Daily Coding - 16번
각 알파벳을 한번씩만 이용해서 만든 단어나 문구인지 판단하라.
public class Isogram {
public boolean isIsogram(String str) { // 각 알파벳을 한번씩만 이용해서 만든 단어나 문구인지 판단하는 메서드
String str2 = str.toUpperCase(); //입력된 전체 문자열을 모두 소문자로 변환
for(int i=0; i<str2.length()-1; i++){ // 뒤에 있는 인덱스값들과 하나씩 비교
for(int j=i+1; j<str2.length(); j++){
if(str2.charAt(i)==str2.charAt(j)) return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}public class Isogram {
public boolean isIsogram2(String str) { // 두번째 방법
if(str.length() == 0) return true; //입력된 문자열이 공백일 경우 true를 리턴
HashMap<Character, String> cache = new HashMap<Character, String>(); //사용된 알파벳을 저장할 HashMap을 선언
str = str.toLowerCase(); //입력된 전체 문자열을 모두 소문자로 변환
for(int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
if(cache.containsKey(str.charAt(i))) { //HashMap에 이미 해당 알파벳이 저장되어 있다면 false 출력
return false;
}
cache.put(str.charAt(i), "Exists"); // //HashMap에 해당 문자열이 저장되어 있지 않다면, 저장
}
return true;
}
}Daily Coding - 17번
Math.sqrt 안쓰고 제곱근을 구하라.
귀납법 이용한 풀이

public class Root {
public String computeSquareRoot(int num) { // Math.sqrt 안쓰고 제곱근 구하기
double num2 = 1.00;
double beforeNum2 = 0.00;
boolean bo = true;
while(bo){
num2 = (num2+num/num2)/2;
if(num2==beforeNum2) bo=false;
beforeNum2 = num2;
}
String result2 = String.format("%.2f", num2);
return result2;
}
}
하나씩 값을 제곱시켜봐서 일치하는지 비교하는 방식의
노가다 풀이
public String computeSquareRoot(int num) {
double[] diffs = new double[]{1, 0.1, 0.01, 0.001}; //소수점 3자리부터 반올림하기 때문에, 배열에 소수점 자리만큼 double값을 선언, 할당
double base = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < diffs.length; i++) {
while (base * base < num) {
base = base + diffs[i];
}
if(base * base == num) {
return String.format("%.2f", base);
}else {
base = base - diffs[i]; //while문에서 오버된 값 한번 빼줘야 함
}
}
return String.format("%.2f", base);
}하나씩 더해가면서 비교한 방식
Section2 - [Spring Core] Spring Framework의 핵심 개념
DI(Dependency Injection)
일반적으로는 생성자를 통한 의존관계 주입을 사용
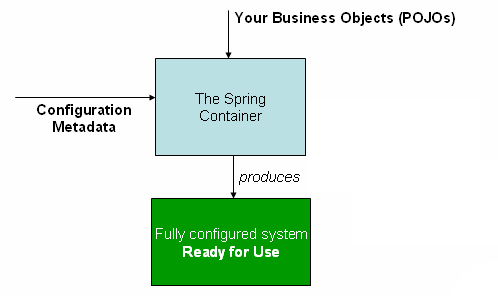
스프링 컨테이너(Spring Container)
ApplicationContext를 스프링 컨테이너라고 하고 인터페이스로 구현되어 있다. (다형성 적용)
-
스프링 컨테이너는 XML, 애너테이션 기반의 자바 설정 클래스로 만들 수 있다.
(cf. 예전에는 개발자가 xml을 통해 모두 설정해줬지만, 이러한 복잡한 부분들을 Spring Boot를 사용하면서 거의 사용하지 않게 되었다.) -
빈의 인스턴스화, 구성, 전체 생명 주기 및 제거까지 처리한다.
- 컨테이너는 개발자가 정의한 Bean을 객체로 만들어 관리하고 개발자가 필요로 할 때 제공
-
스프링 컨테이너를 통해 원하는 만큼 많은 객체를 가질 수 있다.
-
의존성 주입을 통해 애플리케이션의 컴포넌트를 관리한다.
- 애플리케이션의 서로 다른 빈을 연결하는 역할을 함.
- 따라서 모듈 간에 의존 및 결합으로 인해 발생하는 문제로부터 자유로워 짐
- 메서드가 언제, 어디서 호출되어야 하는지, 메서드를 호출하기 위해 필요한 매개 변수를 준비해서 전달하지 않음
스프링 컨테이너를 사용하는 이유
- 객체 간의 의존성을 낮추기 위해 Spring 컨테이너가 사용
(구현 클래스에 있는 의존을 제거하고 인터페이스에만 의존하도록 설계할 수 있다.)
스프링 컨테이너 생성방법
// Spring Container 생성 방법
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(DependencyConfig.class);스프링 컨테이너 생성 과정
- 스프링 컨테이너는 Configuration Metadata를 사용
- 파라미터로 넘어온 설정 클래스 정보를 사용해서 스프링 빈을 등록
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(구성정보.class)로 스프링에 있는 @Bean의 메서드를 등록- 애너테이션 기반 컨테이너 구성
(애너테이션 기반의 자바 설정 클래스로 Spring을 만드는 것을 의미)
ApplicationContext 인터페이스 구현체 확인법
- Windows = Ctrn + N → 클래스에서 ApplicationContext로 검색
- ApplicationContext 인터페이스를 구현한 하위 클래스들 확인 가능
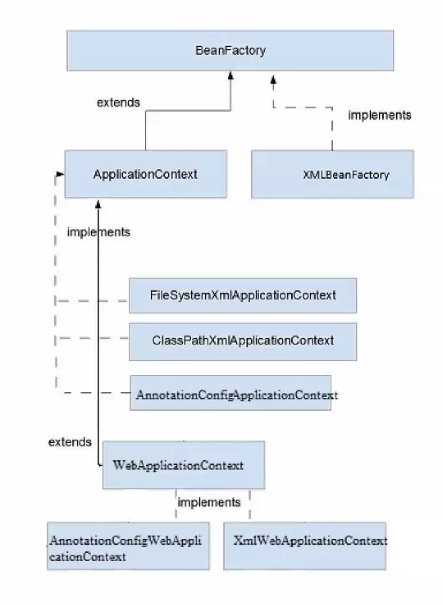
스프링 컨테이너의 종류
BeanFactory
- 스프링 컨테이너의 최상위 인터페이스
- 빈을 등록하고 생성하고 조회하고 돌려주는 등 빈을 관리하는 역할
- getBean() 메소드를 통해 빈을 인스턴스화할 수 있다.
- @Bean이 붙은 메서드의 명을 스프링 빈의 이름으로 사용해
빈 등록을 함
ApplicationContext
- BeanFactory의 기능을 상속받아 제공
- 빈을 관리하고 검색하는 기능을 BeanFactory가 제공하고 그 외에 부가기능을 제공
- 부가기능(참고)
- MessageSource: 메세지 다국화를 위한 인터페이스
- EnvironmentCapable: 개발, 운영 등 환경변수 등으로 나눠 처리하고, 애플리케이션 구동 시 필요한 정보들을 관리하기 위한 인터페이스
- ApplicationEventPublisher: 이벤트 관련 기능을 제공하는 인터페이스
- ResourceLoader: 파일, 클래스 패스, 외부 등 리소스를 편리하게 조회
컨테이너 인스턴스화
// Annotation
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(DependencyConfig.class);
// XML
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("services.xml", "daos.xml");다양한 외부 리소스로부터 구성 메타데이터를 로드할 수 있도록 하는 리소스 문자열이다.
Spring 빈(Bean)
- 스프링 컨테이너가 관리하는 객체
(cf. java Bean = getter와 setter만 가지고 있는 클래스
spring Bean이랑은 다른거임)
-
인스턴스화된 객체를 의미
- 자바 객체를 spring에서는 빈이라 부른다.
-
스프링 컨테이너에 등록된 객체를 스프링 빈이라고 한다.
-
@Bean이 적힌 메서드를 모두 호출해서 반환된 객체를 스프링 컨테이너에 등록
-
빈은 클래스의 등록정보, 게터/세터 메서드를 포함
-
빈은 컨테이너에 사용되는 설정 메타데이터로 생성
-
설정 메타데이터
XML또는자바 애너테이션,자바 코드로 표현- 컨테이너의 명령과 인스턴스화, 설정, 조립할 객체를 정의
bean 접근 방법
// create and configure beans
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("services.xml", "daos.xml");
// retrieve configured instance
PetStoreService service = context.getBean("memberRepository", memberRepository.class);
// use configured instance
List<String> userList = service.getUsernameList();- getBean 을 사용하여 bean의 인스턴스를 가져올 수 있다.
- 실제적으로 응용 프로그램 코드에서는 getBean() 메서드로 호출하여 사용하면 안된다.
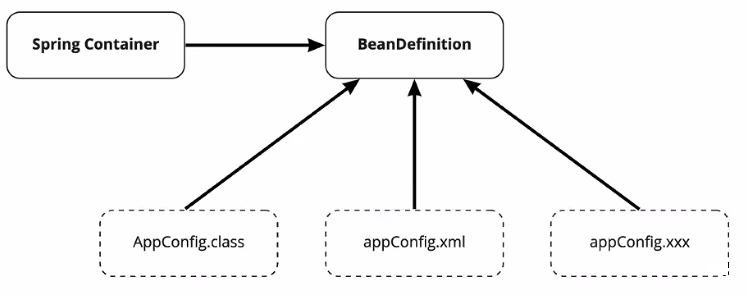
BeanDefinition(빈 설정 메타정보)
추상화 시키는 기능
-
속성에 따라 컨테이너가 Bean을 어떻게 생성하고 관리할지 결정
-
@Beanor<bean>당 각 1개씩 메타 정보가 생성 -
Spring이 설정 메타정보를 BeanDefinition 인터페이스를 통해 관리하기 때문에 컨테이너 설정을 XML, Java로 할 수 있는 것 이다.
(cf. 스프링 컨테이너는 설정 형식이 XML인지 Java 코드인지 모르고 BeanDefinition만 알면 된다.)
Bean은 BeanDefinition(빈 설정 메타정보)으로 정의되고 BeanDefinition에 따라서 활용하는 방법이 달라진다.
빈 스코프(Bean Scope)
빈이 존재할 수 있는 범위
리마인드
- 스프링은 스프링 컨테이너를 통해 객체를 관리한다.
- 스프링 컨테이너에서 관리되는 객체를 빈(Bean)이라고 한다.
특정 bean 정의에서 생성된 개체에 연결할 다양한 의존성 및 구성 값뿐만 아니라 특정 bean 정의에서 생성된 개체의 범위도 제어할 수 있다.
Spring Framework는 6개의 범위를 지원하며, 그 중 4개는 ApplicationContext를 사용하는 경우에만 사용할 수 있다.
bean은 여러 범위 중 하나에 배치되도록 정의할 수 있다.
구성을 통해 생성하는 개체의 범위를 선택할 수 있기 때문에 강력하고 유연하다.
사용자 정의 범위를 생성할 수도 있다.
| Scope | Description |
|---|---|
| singleton | (Default) 각 Spring 컨테이너에 대한 단일 객체 인스턴스에 대한 단일 bean definition의 범위를 지정합니다. |
| prototype | 스프링 컨테이너는 프로토타입 빈의 생성과 의존관계 주입까지만 관여하고 더는 관리하지 않는 매우 짧은 범위의 스코프이다. |
| request | 웹 요청이 들어오고 나갈때 까지 유지되는 스코프이다. |
| session | 웹 세션이 생성되고 종료될 때 까지 유지되는 스코프이다. |
| application | 웹의 서블릿 컨텍스와 같은 범위로 유지되는 스코프이다. |
| websocket | 단일 bean definition 범위를 WebSocket의 라이프사이클까지 확장합니다. Spring ApplicationContext의 컨텍스트에서만 유효합니다. |
싱글톤(singleton) 스코프
클래스의 인스턴스가 딱 1개만 생성되는 것을 보장하는디자인 패턴
-
스프링 컨테이너의 시작과 함께 생성되어서 스프링 컨테이너가 종료될 때 까지 유지
-
(싱글톤 빈의) 하나의 공유 인스턴스만 관리
- private 생성자를 사용해 외부에서 임의로 new를 사용하지 못하도록 막아야 한다.
-
해당 bean definition와 일치하는 ID 또는 ID를 가진 빈에 대한 모든 요청은 스프링 컨테이너에서 해당 특정 빈 인스턴스를 반환한다.
-
스프링 컨테이너 종료시 소멸 메서드도 자동으로 실행
-
단일 인스턴스는 싱글톤 빈의 캐시에 저장
-
이름이 정해진 빈에 대한 모든 요청과 참조는 캐시된 개체를 반환한다.
- 싱글톤 스코프의 스프링 빈은 여러번 호출해도 모두 같은 인스턴스 참조 주소값을 가진다.
Bean 하나에 하나씩 메타 정보가 생성되고, 스프링 컨테이너는 이런 메타 정보를 기반으로 스프링 빈을 생성한다.
싱글톤(singleton) 실습
public class SingletonTest {
// static DependencyConfig dependencyConfig = new DependencyConfig(); // <<이런식으로 (DI 컨테이너만 사용) 하면
// static MemberService memberService1 = dependencyConfig.memberService(); // memberService1,2가 각각 다른 주소값을 갖음
// static MemberService memberService2 = dependencyConfig.memberService(); // 수 많은 객체를 생성하게 되니 메모리 낭비가 심함
static SingletonService singletonService1 = SingletonService.getInstance(); // 이렇게 하면 같은 객체가 됨. (주소값 출력해보면 같음)
static SingletonService singletonService2 = SingletonService.getInstance();
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("memberService1 = " + singletonService1);
System.out.println("memberService2 = " + singletonService2);
}
}public class SingletonService {
private static final SingletonService instance = new SingletonService(); // 인스턴스 한개를 미리 생성
public static SingletonService getInstance() { // getInstance() 메서드를 통해서만 객체 인스터스를 조회할 수 있도록 제한
return instance;
} // 이 메서드를 호출하면 항상 같은 static instance를 호출
private SingletonService() {} // 외부에서 new 키워드로 객체를 생성할 수 없도록 제한
}위 코드처럼 직접 static 인스턴스를 직접 만들지 않아도 됨.
싱글톤 패턴의 문제점
- 싱글톤 패턴을 구현하는 코드량이 많다.
- 클라이언트가 구체 클래스에 의존한다.
- 지정해서 가져오기 때문에 테스트하기 어렵다.
- private 생성자를 사용하여 자식 클래스를 만들기 어렵기 때문에 유연성이 떨어짐.
- 속성 공유
- 멀티쓰레드 환경에서 싱글톤 객체의 속성은 여러 쓰레드에 의해 바뀔 수 있다.
(1개의 인스턴스에서 속성 값을 공유하기 때문에 발생하는 문제점) - 가급적 읽기만 가능해야 한다.
- 멀티쓰레드 환경에서 싱글톤 객체의 속성은 여러 쓰레드에 의해 바뀔 수 있다.
- 구동 시간이 증가할 수 있다.
(싱글톤 빈은 기본적으로 애플리케이션 구동 시 생성되기 때문에)
위와 같은 싱글톤 패턴 문제를 싱글톤 컨테이너가 해결해 준다.
싱글톤 컨테이너
객체 인스턴스를 싱글톤으로 관리하는 컨테이너
(클래스의 인스턴스가 Java JVM 내의 단 하나만 존재한다는 뜻)
- 스프링 컨테이너는 싱글톤 컨테이너 역할을 한다.
- 싱글톤 객체로 생성하고 관리하는 기능을 싱글톤 레지스트리라 한다.
- 스프링 컨테이너의 위 기능 덕분에 싱글턴 패턴의 모든 단점을 해결하며 객체를 싱글톤으로 유지할 수 있다.
import com.codestates.section2week4.coffee.CoffeeRepository;
import com.codestates.section2week4.coffee.CoffeeService;
import com.codestates.section2week4.member.MemberRepository;
import com.codestates.section2week4.member.MemberService;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class DependencyConfig {
@Bean
public MemberService memberService() {
return new MemberService(memberRepository());
}
@Bean
public MemberRepository memberRepository() {
return new MemberRepository();
}
@Bean
public CoffeeService coffeeService() {
return new CoffeeService(coffeeRepository());
}
@Bean
public CoffeeRepository coffeeRepository() {
return new CoffeeRepository();
}
}import com.codestates.section2week4.member.MemberService;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class SingletonTest {
static AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(DependencyConfig.class);
static MemberService memberService1 = ac.getBean("memberService", MemberService.class);
static MemberService memberService2 = ac.getBean("memberService", MemberService.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("memberService1 = " + memberService1);
System.out.println("memberService2 = " + memberService2);
}
}
싱글톤 방식의 주의점
- 싱글톤 객체는 무상태로 설계해야 한다.
- 싱글톤 방식은 여러 클라이언트가 하나의 객체 인스턴스를 공유하기 때문
- 특정 클라이언트가 값을 변경할 수 있으면 안된다.
- 즉, 읽기만 가능해야 한다.
- 스프링 빈의 공유 값을 설정하면 장애가 발생할 수 밖에 없다.
핵심 point
- 스프링 컨테이너에서 빈 스코프의 기본값은 싱글톤 스코프다.
- 싱글톤 패턴을 사용할때 발생하는 문제점을 싱글톤 컨테이너로 해결할 수 있다.
Java 기반 컨테이너(Container) 설정
@Bean and @Configuration
- @Configuration
- 해당 자바 클래스를 스프링 설정 클래스로 바꾸겠다는 선언
- @Bean
- Spring 컨테이너에서 해당 객체를 관리하겠다는 선언
- @Configuration이 달려있는 클래스 내부에서 써야 함.
메서드가 Spring 컨테이너에서 관리할 새 객체를 인스턴스화, 구성 및 초기화한다는 것을 나타내는 데 사용
@Configuration
public class DependencyConfig {
@Bean
public MyService myService() {
return new MyServiceImpl();
}
}AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 를 사용하여 스프링 컨테이너를 인스턴스화 하는 방법
-
ApplicationContext 구현은 아래와 같은 애너테이션이 달린 클래스로 파라미터를 전달 받고 있다.
- @Configuration 클래스
- @Component 클래스
- JSR-330 메타데이터
-
@Configuration 클래스가 입력으로 제공되면 @Configuration 클래스 자체가 Bean 정의로 등록되고 클래스 내에서 선언된 모든 @Bean 메서드도 Bean 정의로 등록
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(DependencyConfig.class);
MyService myService = ctx.getBean(MyService.class);
myService.doStuff();
}- @Component 클래스와 JSR-330 클래스가 제공되면 빈 정의로 등록되며 필요한 경우 해당 클래스 내에서 @Autowired 또는 @Inject와 같은 DI 메타데이터가 사용되는 것으로 가정한다.
// @Component 또는 JSR-330 주석이 달린 클래스는 다음과 같이 생성자에 입력하는 방식으로 사용
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MyServiceImpl.class, Dependency1.class, Dependency2.class);
MyService myService = ctx.getBean(MyService.class);
myService.doStuff();
}@Bean 애너테이션을 사용하기
-
@Bean은 메서드-레벨 애너테이션이다. -
@Bean 애너테이션은 @Configuration-annoted 또는 @Component-annoted 클래스에서 사용할 수 있다.
-
<bean />에서 제공하는 일부 속성을 지원한다.
애너테이션 방식의 configuration
@Configuration
public class DependencyConfig {
@Bean
public TransferServiceImpl transferService() {
return new TransferServiceImpl();
}
}Bean 정의가 있는 인터페이스를 구현하여 bean configuration을 설정할 수도 있다.
public interface BaseConfig {
@Bean
default TransferServiceImpl transferService() {
return new TransferServiceImpl();
}
}
@Configuration
public class DependencyConfig implements BaseConfig {
}@Bean 애너테이션이 추가된(@Bean-annotated) 메서드는 빈을 구축하는데 필요한 의존성을 나타내는데 매개 변수를 사용할 수 있다.
@Configuration
public class DependencyConfig {
@Bean
public TransferService transferService(AccountRepository accountRepository) {
return new TransferServiceImpl(accountRepository);
}
}@Configuration 애너테이션을 사용하기
-
@Configuration는 해당 객체가 bean definitions의 소스임을 나타내는 애너테이션이다.
-
@Configuration는 @Bean-annoted 메서드를 통해 bean을 선언한다.
-
@Configuration 클래스의 @Bean 메서드에 대한 호출을 사용하여 bean 사이의 의존성을 정의할 수도 있다.
Component Scan
설정 정보 없이 자동으로 스프링 빈을 등록하는 기능
(스프링이 제공하는 기능)
-
@Component가 붙은 모든 클래스를 스프링 빈으로 등록해 준다. -
의존관계를 자동으로 주입하는
@Autowired기능도 제공한다. -
컴포넌트 스캔을 사용하면 @Configuration이 붙은 설정 정보도 자동으로 등록
(@Configuration 코드에 @Component 애너테이션이 붙어있기 때문) -
DependencyConfig 등 @Configuration 설정이 된 파일이 있을 시 아래 코드 추가 :
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = @Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION, classes = Configuration.class))
basePackages
탐색할 패키지의 시작 위치를 지정하고, 해당 패키지부터 하위 패키지 모두 탐색
-
@ComponentScan()의 매개변수로 basePackages = “”를 줄 수 있다. -
지정하지 않으면,
@ComponentScan이 붙은 설정 정보 클래스의 패키지가 시작 위치가 된다. -
스프링 부트를 사용하면
@SpringBootApplication를 이 프로젝트 시작 루트 위치에 두는 것을 추천
(@SpringBootApplication에@ComponentScan이 들어있다.)
Component Scan 기본 대상
-
@Component: 컴포넌트 스캔에서 사용됩니다. -
@Controller&@RestController: 스프링 MVC 및 REST 전용 컨트롤러에서 사용된다.@RestController는 소스 코드에 @Component를 포함
-
@Service: 스프링 비즈니스 로직에서 사용- 특별한 처리를 하지 않는다. (기능 없음)
- 개발자들이 핵심 비즈니스 로직(비즈니스 계층)이 여기에 있다고 인식하는데 도움 되는 용도
- 소스 코드에 @Component를 포함
-
@Repository: 스프링 데이터 접근 계층에서 사용된다.- 스프링 데이터 접근 계층으로 인식하고, 데이터 계층의 예외를 스프링 예외로 변환해준다.
- 소스 코드에 @Component를 포함
-
@Configuration: 스프링 설정 정보에서 사용된다.- 스프링 설정 정보로 인식하고, 스프링 빈이 싱글톤을 유지하도록 추가 처리를 한다.
필터
-
includeFilters : 컴포넌트 스캔 대상을 추가로 지정
-
excludeFilters : 컴포넌트 스캔에서 제외할 대상을 지정
-
FilterType 옵션
- ANNOTATION:
기본값, 애너테이션으로 인식해서 동작 - ASSIGNABLE_TYPE: 지정한 타입과 자식 타입을 인식해서 동작
- ASPECTJ: AspectJ 패턴을 사용
- REGEX: 정규 표현식을 나타냄
- CUSTOM:
TypeFilter라는 인터페이스를 구현해서 처리
- ANNOTATION:
다양한 의존관계 주입 방법
생성자 주입 << 가장 추천
생성자를 통해서 의존 관계를 주입 받는 방법
- 생성자에 @Autowired를 하면 스프링 컨테이너에 @Component로 등록된 빈에서 생성자에 필요한 빈들을 주입한다.
-
생성자 호출 시점에 딱 1번만 호출되는 것이 보장된다.
-
불변과 필수 의존 관계에 사용된다.
-
생성자가 1개만 존재하는 경우에는 @Autowired를 생략해도 자동 주입 된다.
- 스프링이 해당 클래스 객체를 생성하여 빈에 넣어야하는데 생성할 때 생성자를 부를 수 밖에 없다. 그렇기 때문에 빈을 등록하면서 의존 관계 주입도 같이 된다.
-
NullPointerException 을 방지할 수 있다.
-
주입받을 필드를 final 로 선언 가능하다.
@Component
public class CoffeeService {
private final MemberRepository memberRepository;
private final CoffeeRepository coffeeRepository;
@Autowired
public CoffeeService(MemberRepository memberRepository, CoffeeRepository coffeeRepository) {
this.memberRepository = memberRepository;
this.coffeeRepository = coffeeRepository;
}
}수정자 주입 (setter 주입)
setter라 불리는 필드의 값을 변경하는 수정자 메서드를 통해서 의존 관계를 주입하는 방법
- 선택과 변경 가능성이 있는 의존 관계에 사용
- 자바빈 프로퍼티 규약의 수정자 메서드 방식을 사용하는 방법
@Component
public class CoffeeService {
private MemberRepository memberRepository;
private CoffeeRepository coffeeRepository;
@Autowired
public void setMemberRepository(MemberRepository memberRepository) {
this.memberRepository = memberRepository;
}
@Autowired
public void setCoffeeRepository(CoffeeRepository coffeeRepository) {
this.coffeeRepository = coffeeRepository;
}
}-
생성자 주입과 차이점은 생성자 대신 set필드명 메서드를 생성하여 의존 관계를 주입
-
@Autowired를 입력하지 않으면 실행이 되지 않는다.@Component가 실행하는 클래스를 스프링 빈으로 등록- 스프링 빈으로 등록한 다음
@Autowired있는 것들을 자동으로 의존 관계를 주입
필드 주입
필드에 @Autowired 붙여서 바로 주입하는 방법
-
코드가 간결해서 예전에 많이 사용했다.
-
but 외부에서 변경이 불가능하여 테스트하기 힘들다는 단점이 있다.
-
DI 프레임워크가 없으면 아무것도 할 수 없다.
-
실제 코드와 상관 없는 특정 테스트를 하고 싶을 때 사용할 수 있다.
- 하지만 정상적으로 작동되게 하려면 결국 setter가 필요하게 돼서 수정자 주입을 사용하는게 더 편리하다.
@Component
public class CoffeeService {
@Autowired
private MemberRepository memberRepository;
@Autowired
private CoffeeRepository coffeeRepository;
}일반 메서드 주입
일반 메서드를 사용해 주입하는 방법
- 한번에 여러 필드를 주입 받을 수 있다.
- 일반적으로 사용되지 않는다.
옵션 처리
-
주입할 스프링 빈이 없을 때 동작해야하는 경우가 있다.
- @Autowired만 사용하는 경우 required 옵션 기본값인 true가 사용되어 자동 주입 대상이 없으면 오류가 발생하는 경우가 있을 수 있다.
- 스프링 빈을 옵셔널하게 해둔 상태에서 등록이 되지 않고, 기본 로직으로 동작하게 하는 경우
-
자동 주입 대상 옵션 처리 방법
@Autowired(required=false)- 자동 주입할 대상이 없으면 수정자 메서드 호출 자체가 안된다.
org.springframework.lang.@Nullable- 자동 주입할 대상이 없으면 null이 입력된다.
Optional<>- 자동 주입할 대상이 없으면
Optional.empty가 입력된다.
- 자동 주입할 대상이 없으면
생성자 주입을 사용해야하는 이유
1. 불변
-
의존 관계 주입은 처음 애플리케이션이 실행될 때 대부분 정해지고 종료 전까지 변경되지 않고 변경돼서는 안된다.
- 따라서 수정자 주입 같은 경우에는 이름 메서드를 public으로 열어두어 변경이 가능하기 때문에 적합하지 않다.
-
생성자 주입은 객체를 생성할 때 최초로 한번만 호출되고 그 이후에는 다시는 호출되는 일이 없기 때문에 불변하게 설계할 수 있다.
2. 누락
호출했을 때는 NPE(Null Point Exception)이 발생하는데 의존관계 주입이 누락되었기 때문에 발생하는 것이다.생성자 주입을 사용하면 주입 데이터 누락 시 컴파일 오류가 발생한다.필드 주입과수정자 주입은 빈이 생성된 후에 참조를 하기 때문에 애플리케이션이 어떠한 오류와 경고 없이 구동 됨.
3. final 키워드 사용 가능
- 생성자 주입을 사용하면 필드에 final 키워드를 사용할 수 있다.
- 생성자에서 값이 설정되지 않으면 컴파일 시점에서 오류를 확인할 수 있다.
java: variable (데이터 이름) might not have been initialized
- 생성자 주입을 제외한 나머지 주입 방식은 생성자 이후에 호출되는 형태이므로 final 키워드를 사용할 수 없다.
4. 순환 참조
- 순환 참조를 방지할 수 있다.
생성자 주입 방식의 장점 요약
-
의존관계 설정이 되지 않으면 객체생성이 불가능
- 컴파일 타임에 오류 인지가 가능
- NPE 에러 방지가 가능
-
의존성 주입이 필요한 필드를 final 로 선언 가능
-
(스프링에서) 순환참조 감지가 가능
- 순환 참조 시 앱구동이 실패
-
테스트 코드 작성 용이
수정자 주입이 필요한 경우에만 수정자 주입 사용하고 가능한한 생성자 주입 방식을 사용하자.