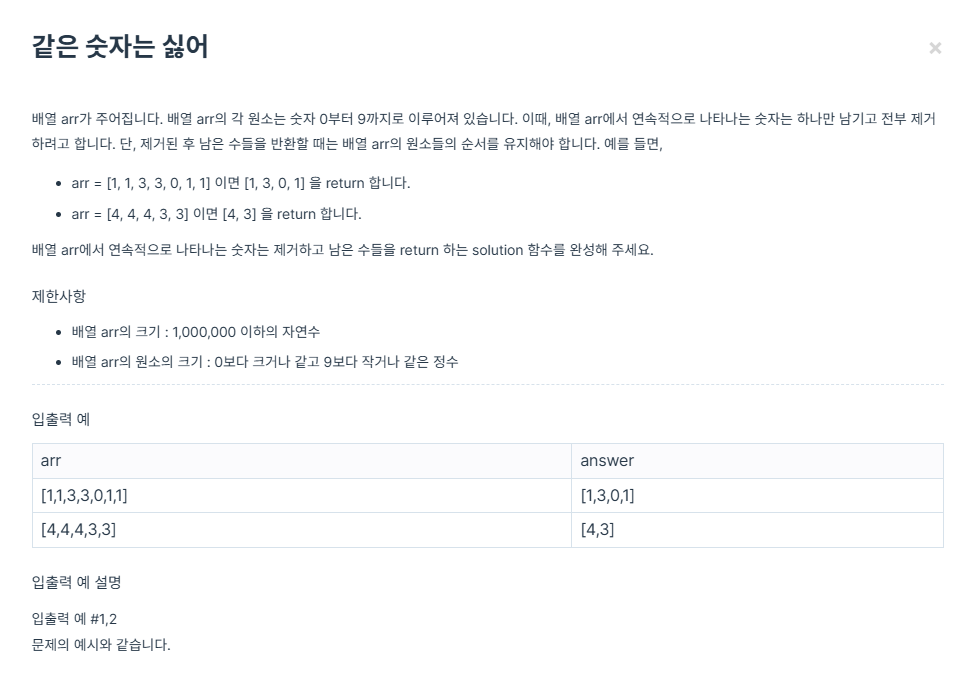
public class Solution {
public int[] solution(int []arr) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(arr[0]);
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
if(list.get(list.size() - 1) != arr[i + 1]) {
list.add(arr[i + 1]);
}
}list에 첫 번째 값을 저장하고 그 값과 +1 자리에 있는 값을 비교한다
int[] rst = new int[list.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < rst.length; i++) {
rst[i] = list.get(i);
}
return rst;
}
}
배열로 만들어 리턴한다.
다른 사람 풀이
public class Solution {
public Stack<Integer> solution(int []arr) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
for(int num : arr){
if(stack.size() == 0 || stack.peek() != num){
stack.push(num);
}
}
return stack;
}
}리턴값을 바꿔 바로 리턴할수도 있다.
stack의 peek()를 사용한 점이 마음에 든다.
peek()
가장 위에 있는 값을 반환한다.