Daily Coding 23번
피보나치 수열 num번째 값을 리턴하시오.
- 반복문 사용 금지
public int fibonacci(int num) {
int result = 0;
if(num==1) return 0;
else if(num==2||num==3) return 1;
else {
result = fibonacci(num - 2) + fibonacci(num - 1);
}
return result;
}제한시간 초과...
public int fibonacci(int num) {
ArrayList<Integer> arrList =new ArrayList<>(num);
arrList.add(0);
arrList.add(1);
int result = fibonacci(arrList.get(num-1))+fibonacci(arrList.get(num-2));
arrList.add(result);
return result;
}뭔가 리스트를 이용해서 값을 저장해두고 꺼내와서 재귀 횟수를 절반 가까이 줄일 수 있을 것 같은데 잘안된다. 초기값 설정이 안된다.
list를 다루는 스킬이 부족한 것 같아 일단 포기하고 배열로 시도해 봤다.
public int fibonacci(int num) {
if(num==0) return 0;
else if(num>0) {
int[] result = new int[num + 1];
result[0] = 0;
result[1] = 1;
return fibo(num, result);
}
return 0;
}
public int fibo(int num, int[] arr){
if(num==1) return 1;
if(num==0) return 0;
arr[num] = fibo(num-2, arr)+fibo(num-1, arr);
return arr[num];
}배열로 해서 올바른 결과가 나오기는 하는데 이것도 시간초과가 나온다.
이런식으로 할 것 같으면 조삼모사 같다...
public int fibonacci(int num) {
if(num==0) return 0;
else if(num>0) {
int[] result = new int[num + 1];
result[0] = 0;
result[1] = 1;
return fibo(num, result);
}
return 0;
}
public int fibo(int num, int[] arr){
if(arr[num]==0) {
if (num == 1) return 1;
if (num == 0) return 0;
arr[num] = fibo(num - 2, arr) + fibo(num - 1, arr);
}
return arr[num];
}디버깅해보니 배열의 n번째 요소에 값이 이미 들어갔는데 n번째 요소값을 찾아주기 위한 반복이 한번 더 반복되는 것을 볼 수 있었다.(재귀를 두번하기 때문)
따라서 앞 재귀에서 이미 값을 채워 넣었다면 필요없는 재귀를 추가하지 말고 중단할 수 있도록 arr[num]==0 조건을 추가하니 시간복잡도가 줄어들어 모든 테스트에 통과할 수 있었다.
비슷한 방식으로 다시 list를 이용해 풀어보면
public int fibonacci2(int num) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(0);
list.add(1);
return fibo2(list, num);
}
public int fibo2(ArrayList<Integer> list, int num) {
if (list.size() <= num) {
list.add(fibo2(list, num - 1) + fibo2(list, num - 2));
}
return list.get(num);
}이렇게도 풀 수 있다.
결국 시간복잡도를 줄이기 위한 키포인트는 이미 구한 n번째 피보나치 수열값을 다시 구하지 않도록 하는 것이였다.
[Spring MVC] 예외 처리
@ExceptionHandler를 이용한 Controller 레벨에서의 예외 처리
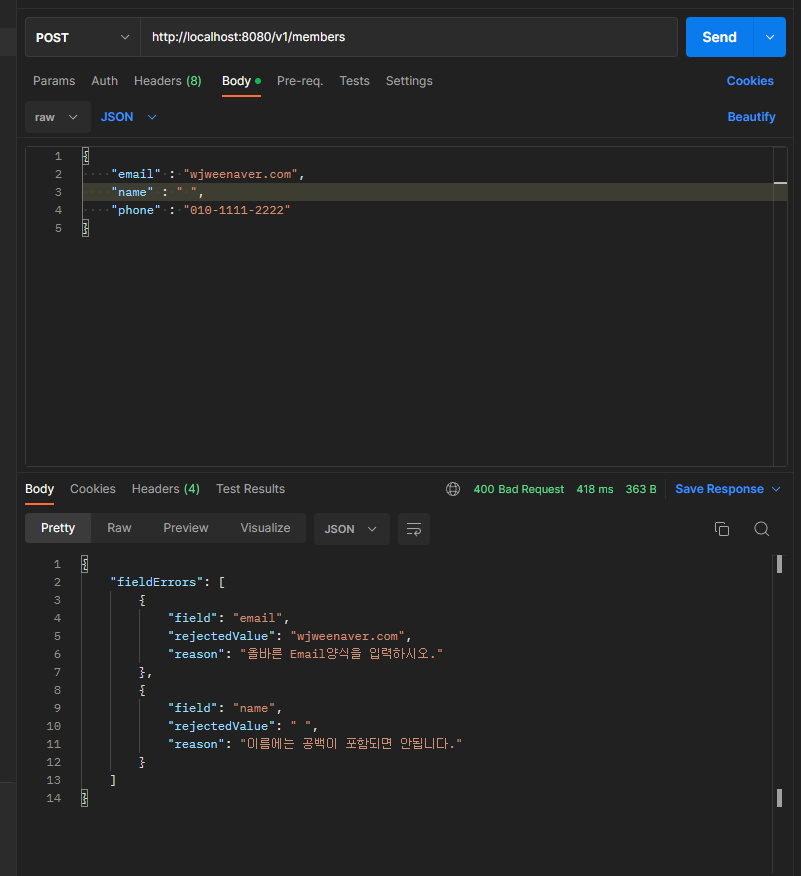
// 클라이언트에서 핸들러 메서드에 요청을 전송했을 때
// 각 메서드의 맞는 유효한 데이터가 아니면 유효성 검증에 실패하고, ``MethodArgumentNotValidException``이 발생
@ExceptionHandler // ``MethodArgumentNotValidException``이 발생하면 전달해주는 애너테이션
public ResponseEntity handleException(MethodArgumentNotValidException e) { // 예외처리 메서드
final List<FieldError> fieldErrors = e.getBindingResult().getFieldErrors();
// MethodArgumentNotValidException 객체(e)에서 getBindingResult().getFieldErrors()를 통해 발생한 에러 정보를 확인할 수 있다.
return new ResponseEntity(fieldErrors, HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}Controller 클래스에 위와 같이 MethodArgumentNotValidException이 발생했을 때(유효하지 않은 요청일 때) @ExceptionHandler 애너테이션을 이용해 예외를 처리하는 메서드로 유효성 검증 실패의 원인을 가져올 수 있다.
그런데 위와 같이 하면 List(fieldErrors)에 필요없는 정보가 많이 담겨 있다.
fieldErrors를 편집할 클래스(ErrorResponse 클래스)를 추가하면 클라이언트에 표기해줄 오류문의 가독성을 더 좋게할 수 있다.
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Getter;
import java.util.List;
@Getter
@AllArgsConstructor
public class ErrorResponse {
private List<FieldError> fieldErrors;
@Getter
@AllArgsConstructor // 해당 객체 내에 있는 모든 변수들을 인수로 받는 생성자를 만들어냄
public static class FieldError{ // ErrorResponse 클래스의 static 멤버 클래스
private String field;
private Object rejectedValue;
private String reason;
// public FieldError(String field, Object rejectedValue, String reason) { // << @AllArgsConstructor가 이걸 만들어 줌
// this.field = field;
// this.rejectedValue = rejectedValue;
// this.reason = reason;
// }
}
}
@ExceptionHandler
public ResponseEntity handleException(MethodArgumentNotValidException e) { // 예외처리 메서드
final List<FieldError> fieldErrors = e.getBindingResult().getFieldErrors();
// MethodArgumentNotValidException 객체(e)에서 getBindingResult().getFieldErrors()를 통해 발생한 에러 정보를 확인할 수 있다.
List<ErrorResponse.FieldError> errors = fieldErrors.stream()
.map(error -> new ErrorResponse.FieldError(
error.getField(),
error.getRejectedValue(),
error.getDefaultMessage()))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return new ResponseEntity(new ErrorResponse(errors), HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
@ExceptionHandler의 단점
-
각 Controller 클래스마다 코드 중복이 발생
- 각각의 Controller 클래스에서 @ExceptionHandler 애너테이션을 사용하여 Request Body에 대한 유효성 검증 실패에 대한 에러 처리를 해야 됨.
-
예외의 종류별로
@ExceptionHandler를 추가한 에러 처리 핸들러 메서드를 만들어 줘야 한다.- Controller에서 처리해야 되는 예외(Exception)가 유효성 검증 실패에 대한 예외(MethodArgumentNotValidException)만 있는것이 아니다.
@RestControllerAdvice를 이용한 예외처리
@RestControllerAdvice
- 예외를 클래스로 가져오는 애너테이션
- 예외 처리 공통화하는데 사용
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionAdvice {
// 유효성 검증에 실패 예외(MethodArgumentNotValidException) 처리 메서드
@ExceptionHandler
public ResponseEntity handleMethodArgumentNotValidException(
MethodArgumentNotValidException e) {
~~~
return ~~~;
}
// 제약 조건 위반예외(ConstraintViolationException) 처리 메서드
@ExceptionHandler
public ResponseEntity handleConstraintViolationException(
ConstraintViolationException e) {
~~~
return ~~~;
}
}위와 같이 클래스 하나에 오류처리를 몰아서 코드의 중복을 없앨 수 있다.
실습
GlobalExceptionAdvice 클래스
- 다양한 종류의 예외를 처리하는 메서드들을 모아둔 클래스
import com.codestates.section3week1.response.ErrorResponse;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestControllerAdvice;
import javax.validation.ConstraintViolationException;
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionAdvice { // 예외처리 클래스
@ExceptionHandler // 예외 전달해주는 애너테이션
//@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
public ResponseEntity handleMethodArgumentNotValidException(MethodArgumentNotValidException e) { // 유효성 검증에 실패 예외(MethodArgumentNotValidException) 처리 메서드
final ErrorResponse response = ErrorResponse.of(e.getBindingResult());
return new ResponseEntity(response, HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
// 핸들러 메서드의 URI 변수인 “/{member-id}”에 0이 넘어올 경우, ConstraintViolationException이 발생
@ExceptionHandler
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
public ErrorResponse handleConstraintViolationException(
ConstraintViolationException e) {
final ErrorResponse response = ErrorResponse.of(e.getConstraintViolations());
return response;
}
}
@RestControllerAdvice 애너테이션을 사용하면 ResponseEntity로 래핑할 필요가 없다.
@RestControllerAdvice는 @ResponseBody가 추가로 붙어있어, 응답을 JSON으로 내려준다.
ResponseEntity를 사용하지 않아도 위handleConstraintViolationException()메서드와 같이@ResponseStatus애너테이션을 사용해HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST도 포함시켜 응답을 보낼 수 있다.
ErrorResponse 클래스
- 예외응답을 간결화하는 메서드를 각 예외 타입별로 멤버 클래스 형태로 정리해둔 클래스
package com.codestates.section3week1.response;
import lombok.Getter;
import org.springframework.validation.BindingResult;
import javax.validation.ConstraintViolation;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@Getter
public class ErrorResponse { // 에러문 간략화해서 필요한 정보만 담는 용도의 클래스
private List<FieldError> fieldErrors;
private List<ConstraintViolationError> violationErrors;
// ErrorResponse 생성자
private ErrorResponse(List<FieldError> fieldErrors, List<ConstraintViolationError> violationErrors) {
this.fieldErrors = fieldErrors;
this.violationErrors = violationErrors;
}
// BindingResult에 대한 ErrorResponse 객체 생성
public static ErrorResponse of(BindingResult bindingResult){
return new ErrorResponse(FieldError.of1(bindingResult), null);
}
// Set<ConstraintViolation<?>> 객체에 대한 ErrorResponse 객체 생성
// 메서드 오버로딩
public static ErrorResponse of(Set<ConstraintViolation<?>> violations) {
return new ErrorResponse(null, ConstraintViolationError.of2(violations));
}
@Getter
public static class FieldError{ // ErrorResponse 클래스의 static 멤버 클래스
private String field;
private Object rejectedValue;
private String reason;
private FieldError(String field, Object rejectedValue, String reason) {
this.field = field;
this.rejectedValue = rejectedValue;
this.reason = reason;
}
private static List<FieldError> of1(BindingResult bindingResult) { // MethodArgumentNotValidException = BindingResult
final List<org.springframework.validation.FieldError> fieldErrors = bindingResult.getFieldErrors();
return fieldErrors.stream()
.map(error -> new FieldError(
error.getField(),
error.getRejectedValue() == null ? "" : error.getRejectedValue().toString(),
error.getDefaultMessage()))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}
@Getter
public static class ConstraintViolationError {
private String propertyPath;
private Object rejectedValue;
private String reason;
private ConstraintViolationError(String propertyPath, Object rejectedValue, String reason) {
this.propertyPath = propertyPath;
this.rejectedValue = rejectedValue;
this.reason = reason;
}
private static List<ConstraintViolationError> of2(Set<ConstraintViolation<?>> constraintViolations) {
return constraintViolations.stream()
.map(constraintViolation -> new ConstraintViolationError(
constraintViolation.getPropertyPath().toString(),
constraintViolation.getInvalidValue().toString(),
constraintViolation.getMessage()))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}
}
MethodArgumentNotValidException와 BindingResult
BindingResult 인터페스를 구현하고 Exception 클래스를 상속받은 BindException 클래스을 상속받은 클래스가 MethodArgumentNotValidException이다.
대충 말하자면 MethodArgumentNotValidException는
MethodParameter객체 + BindingResult객체라고 할 수 있다.
여기서 원하는 에러문은 BindingResult에 있기 때문에 getBindingResult() 메소드를 이용해 MethodParameter객체를 버리고 가져온 것이다.
BindingResult 인터페이스
- 검증 오류가 발생할 경우 오류 내용을 보관하는 스프링 프레임워크에서 제공하는 객체
