1. 문제
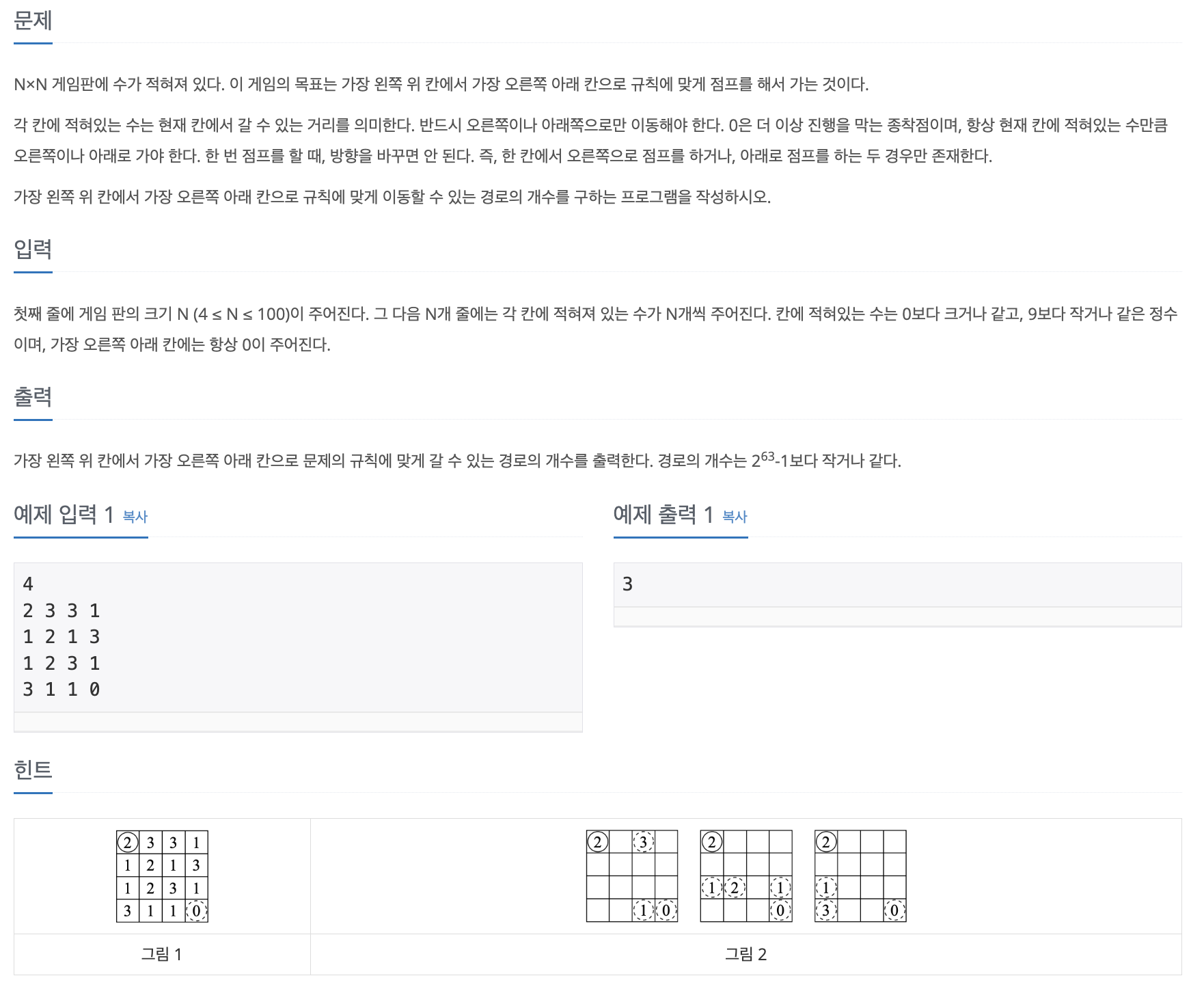
2. 코드
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static int n;
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
n= s.nextInt(); // 게임판의 크기
int list[][] = new int[n+1][n+1];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++) {
list[i][j] = s.nextInt();
}
}
long dp[][] = new long[n+1][n+1]; // 경로의 개수는 2^63-1보다 작거나 같으니 long타입
dp[1][1]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++) {
int next = list[i][j];
if(i==n&&j==n) {
continue;
}
if(j+next<=n) {
dp[i][j+next] += dp[i][j];
}
if(i+next<=n) {
dp[i+next][j] += dp[i][j];
}
}
// dp 변화 출력확인
//print(dp);
//System.out.println();
}
System.out.println(dp[n][n]);
}
public static void print(long[][] dp){
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
for(int j=1; j<=n; j++){
System.out.print(dp[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
3. 풀이
-
DFS와 다이나믹 프로그래밍으로 풀 수 있는 문제이다.
-
답이 263 - 1 로 매우 큰 수이기때문에 DFS로 하다가는 중복된 구간을 계속 방문하게 되어, 필연적으로 시간초과가 발생한다. 따라서 long[][] 타입의 dp를 정의하여 메모이제이션을 수행해야한다.
-
게임판에 적혀있는 정수들의 배열을 list[][], 그 칸에 도착하게되는 경로의 개수를 dp[][]라고 하면, 각 칸에 적혀져 있는 수만큼 오른쪽 or 아래방향으로 움직이게 되니까, list[i][j]에서의 다음 이동 칸은 list[i+list[i][j]][j] 또는 list[i]j+list[i][j]], 이 두가지 경우가 될 수 있다.
-
즉, 다음으로 도착하게 되는 이동칸에 이전 칸까지 오는 경로의 개수를 더해주면 된다.
-
dp[i+list[i][j]][j] += dp[i][j], dp[i]j+list[i][j]] += dp[i][j] 인 셈이다.
-
이 때, i+list[i][j] 와 j+list[i][j]는 N보다 같거나 작은 범위에서만 가능하다.
-
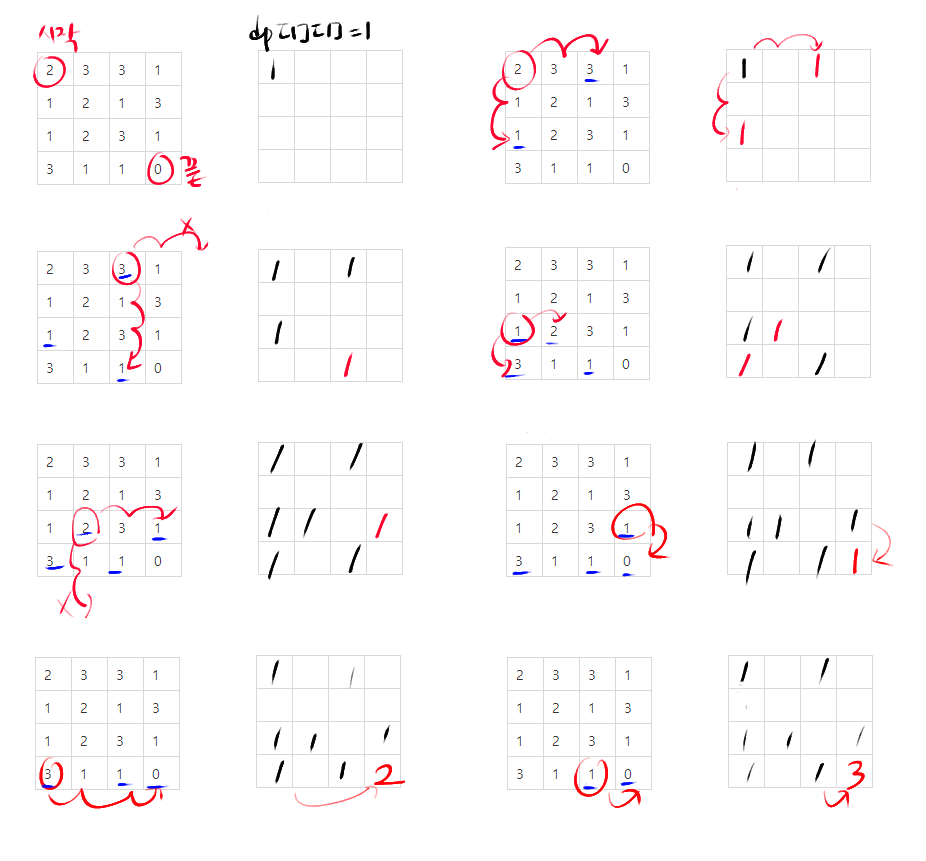
왼쪽이 게임판인 list, 오른쪽이 경로의 개수를 더하는 dp이다.
4. 링크
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1890
https://hu-coding.tistory.com/36
