파이썬 데코레이터
- 데코레이터(Decorator): 장식하다, 꾸미다
- What: 함수를 장식하다.
- 원래의 함수를 감싸서 (Wrapping) 바깥에 기능을 붙일 수 있는 방법
함수를 감싼다?
- 파이썬은 함수 안에 함수를 선언하는 것이 가능하고
- 함수의 인자로 함수를 전달하는 것이 가능하며
- 함수 자체를 리턴하는 것이 가능하다
def outer_func(target func):
def inner_func():
print(`target 함수 실행 전입니다`)
target_func()
print(`target 함수 실행 후입니다`)
return inner_func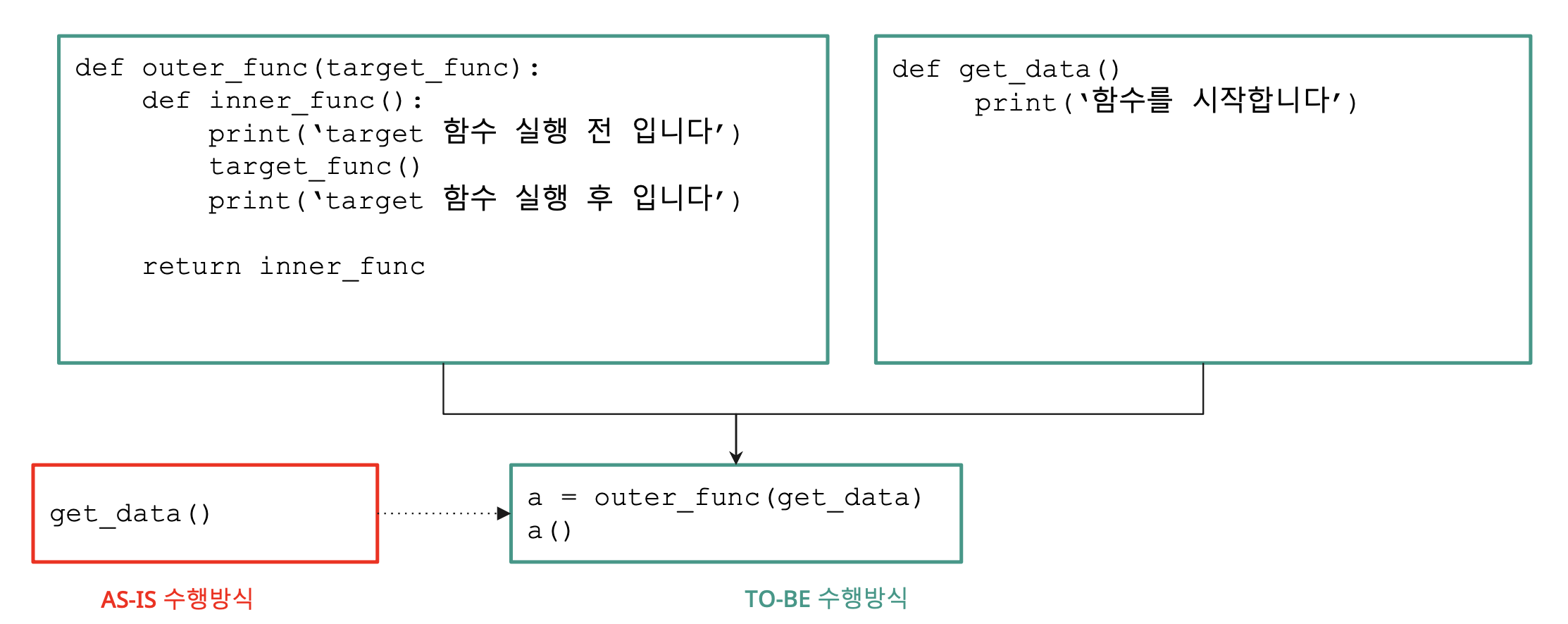
데코레이터를 쓴다면?
@outer_func
def get_data()
print(`func 함수를 시작합니다`)데코레이터의 힘

get_data1()
get_data2()
get_data3()Task 데코레이터
- 파이썬 함수 정의만으로 쉽게 TASK 생성
def python_function1():
...
py_task_1 = PythonOperator(
task_id='py_task'
python_callable=python_function1
)
py_task_1- 이렇게 작성했던 TASK를 이렇게 작성할 수 있습니다.
@task(task_id='py_task_1')
def python_function1():
...
py_task_1 = python_function1()이후에 알게 되겠지만, PythonOperator를 쓰는 것보다, Task 데코레이터를 쓸 때, 변수 공유가 간단해집니다. 에어플로우 공식적으로도 추천하는 방법입니다.
DAG
from airflow import DAG
from airflow.decorators import task
import pendulum
with DAG(
dag_id="dags_python_task_decorator",
schedule="0 2 * * 1",
start_date=pendulum.datetime(2023, 3, 1, tz="Asia/Seoul"),
catchup=False,
) as dag:
@task(task_id="python_task_1")
def print_context(some_input):
print(some_input)
python_task_1 = print_context("task_decorator 실행")task 데코레이터는 PythonOperator를 직접 import하지 않아도, 간단하고 단순하게 만들 수 있습니다.
