client로부터 받은 http headers 값 Resolver에서 조회하기
(1) 미들웨어를 먼저 구현한다.
미들웨어에서는 client에서 온 http headers를 받아 해당 사용자가 누구인지 찾는 작업을 할 것 이다. middleware의 구현은 별도의 클래스에서 구현한다. (또는 함수 자체를 구현해서, 그것을 consumer에 등록해서 사용할수도 있다.) nest와 express 타입을 이용해서 구현한다.
// src/jwt/jwt.middleware.ts
import { NestMiddleware } from '@nestjs/common';
import { NextFunction, Request, Response } from 'express';
export class JwtMiddleware implements NestMiddleware {
use(req: Request, res: Response, next: NextFunction) {
// 어떤 동작을 하고
console.log(req)
// 동작이 끝나면 next()가 실행되도록 구현
next();
}
}(2) 구현한 미들웨어를 사용한다. 예시에서는 모든 모듈에서 사용할 수 있도록 app.module.ts에 등록해본다.
export class AppModule implements NestModule {
configure(consumer: MiddlewareConsumer) {
consumer.apply(JwtMiddleware).forRoutes({
path: '/graphql',
method: RequestMethod.POST,
});
}
}forRoutes를 통해서 어떤 path에서 이 미들웨어를 작동시킬 것인지, 나아가 어떤 메소드에서 이 미들웨어를 작동시킬 것인지까지 설정 할 수 있다.
- 특정 경로만 제외하고 싶을 때는
apply().exclude를 통해서 제외할 수 있다.
(3) 미들웨어 로직을 구체화 한다.
미들웨어 내에서 DI를 하기 위해 @Injectable()를 붙여준다. @Injectable()가 없는 레이어에서는 DI를 할 수 없다.
- jwtService를 DI 해주고, jwtService를 이용해서
this.jwtService.verify()를 통해 client 받아온 token을 vaify 한다. - 그리고 varify한 토큰을 통해 db에서 사용자 조회를 한다. 이것을 하기 위해 userService에
findById()라는 메서드를 생성하고, jwtMiddleware에 DI 한다. 그러면 아래와 같은 에러 메시지가 터미널에 표시된다.
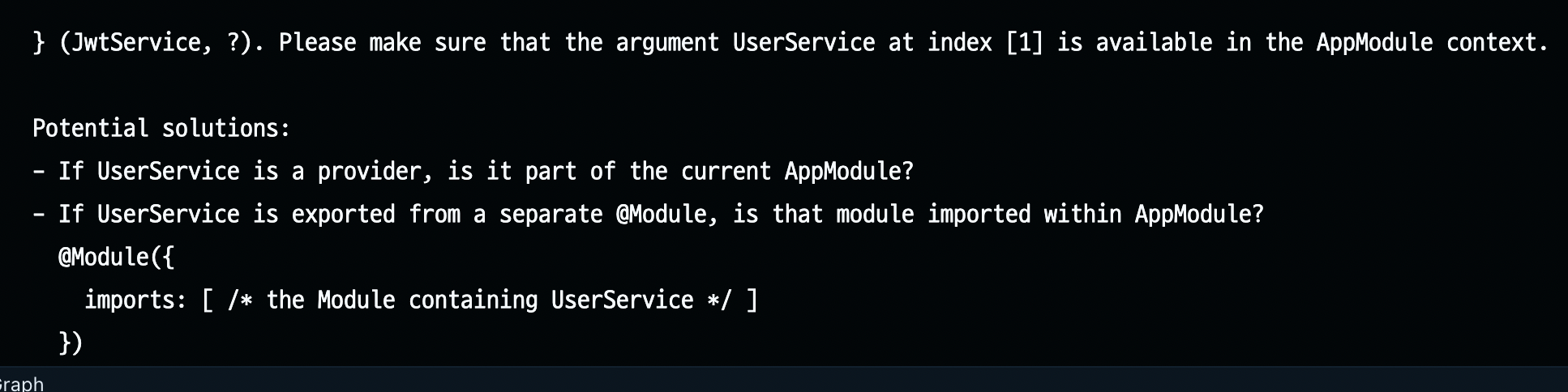
위 에러가 나타나는 이유는UserService를Provider로 가지고 있는user.module.ts에서export해주지 않고 있기 때문이다.
@Module({
imports: [TypeOrmModule.forFeature([User]), ConfigService], // Repository
exports: [UserService], // 다른 Provider에서 사용하고자 하는 것을 exports에 추가한다.
providers: [UserService, UsersResolver], // Service, Resolver
})
export class UsersModule {}exports에 useService를 추가하고, 다시 jwtMiddleware에 돌아와서 this.useService.findById()를 이용해서 유저의 정보를 db에서 조회하는 메서드를 구현한다.
기타 개념
- implements 와 extends는 다르다. implements는 새로 생기는 클래스가 implements된 클래스 처럼 행동해야 한다는 것을 의미한다.
- verify는 시크릿키로 검증하지만, decode는 검증하지 않고 해독된 payload를 반환한다.
