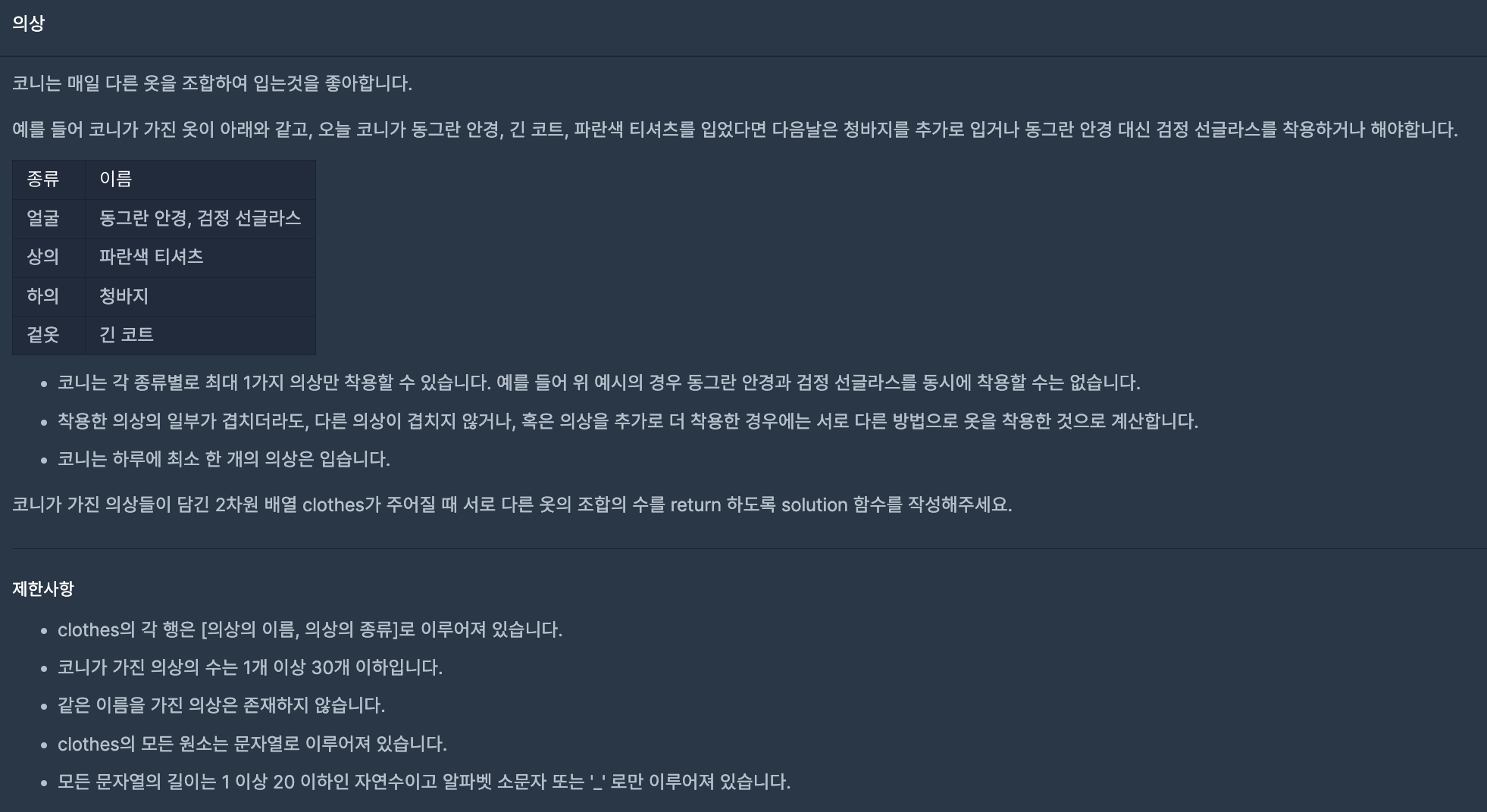
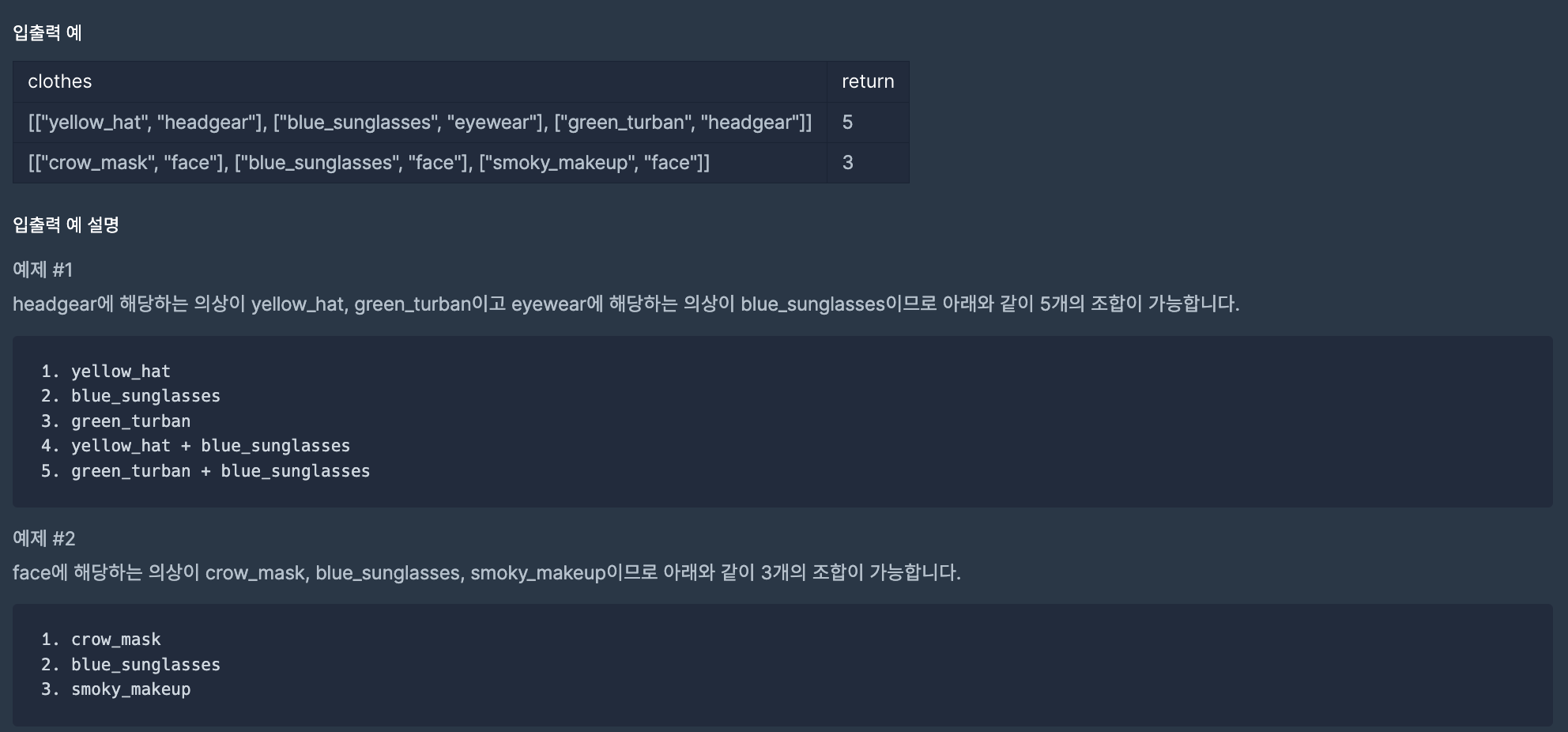
1. 문제
2. 코드
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int solution(String[][] clothes) {
int answer = 1;
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (String[] cloth : clothes) {
String type = cloth[1];
if (map.containsKey(type)) {
map.put(type, map.get(type) + 1);
} else {
map.put(type, 1);
}
}
for (int count : map.values()) {
answer *= (count + 1);
}
return answer - 1;
}
}
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
class Solution {
public int solution(String[][] clothes) {
// 종류별로 옷의 개수를 저장할 HashMap 선언
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
// 옷을 종류별로 구분하기 -> [옷 종류, 개수]
for (int i = 0; i < clothes.length; i++) {
String clothesType = clothes[i][1]; // 옷의 종류는 clothes 배열에서 [i][1] 위치에 존재한다. -> clotheType 변수에 넣어주기
if (map.get(clothesType) == null) { // 만약 처음 보는 종류이면
map.put(clothesType, 1); // 개수는 1개
} else { // 처음 보는 종류가 아닌, map에 이미 있는 종류라면
map.put(clothesType, (map.get(clothesType) + 1)); // 해당 종류의 옷의 개수 +1 증가해서 업데이트
}
}
int answer = 1;
// 옷 조합의 수 구하기
for (String c : map.keySet()) { // 옷 종류들 = key 값, 해당 종류에 대한 개수 = value 값
answer *= (map.get(c) + 1); // 각 종류 별 옷의 개수를 곱해나감
// map.get(c)+1에서 +1의 이유는 아무것도 없는 경우까지 포함하여 곱해야 하는데 map에는 반영이 안되어있기 때문
}
answer = answer - 1; // 모든 종류를 입지 않았을 때의 경우의 수 1 제거
return answer;
}
}3. 풀이
- answer=(a+1)×(b+1)×(c+1)×⋯−1
- 각 종류의 옷을 입거나, 입지 않는 두 가지 경우의 수를 고려하면서, 모든 종류의 옷에 대한 조합을 구한 후, 아무것도 입지 않은 경우를 빼준다
- 코드에서는 Map<String, Integer> map을 이용하여 각 의상 종류별로 입을 수 있는 옷의 개수를 구하였고, for (int count : map.values()) 구문에서는 위의 공식에 따라 계산한 값을 answer 변수에 곱해주었다.
- 마지막으로, return answer - 1 구문에서는 아무것도 입지 않은 경우를 빼주었다.
4. 링크
https://school.programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/42578
