출처: https://react.vlpt.us/using-typescript/01-practice.html
🤔Interface 사용법
- 클래스에서 interface(클래스 또는 객체를 위한 타입을 지정할 때 사용)를 implements하기
- implements : A라는 클래스가 B라는 인터페이스에 있는 모든 조건을 충족한다, 부합하다 그래서 B interface를 사용할 수 있다.
// Shape 라는 interface 를 선언
interface Shape {
getArea(): number; // Shape interface 에는 getArea 라는
//함수가 꼭 있어야 하며 해당 함수의 반환값은 숫자
}
class Circle implements Shape {
// `implements` 키워드를 사용하여 해당 클래스가
// Shape interface의 조건을 충족하겠다는 것을 명시
radius: number; // 멤버 변수 radius 값을 설정
constructor(radius: number) {
this.radius = radius;
}
// 너비를 가져오는 함수를 구현
getArea() {
return this.radius * this.radius * Math.PI;
}
}
class Rectangle implements Shape {
width: number;
height: number;
constructor(width: number, height: number) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
getArea() {
return this.width * this.height;
}
}
const circle: Circle = new Circle(5);
const rec: Rec = new Rec(3, 5)
console.log(circle.getArea(), rec.getArea())
// 값은 78.58~~~, 50 이렇게 나옴
////////////////////
//배열에 담아 꺼내는 방법
const shapes: Shape[] = [new Circle(5), new Rectangle(10, 5)];
//인터페이스에 배열을 선언
shapes.forEach(shape => {
console.log(shape.getArea());
});
// 값은 78.58~~~, 50 이렇게 나옴public,private사용하여 반복되는 코드 줄이기
-public선언된 값은 클래스 외부에서 조회 가능private선언된 값은 클래스 내부에서만 조회가능- 컴파일될 때는 js파일에
public,private선언은 나오지 않음
class Circle implements Shape {
constructor(public radius: number) {
this.radius = radius;
// 너비를 가져오는 함수를 구현
getArea() {
return this.radius * this.radius * Math.PI;
}
}- 일반 객체를 interface로 타입 설정
interface Person {
name: string;
age?: number;
// 물음표가 들어갔다는 것은,
//설정을 해도 되고 안해도 되는 값이라는 것을 의미합니다.
}
interface Developer {
name: string;
age?: number;
skills: string[];
}상태가 유사할 때 interface를 extends 키워드를 사용하여 상속 가능
interface Person {
name: string;
age?: number;
}
interface Developer extends Person {
skills: string[];
}- Type Alias 사용하기
type은 특정 타입에 별칭을 붙이는 용도, 객체를 위한 타입 설정도 가능, 그 어떤 타입이던 별칭지을 수 있음
type Person = {
name: string;
age?: number;
};
type Developer = Person & {
skills: string[];
};
const person: Person = {
name: '김사람'
};
const expert: Developer = {
name: '김개발',
skills: ['javascript', 'react']
};
type People = Person[]; // Person[] 를 이제 앞으로 People 이라는 타입으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
const people: People = [person, expert];😶Generics
- 제너릭은 ts에서 호환을 맞출 때 사용
- 실제 파라미터에 넣는 타입의 유추가 가능
- any를 사용하지 않고 타입을 지키고 싶을 때 사용
- any를 쓰게 되면 타입 유추가 깨질 수 있음, 결과가 any라는 것은 무엇이 있는지 알 수 없음
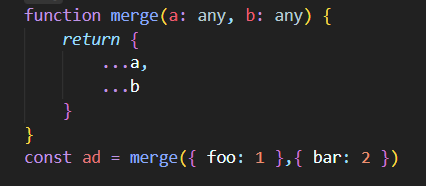
아래와 같이 사용가능
function merge<A, B>(a: A, b: B): A & B {
return {
...a,
...b
};
}
const merged = merge({ foo: 1 }, { bar: 1 });제너릭 예시 큐(Queue) 선입선출(FIFO)
interface Items<T> {
list: T[]
}
type Item<T> = {
list: T[]
}
const items: Items<number> = {
list: [1, 2, 3]
}
class Queue<T> {
list: T[] = []
get length() {
return this.list.length
}
enqueue(item: T) {
this.list.push(item)
}
dequeue() {
return this.list.shift();
}
}
const queue = new Queue<number>()
queue.enqueue(0);
queue.enqueue(1);
queue.enqueue(2);
queue.enqueue(3);
console.log(queue.dequeue())
console.log(queue.dequeue())
console.log(queue.dequeue())
