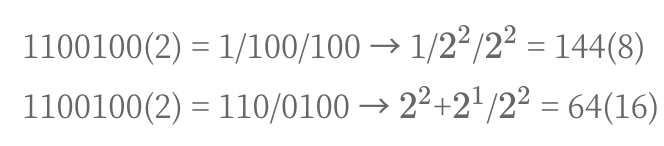String 의 static 메서드인 format 메서드는 문자열의 형식을 설정하는 메서드이다.
1. %d (10진수 형식)
- 10진수 integer의 형식을 설정할 때 이용한다.
- %5d 와 같이 %와 d 사이에 정수를 설정하면, 글자 길이를 설정할 수 있다.
- 기본적으로 오른쪽 정렬이고, -를 붙일 경우 왼쪽정렬이다.
- 표현할 숫자인 i의 길이가 5보다 작을 경우 0을 붙인다.(leading 0s) (ln 6)
- % 바로 뒤에 , 를 붙이면 3자리 단위로 쉼표를 찍어준다
- ※ %d 와 %-5d의 구분을 위해 맨 마지막에 _ 을 포함
int i = 23;
System.out.println(String.format("%d_", i));
System.out.println(String.format("%5d_", i));
System.out.println(String.format("%-5d_", i));
System.out.println(String.format("%05d_", i));
/*
23_
23_
23 _
00023_
*/
int j = 123456789;
System.out.println(String.format("%,d_", j));
// 123,456,789_2. %s (문자열 형식)
-
문자열의 형식을 설정할 때 이용한다.
-
%s는 문자열을 그대로 출력하고,
-
%s 앞에 숫자(N)를 설정할 경우, str.length()가 N보다 작을 경우 공백을 추가한다.
-
' - ' 를 붙일 경우, 왼쪽 정렬. (default는 오른쪽 정렬)
-
'.숫자(N)'를 설정할 경우, 최대 N길이 만큼만 출력
String str = "tete";
System.out.println(String.format("%s_", str));
System.out.println(String.format("%12s_", str));
System.out.println(String.format("%-12s_", str));
System.out.println(String.format("%.2s_", str));
System.out.println(String.format("%-12.2s_", str));
System.out.println(String.format("%12.2s_", str));
/*
tete_
tete_
tete _
te_
te _
te_
*/3. %f (실수형 형식)
-
실수형 숫자 형식을 설정할 때 이용한다.
-
floating point 표현법의 기본 설정인 %f는 %.6f 와 같다.(ln 7~9)
-
%15.2f 는 글자 길이 15, 소수점 아래 2자로 나타내라는 의미로, .도 글자길이에 포함된다.(ln 12~15)
-
소수점 아래는 반올림하여 출력된다.
-
%d와 마찬가지로, 숫자 %뒤의 정수부 앞에 0을 붙이면, 왼쪽에 공백으로 표시될 부분을 0으로 채워준다 (ln 16~17)
double n = 123.45678;
System.out.println(3.4);
System.out.println(n);
System.out.println();
System.out.println(String.format("%f_", 3.4));
System.out.println(String.format("%f_", n));
System.out.println(String.format("%.6f_", n));
System.out.println(String.format("%15f_", n));
System.out.println(String.format("%-15f_", n));
System.out.println(String.format("%.3f_", n));
System.out.println(String.format("%.2f_", n));
System.out.println(String.format("%15.2f_", n));
System.out.println(String.format("%-15.2f_", n));
System.out.println(String.format("%015f_", n));
System.out.println(String.format("%015.2f_", n));
/*
3.4
123.45678
3.400000_
123.456780_
123.456780_
123.456780_
123.456780 _
123.457_
123.46_
123.46_
123.46 _
00000123.456780_
000000000123.46_
*/4. Locale 설정
- String.format(포맷, 값);
- 같은 메서드명의 overloading 된 String.format(Locale, 포맷, 값); 메서드를 이용하면 국가별 포맷 설정이 가능하다.
- Locale을 설정하지 않을 경우, 기본적으로는 OS에 설정되어있는 값이 default로 적용된다.
- GERMANY에서 사용하는 금액 단위인 유로화는 3자리 구분자를 .을 이용하기 때문에 3자리수 단위로 .이 표기되며,
- 오전 오후를 표시하는 포맷인 %tp의 경우에도 기본값으로는 '오후'를, Locale.ENGLISH에서는 'pm'을 출력한다.
int money = 35000;
Date today = new Date();
System.out.println(String.format("₩ %,d", money));
System.out.println(String.format(Locale.GERMANY, "%,d €", money));
System.out.println(String.format("%tp", today));
System.out.println(String.format(Locale.ENGLISH, "%tp", today));
/*
₩ 35,000
35.000 €
오후
pm
*/5. %t (날짜시간 형식)
-
y: 연, year
M: 월, month
d: 일, day of month
H: 시, 24-hour
h: 시, 12-hour
M: 분, minute
s: 초, second -
기본적으로 시간 및 날짜 형식에는 leading-0s를 붙인다.
-
가장 많이 이용될 포맷 형식은 %tF와 %tT로, 날짜와 시각을 연-월-일 시:분:초 로 나타낸다.
-
연월일을 yyMMdd 형태로 출력(leading-0s 포함)하고 싶을 때엔 %ty%tm%d
-
시분초를 HH:mm:ss 형태로 출력(leading-0s 포함)하고 싶을 때엔 %tH%tM%tS
-
포맷에 %문자를 쓰고 싶다면 %% 와 같이 % 문자를 2번 쓰면 된다.
Date n = new Date();
System.out.println(n +"\n");
System.out.println(String.format("%%tF(yyyy-MM-dd): %tF", n));
System.out.println(String.format("%%tT(02H:02m:02s): %tT, %%tR(02H:02m): %tR", n, n));
System.out.println(String.format("%%ty(2y): %ty, %%tY(4y): %tY", n, n));
System.out.println(String.format("%%tm(02M): %tm", n));
System.out.println(String.format("%%td(02d): %td, %%te(d): %te", n, n));
System.out.println(String.format("%%tH(02H): %tH", n));
System.out.println(String.format("%%tM(02m): %tM", n));
System.out.println(String.format("%%tS(02s): %tS", n));
System.out.println(String.format("%%tZ(time zone): %tZ, %%tz(time zone offset): %tz", n, n));
/*
Thu Mar 05 14:07:09 KST 2020
%tF(yyyy-MM-dd): 2020-03-05
%tT(02H:02m:02s): 14:07:09, %tR(02H:02m): 14:07
%ty(2y): 20, %tY(4y): 2020
%tm(02M): 03
%td(02d): 05, %te(d): 5
%tH(02H): 14
%tM(02m): 07
%tS(02s): 09
%tZ(time zone): KST, %tz(time zone offset): +0900
*/System.out.println(String.format("%%tA(day of Week, Full name): %tA, %%ta: %ta", n, n));
System.out.println(String.format("%%tB(month, Full name): %tB, %%tb: %tb", n, n));
System.out.println(String.format(Locale.ENGLISH, "%%tB(month, Full name): %tB, %%tb: %tb", n, n));
System.out.println(String.format("%%tc(= %%ta %%tb %%td %%tT %%tZ %%tY): %tc", n));
System.out.println(String.format("%%tD(MM/dd/yy): %tD", n));
System.out.println(String.format("%%td(02d): %td, %%te(d): %te", n, n));
System.out.println(String.format("%%tF(yyyy-02M-02d): %tF", n));
System.out.println(String.format("%%tH(02H, 00-23): %tH, %%tk(H, 0-23): %tk", n, n));
System.out.println(String.format("%%tI(02h, 01-12): %tI, %%tl(h, 1-12): %tl", n, n));
System.out.println(String.format("%%tj(day of Year, 001-366): %tj", n));
System.out.println(String.format("%%tp(오전 또는 오후): %tp", n));
/*
%tA(day of Week, Full name): 목요일, %ta: 목
%tB(month, Full name): 3월, %tb: 3월
%tB(month, Full name): March, %tb: Mar
%tc(= %ta %tb %td %tT %tZ %tY): 목 3월 05 14:07:09 KST 2020
%tD(MM/dd/yy): 03/05/20
%td(02d): 05, %te(d): 5
%tF(yyyy-02M-02d): 2020-03-05
%tH(02H, 00-23): 14, %tk(H, 0-23): 14
%tI(02h, 01-12): 02, %tl(h, 1-12): 2
%tj(day of Year, 001-366): 065
%tp(오전 또는 오후): 오후
*/
6. %c (유니코드 문자 형식)
- 숫자를 유니코드로 변환해줍니다.

System.out.println("Unicode 코드 → 문자");
System.out.println(String.format("48 → %c, 57 → %c", 48, 57));
System.out.println(String.format("65 → %c, 90 → %c", 65, 90));
System.out.println(String.format("97 → %c, 122 → %c", 97, 122));
System.out.println(String.format("44032 → %c, 55203 → %c", 44032, 55203)); // U+AC00, U+D7A3
/*
Unicode 코드 → 문자
48 → 0, 57 → 9
65 → A, 90 → Z
97 → a, 122 → z
44032 → 가, 55203 → 힣
*/7. %o, %x(8진수, 16진수 형식)
int n = 100;
System.out.println(String.format("10진수(%d) : 2진수(%s), 8진수(%o), 16진수(%x)", n, Integer.toBinaryString(n), n, n));
/*
10진수(100) : 2진수(1100100), 8진수(144), 16진수(64)
*/