num) => {
return {
type: 'SET_NUMBER',
payload: num
}
}이번에는 Action 객체를 완성해봅시다!
Action은 어떻게 state를 변경할지 정의해놓은 객체입니다.
Action 객체는 Dispatch 함수를 통해 Reducer 함수 두번째 인자로 전달됩니다.
Action 객체 안의 type은 필수로 지정을 해주어야 합니다.
여기서 지정한 type에 따라 Reducer 함수에서 새로운 state를 리턴하게 됩니다.
- index.js
안내한 순서에 따라 index.js를 완성해주세요!
1. 유어클래스에 있는 Action 예제 중 Action Creator 함수 increase를
복사해오세요.
2. Action Creator 함수 decrease를 만들어 주세요. type은 'DECREASE'로
설정해주세요.
3. 앞서 만든 Action Creator 함수를 다른 파일에도 사용하기 위해 export를
붙혀주세요.// ✅ 구현한 코드 - index.js
import React from 'react';
import { createRoot } from 'react-dom/client';
import App from './App';
import { Provider } from 'react-redux';
import { legacy_createStore as createStore } from 'redux';
const rootElement = document.getElementById('root');
const root = createRoot(rootElement);
const count = 1;
// 1, 3
// payload가 필요 없는 경우
export const increase = () => {
return {
type: 'INCREASE',
};
};
// 2, 3
export const decrease = () => {
return {
type: 'DECREASE',
};
};
// payload가 필요한 경우
export const setNumber = (num) => {
return {
type: 'SET_NUMBER',
payload: num,
};
};
// Reducer를 생성할 때에는 초기 상태를 인자로 요구합니다.
const counterReducer = (state = count, action) => {
// Action 객체의 type 값에 따라 분기하는 switch 조건문입니다.
switch (action.type) {
//action === 'INCREASE'일 경우
case 'INCREASE':
return state + 1;
// action === 'DECREASE'일 경우
case 'DECREASE':
return state - 1;
// action === 'SET_NUMBER'일 경우
case 'SET_NUMBER':
return action.payload;
// 해당 되는 경우가 없을 땐 기존 상태를 그대로 리턴
default:
return state;
}
};
const store = createStore(counterReducer);
root.render(
<Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>
);Dispatch
Dispatch는 Reducer로 Action을 전달해 주는 함수이다. Dispatch의 전달인자로 Action 객체가 전달된다.
// Action 객체를 직접 작성하는 경우
dispatch( { type: 'INCREASE' } );
dispatch( { type: 'SET_NUMBER', payload: 5 } );
// 액션 생성자(Action Creator)를 사용하는 경우
dispatch( increase() );
dispatch( setNumber(5) );
Action 객체를 전달받은 Dispatch 함수는 Reducer를 호출한다.
여기까지 Store, Reducer, Action, Dispatch 개념들을 코드로 구성하는 것은 완료했다.
그렇다면 이제 이 개념들을 어떻게 연결시켜주어야 할까?
바로 Redux Hooks를 이용하면 된다.
Redux Hooks
Redux Hooks는 React-Redux에서 Redux를 사용할 때 활용할 수 있는 Hooks 메서드를 제공한다.
그중에서 크게 useSelector(), useDispatch() 이 두 가지의 메서드를 기억하면 된다.
useDispatch()
useDispatch()는 Action 객체를 Reducer로 전달해 주는 Dispatch 함수를 반환하는 메서드이다.
위에서 Dispatch를 설명할 때 사용한 dispatch 함수도 useDispatch()를 사용해서 만든 것이다.
import { useDispatch } from 'react-redux'
const dispatch = useDispatch()
dispatch( increase() )
console.log<(counter) // 2
dispatch( setNumber(5) )
console.log(counter) // 5이번에는 Dispatch 함수를 완성해봅시다!
dispatch 함수는 이벤트 핸들러 안에서 사용됩니다.
그리고 dispatch 함수는 action 객체를 Reducer 함수로 전달해줍니다.
- App.js
안내한 순서에 따라 App.js를 완성해주세요!
1. import { useDispatch } from 'react-redux';를 통해
react-redux에서 useDispatch를 불러와주세요.
2. import { increase,decrease } from './index.js';를 통해
Action Creater 함수 increase, decrease를 불러와주세요.
3. useDispatch의 실행 값을 변수에 저장해서 dispatch 함수를
사용합니다.(주석을 해제한 후 콘솔결과를 확인해보세요!)
4. 유어클래스 dispatch 예제를 참고해서 이벤트 핸들러 안에서 dispatch를
통해 action 객체를 Reducer 함수로 전달해주세요.
5. 유어클래스 dispatch 예제를 참고해서 이벤트 핸들러 안에서 dispatch를
통해 action 객체를 Reducer 함수로 전달해주세요.// ✅ 구현한 코드 - App.js
import React from 'react';
import './style.css';
// 1
import { useDispatch } from 'react-redux';
// 2
import { increase, decrease } from './index.js';
export default function App() {
// 3
const dispatch = useDispatch();
console.log(dispatch);
const plusNum = () => {
// 4
dispatch(increase());
};
const minusNum = () => {
// 5
dispatch(decrease());
};
return (
<div className="container">
<h1>{`Count: ${1}`}</h1>
<div>
<button className="plusBtn" onClick={plusNum}>
+
</button>
<button className="minusBtn" onClick={minusNum}>
-
</button>
</div>
</div>
);
}useSelector()
useSelector()는 컴포넌트와 state를 연결하여 Redux의 state에 접근할 수 있게 해주는 메서드이다.
// Redux Hooks 메서드는 'redux'가 아니라 'react-redux'에서 불러옵니다.
import { useSelector } from 'react-redux'
const counter = useSelector(state => state)
console.log(counter) // 1이번에는 useSeletor를 완성해봅시다!
useSeletor를 통해 state가 필요한 컴포넌트에서
전역 변수 저장소 store에 저장된 state를 쉽게 불러올 수 있습니다.
- App.js
안내한 순서에 따라 App.js를 완성해주세요!
1. import { useDispatch, useSelector } from 'react-redux';를 통해
react-redux에서 useSelector를 불러와주세요.
2. useSelector의 콜백 함수의 인자에 Store에 저장된 모든 state가
담깁니다. 그대로 return을 하게 되면 Store에 저장된 모든 state를
사용할 수 있습니다.
3. 변수 state를 콘솔에서 확인해보세요. Store에 저장된 기존 state 값인
1이 찍히는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
4. Store에서 꺼내온 state를 화면에 나타내기 위해 변수 state를 활용해보세요.
5. +, - 버튼을 누를 때마다 state가 변경되는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다!// ✅ 구현한 코드 - App.js
import React from 'react';
import './style.css';
// 1
import { useDispatch, useSelector } from 'react-redux';
import { increase, decrease } from './index.js';
export default function App() {
const dispatch = useDispatch();
// 2
const state = useSelector((state) => state);
// 3
console.log(state);
const plusNum = () => {
dispatch(increase());
};
const minusNum = () => {
dispatch(decrease());
};
return (
<div className="container">
{/* 4 */}
<h1>{`Count: ${state}`}</h1>
<div>
<button className="plusBtn" onClick={plusNum}>
+
</button>
<button className="minusBtn" onClick={minusNum}>
-
</button>
</div>
</div>
);
}Redux의 세 가지 원칙
-
Single source of truth
동일한 데이터는 항상 같은 곳에서 가지고 와야 한다는 의미이다.
즉, Redux에는 데이터를 저장하는 Store라는 단 하나뿐인 공간이 있음과 연결이 되는 원칙이다. -
State is read-only
상태는 읽기 전용이라는 뜻으로, React에서 상태갱신함수로만 상태를 변경할 수 있었던 것처럼, Redux의 상태도 직접 변경할 수 없음을 의미한다. 즉, Action 객체가 있어야만 상태를 변경할 수 있음과 연결되는 원칙이다. -
Changes are made with pure functions
변경은 순수함수로만 가능하다는 뜻으로, 상태가 엉뚱한 값으로 변경되는 일이 없도록 순수함수로 작성되어야 하는 Reducer와 연결되는 원칙이다.
Redux 실습
1. Store
// ✅ 구현한 코드 - Store > index.js
import { legacy_createStore as createStore } from 'redux';
import { counterReducer } from '../Reducers';
// createStore 함수를 사용하여 스토어를 생성
export const store = createStore(counterReducer);// ✅ 구현한 코드 - index.js
import React from 'react';
import { createRoot } from 'react-dom/client';
import App from './App';
// Provider는 Redux 스토어를 React 애플리케이션에 제공하기 위한 컴포넌트
import { Provider } from 'react-redux';
// store는 Redux에서 createStore 함수를 사용하여 생성한 스토어 객체
import { store } from './Store';
const rootElement = document.getElementById('root');
const root = createRoot(rootElement);
root.render(
// <Provider> 컴포넌트를 사용하여 store를 스토어로 설정
<Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>
);2. Reducer
// ✅ 구현한 코드 - Reducers > index.js
import { initialState } from './initialState.js';
import { INCREASE, DECREASE } from '../Actions/index.js';
export const counterReducer = (state = initialState, action) => {
// Action 객체의 type 값에 따라 분기하는 switch 조건문
switch (action.type) {
//action === 'INCREASE'일 경우
case INCREASE:
return state + 1;
// action === 'DECREASE'일 경우
case DECREASE:
return state - 1;
// 해당 되는 경우가 없을 땐 기존 상태를 그대로 리턴
default:
return state;
}
};
---
// import { INCREASE, DECREASE, increase, decrease } from '../Actions/index.js'; 로 할 수는 있음
// case INCREASE:
// return increase(state).type === INCREASE ? state + 1 : state;
// case DECREASE:
// return decrease(state).type === DECREASE ? state - 1 : state;
---
// 위 import일 때, 아래와 같은 형태로 Reducer 지정해주면, 액션 객체가 아닌 함수 자체를 반환하게 되어 오류 발생
// return increase(state), return decrease(state) // ✅ 구현한 코드 - Reducers > initialState.js
export const initialState = 1;3. Action
// ✅ 구현한 코드 - Actions > index.js
export const INCREASE = 'INCREASE';
export const DECREASE = 'DECREASE';
// increase 액션 생성자 함수 정의
// 액션 객체는 type 속성을 가지고 있으며, 그 값은 INCREASE 상수와 같다.
// 이렇게 함으로써 App에서 increase 액션을 디스패치(dispatch)할 때마다
// 리듀서(reducer)에서 해당 액션을 식별할 수 있다.
export const increase = () => {
return {
type: INCREASE,
};
};
// decrease 액션 생성자 함수 정의
// 액션 객체는 type 속성을 가지고 있으며, 그 값은 DECREASE 상수와 같다.
// 이렇게 함으로써 App에서 decrease 액션을 디스패치(dispatch)할 때마다
// 리듀서(reducer)에서 해당 액션을 식별할 수 있다.
export const decrease = () => {
return {
type: DECREASE,
};
};
4. useDispatch
// ✅ 구현한 코드 - App.js
import React from 'react';
import './style.css';
// useDispatch Hook은 Redux 스토어에 액션을 디스패치하기 위해 사용
import { useDispatch } from 'react-redux';
import { increase, decrease } from './Actions';
export default function App() {
// dispatch 함수는 액션을 디스패치하기 위해 사용
const dispatch = useDispatch();
return (
<div className="container">
<h1>{`Count: ${1}`}</h1>
// dispatch 함수를 호출하여 해당 액션을 디스패치
<div>
<button className="plusBtn" onClick={() => dispatch(increase())}>
+
</button>
<button className="minusBtn" onClick={() => dispatch(decrease())}>
-
</button>
</div>
</div>
);
}5. useDispatch
// ✅ 구현한 코드 - App.js
import React from 'react';
import './style.css';
// useSelector Hook은 Redux 스토어의 상태를 선택하기 위해 사용
import { useSelector, useDispatch } from 'react-redux';
import { increase, decrease } from './Actions';
export default function App() {
const dispatch = useDispatch();
// state 변수를 통해 상태 값을 가져온다.
const state = useSelector((state) => state);
return (
<div className="container">
// state 변수를 사용하여 상태 값을 표시
<h1>{`Count: ${state}`}</h1>
<div>
<button className="plusBtn" onClick={() => dispatch(increase())}>
+
</button>
<button className="minusBtn" onClick={() => dispatch(decrease())}>
-
</button>
</div>
</div>
);
}