Spring Bean
。Spring Context( = IoC Container )에 등록되어 관리되는 자바 객체
。Spring Bean은 개발자가 직접 제어가 불가능하고 오직 Spring Context에 의해 제어
。Spring Context내 Bean Repository에 객체로서 저장되어 Life Cycle와 Dependencies를 자동으로 관리
▶ 필요한 곳에 Auto-Wiring 후 Dependency Injection을 통해 주입
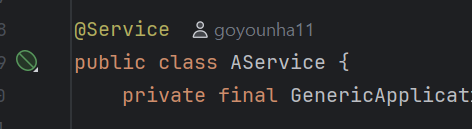
▶ Intellij에서 Spring Bean 선언 시 다음처럼 아이콘이 도출
POJO와 차이점
。Spring Conext에 의해 관리되는 모든 자바객체들은 모두 Spring Bean
▶ 관리되지않는 경우 POJO
。 Spring Bean의 경우 Spring Context 내 Bean Registry에서 Spring Context에 의해 생성 및 파괴
▶ 일반 POJO는 new를 통해 Heap 영역상에서 생성되어 GC에 의해 메모리 해제
A a = A()
A b = new A()
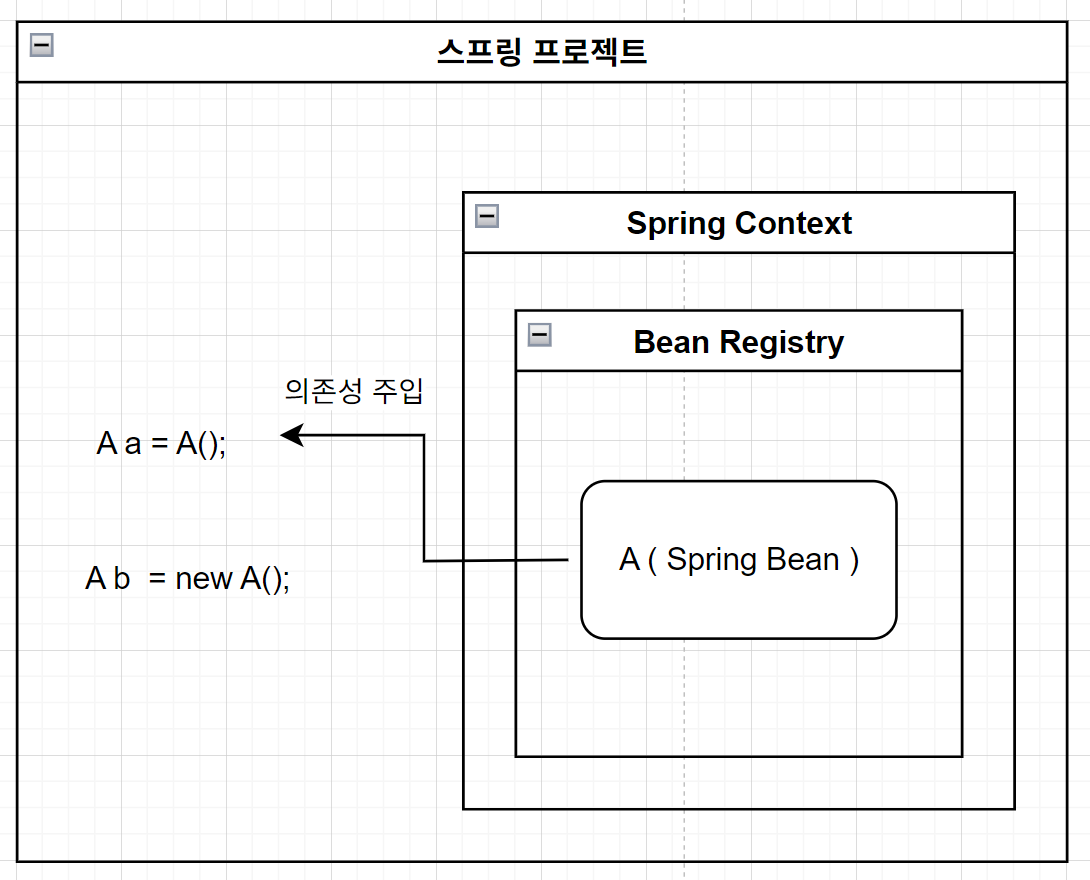
。 Spring Context로 등록된 A 클래스의 Spring Bean을 생성 시 new 없이 A a = A()를 선언
▶ Spring Context의 Bean Registry에서 가져와서 Auto-Wiring을 거쳐 DI를 통해 Spring Bean을 주입
Spring Bean의 초기화
Eager Initialization : default
。Spring Bean의 기본 초기화 방식으로서 주로 사용되는 방식
。Spring Context의 각각의 Spring Bean은 어플리케이션이 실행되는 즉시 초기화가 적용.
。Error 발생 시 어플리케이션이 실행 되지 않는다.
▶ 런타임 시 발생하는 Error을 즉각 확인이 가능하므로 사용을 권장
Lazy Initialization :
。@Lazy로 선언하여 Eager Init'을 억제하도록 설정
。@Lazy가 선언된 Spring Bean이 참조되거나 활용되는 시점에 초기화가 적용
。런타임 전 초기화로 인한 Spring Bean에서 발생되는 Error을 확인하는게 어려우므로 권장되는 방식은 아님
▶ Error 발생 시 Runtime Exception이 발생.
@Component
class EagerInit{
public EagerInit(){
System.out.println("Eager 초기화");
}
}
@Component
@Lazy
class LazyInit{
public LazyInit(){
System.out.println("Lazy 초기화");
}
}
@ComponentScan
public class LazyInitialize {
public static void main(String[] args) {
var context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(LazyInitialize.class);
System.out.println("Context 초기화");
context.getBean(LazyInit.class);
}
}
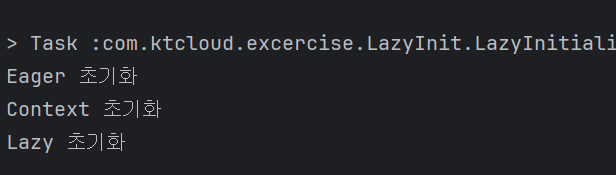
。 어플리케이션이 실행되는 시점에서 EagerInit이 먼저 자동초기화
。이후 Spring Context가 초기화된 후 LazyInit이 호출되는 시점에서 지연초기화가 수행됨
Spring Bean Scope
。Spring Bean은 각각 다른 Scope를 가질 수 있다.
▶ @Scope 어노테이션을 통해 설정이 가능
Singleton : default
@Scope(value= ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_SINGLETON)
。Spring Context 당 Spring Bean을 1개만 생성
▶ 생성된 Spring Bean을 요청 시 Bean Registry에서 가져와서 제공
。Spring Bean의 기본 Scope로서 Spring Context의 시작과 종료까지 유지되는 가장 넓은범위의 Scope
Prototype
@Scope(value = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE)
。요청마다 Spring Bean을 새로 생성하도록 설정
▶ Spring Context 당 복수의 Context Instance가 존재할 수 있음.
。Prototype 선언 시 Spring은 Spring Bean의 생성 및 의존성 주입만 관여하고 더는 관리하지 않는다.
Request
。 Http Request 시 마다 새로운 Spring Bean을 생성
Session
。세션 마다 새로운 Spring Bean을 생성
▶ 사용자의 HTTP Session(동일 사용자로서 여러번의 Http Request가 하나의 Session에 속할 경우)당 새로운 Spring Bean 생성
Application scope :
。WAS당 하나의 Spring Bean이 할당
Spring Bean의 생성 또는 파괴 시 호출하는 메서드 정의
。@PostConstruct , @PreDestroy
。주로 Spring Bean의 초기화 / Clean up 시 호출하는 메서드에 다음 어노테이션을 정의
@PostConstruct :
。Spring Bean 생성 및 의존성 주입이 완료된 직후 자동으로 호출할 Spring Bean의 초기화 메서드에 선언하는 어노테이션
▶ @PostConstruct가 선언된 메서드는 Spring Bean을 참조하기 전에 먼저 호출
。초기화 메서드는 주로 Spring Bean의 resource, default value, logging 을 설정하는 코드를 작성
@PreDestroy :
。Spring Context에서 Spring Bean을 파괴하기전 자동으로 호출할 cleanup method에 선언하는 어노테이션
。cleanup method는 Spring Context가 보유하고 있는 Resource를 해제하는 용도로 사용
▶ Spring Bean이 삭제되기 전 @PreDestory로 선언된 cleanup method를 수행하여 활성화된 연결들을 모두 닫아야한다.
cleanup 메서드는 주로 Spring Bean의 DB Connection 해제 , Resource 해제하는 코드를 작성
@Component
class EagerInit{
public EagerInit(){
System.out.println("Spring Bean 초기화");
}
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("Init 메서드 호출");
}
@PreDestroy
public void cleanUp(){
System.out.println("CleanUp 메서드 호출");
}
}
@ComponentScan
public class InitandDestroy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
var context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(InitandDestroy.class);
System.out.println("Context 초기화");
context.close();
}
}

。Eager Initialization으로 Application 실행 직후 Spring Bean 생성 직후 @PostConstruct 메서드 호출
。Spring Context에 등록된 후 Spring Context가 종료하기 이전 @PreDestroy 메서드를 호출 후 Spring Bean이 파괴




