2024-10-19 작성한 글 입니다.(블로그 마이그레이션)
Next.js(14) 애플리케이션을 개발할 때, client-side 라우팅 중 중복 라우팅이 발생할 수 있습니다. 여기서 client-side 라우팅이란 Link 컴포넌트나 useRouter 훅을 이용한 라우팅을 의미하며, 중복 라우팅은 라우팅 처리 도중 다른 라우팅을 추가로 시도하는 경우를 말합니다.이러한 상황이 발생하면 모든 라우팅이 의도한 대로 완료되지 않을 수 있습니다. 이 글에서는 중복 라우팅이 Next.js에서 어떻게 처리되는지에 대해 집중적으로 살펴보겠습니다.
라우팅 관련 핵심 데이터
next 애플리케이션에서 클라이언트 사이드 라우팅은 주로 세 가지 핵심 데이터 appRouterState, actionQueue, 그리고 appRouter에 의해 관리됩니다.
1. appRouterState
appRouterState는 애플리케이션의 현재 라우터 상태를 유지하는 데이터입니다.
type AppRouterState = {
buildId: string;
/**
* The router state, this is written into the history state in app-router using replaceState/pushState.
* - Has to be serializable as it is written into the history state.
* - Holds which segments and parallel routes are shown on the screen.
*/
tree: FlightRouterState;
/**
* The cache holds React nodes for every segment that is shown on screen as well as previously shown segments.
* It also holds in-progress data requests.
* Prefetched data is stored separately in `prefetchCache`, that is applied during ACTION_NAVIGATE.
*/
cache: CacheNode;
/**
* Cache that holds prefetched Flight responses keyed by url.
*/
prefetchCache: Map<string, PrefetchCacheEntry>;
/**
* Decides if the update should create a new history entry and if the navigation has to trigger a browser navigation.
*/
pushRef: PushRef;
/**
* Decides if the update should apply scroll and focus management.
*/
focusAndScrollRef: FocusAndScrollRef;
/**
* The canonical url that is pushed/replaced.
* - This is the url you see in the browser.
*/
canonicalUrl: string;
/**
* The underlying "url" representing the UI state, which is used for intercepting routes.
*/
nextUrl: string | null;
};Promise<AppRouterState> | AppRouterState 타입의 React context로 관리되며, context는 React의 useState로 정의된 상태를 가지고 있습니다. 이 상태는 애플리케이션의 history와 동기화됩니다.appRouterState가 변경되면 이를 구독하는 effect가 실행되어 history가 업데이트되며, history의 변경은 popstate 이벤트 핸들러를 통해 appRouterState를 업데이트합니다.
// AppRouterStateContext.Provider보다 상위 레벨에서 렌더링
function HistoryUpdater({
appRouterState,
}: {
// use(appRouterStateContext)로 전달됨
appRouterState;
}) {
useInsertionEffect(() => {
// histoy update...
}, [appRouterState]);
return null;
}2. actionQueue
actionQueue는 라우팅 액션의 실행을 관리하는 데이터로, context로 관리됩니다.
type AppRouterActionQueue = {
state: AppRouterState | null;
devToolsInstance?: ReduxDevToolsInstance;
dispatch: (payload: ReducerActions, setState: DispatchStatePromise) => void;
action: (state: AppRouterState, action: ReducerActions) => ReducerState;
pending: ActionQueueNode | null;
needsRefresh?: boolean;
last: ActionQueueNode | null;
};actionQueue의 주요 프로퍼티는 다음과 같습니다:
actionQueue.pending: 현재 처리 중인 action node를 담고 있으며,actionQueue.pending.next를 통해 다음 대기 중인 action node를 참조할 수 있습니다.type ActionQueueNode = { payload: ReducerActions; next: ActionQueueNode | null; resolve: (value: ReducerState) => void; reject: (err: Error) => void; discarded?: boolean; };actionQueue.last: queue의 마지막 노드를 나타냅니다.actionQueue.state: 라우트 변경 전의appRouterState를 가지고 있으며, 라우팅 처리 후newAppRouterState로 업데이트하기 직전에 할당됩니다.actionQueue.dispatch는 두 가지 주요 작업을 수행합니다:- 새로운 promise를 생성하고,
appRouterStateContext를 해당 promise로 업데이트하여 현재 라우팅 중임을 알립니다. - 들어온 라우팅 액션을 처리하거나 대기시킵니다.
- 새로운 promise를 생성하고,
actionQueue.action: 핵심 라우팅 과정을 수행하는 함수로, 라우트 데이터 프리패칭, 트리 구성 등의 작업을 처리합니다.actionQueue.action의 실행이 완료된 후, 반환값에 기반하여appRouterState가 업데이트됩니다.
3. appRouter
클라이언트 라우팅 함수들을 포함하고 있으며, context로 관리됩니다.
/**
* The app router that is exposed through `useRouter`. It's only concerned with dispatching actions to the reducer, does not hold state.
*/
const appRouter = {
back: () => window.history.back(),
forward: () => window.history.forward(),
prefetch: (href, options) => {
const action = {
type: ACTION_PREFETCH,
url,
};
const url = new URL(addBasePath(href), window.location.href);
actionQueue.dispatch(action, setAppRouterStateContext);
},
replace: (href, options = {}) => {
const action = {
type: ACTION_NAVIGATE,
url,
navigateType: 'replace',
};
actionQueue.dispatch(action, setAppRouterStateContext);
},
push: (href, options = {}) => {
const action = {
type: ACTION_NAVIGATE,
url,
navigateType: 'push',
};
actionQueue.dispatch(action, setAppRouterStateContext);
},
refresh: () => {
const action = {
type: ACTION_REFRESH,
origin: window.location.origin,
};
actionQueue.dispatch(action, setAppRouterStateContext);
},
fastRefresh: () => {
const action = {
type: ACTION_FAST_REFRESH,
origin: window.location.origin,
};
actionQueue.dispatch(action, setAppRouterStateContext);
},
};appRouter context는 useRouterHook을 통해 노출되며, 이 인터페이스를 통해 실제 클라이언트 라우팅 요청을 수행할 수 있습니다.
다음으로, actionQueue.dispatch에서 수행되는 두 번째 작업을 좀 더 살펴보겠습니다.
actionQueue.dispatch
queue가 비어있는 경우, 새로운 action node를 추가한 즉시 라우팅을 수행합니다.
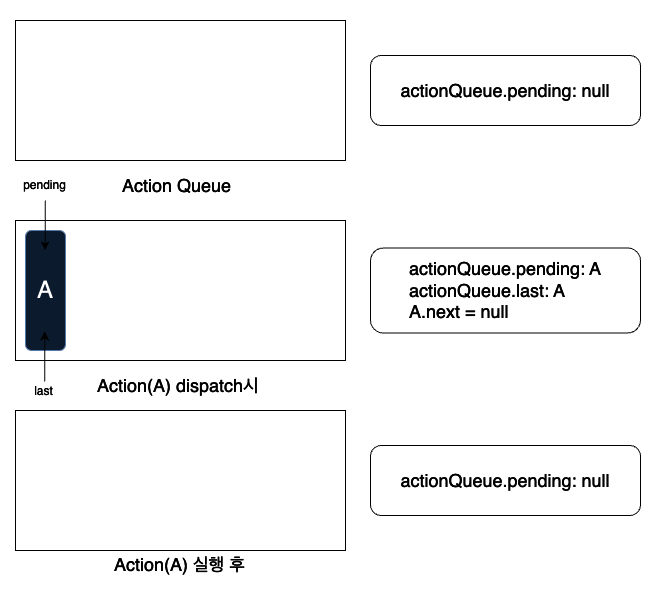
queue가 비어있지 않은 경우, action type에 따라 처리 방식이 달라집니다.
type ReducerActions = Readonly<
| RefreshAction
| NavigateAction
| RestoreAction
| ServerPatchAction
| PrefetchAction
| FastRefreshAction
| ServerActionAction
>;라우팅 액션은 총 여섯 가지 타입으로 나뉘며, router.back() 및 router.forward()를 통해 dispatch되는 RestoreAction과 router.push() 및 router.replace()를 통해 dispatch되는 NavigateAction 타입은 합쳐서 Navigation 타입으로 불립니다.
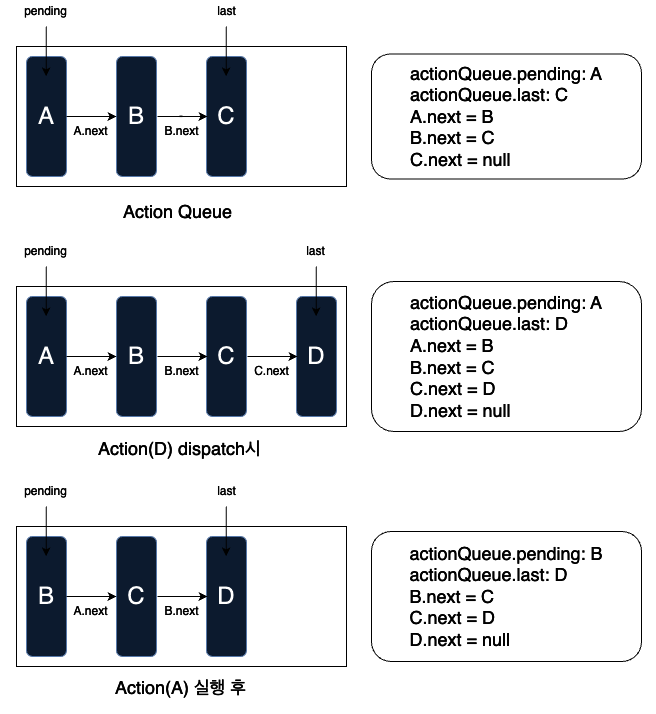
Navigation Action이 아닌 경우: action node를 queue에 추가하여 대기시킵니다.
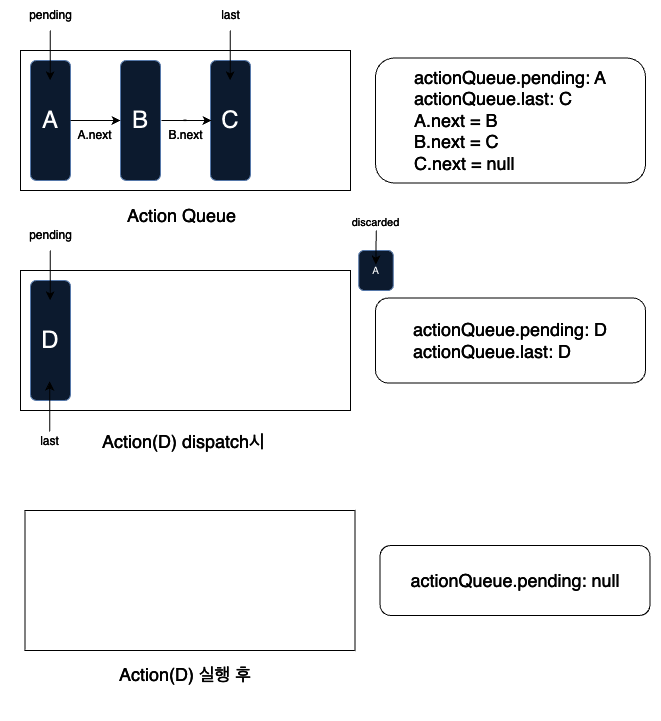
Navigation Action인 경우: dispatch된 action type이 Navigation인 경우, 대기열에 있는 모든 action(실행중인 action 포함)을 취소하고, dispatch된 액션을 queue에 추가한 즉시 실행합니다.
actionQqueue.dispatch 일부 구현 코드는 다음과 같습니다.
const actionQueue: AppRouterActionQueue = {
// ...
dispatch: (
payload: ReducerActions,
setState: DispatchAppRouterStatePromise
) => {
// step 1
let resolvers: {
resolve: (value: ReducerState) => void;
reject: (reason: any) => void;
} = { resolve: setState, reject: () => {} };
const deferredPromise = new Promise<AppRouterState>(
(resolve, reject) => {
resolvers = { resolve, reject };
}
);
startTransition(() => {
// we immediately notify React of the pending promise -- the resolver is attached to the action node
// and will be called when the associated action promise resolves
setAppRouterStateContext(deferredPromise);
});
// step 2
const newAction: ActionQueueNode = {
payload,
next: null,
resolve: resolvers.resolve,
reject: resolvers.reject,
};
if (actionQueue.pending === null) {
// The queue is empty, so add the action and start it immediately
// Mark this action as the last in the queue
actionQueue.last = newAction;
actionQueue.pending = newAction;
actionQueue.action(actionQueue.state, action.payload);
} else if (
payload.type === ACTION_NAVIGATE ||
payload.type === ACTION_RESTORE
) {
// Navigations (including back/forward) take priority over any pending actions.
// Mark the pending action as discarded (so the state is never applied) and start the navigation action immediately.
actionQueue.pending.discarded = true;
// Mark this action as the last in the queue
actionQueue.last = action;
actionQueue.pending = action;
actionQueue.action(action);
} else {
actionQueue.last.next = newAction;
actionQueue.last = newAction;
}
},
};결론적으로, Next.js에서 라우팅 작업은 일반적으로 순차적으로 처리되지만, Navigation 작업은 항상 최우선으로 실행됩니다. 이로 인해 실행 중이거나 대기 중인 작업들이 취소되고, 새로운 Navigation이 즉시 수행됩니다. 중복 라우팅 상황에서도 이러한 원칙을 고려하여 라우팅을 처리하면 애플리케이션이 의도한 대로 안정적으로 동작할 수 있습니다.