⭐ 자료구조
🤔 이걸 왜 배울까
-
알고리즘 공부의 기반이 된다.
-
컴퓨터 안의 데이터를 어떻게 저장 시킬 것인지 논하는 과목. -> 최적화의 방법을 생각 할 수 있음
-
C#의 List는 어떤식으로 내부에 저장될까? 배열이랑 같은 방식으로 저장된다.
List< T > list = new List(10); => 크기를 먼저 잡아주는 것이 좋다. 만약 10 크기로 잡았는데 100이 필요하다면 전체 리스트를 복사해서 옮겨진다. 따라서, 애초부터 크기를 생각하고 잡는 것이 좋다. -
과거의 조상님들이 프로그래밍을 어떤 생각을 통해 발전시켰는지 알 수 있음.
-
다른 프로그래머들과 의사소통을 할 수 있고, 알아보기 쉬운 . 즉, 가독성 있는 프로그램을 짤 수 있는 기반이 된다.
-
문제를 어떻게 해결하는가에 대한 경험을 해볼 수 있다.
-
전공 하지 않으신 분들은 전공 지식을 공부 할 수 있는 기반을 마련할 수 있다.
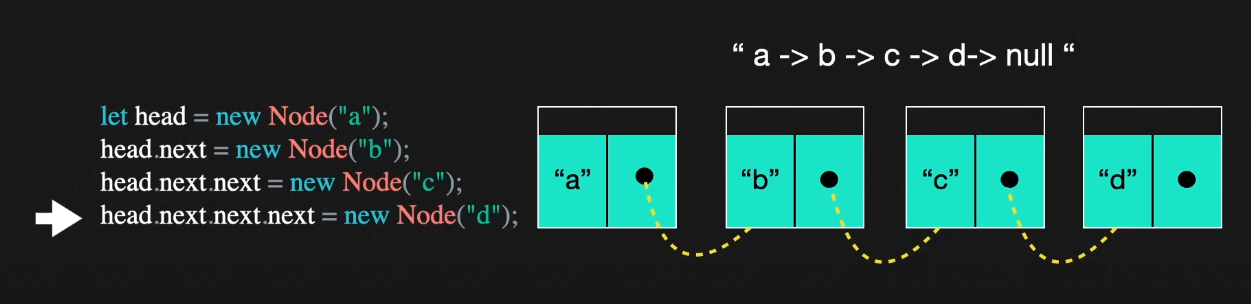
⭐ LinkedList
- 연속된 노드의 연결체
⭐ LinkedList에서 Node란?
- Node는 연결리스트에서 사용되는 데이터 덩어리이다. Node안에는 데이터와 링크가 존재한다.

⭐ LinkedList의 구조는? (단일 연결리스트 기준)
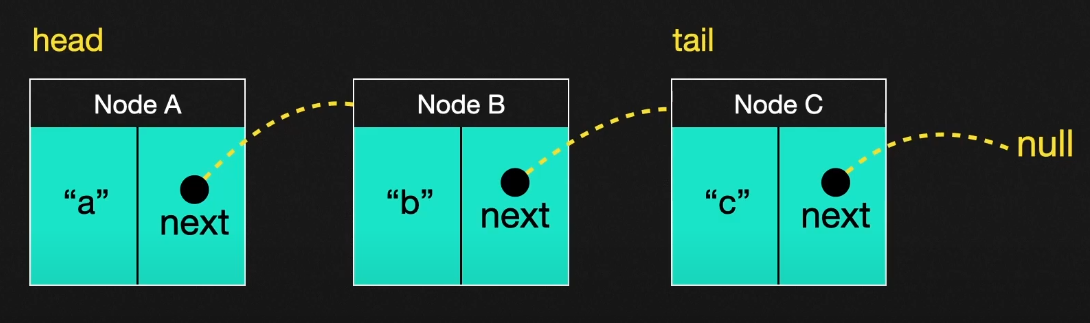
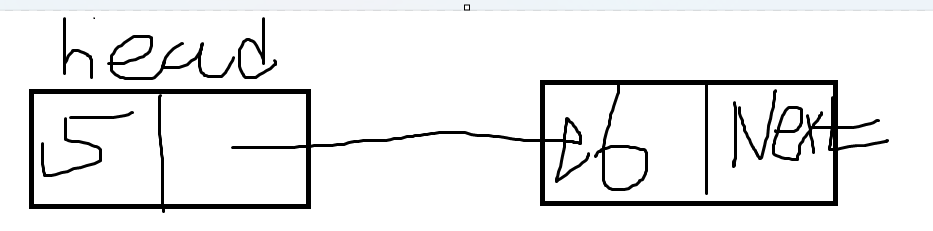
- 노드의 next는 다음 노드의 이름을 가리킨다.
- 마지막 노드의 다음은 없으므로 null 이 될 것이고, 첫번째 노드는 head 노드 , 마지막노드는 tail 노드이다.
⭐ 배열 vs LinkedList
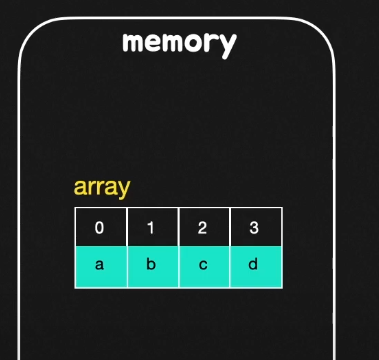
- 메모리 공간안에 배열이 존재한다고 했을 때, 이 자료구조의 특징 상 모든 원소들이 이어진 메모리 공간에 자리를 잡는 것을 볼 수 있다. 따라서, 배열의 인덱스를 활용한 원소 탐색을 효율적으로 그리고 빠르게 실행할 수 있다.
- 랜덤 액세스가 가능하다. 배열의 n번째 원소 방문 시 O(1) 시간으로 가능하다. EX) arr[3]
- 상수 시간으로 바로바로 접근이 가능하다. 원소 삽입과 삭제 부분은 O(n) 시간으로 가능하다. O(n)은 Linear Time(선형 시간)이라고도 한다.
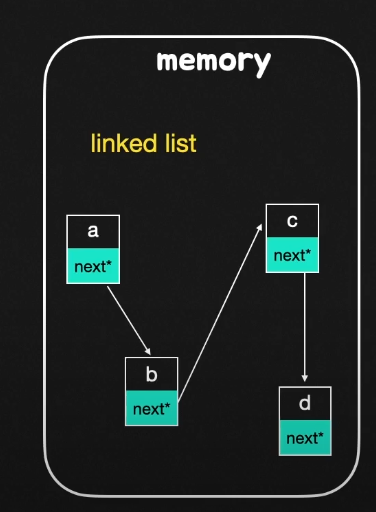
- 메모리 공간안에 하나의 노드들이 각자 위치를 잡고 있고, 즉, 이어진 메모리 공간이 아닌 불특정한 공간에 존재하기 때문에 포인터 또는 주소를 참조하는 필드(변수)를 통해서 연결을 시켜줘야 한다. 그로 인해서 노드의 탐색은 선형 시간이 걸린다.
- 예를 들어 c 노드까지 가고 싶다면 a와 b 노드를 필수적으로 거쳐야만 갈 수 있게 되는것이다.
- 랜덤 엑세스 불가능하다.
- 리스트의 n번째 노드 방문 시 O(n) 시간 소요 한다. 예를 들어 head 노드부터 n번째 노드까지 순회하려면, n번째 노드 앞에 위치한 모든 노드를 방문해야 한다.
- 하지만, 배열보다 빠른 노드 삽입과 노드 삭제가 가능하다. 예를 들어, 연결리스트에 노드를 맨 앞에 삽입시켜야 된다면 헤드 노드의 참조 위치만 바뀌는 것이기 때문에 O(1) 시간으로 가능하므로 굉장히 빠르다.
⭐ 연결리스트의 종류
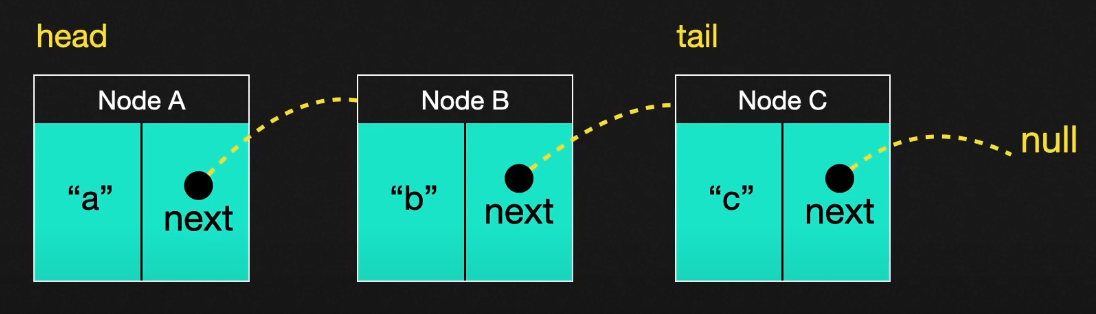
- 단일 연결리스트 : 다음 노드에 대한 포인터들만 가지고 있고, 한쪽 방향으로만 흐른다.
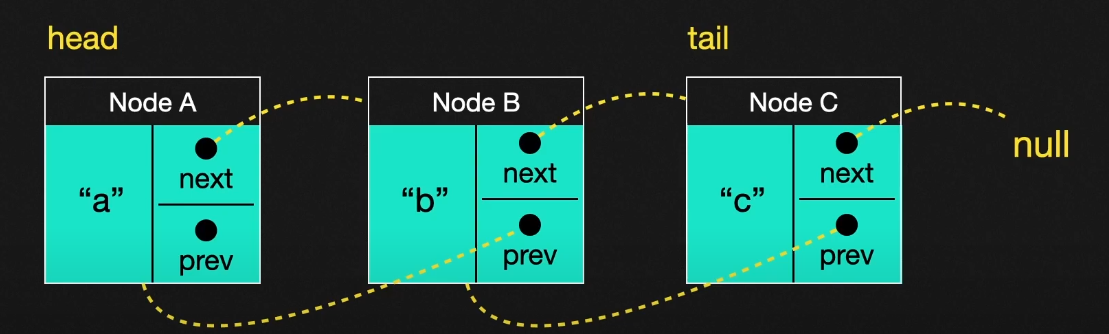
- 이중 연결리스트 : 다음 노드에 대한 포인터뿐만 아니라, 이전 노드를 가리키는 포인터를 가지고 있다. 앞 뒤로 탐색하는게 빠르다는 장점이 있지만, 노드마다 2개의 포인터를 관리를 해줘야 되기 때문에 데이터의 구조와 흐름이 오히려 복잡해질 수도 있다는 부분이 있다.
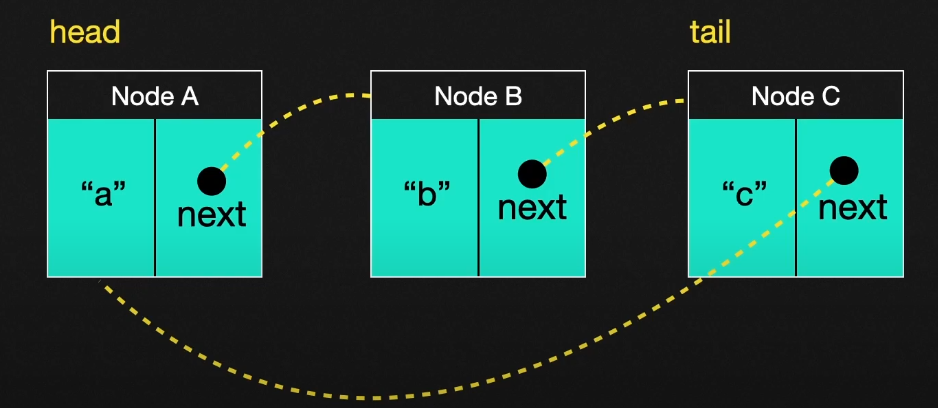
- 원형 연결 리스트 : 일반적인 연결리스트이지만, 리스트에 마지막 노드가 가리키는 포인터가 다시, 헤드 노드를 가리키게 된다.
⭐ 연결리스트의 구현 방법
⭐ 노드 구현
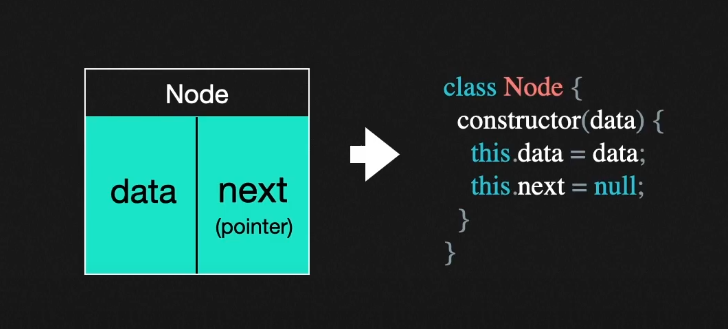
- 연결리스트는 노드의 연결체이다. 노드의 구현 방법은 아래와 같다. 데이터 필드와, 다음 노드를 저장하는 next 포인터가 필요하다.
⭐ 노드 연결
- next 포인터를 이용해서 연결해야 한다.


⭐ Add , 데이터 추가하는 코드 작성
namespace LionStudy_00
{
public class LinkedListNode<T> //방 1개를 만든 것. Data와 다음 노드로 갈 Next가 필요함.
{ //LinkedListNode는 헤드 노드(첫 노드)만 알고 있다.
public T Data;
public LinkedListNode<T> Next;
public LinkedListNode(T data)
{
Data = data;
Next = null;
}
}
public class LinkedList<T>
{
private LinkedListNode<T> head; //헤드 노드를 선언
public LinkedList()
{
head = null; //현재 헤드 노드는 아무것도 들어있지 않으므로 생성자에서 null로 초기화
}
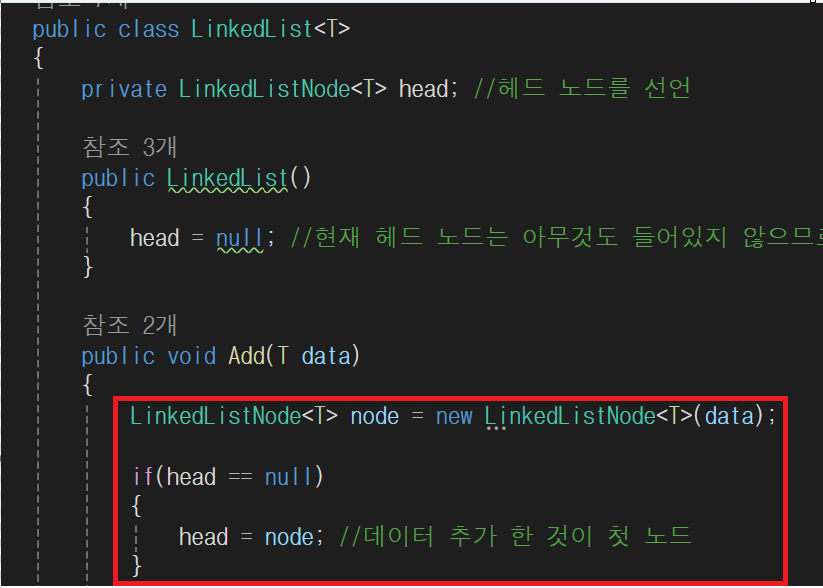
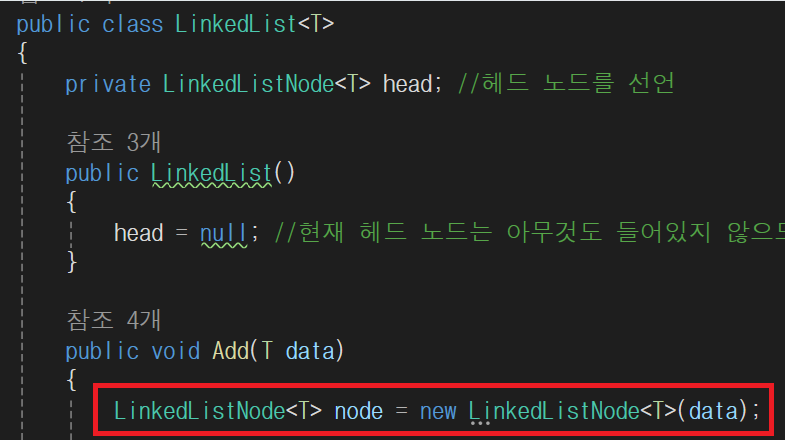
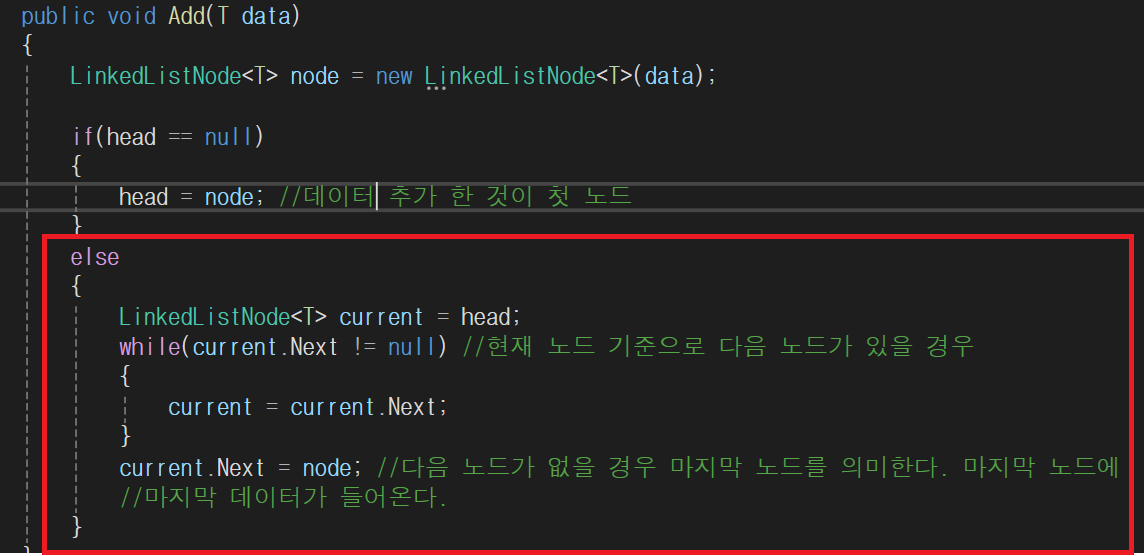
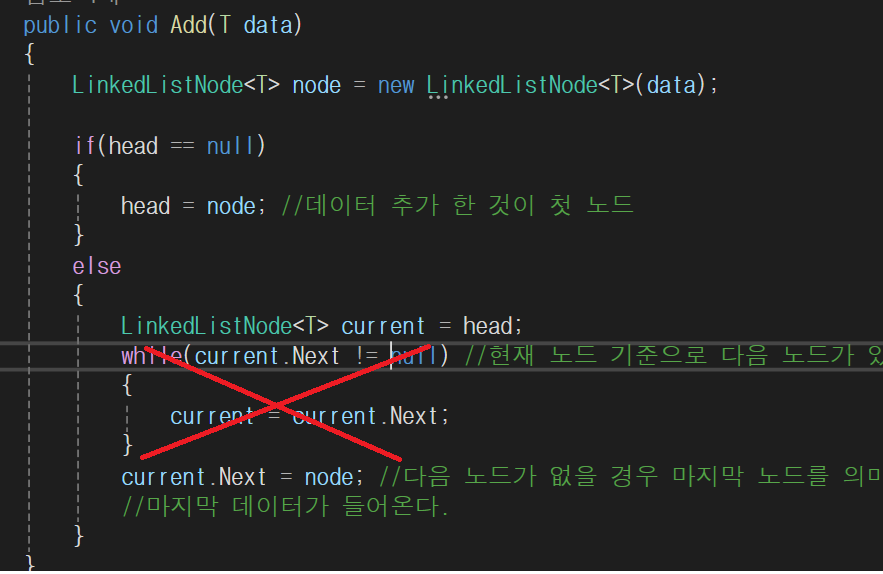
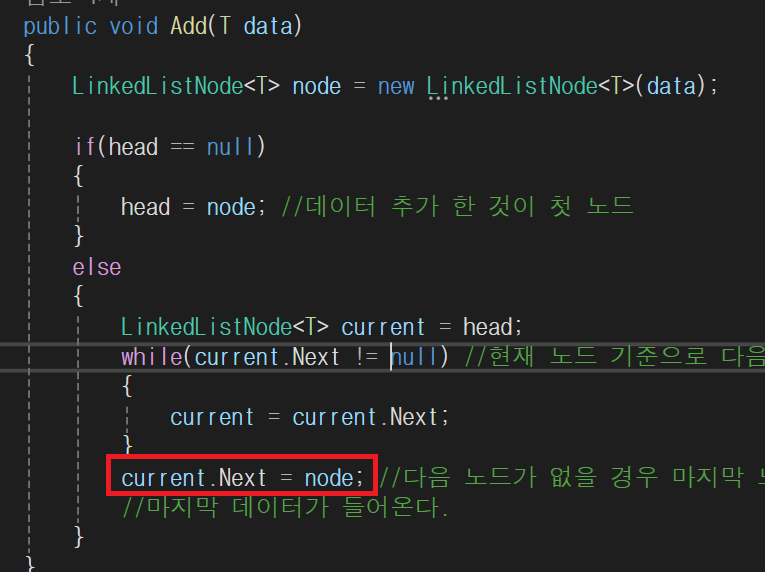
public void Add(T data)
{
LinkedListNode<T> node = new LinkedListNode<T>(data);
if(head == null)
{
head = node; //데이터 추가 한 것이 첫 노드
}
else
{
LinkedListNode<T> current = head;
while(current.Next != null) //현재 노드 기준으로 다음 노드가 있을 경우
{
current = current.Next;
}
current.Next = node; //다음 노드가 없을 경우 마지막 노드를 의미한다. 마지막 노드에
//마지막 데이터가 들어온다.
}
}
public void Print()
{
if(head == null)
{
Console.WriteLine("리스트가 비어있음");
return;
}
LinkedListNode<T> current = head;
while(current != null)
{
Console.Write(current.Data + "=>");
current = current.Next;
}
Console.WriteLine("null");
}
}
}
⭐ 호출 코드
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
LionStudy_00.LinkedList<string> list = new LionStudy_00.LinkedList<string>();
list.Add("어허");
list.Add("이건");
list.Add("뭔가요?");
list.Print(); //어허 => 이건 => 뭔가요? => null
}
}📄 개념 정리
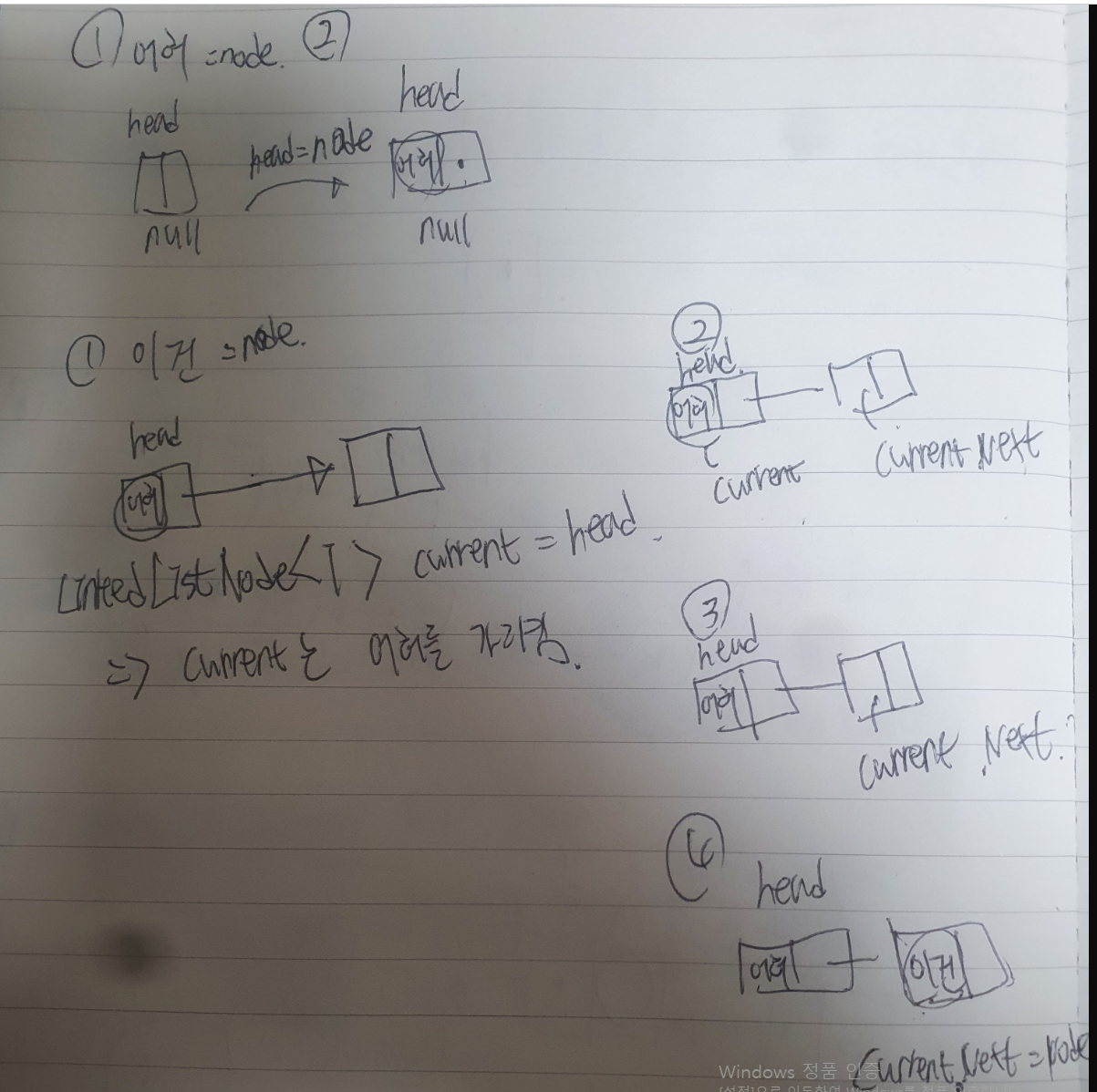
- 먼저, 어허,이건,뭔가요 순으로 데이터를 추가하였다. 그 결과 어허 -> 이건 -> 뭔가요 -> null이 될 것이다.
⭐ 1. 먼저 처음 데이터 추가 ("어허"라는 문자열 추가)
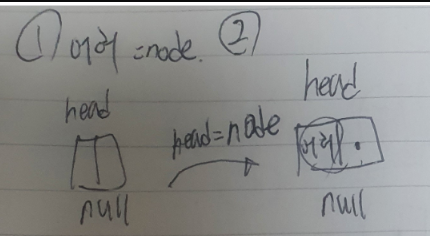
LinkedListNode<T> node = new LinkedListNode<T>(data); //이 과정을 통해 방 하나가 생성되었다.- 처음 헤드 노드는 null 이므로 , 아래 코드로 인해 "어허"라는 데이터는 head가 될 것이다.
if(head == null)
{
head = node; //데이터 추가 한 것이 첫 노드
}⭐ 2. 두번째 데이터 추가 ("이건"이라는 문자열 추가)
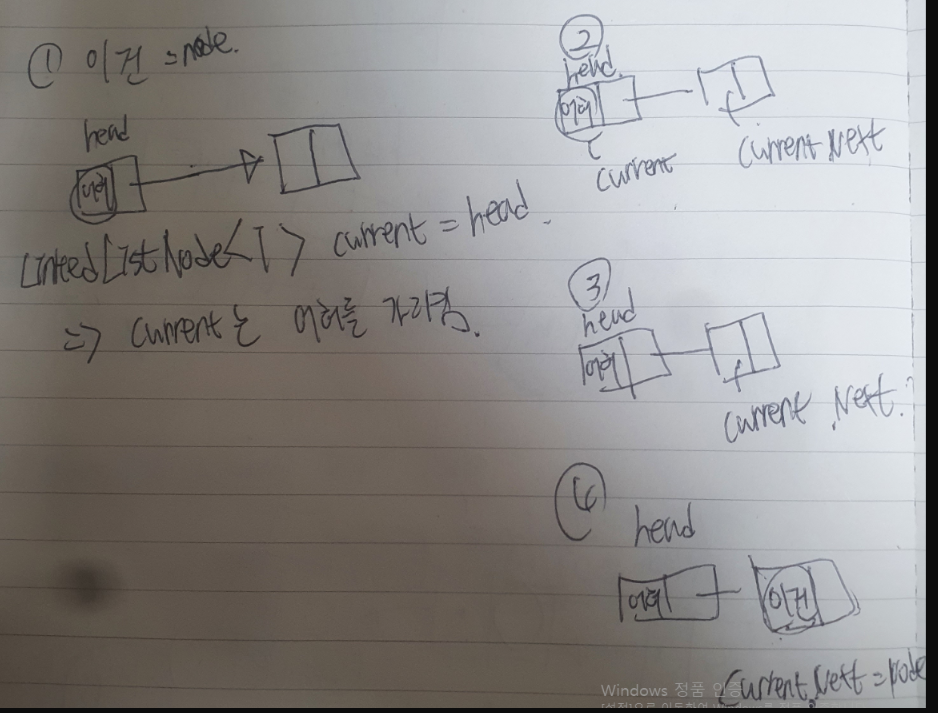
- 아래 코드로 인해 처음 head 노드였던 "어허"는 current가 될 것이다.
else
{
LinkedListNode<T> current = head;
//..생략
}- 아래 코드 중 while문에 의해 current.Next 인 헤드 노드("어허"가 들어간 노드)의 다음 노드를 current가 된다.
else
{
LinkedListNode<T> current = head;
while(current.Next != null) //현재 노드 기준으로 다음 노드가 있을 경우
{
current = current.Next;
}
}- current.Next = node;에 의해 "이건"이라는 노드가 다음노드를 가리킨다. 즉, 최종적으로 어허 -> 이건 이 된다.
else
{
LinkedListNode<T> current = head;
while(current.Next != null) //현재 노드 기준으로 다음 노드가 있을 경우
{
current = current.Next;
}
current.Next = node; //다음 노드가 없을 경우 마지막 노드를 의미한다. 마지막 노드에
//마지막 데이터가 들어온다.
}⭐ 3. 마지막 데이터 추가 ("뭘까요?"라는 문자열 추가)
- 2번과 동일하다.
⭐ Remove , 데이터 삭제하는 코드 작성
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace LionStudy_00
{
public class LinkedListNode<T> //방 1개를 만든 것. Data와 다음 노드로 갈 Next가 필요함.
{ //LinkedListNode는 헤드 노드(첫 노드)만 알고 있다.
public T Data;
public LinkedListNode<T> Next;
public LinkedListNode(T data)
{
Data = data;
Next = null;
}
}
public class LinkedList<T>
{
private LinkedListNode<T> head; //헤드 노드를 선언
public LinkedList()
{
head = null; //현재 헤드 노드는 아무것도 들어있지 않으므로 생성자에서 null로 초기화
}
public void Add(T data)
{
//..생략
}
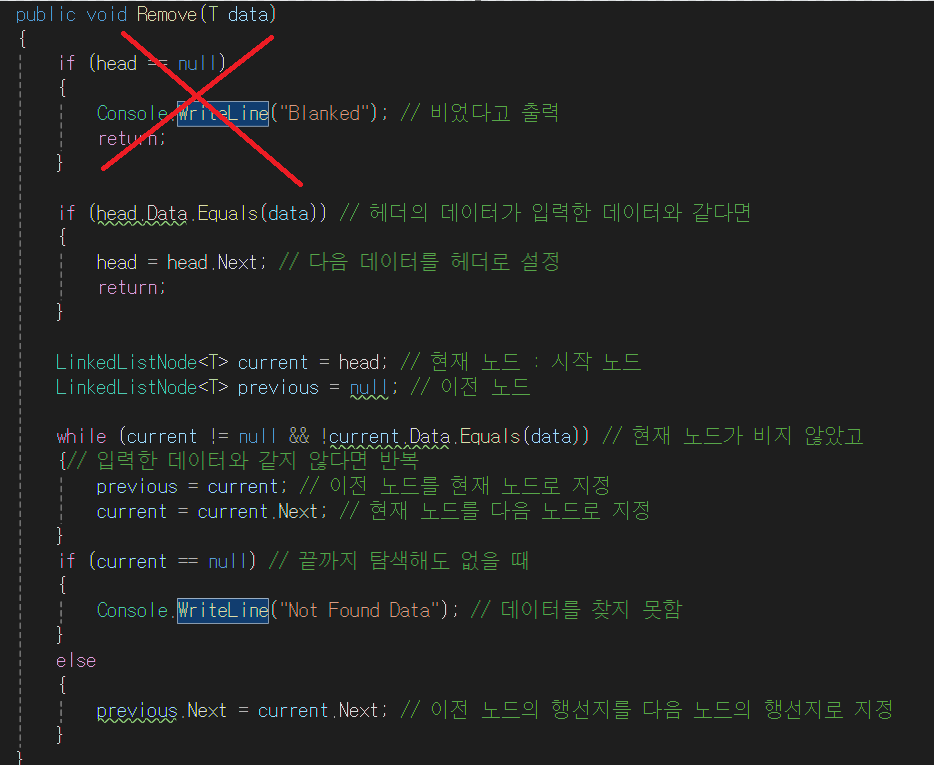
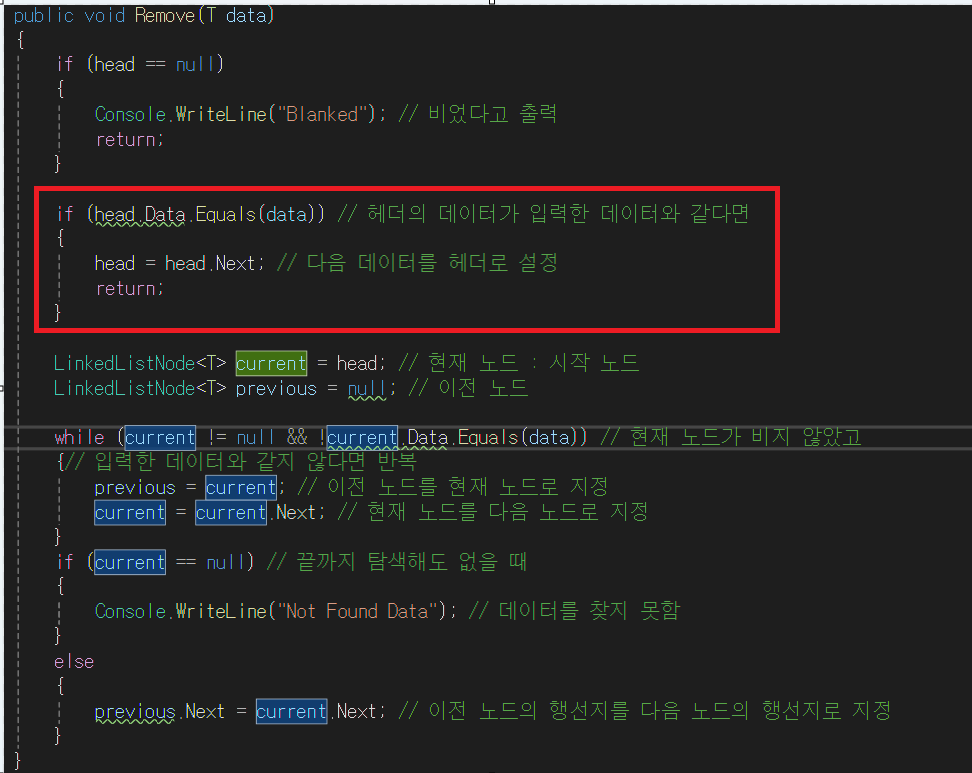
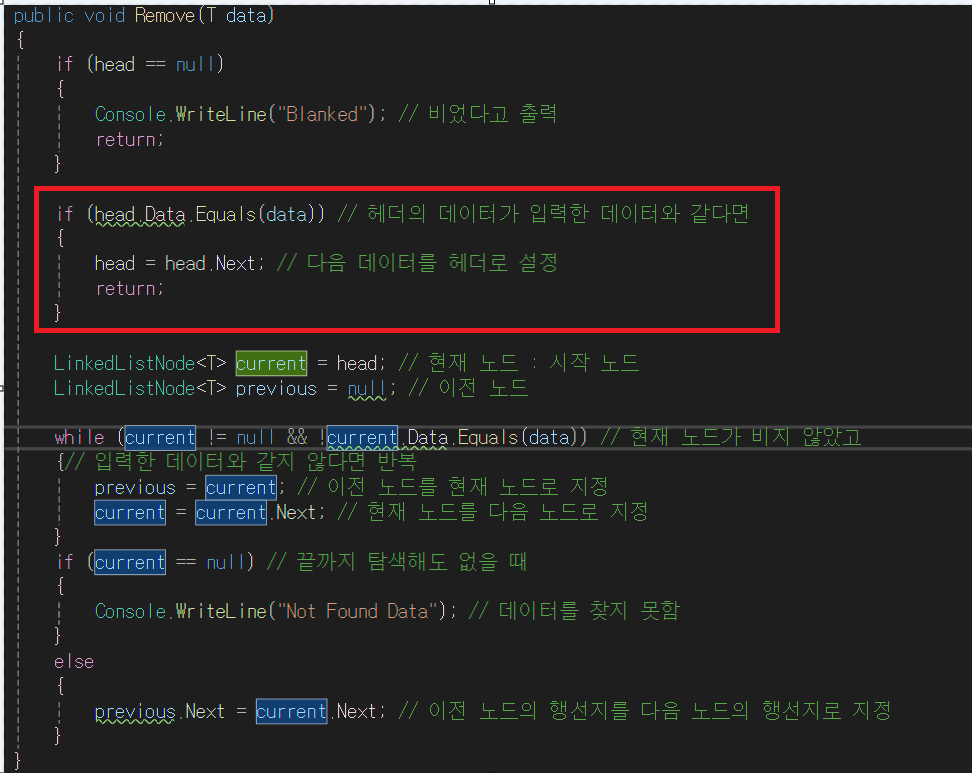
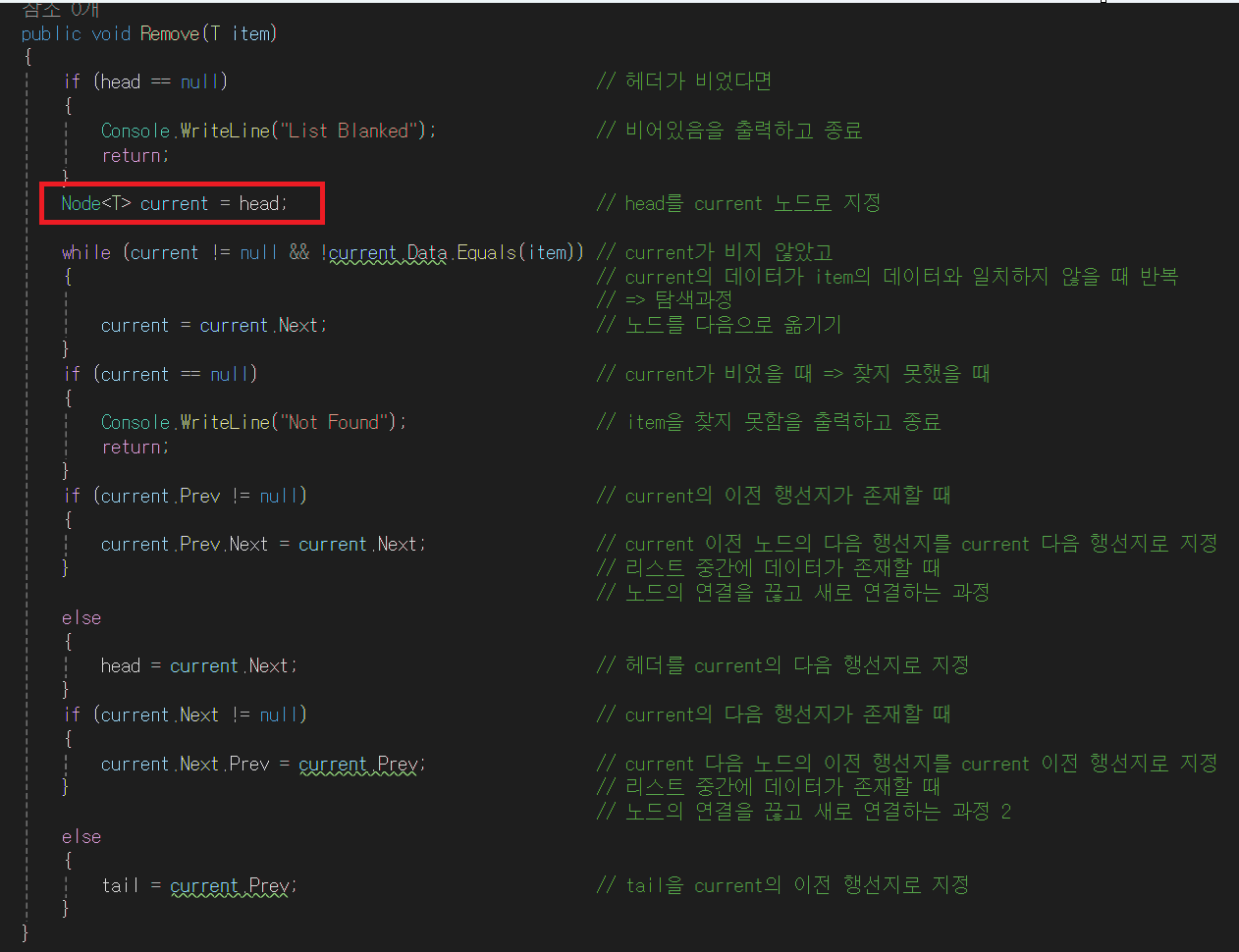
public void Remove(T data)
{
if (head == null)
{
Console.WriteLine("Blanked"); // 비었다고 출력
return;
}
if (head.Data.Equals(data)) // 헤더의 데이터가 입력한 데이터와 같다면
{
head = head.Next; // 다음 데이터를 헤더로 설정
return;
}
LinkedListNode<T> current = head; // 현재 노드 : 시작 노드
LinkedListNode<T> previous = null; // 이전 노드
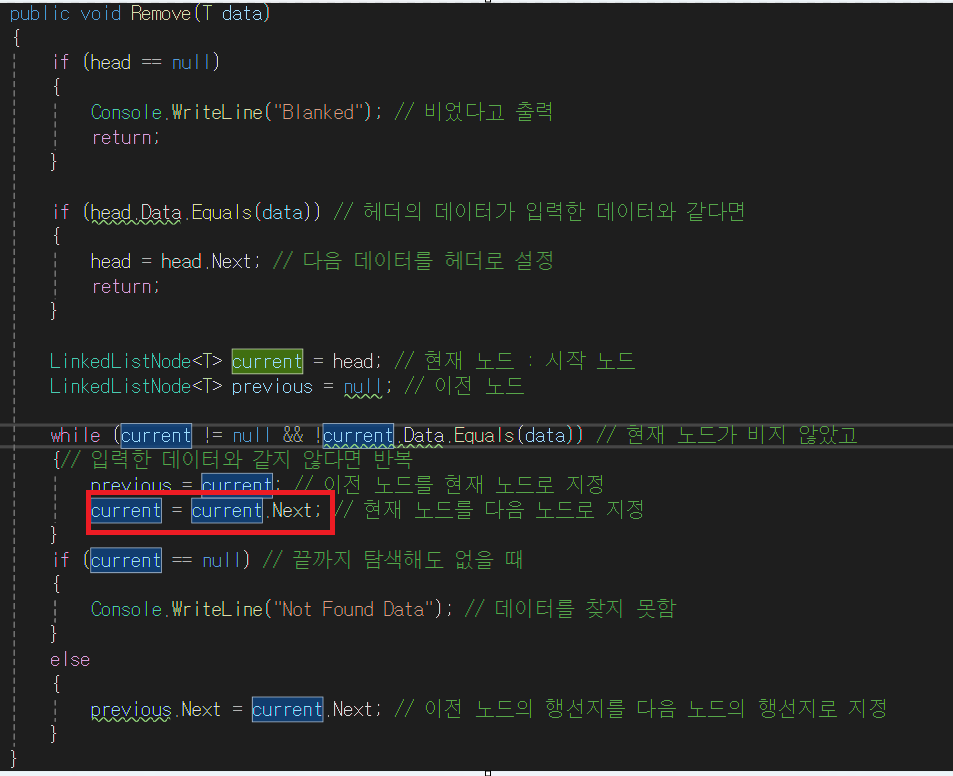
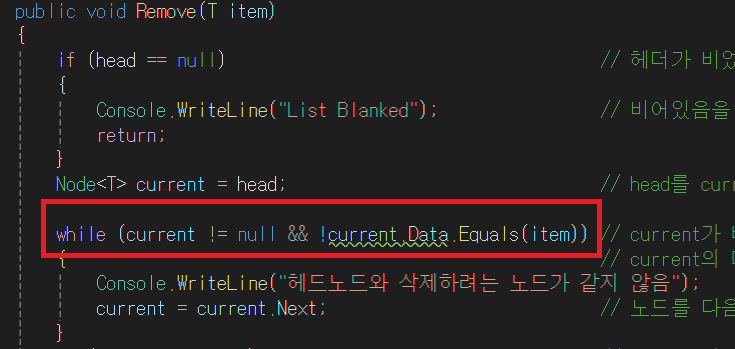
while (current != null && !current.Data.Equals(data)) // 현재 노드가 비지 않았고
{// 입력한 데이터와 같지 않다면 반복
previous = current; // 이전 노드를 현재 노드로 지정
current = current.Next; // 현재 노드를 다음 노드로 지정
}
if (current == null) // 끝까지 탐색해도 없을 때
{
Console.WriteLine("Not Found Data"); // 데이터를 찾지 못함
}
else
{
previous.Next = current.Next; // 이전 노드의 행선지를 다음 노드의 행선지로 지정
}
}
public void Print()
{
if(head == null)
{
Console.WriteLine("리스트가 비어있음");
return;
}
LinkedListNode<T> current = head;
while(current != null)
{
Console.Write(current.Data + "=>");
current = current.Next;
}
Console.WriteLine("null");
}
}
//데이터 추가, 삭제 , 찾기
}
⭐ 호출 코드
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
LionStudy_00.LinkedList<string> list = new LionStudy_00.LinkedList<string>();
list.Add("어허");
list.Add("이건");
list.Add("뭔가요?");
list.Remove("이건");
list.Print(); //어허 -> 뭔가요 -> null
}
}📄 개념 정리
-
어허 -> 이건 -> 뭔가요 부분에서 이건을 Remove하게 되면 어허 -> 뭔가요가 된다. 즉, 중간에 있는 노드를 삭제하면 첫번째 노드가 세번째 노드를 가리킨다.
만약, 첫번째 노드를 삭제하면 두번째 노드가 세번재 노드를 가리킨다.⭐ 첫번째 노드 삭제 시,
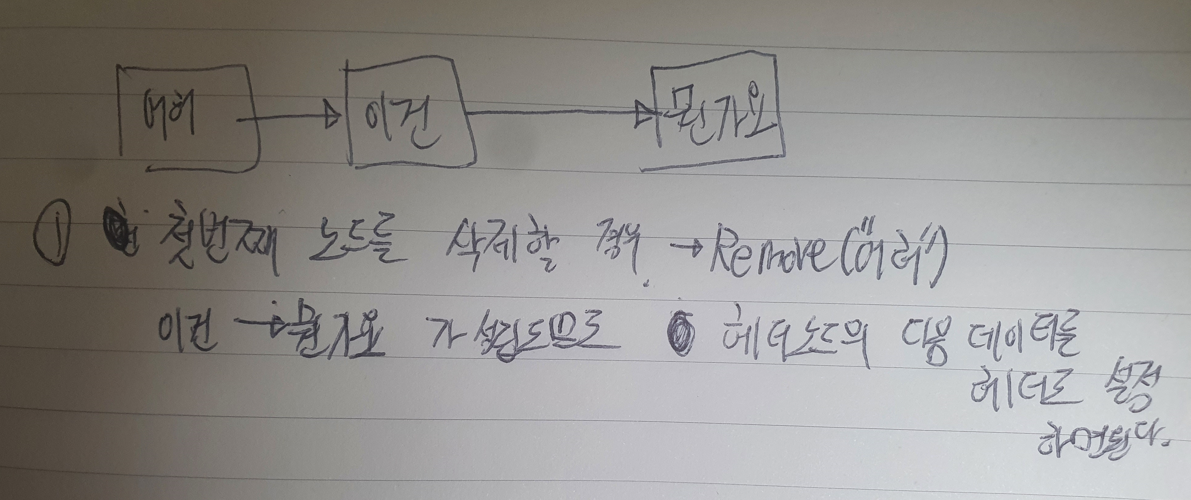
-
따라서, 코드를 작성하면
if (head.Data.Equals(data)) // 헤더의 데이터가 입력한 데이터와 같다면
{
head = head.Next; // 다음 데이터를 헤더로 설정
return;
}⭐ 두번째 노드 삭제 시,

- 1번 과정
LinkedListNode<T> current = head; // 현재 노드 : 시작 노드
LinkedListNode<T> previous = null; // 이전 노드- 2번 과정
while (current != null && !current.Data.Equals(data)) // 현재 노드가 비지 않았고
{// 입력한 데이터와 같지 않다면 반복
previous = current; // 이전 노드를 현재 노드로 지정
current = current.Next; // 현재 노드를 다음 노드로 지정
}- 3번 과정
else
{
previous.Next = current.Next; // 이전 노드의 행선지를 다음 노드의 행선지로 지정
}⭐ PopFirst() , 첫번째 노드의 데이터만 삭제하기
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace LionStudy_00
{
public class LinkedListNode<T> //방 1개를 만든 것. Data와 다음 노드로 갈 Next가 필요함.
{ //LinkedListNode는 헤드 노드(첫 노드)만 알고 있다.
public T Data;
public LinkedListNode<T> Next;
public LinkedListNode(T data)
{
Data = data;
Next = null;
}
}
public class LinkedList<T>
{
private LinkedListNode<T> head; //헤드 노드를 선언
public LinkedList()
{
head = null; //현재 헤드 노드는 아무것도 들어있지 않으므로 생성자에서 null로 초기화
}
public void Add(T data)
{
LinkedListNode<T> node = new LinkedListNode<T>(data);
if(head == null)
{
head = node; //데이터 추가 한 것이 첫 노드
}
else
{
LinkedListNode<T> current = head;
while(current.Next != null) //현재 노드 기준으로 다음 노드가 있을 경우
{
current = current.Next;
}
current.Next = node; //다음 노드가 없을 경우 마지막 노드를 의미한다. 마지막 노드에
//마지막 데이터가 들어온다.
}
}
//...생략
public T PopFirst()
{
if (head == null)
{
return default;
}
T data = head.Data; // 첫 데이터를 가져옴
head = head.Next; // 헤더를 다음 데이터로 지정
return data;
}
//...생략
}
⭐ 호출 코드 작성
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
LionStudy_00.LinkedList<string> list = new LionStudy_00.LinkedList<string>();
list.Add("어허");
list.Add("이건");
list.Add("뭔가요?");
list.Remove("이건"); ///어허 -> 뭔가요 -> null
list.PopFirst(); //뭔가요 -> null
list.Print(); // 뭔가요 -> null
}
}📄 개념 정리
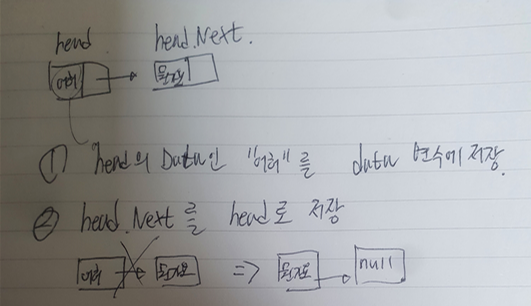
- 1번 과정
T data = head.Data; // 첫 데이터를 가져옴- 2번 과정
head = head.Next; // 헤더를 다음 데이터로 지정
⭐ PopLast() , 마지막 노드의 데이터만 삭제하기
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace LionStudy_00
{
public class LinkedListNode<T> //방 1개를 만든 것. Data와 다음 노드로 갈 Next가 필요함.
{ //LinkedListNode는 헤드 노드(첫 노드)만 알고 있다.
public T Data;
public LinkedListNode<T> Next;
public LinkedListNode(T data)
{
Data = data;
Next = null;
}
}
public class LinkedList<T>
{
private LinkedListNode<T> head; //헤드 노드를 선언
public LinkedList()
{
head = null; //현재 헤드 노드는 아무것도 들어있지 않으므로 생성자에서 null로 초기화
}
public void Add(T data)
{
//..생략
}
public void Remove(T data)
{
//..생략
}
public T PopFirst()
{
//..생략
}
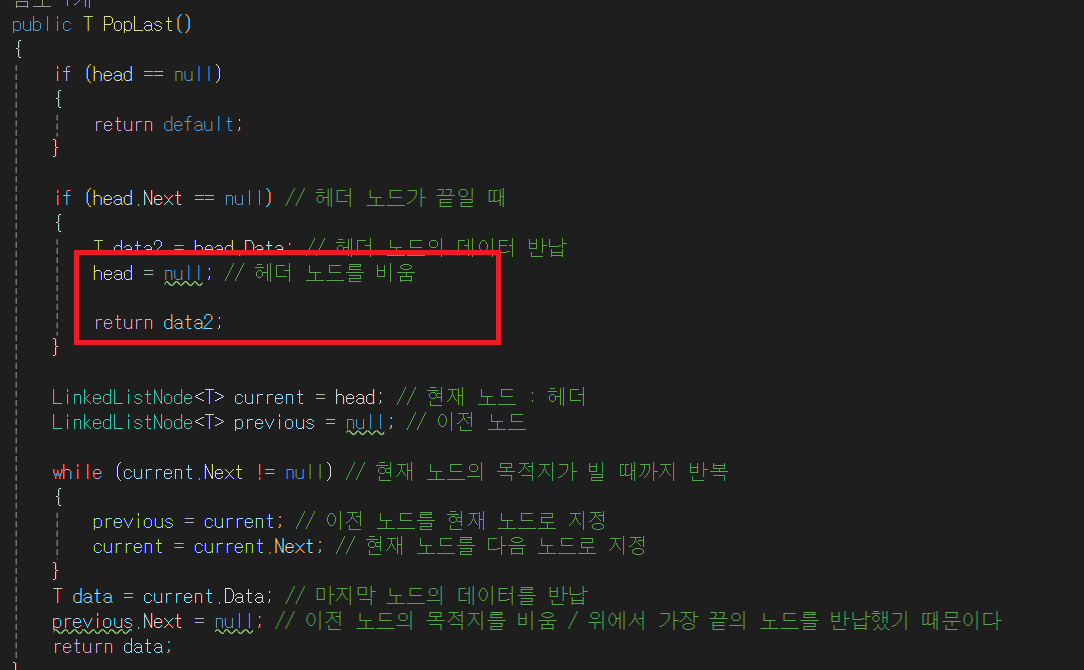
public T PopLast()
{
if (head == null)
{
return default;
}
if (head.Next == null) // 헤더 노드가 끝일 때
{
T data2 = head.Data; // 헤더 노드의 데이터 반납
head = null; // 헤더 노드를 비움
return data2;
}
LinkedListNode<T> current = head; // 현재 노드 : 헤더
LinkedListNode<T> previous = null; // 이전 노드
while (current.Next != null) // 현재 노드의 목적지가 빌 때까지 반복
{
previous = current; // 이전 노드를 현재 노드로 지정
current = current.Next; // 현재 노드를 다음 노드로 지정
}
T data = current.Data; // 마지막 노드의 데이터를 반납
previous.Next = null; // 이전 노드의 목적지를 비움 / 위에서 가장 끝의 노드를 반납했기 때문이다
return data;
}
public void Print()
{
//..생략
}
}
//데이터 추가, 삭제 , 찾기
}
⭐ 호출 코드 작성
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
LionStudy_00.LinkedList<string> list = new LionStudy_00.LinkedList<string>();
list.Add("어허");
list.Add("이건");
list.Add("뭔가요?");
list.Remove("이건"); ///어허 -> 뭔가요 -> null
list.PopLast(); //어허 -> null
list.Print(); // 어허 -> null
}
}📄 개념 정리
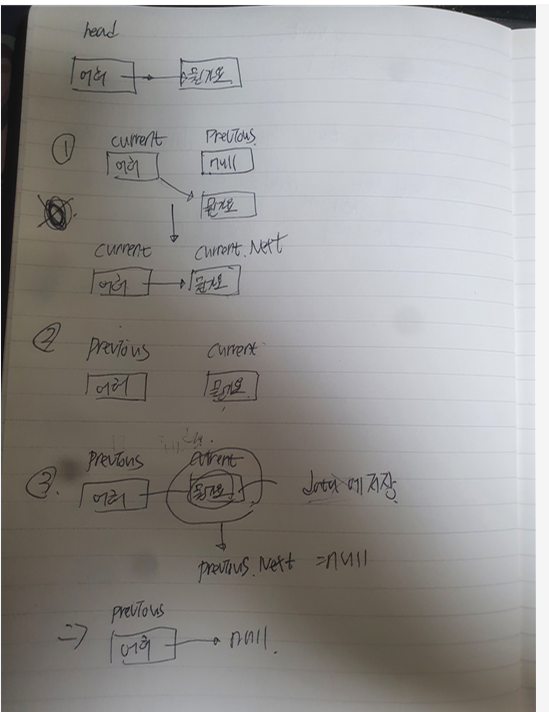
- 1번 과정 : "어허" -> "뭔가요" 에서 head 는 "어허"지만 current 로 변경하고, 이전 노드를 저장할 previous 노드를 만든다.
즉, "어허"(current) -> "뭔가요"(current.Next)
LinkedListNode<T> current = head; // 현재 노드 : 헤더
LinkedListNode<T> previous = null; // 이전 노드- 2번 과정 : current.Next 노드에 "뭔가요"라는 데이터가 있으므로 while문 실행. current 노드인 "어허"를 previous노드로 변경, current.Next 노드인 "뭔가요"를 current 노드로 변경. 즉, "어허"(previous) -> "뭔가요"(current)
while (current.Next != null) // 현재 노드의 목적지가 빌 때까지 반복
{
previous = current; // 이전 노드를 현재 노드로 지정
current = current.Next; // 현재 노드를 다음 노드로 지정
}- 3번 과정 : current.Data 인 "뭔가요"를 data 변수에 저장. previous.Next 노드인 current 노드("뭔가요" 데이터가 있는 노드)를 null 처리 . 즉, "어허" -> null 이 된다.
T data = current.Data; // 마지막 노드의 데이터를 반납
previous.Next = null; // 이전 노드의 목적지를 비움 / 위에서 가장 끝의 노드를 반납했기 때문이다
return data;1. 헤드노드 설정
1. 헤드 노드를 LinkedListNode의 객체 선언
- why ? : 동적으로 생성될 노드를 관리하고, 연결 리스트의 시작점을 가리키기 위해서. 즉, 참조 변수를 먼저 선언해 놓고, 나중에 노드가 생성되면 이름 참조하도록 하여 객체를 유연하게 관리하기 위함.
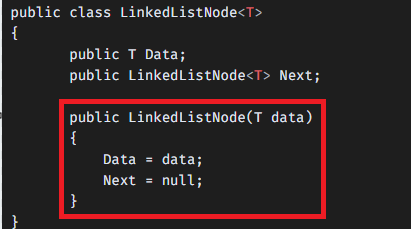
public class LinkedListNode<T>
{
public T Data;
public LinkedListNode<T> Next;
public LinkedListNode(T data)
{
Data = data;
Next = null;
}
}
public class LinkedList<T>
{
private LinkedListNode<T> head; //참조 변수 선언
public LinkedList() //생성자 실행 시,
{
head = null; //⭐ 처음 노드. 즉, 헤드 노드는 아무런 값이 들어있지 않으므로 null 처리 한다. ⭐
}
}- 참조 변수만 선언 했지만, LinkedListNode 클래스의 인스턴스화를 하지 않았으므로, LinkedListNode의 생성자도 LinkedList 클래스의 인스턴스화를 하지 않았으므로 호출되지 않음.
⭐ 중요 ⭐
- 나중에 노드가 추가되었을 때 head 변수를 접근함으로써, head변수의 자료형인 LinkedListNode 클래스의 멤버 변수와 생성자를 이용할 수 있게만 해준 것.
2. 데이터 추가 - 1
public class LinkedList<T>
{
private LinkedListNode<T> head; //헤드 노드를 선언
public LinkedList()
{
head = null; //현재 헤드 노드는 아무것도 들어있지 않으므로 생성자에서 null로 초기화
}
public void Add(T data) //다른 클래스에서 Add(5); 할 경우, data = 5
{
LinkedListNode<T> node = new LinkedListNode<T>(data);
if(head == null)
{
head = node; //데이터 추가 한 것이 첫 노드
}
else
{
LinkedListNode<T> current = head;
while(current.Next != null) //현재 노드 기준으로 다음 노드가 있을 경우
{
current = current.Next;
}
current.Next = node; //다음 노드가 없을 경우 마지막 노드를 의미한다. 마지막 노드에
//마지막 데이터가 들어온다.
}
}
}LinkedListNode<T> node = new LinkedListNode<T>(data);
⭐ 중요 ⭐ 데이터 추가 방식
- data = 5 을 할 경우, 이 5를 LinkedListNode 클래스의 인스턴스화를 통해 LinkedListNode 생성자를 실행하여, 5를 노드의 Data로 저장한다. 그리고, 다음 노드의 값(주소)에 대하여 잘 모르므로, Next = null 이 된다.
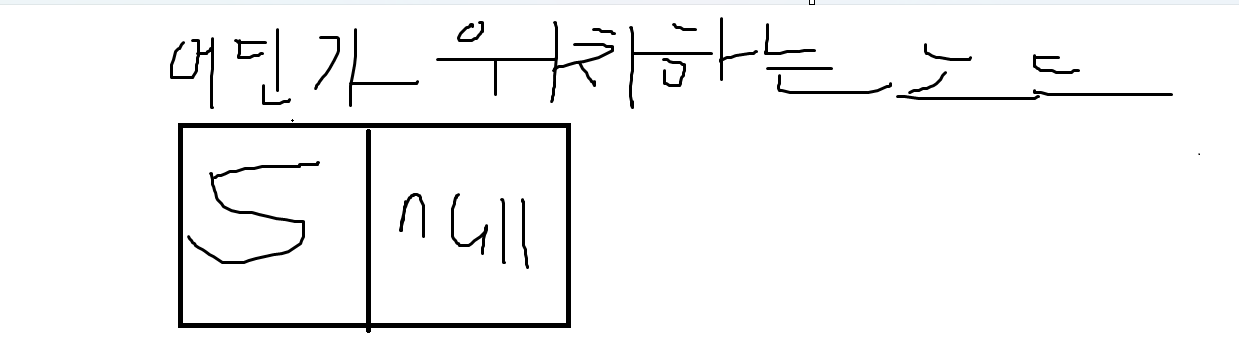
if(head == null)
{
head = node; //데이터 추가 한 것이 첫 노드
}- 이전에 어떤 위치에 존재하는 노드에 Data 5가 추가 되었었다. 해당 노드를 head 노드로 설정한다.
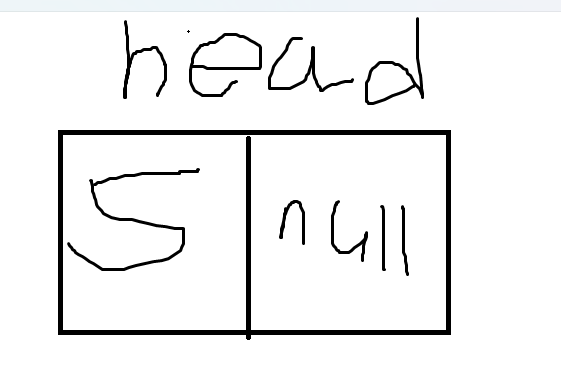
클래스 인스턴스화
using LionStudy_00;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
LionStudy_00.LinkedList<string> list = new LionStudy_00.LinkedList<string>();
//LinkedList 생성자 호출 -> head = null
}
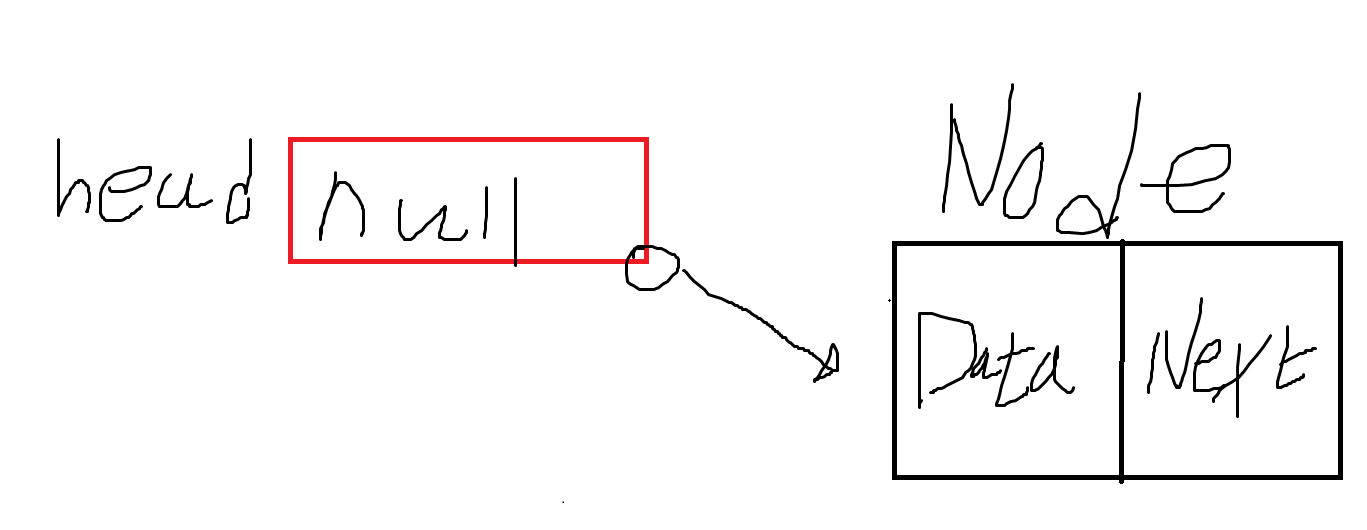
}1. 노드에 대한 정보를 가지고 있는 LinkedListNode 클래스에 접근할 수 있게 head 객체 선언 후 head = null 로 초기화

- 아래 그림처럼 head 객체를 통해 LinkedListNode 클래스에 접근이 가능하다.
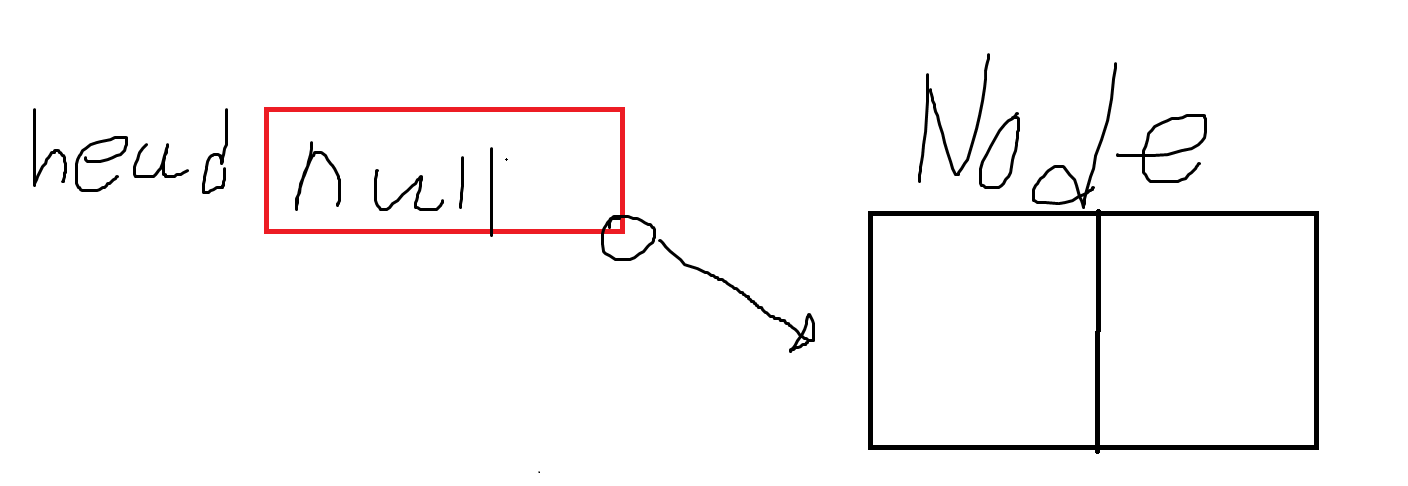
2. 노드에 대한 정보 저장. (이 과정은 데이터 추가,데이터 삭제, 데이터 뽑아내기 과정이 있어야 실행 되는 것)
- 아직까지는 이 상태이다.
데이터 1번째 추가 ( Add )
using LionStudy_00;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
LionStudy_00.LinkedList<string> list = new LionStudy_00.LinkedList<string>();
list.Add("5");
}
}1. LinkedListNode 클래스의 인스턴스화를 통해 LinkedListNode의 생성자 호출. 즉, 5라는 data가 노드의 Data로 저장한다. 인스턴스화 하기 전에 head 객체를 접근한 적이 없으므로 head는 아직까지 null상태이다.
- head는 null 이므로 5라는 data가 들어간 노드를 head 노드로 설정
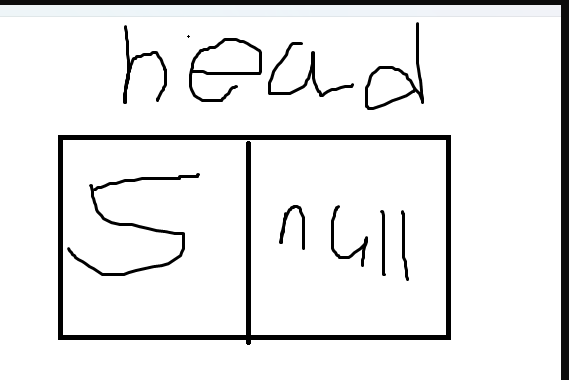
정리한 그림
- Next는 여전히 null이다.
데이터 2번째 추가 ( Add )
- head 노드에는 현재 5라는 데이터와 다음 노드를 가리키는 Next가 null인 상태이다. 즉, head.Data = 5; head.Next = null;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
LionStudy_00.LinkedList<string> list = new LionStudy_00.LinkedList<string>();
list.Add("5");
list.Add("6");
}
} - 6을 추가하면, 아래 코드로 인해, 새로운 노드가 생긴다.
- 6을 추가하면, 아래 코드로 인해, 새로운 노드가 생긴다.
- 이전의 5를 추가했을 때와 똑같다. 어떤 위치에 6이라는 Data와 다음 노드로 갈 Next는 null일 것이다.

- head 는 null 이 아니므로, if문은 건너뛰고 else문 실행한다.
- head 는 null 이 아니므로, if문은 건너뛰고 else문 실행한다.
- 현재 head 노드를 current 노드로 변경한다.
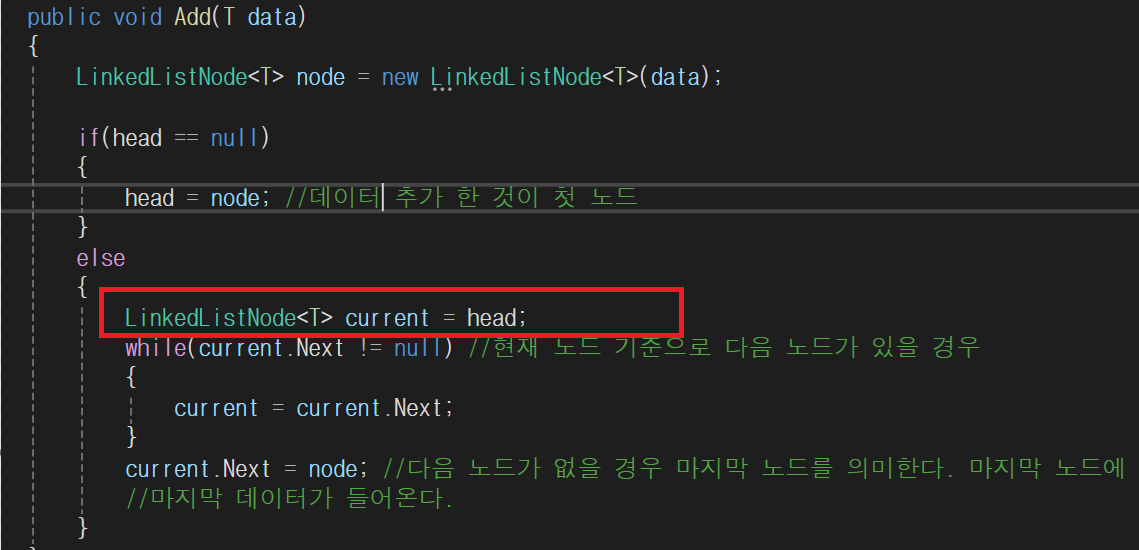

- 현재 head 노드를 current 노드로 변경한다.
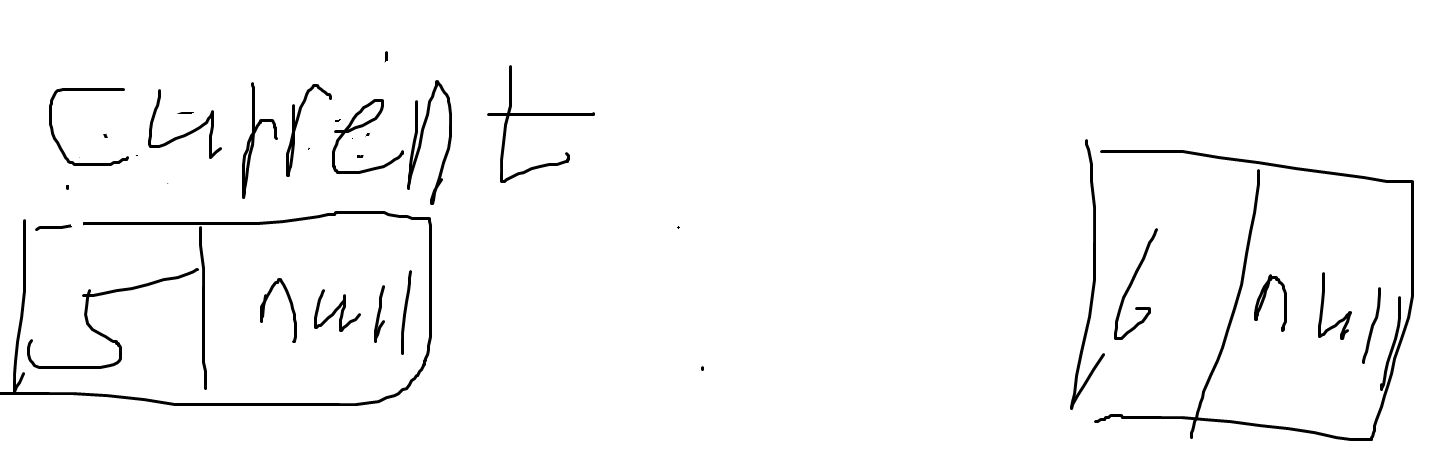
- current.Next = null 이므로, while문이 실행되지 않는다.
- current.Next를 이전에 생성된 노드에 연결한다.

- current.Next를 이전에 생성된 노드에 연결한다.
데이터 3번째 추가도 위와 같이 진행된다.
데이터 삭제 ( Remove )
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
LionStudy_00.LinkedList<string> list = new LionStudy_00.LinkedList<string>();
list.Add("5");
list.Add("6");
list.Remove("5"); //5 삭제
}
}
-
- 현재 헤드 노드는 null이 아니다. 그 이유는 처음에 Add("5")을 했었기 때문에 , 헤드 노드에 데이터 5가 담겨져 있기 때문이다.
- 현재 헤드 노드는 null이 아니다. 그 이유는 처음에 Add("5")을 했었기 때문에 , 헤드 노드에 데이터 5가 담겨져 있기 때문이다.
-
아래는 현재 상태이다. 처음에 5 데이터 삽입 -> 6 데이터 삽입을 하였다.
-
- head.Data = 5 이며, list.Remove("6"); 하였기 때문에 Remove의 매개변수 data = 6이다. 따라서 아래 if문은 거짓이므로 실행하지 않는다.
- head.Data = 5 이며, list.Remove("6"); 하였기 때문에 Remove의 매개변수 data = 6이다. 따라서 아래 if문은 거짓이므로 실행하지 않는다.
-
- head 노드를 current 노드에 저장한다. 즉, current 노드도 head노드가 연결한 노드를 가리킨다.
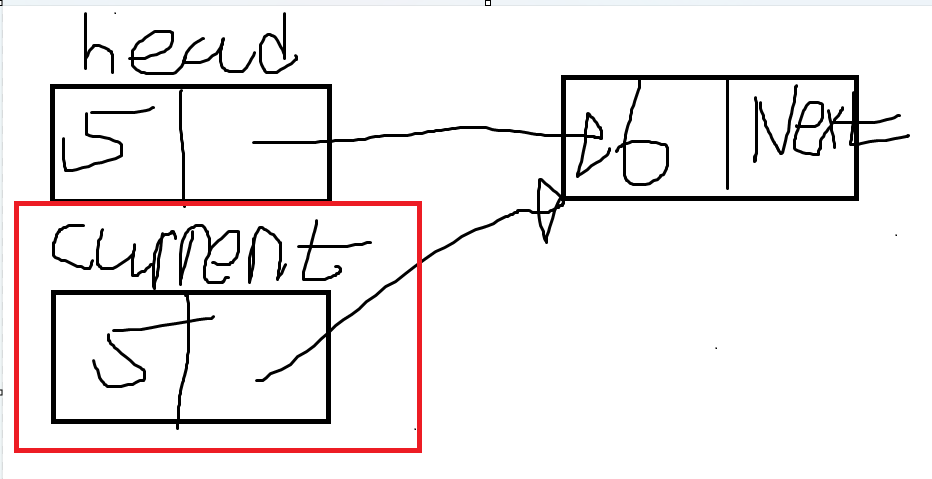
- head 노드를 current 노드에 저장한다. 즉, current 노드도 head노드가 연결한 노드를 가리킨다.
-
- 이전 노드를 저장할 객체를 선언한다. 주로 리스트를 탐색할 때, 현재 노드의 이전 노드를 기억하기 위해 사용되기 때문입니다.
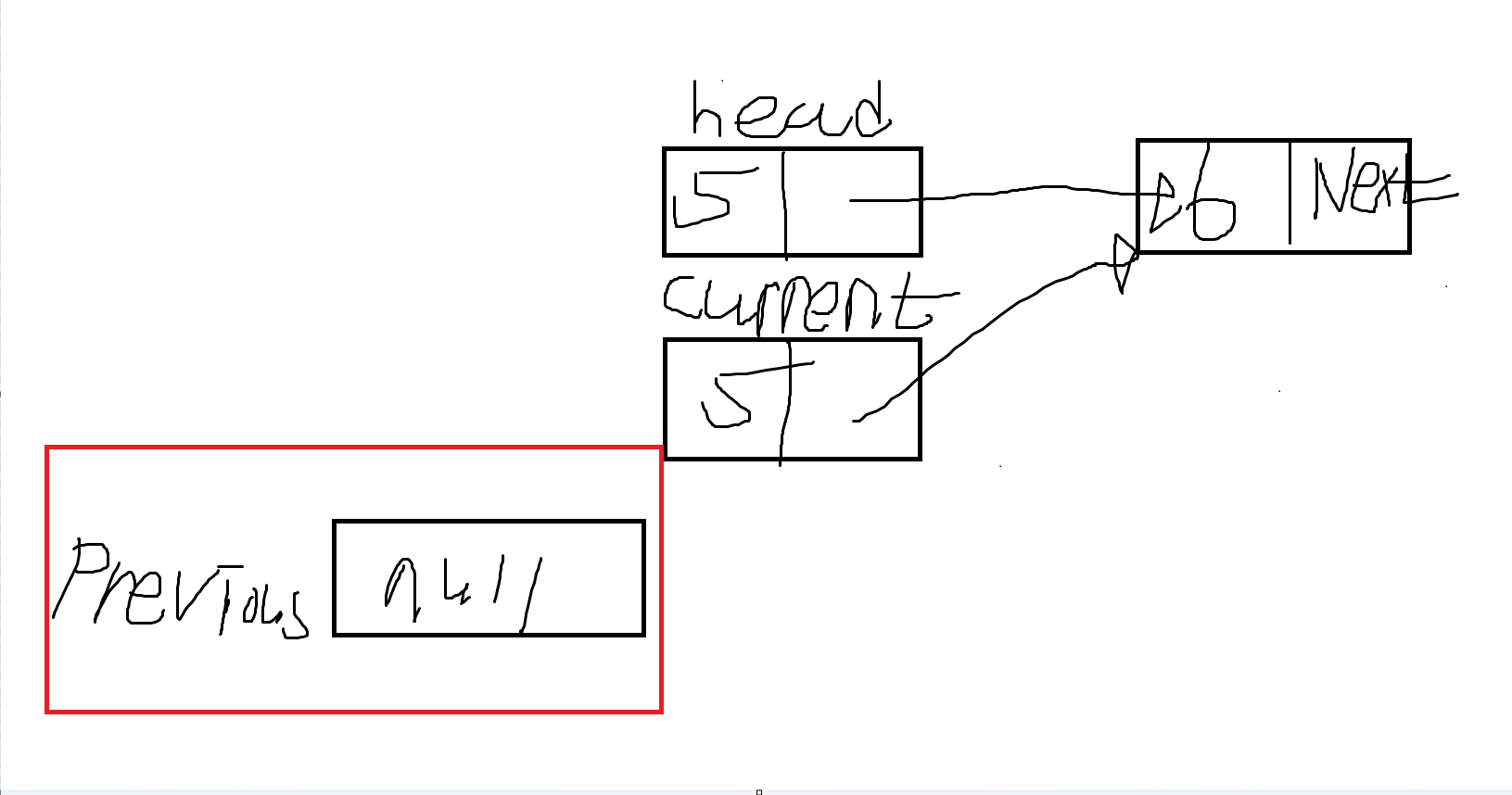
- 이전 노드를 저장할 객체를 선언한다. 주로 리스트를 탐색할 때, 현재 노드의 이전 노드를 기억하기 위해 사용되기 때문입니다.
-
- while문의 조건은 참이 된다. current는 데이터가 들어있으므로 null이 아니고, current의 데이터가 5, 삭제하려는 데이터는 6이므로, 조건이 true가 된다.
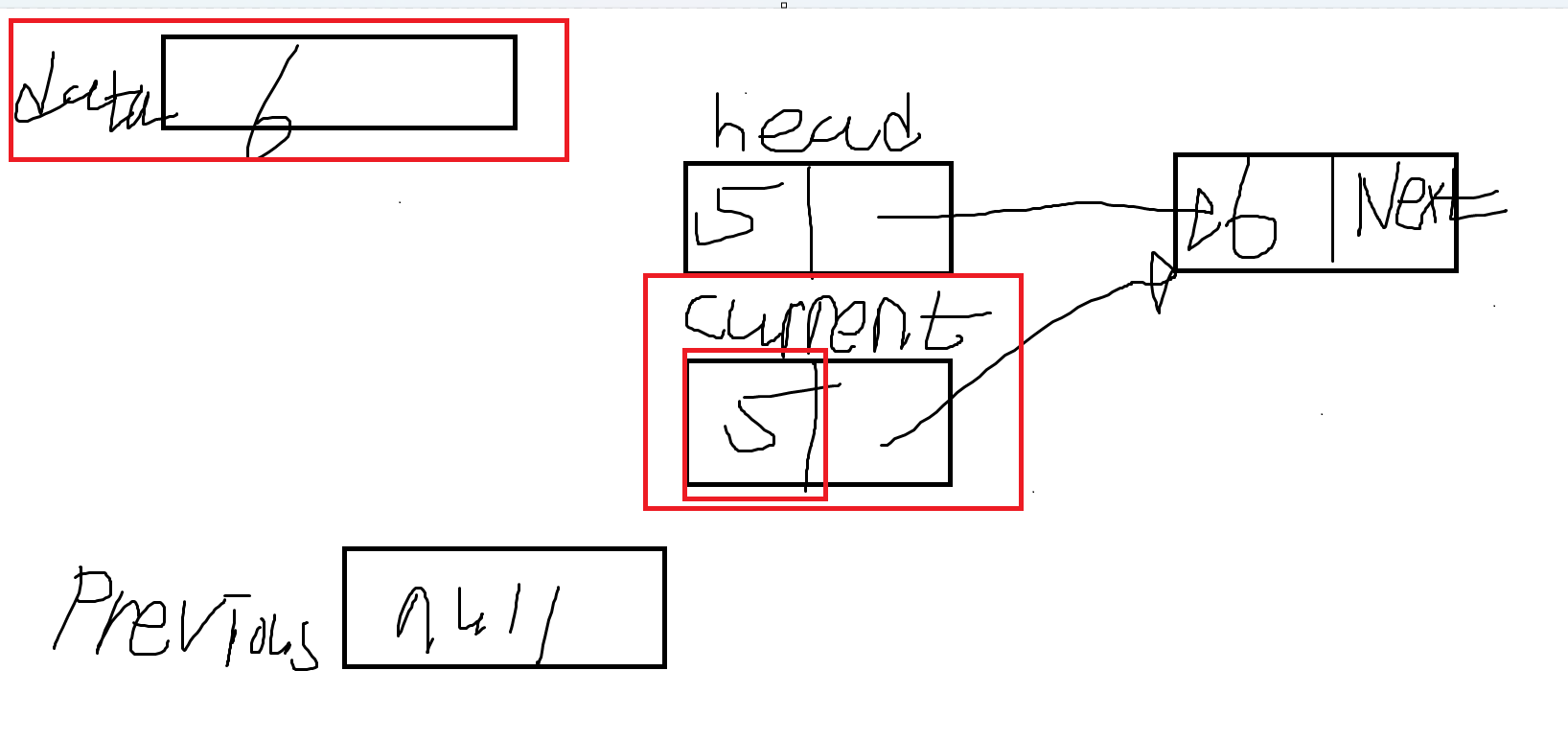
- while문의 조건은 참이 된다. current는 데이터가 들어있으므로 null이 아니고, current의 데이터가 5, 삭제하려는 데이터는 6이므로, 조건이 true가 된다.
-
- current 노드를 previous로 저장
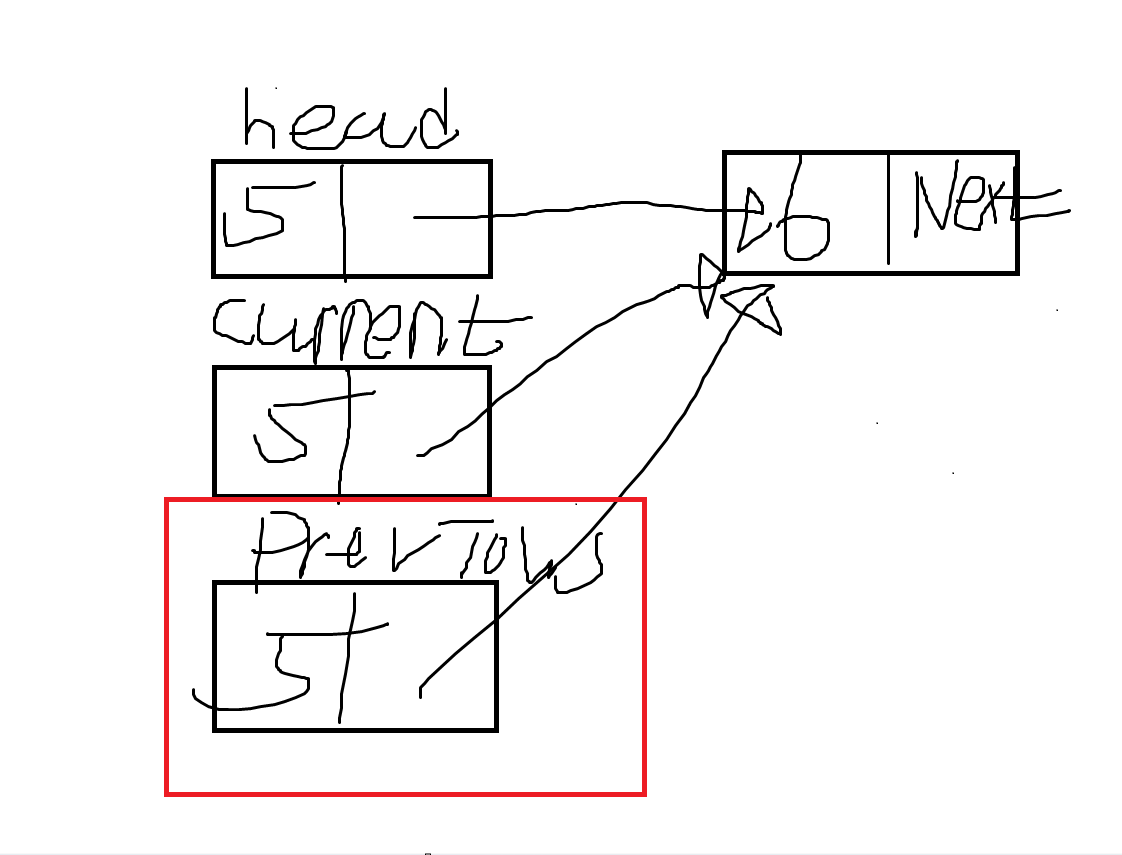
- current 노드를 previous로 저장
-
- current.Next는 현재 6이 들어간 노드를 가리키고 있다. 따라서 current = current.Next에 의해 아래 그림처럼 된다.
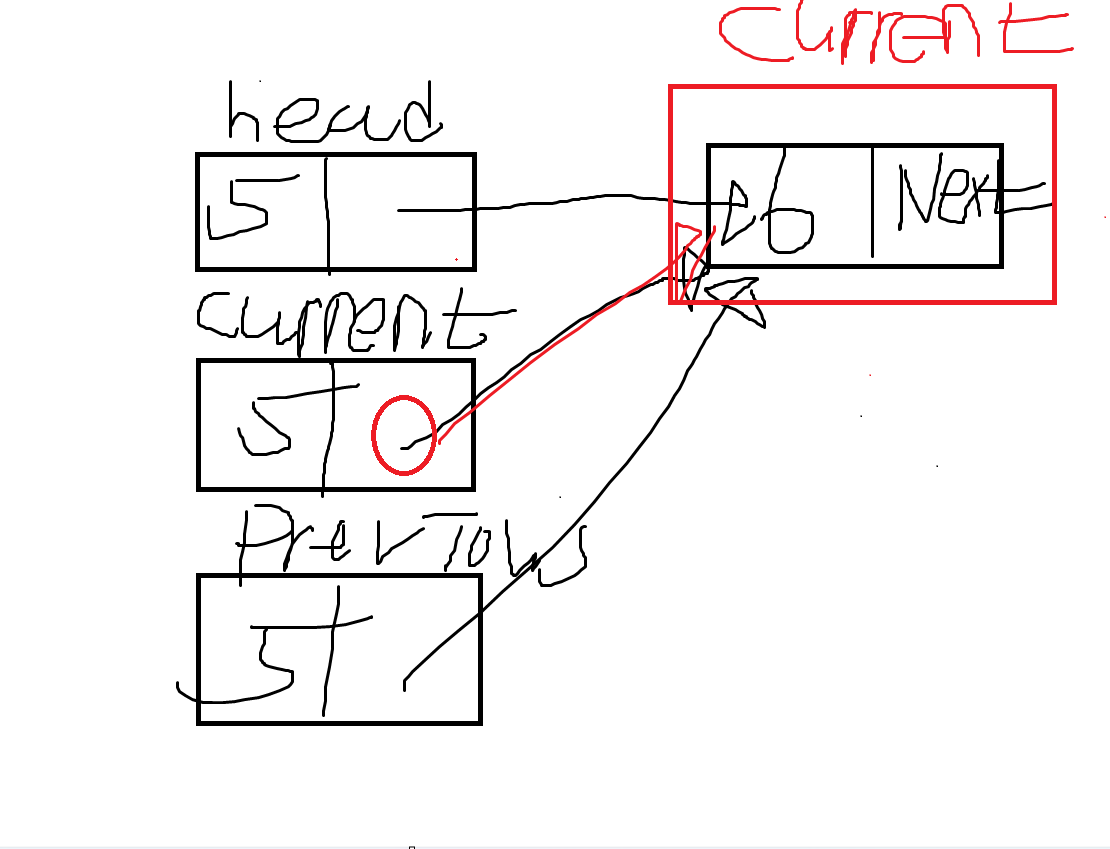
- current.Next는 현재 6이 들어간 노드를 가리키고 있다. 따라서 current = current.Next에 의해 아래 그림처럼 된다.
-
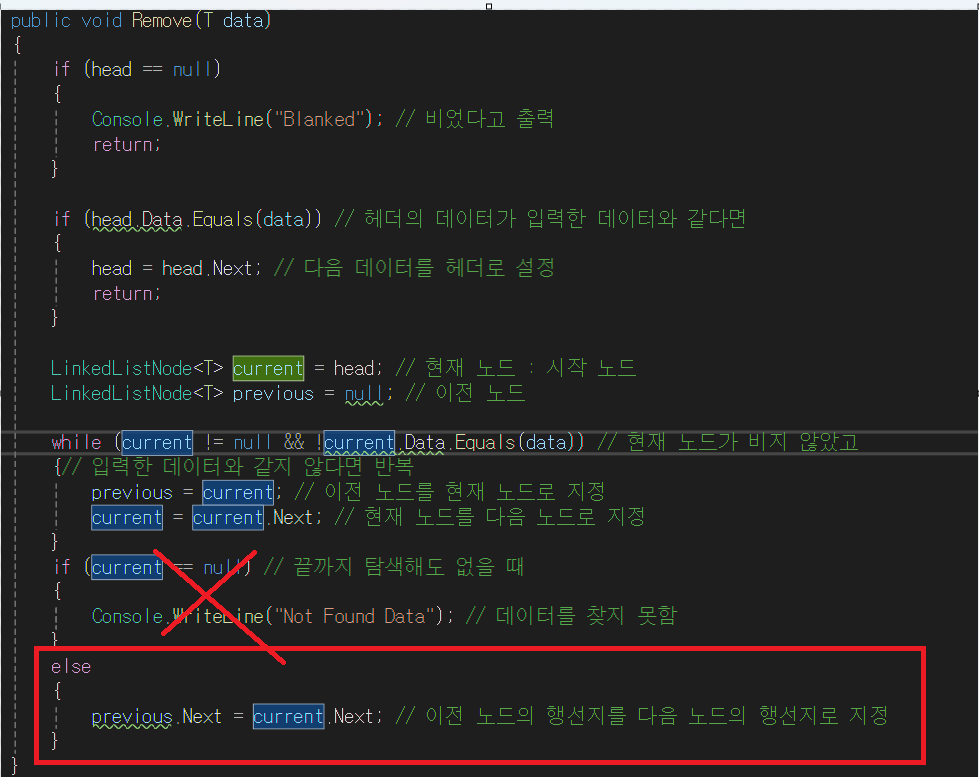
- current.Next는 null이다. 왜냐하면 처음에 5와 6을 삽입했고, 6을 삭제하는 과정이였다. 6 다음으로 삽입한게 없으므로 current.Next = null; 이 된다. previous.Next = current.Next; 에 의해 previous.Next가 가리키는 current 노드는 null이 되서 previous 노드가 마지막 노드가 된다.
-
if문은 실행 하지 않고, else문이 실행된다.
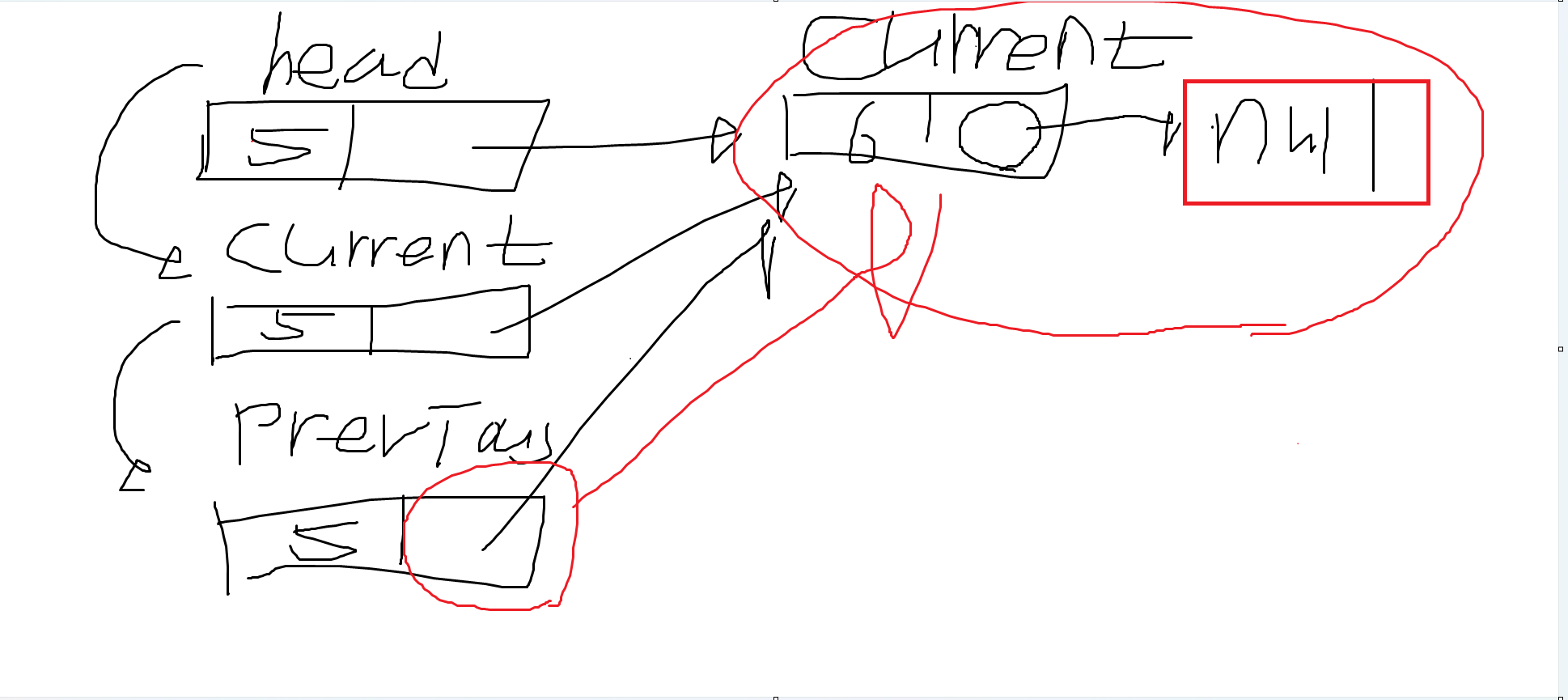
만약 list.Remove("5) 일 경우
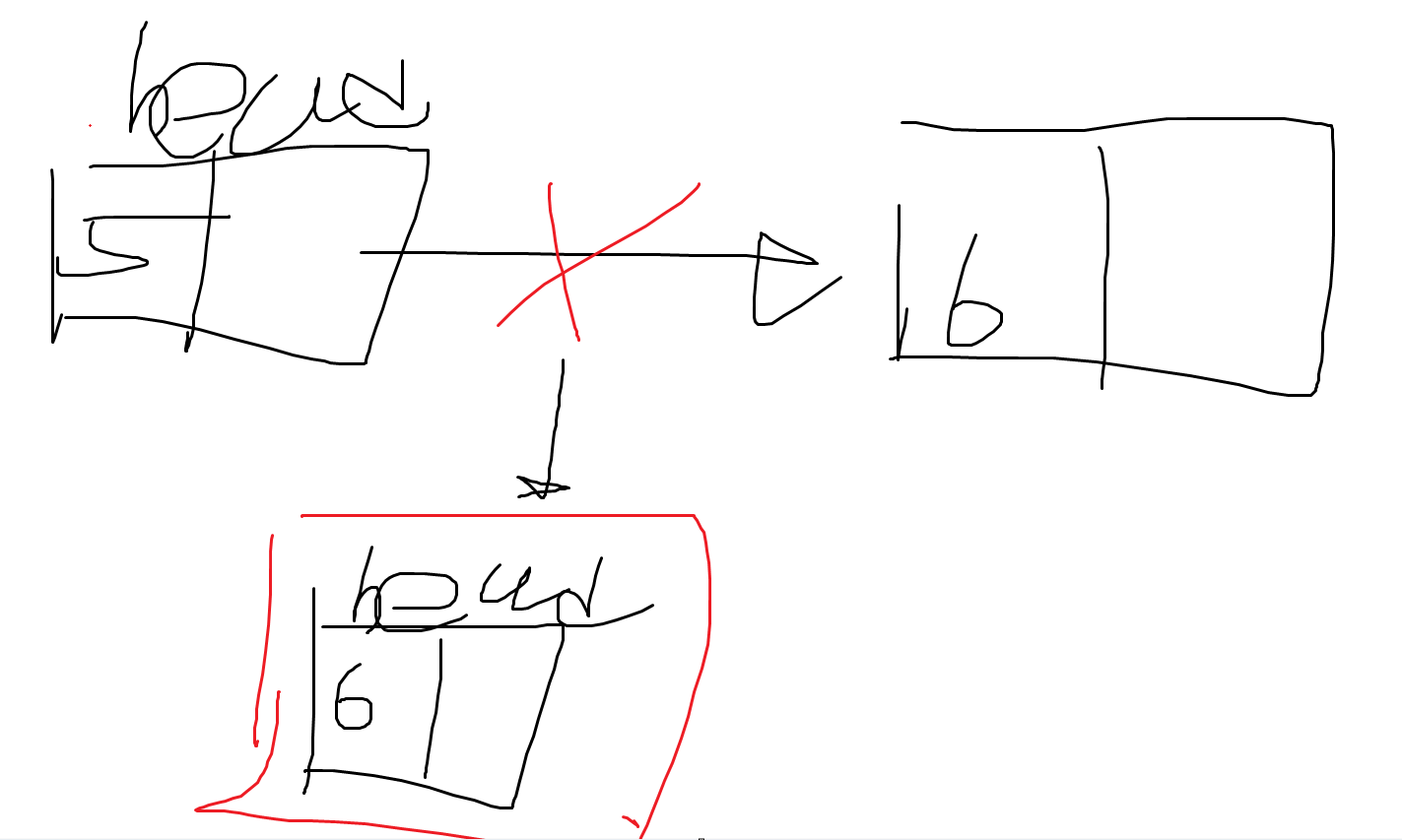
- head.Data 와 Remove()의 매개변수(data)가 같으므로 아래 if문이 실행된다.
- 기존 head가 가리키는 노드를 끊어버리고, 가리키는 노드가 head가 되는 것이다.
PopFirst()
using LionStudy_00;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
LionStudy_00.LinkedList<string> list = new LionStudy_00.LinkedList<string>();
list.Add("5");
list.Add("6");
list.PopFirst();
}
}처음 삽입한 데이터를 뽑아낸다.
- head 노드는 null이 아니므로, if문이 실행되지 않는다. 왜냐하면 5를 삽입한 노드가 head 노드가 된 상태이기 때문이다.
- head 노드는 null이 아니므로, if문이 실행되지 않는다. 왜냐하면 5를 삽입한 노드가 head 노드가 된 상태이기 때문이다.
- head.Data를 data 변수에 저장한다.
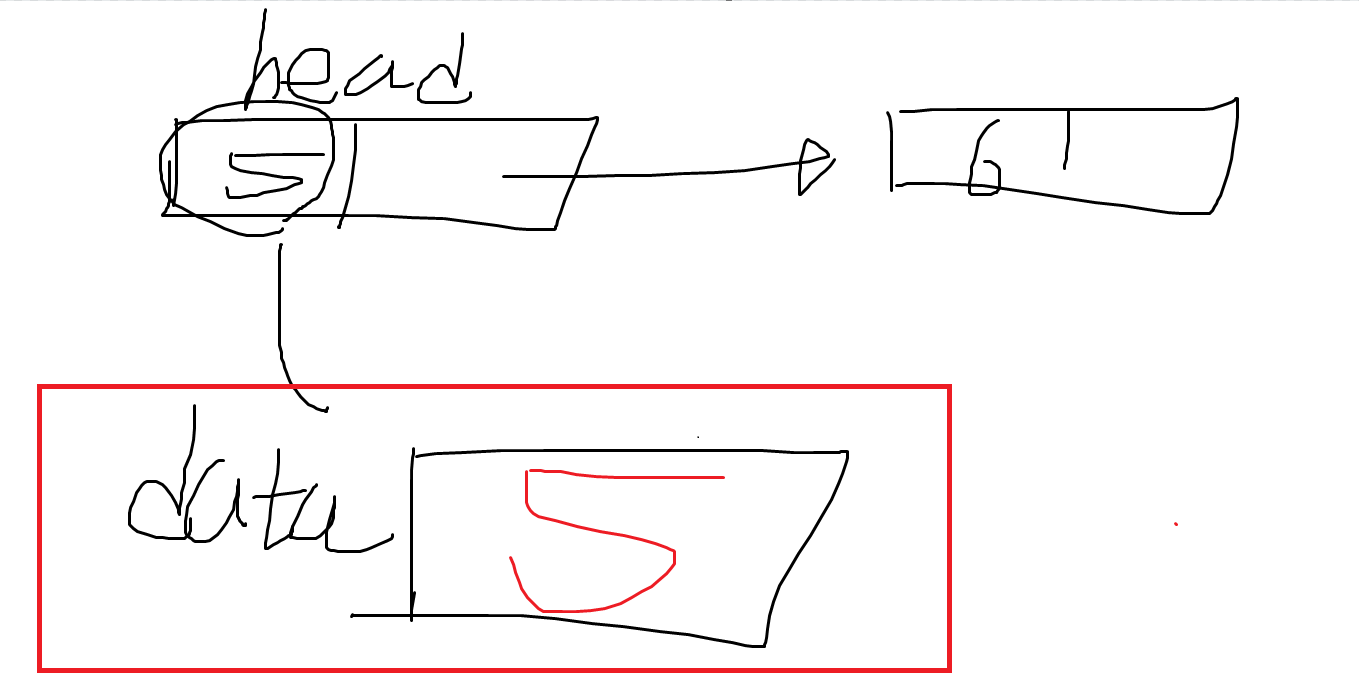
- head.Data를 data 변수에 저장한다.
- head 노드가 가리키는 노드를 head로 설정하고, data(5)를 return한다.
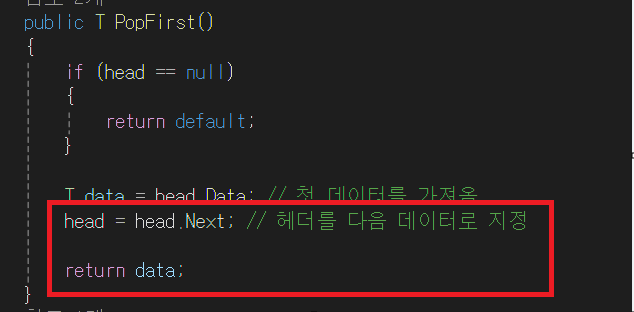
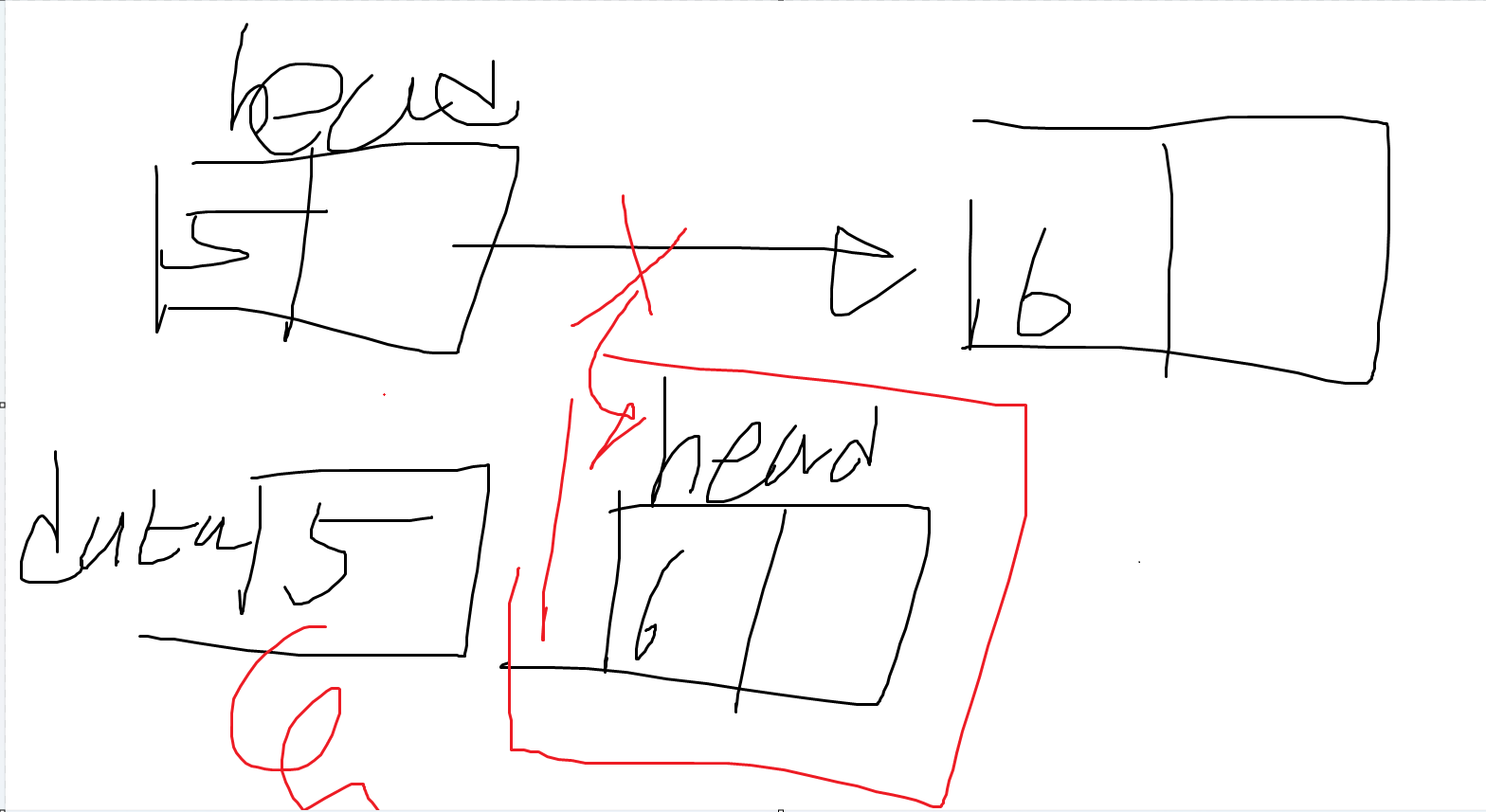
즉, PopFirst()는 처음 삽입한 데이터를 뽑아내는 것이다. 뽑아 낼때 노드 연결한 것을 끊어 버린다.
- head 노드가 가리키는 노드를 head로 설정하고, data(5)를 return한다.
PopLast()
using LionStudy_00;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
LionStudy_00.LinkedList<string> list = new LionStudy_00.LinkedList<string>();
list.Add("5");
list.Add("6");
list.PopLast();
}
}마지막으로 삽입한 데이터를 뽑아낸다.
- head는 null이 아니며, head가 가리키는 다음 노드 또한 null이 아니므로 두 if문은 실행하지 않는다.
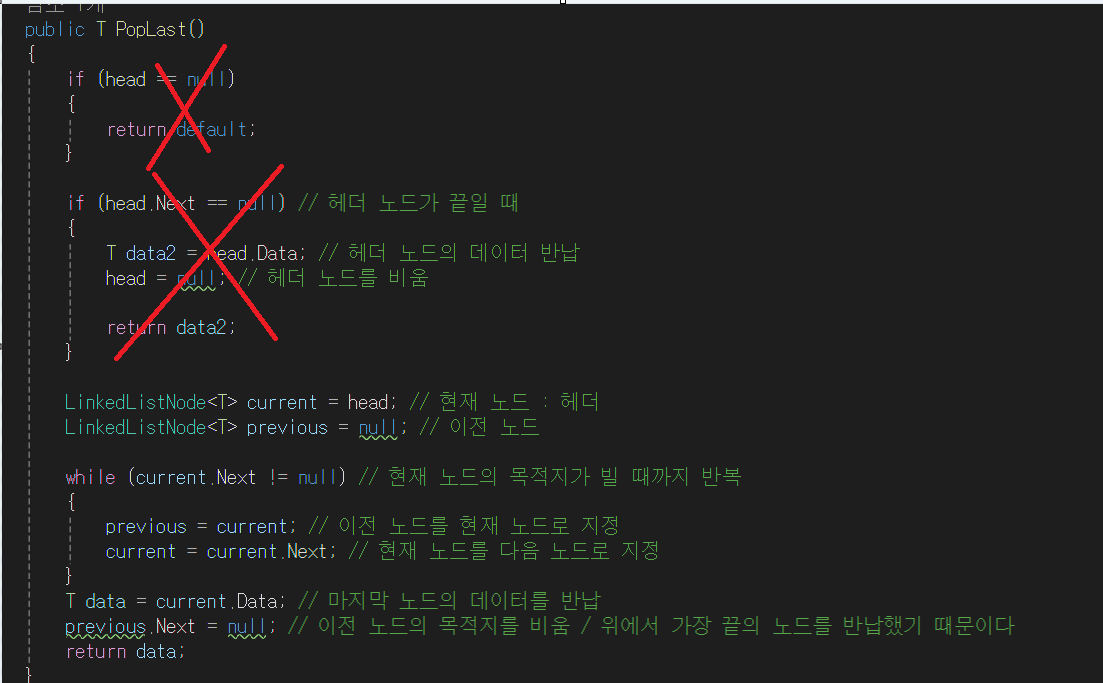

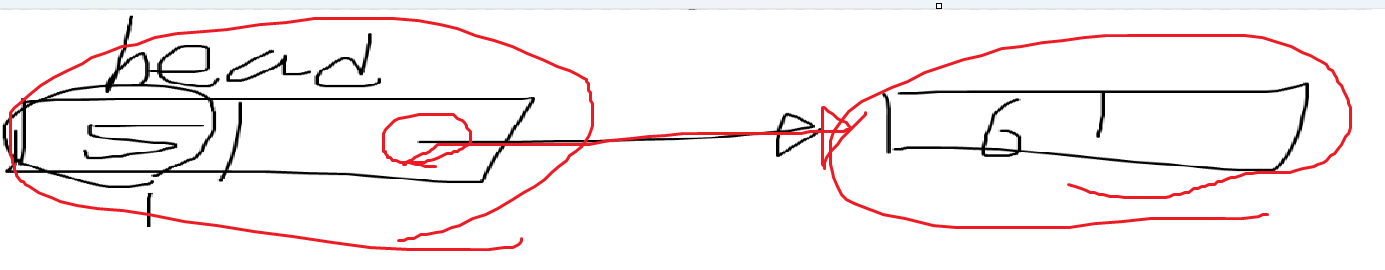
- head는 null이 아니며, head가 가리키는 다음 노드 또한 null이 아니므로 두 if문은 실행하지 않는다.
- head 노드를 current 노드에 저장한다. 즉, current 노드도 head노드가 연결한 노드를 가리킨다.

- head 노드를 current 노드에 저장한다. 즉, current 노드도 head노드가 연결한 노드를 가리킨다.
- 이전 노드를 저장할 객체를 선언한다. 주로 리스트를 탐색할 때, 현재 노드의 이전 노드를 기억하기 위해 사용되기 때문입니다.

- 이전 노드를 저장할 객체를 선언한다. 주로 리스트를 탐색할 때, 현재 노드의 이전 노드를 기억하기 위해 사용되기 때문입니다.
- current.Next . current 노드가 가리키는 노드는 null 이 아니다. 그 이유는 current 노드는 6이란 데이터를 갖고 있는 노드를 가리키고 있기 때문이다.
- current 노드를 previous로 저장

- current 노드를 previous로 저장
- current.Next는 현재 6이 들어간 노드를 가리키고 있다. 따라서 current = current.Next에 의해 아래 그림처럼 된다.

- current.Next는 현재 6이 들어간 노드를 가리키고 있다. 따라서 current = current.Next에 의해 아래 그림처럼 된다.
- current.Data = 6 이므로, 6을 data 변수에 저장한다.
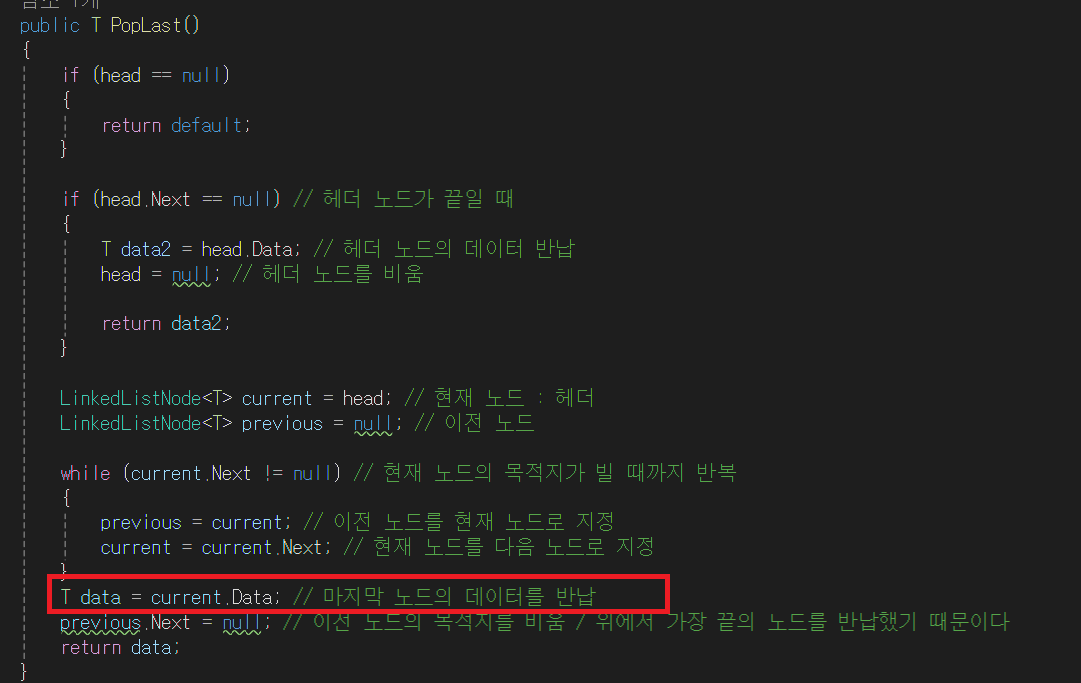
- current.Data = 6 이므로, 6을 data 변수에 저장한다.
- previous.Next = null; 즉, previous가 가리키는 노드를 null로 만들고, data(6)을 리턴한다.
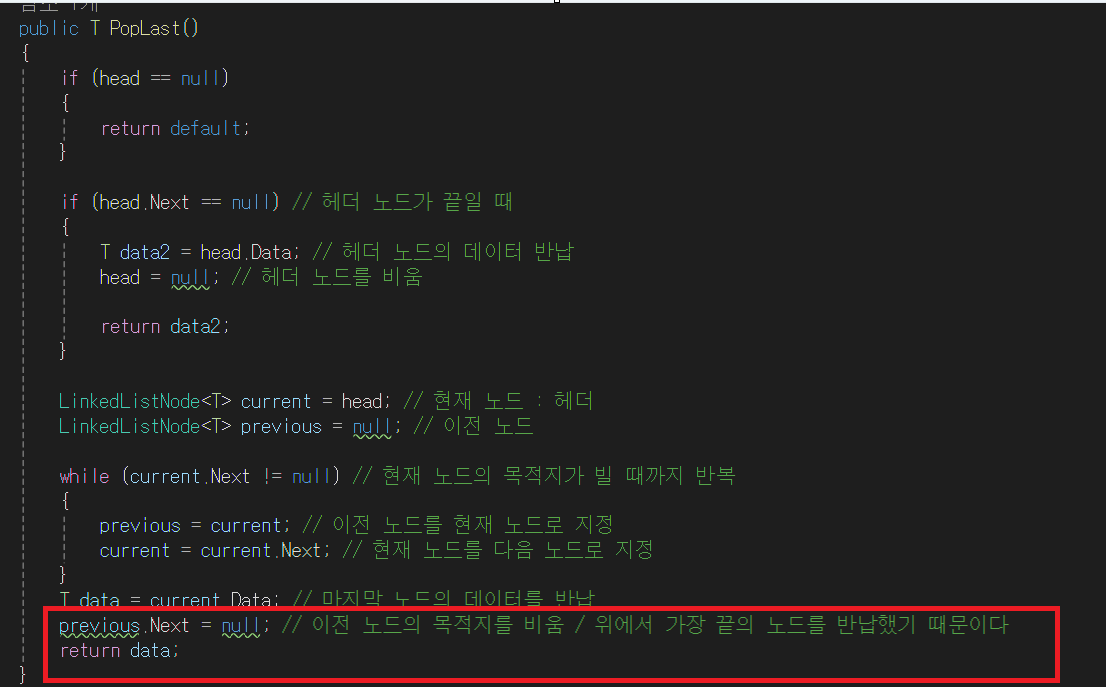
- previous.Next = null; 즉, previous가 가리키는 노드를 null로 만들고, data(6)을 리턴한다.
만약, 5 -> 6 -> null 상태에서 PopLast() 을 2번 호출한다면?
using LionStudy_00;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
LionStudy_00.LinkedList<string> list = new LionStudy_00.LinkedList<string>();
list.Add("5");
list.Add("6");
list.PopLast(); //6이 뽑힘
list.PopLast(); //5가 뽑힘
}
}먼저, 처음 list.PopLast(); 을 했을 때 6이란 데이터가 뽑혔다. 노드의 상황은 아래와 같다.
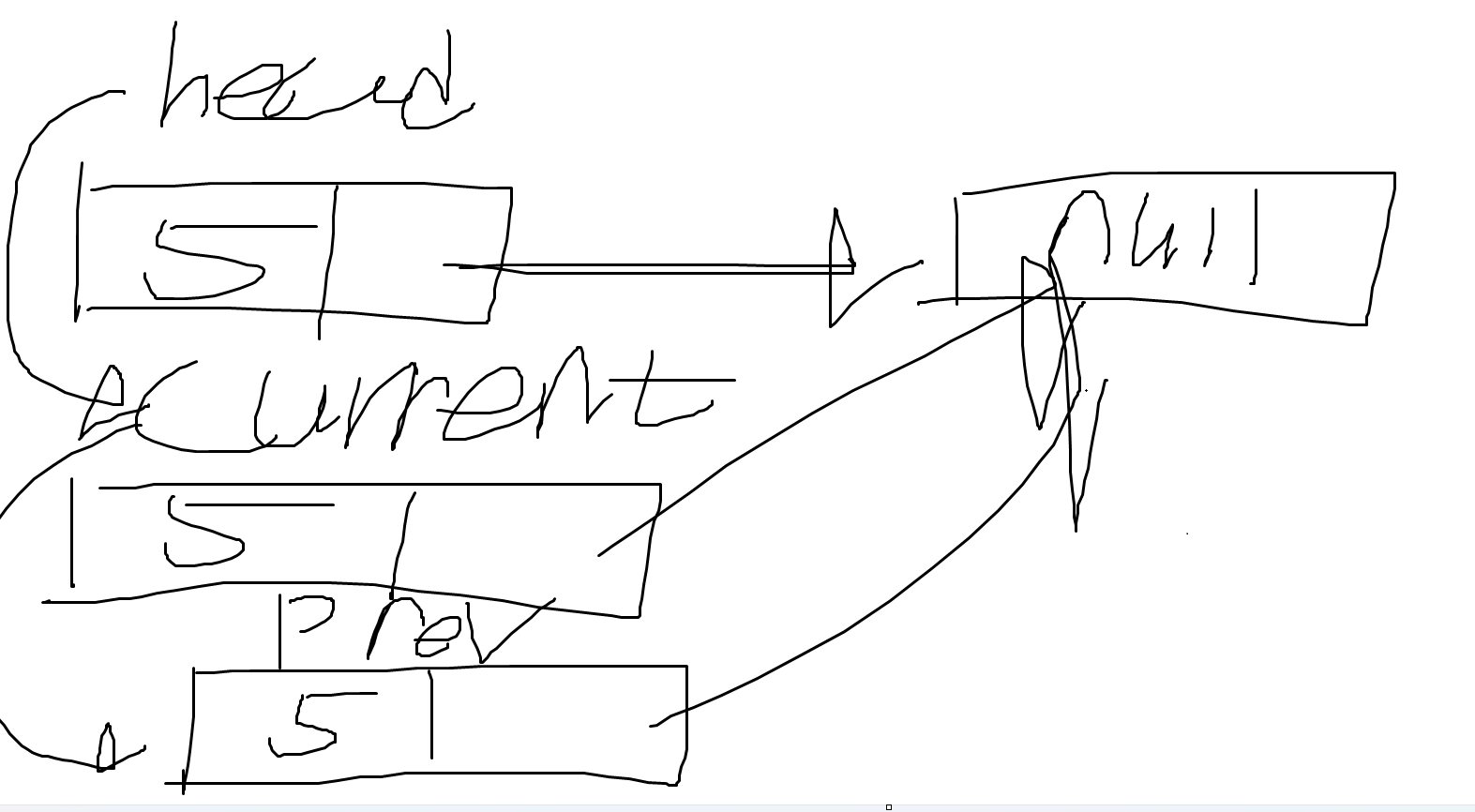
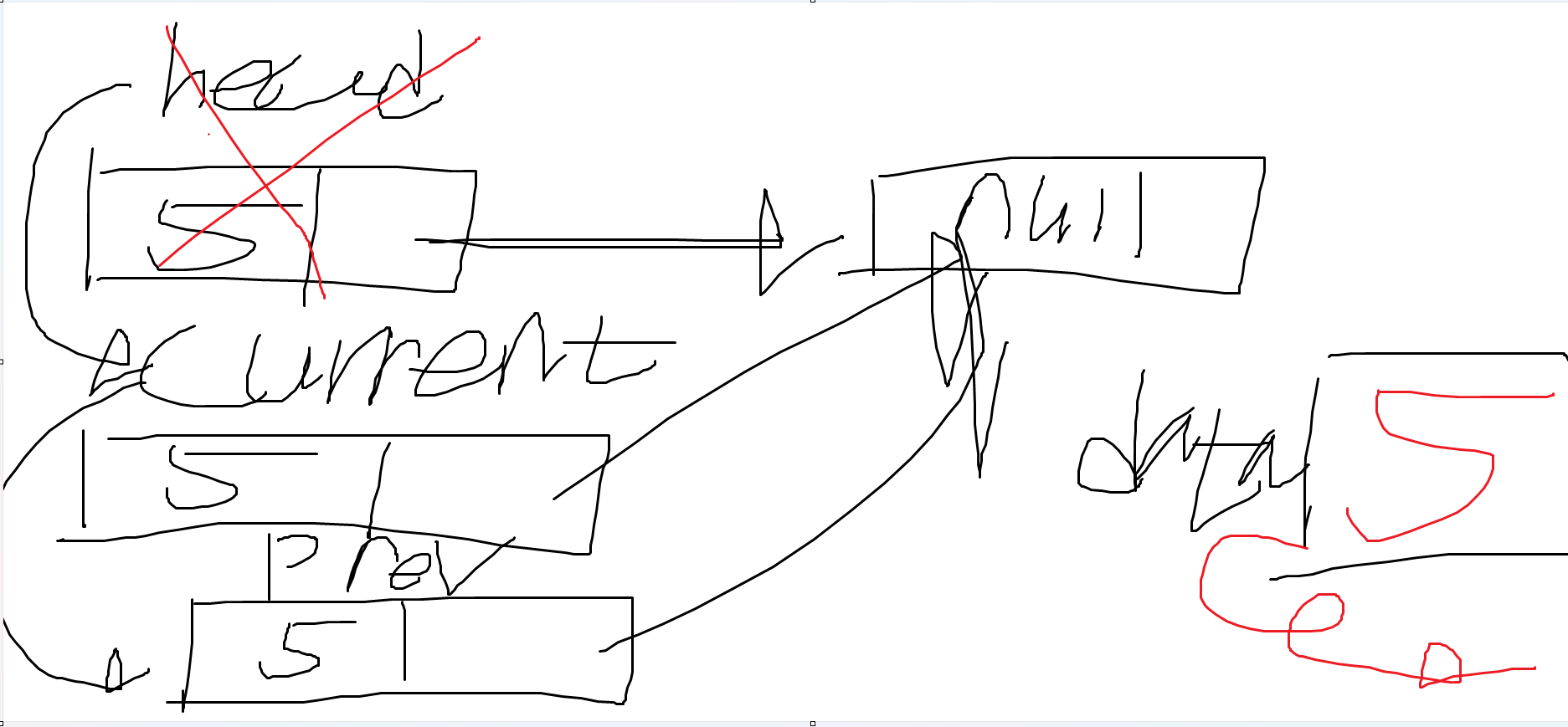
- if문의 조건이 참이 된다. head 노드가 가리키는 노드는 null이다.
- if문의 조건이 참이 된다. head 노드가 가리키는 노드는 null이다.
- head의 Data인 5를 data2에 저장한다.
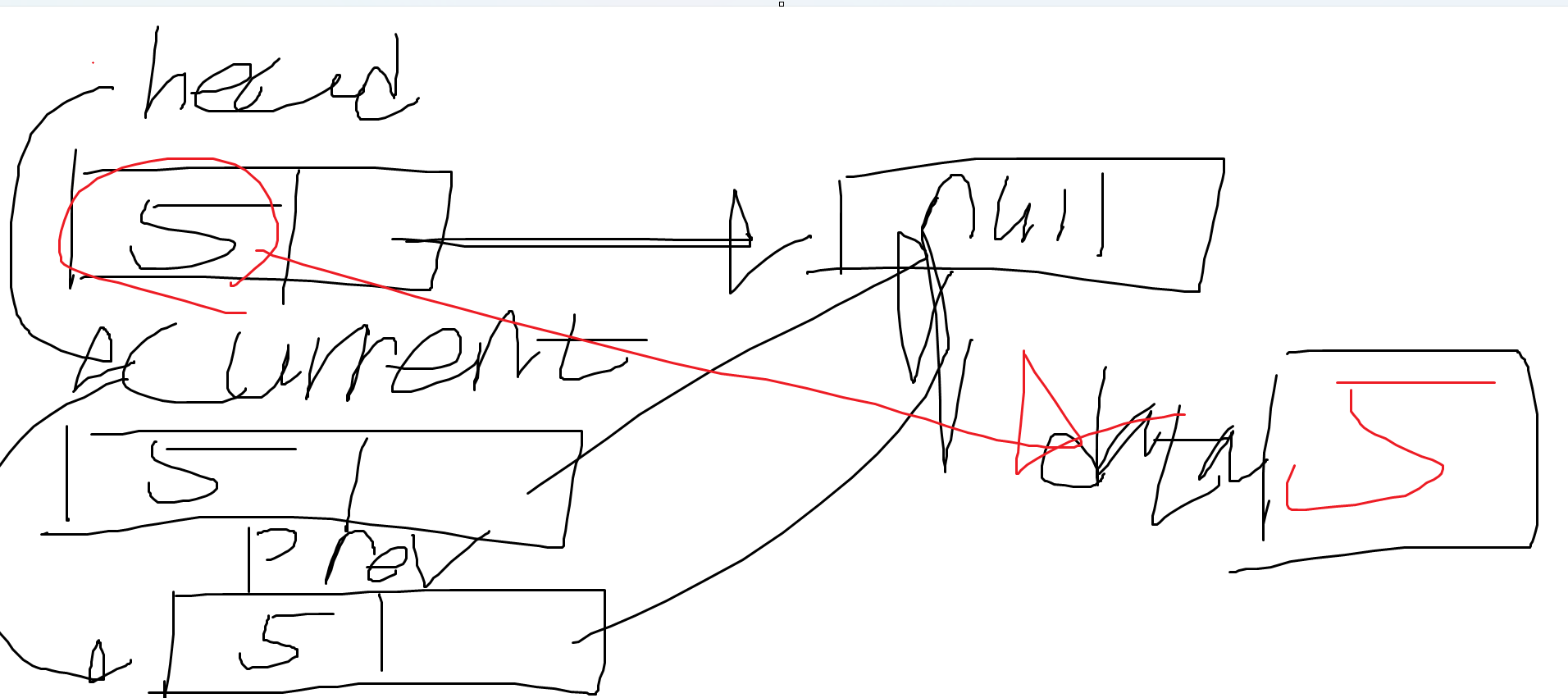
- head의 Data인 5를 data2에 저장한다.
- head를 null로 만들고 data2인 5를 리턴한다.
- head를 null로 만들고 data2인 5를 리턴한다.
⭐ 이중 연결 리스트
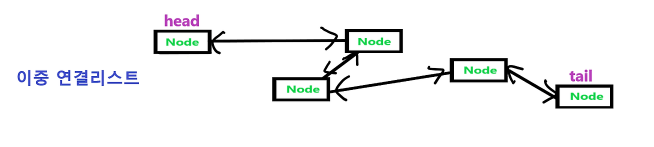
- 각 노드가 이전의 노드와, 다음 노드를 모두 가리키는 양방향 구조이다.
- 데이터를 앞이나 뒤에 추가할 수 있다.
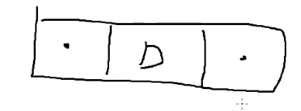
⭐ 1. 이중 연결 리스트의 노드 구조 설계

- 노드에는 Data와 이전의 노드를 가리키는 Prev, 다음 노드를 가리키는 Next로 이루어져 있다. 처음 노드를 만들었을 때 Data는 들어오겠지만, 이전 노드와 다음 노드는 모르므로 null로 만든다. 노드를 만들게 되면 아래 처럼 된다.
⭐ 2. 이중 연결 리스트는 head 노드와 tail 노드를 빈 껍데기로 만들기
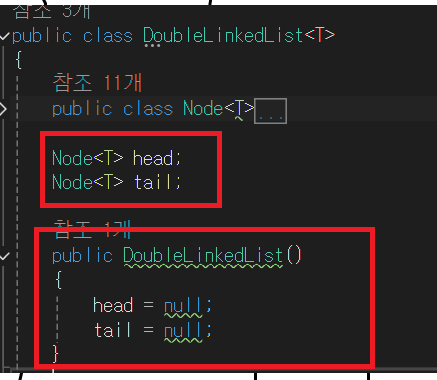
- 또한, head 와 tail을 null로 하여 아무것도 들어있지 않는 노드로 초기화한다. 이유는 이중 연결리스트를 처음 생성할 때, 비어있는 상태로 나타내기 위해서이다.
- 비어있는 상태를 만들게 되면 리스트에 노드를 추가하기 전까지는 리스트가 비어 있음을 명확히 표현하고, 첫 번째 노드를 추가할 때 이를 처리하는 로직을 쉽게 구현할 수 있다.
⭐ 3. 노드 만들기
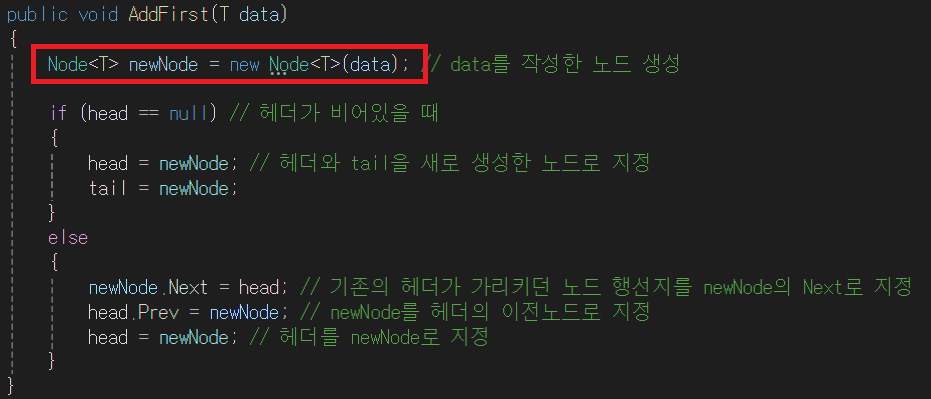
- 들어온 데이터를 노드로 만든다. 만들게 되면 Node 클래스의 생성자에 의해 Prev(이전 노드)와 Next(다음 노드)는 null이 된다. 들어온 데이터가 아직 어딜 가리키는지 모르므로 null처리를 한다.
⭐⭐ 데이터를 앞에 추가하기.
- 이중 연결 리스트에 데이터를 앞에 추가하기 전, 리스트의 head노드의 데이터가 비어있을 때와 비어있지 않을 때로 나뉜다.
⭐ head 노드가 비어있을 때
1. head 노드가 비어있을 때는 새로 추가하는 데이터 노드가 head노드이자 tail 노드일 것이다. 즉, 유일한 노드가 된다.
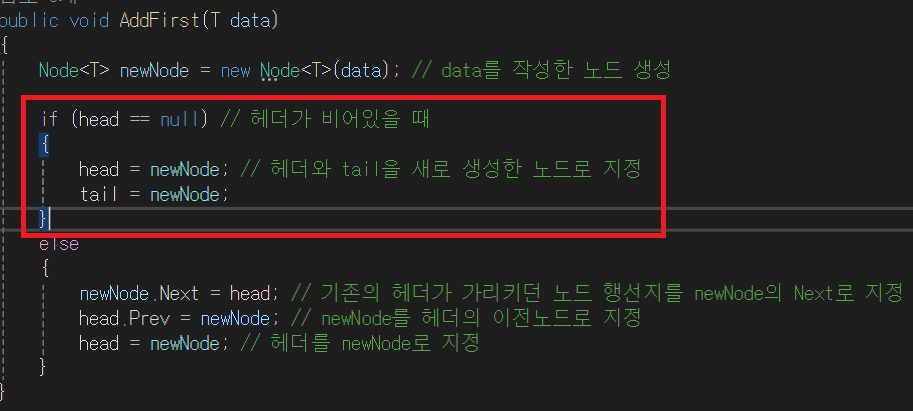
- head 와 tail이 새로 추가한 노드를 가리키고 있다.(⭐ 새로 추가한 데이터를 가리키는 것 아니다. 새로 추가한 노드를 가리키는 것⭐ )
⭐ head 노드가 비어있지 않을 때
- 먼저 최종 결과 사진이다. head가 새로 추가된 데이터 노드가 되야 한다.
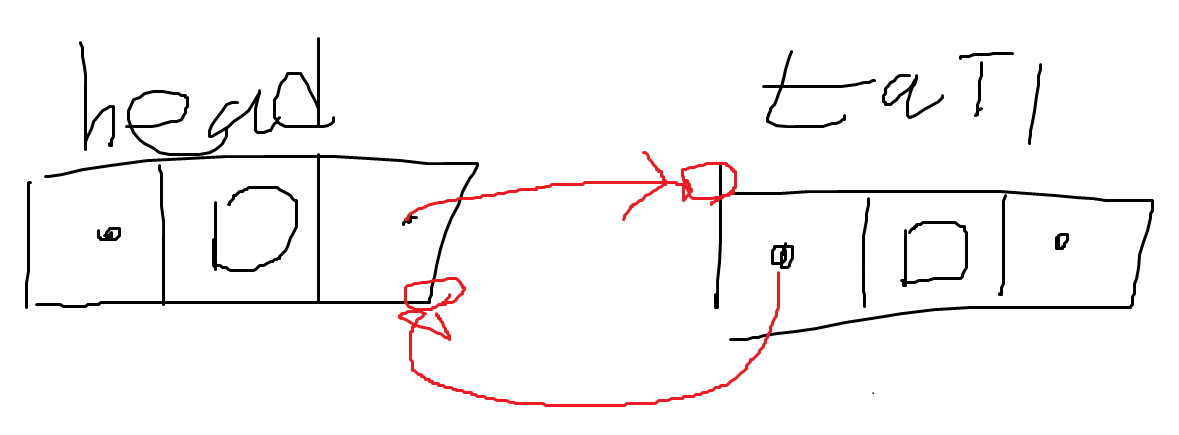
⭐ 순서 1 : 이중 연결 리스트의 노드 구조 상 이전 노드의 Next 가 다음 노드를 가리켜야 한다.
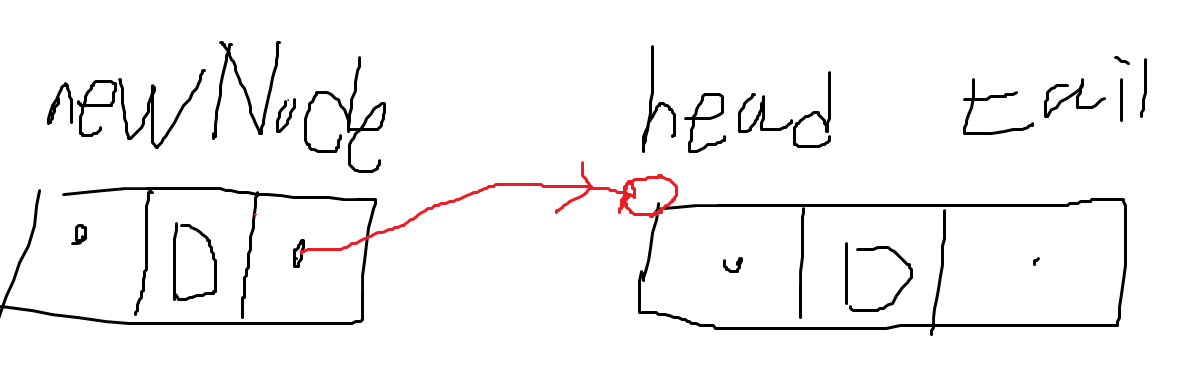
nextNode.Next = head; // 새로 추가 된 노드의 Next가 head를 가리킨다. (가리키기 위해 nexNode.Next가 head의 주소를 알고 있어야 한다.)⭐ 순서 2: 다음 노드의 Prev 가 이전 노드를 가리켜야 한다.
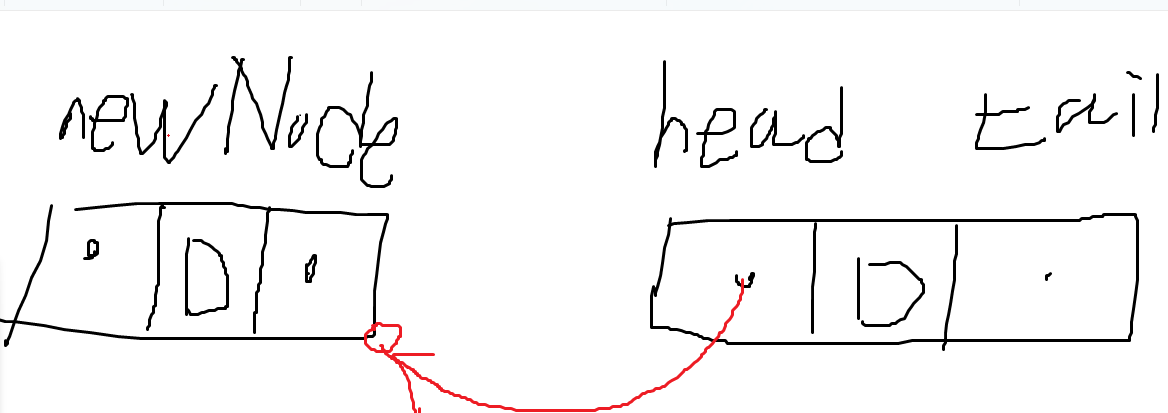
head.Prev = nextNode; // head 노드의 Prev가 nextNode를 가리켜야 한다. (가리키기 위해 head가 nextNode의 주소를 알고 있어야 한다.)⭐ 순서 3: 양 방향 연결이 끝났으므로, head 노드가 nextNode를 가리켜야 한다.
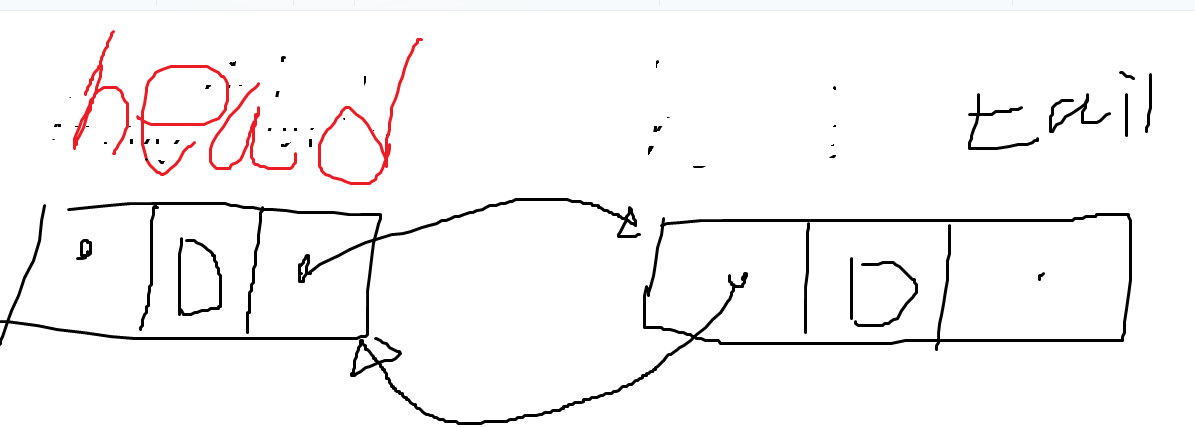
head = nextNode; //head 노드가 nextNode를 가리켜야 한다. (가리키기 위해 head가 nextNode의 주소를 알고 있어야 한다)⭐⭐ 데이터를 뒤에 추가하기.
- 이중 연결 리스트에 데이터를 뒤에 추가하기 전, 리스트의 tail노드의 데이터가 비어있을 때와 비어있지 않을 때로 나뉜다.
⭐ tail 노드가 비어 있을 때 (이 경우는 현재 이중 연결 리스트에 아무런 노드가 없을 때 실행 된다.)
- 즉 , 코드로는 아래와 같을 때 실행된다.
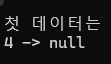
- head와 tail이 새로 추가된 노드를 가리킨다. 추가된 노드를 가리키기 위해서 head와 tail이 추가된 노드의 주소를 알고 있어야 한다.
head = newNode;
tail = newNode;
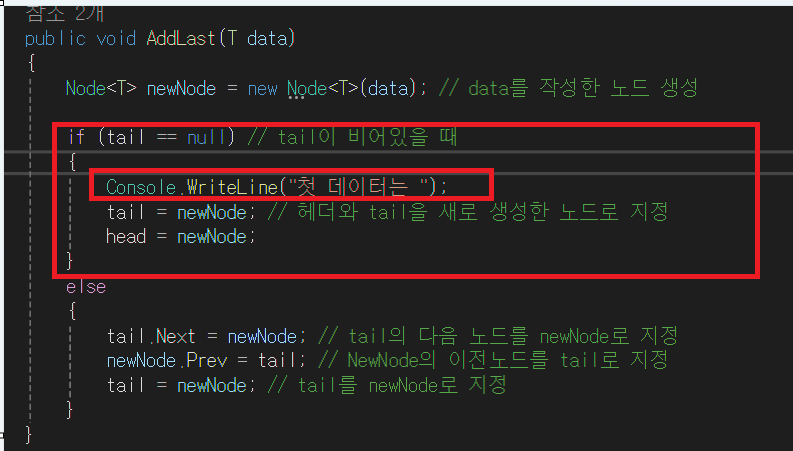
⭐ tail 노드가 비어 있지 않을 때 (이 경우는 현재 이중 연결 리스트에 아무런 노드가 없을 때 실행 된다.)
⭐ 새로운 노드가 만들어졌다. 현재 head와 tail이 이전에 추가된 노드를 이미 가리키고 있으므로 if문의 조건은 false가 되어 실행하지 않는다. else문 실행
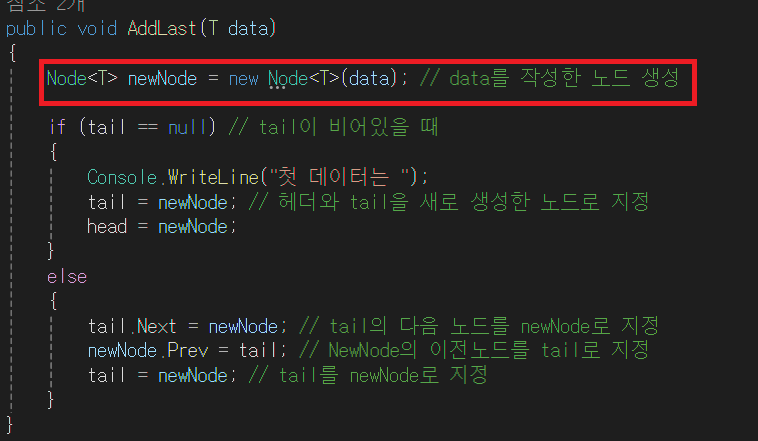
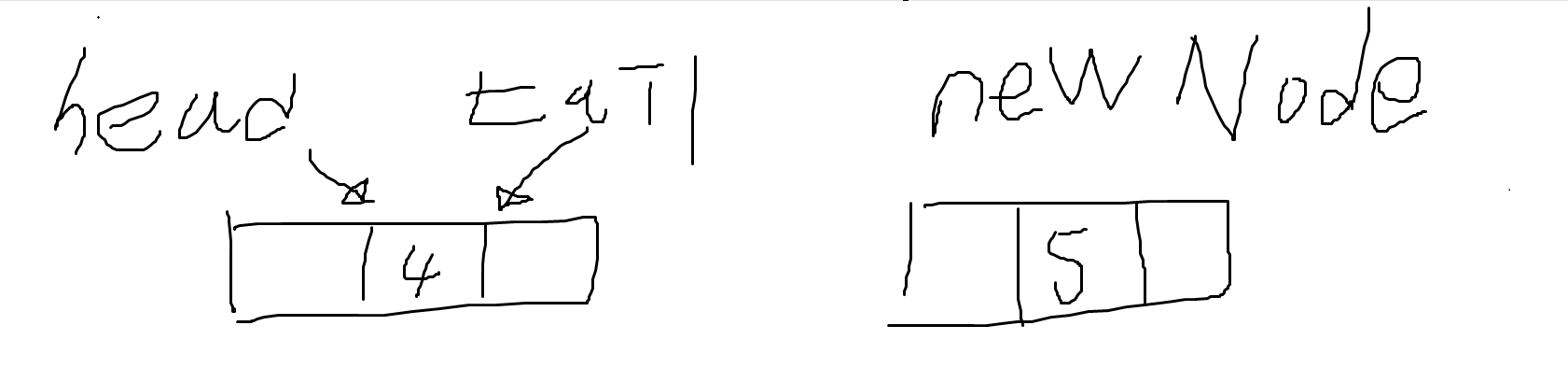
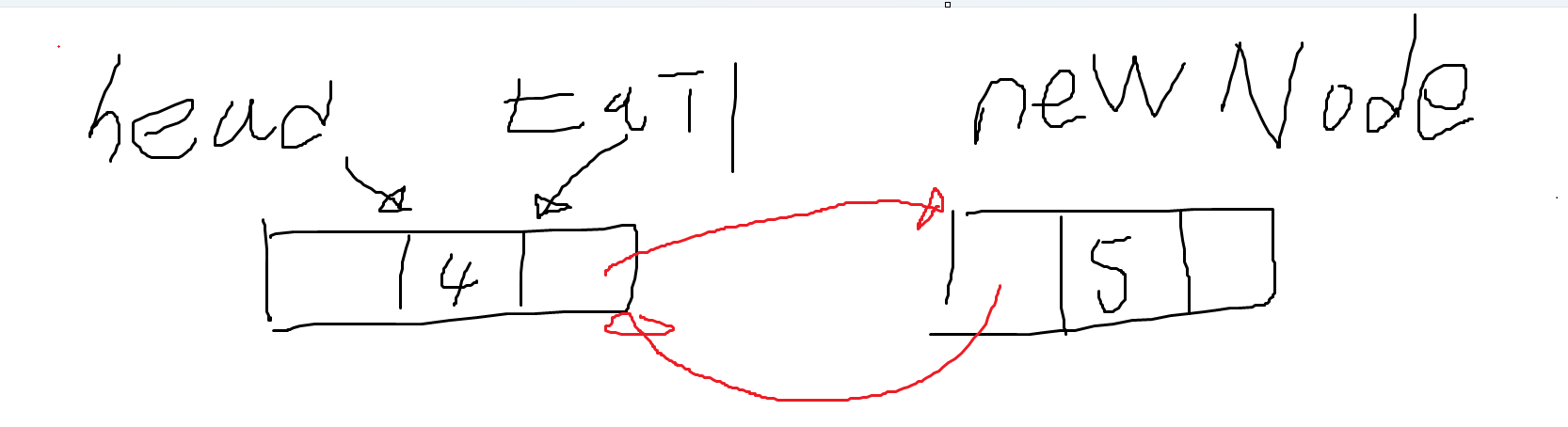
⭐ 1. 이중 연결 리스트를 만들어주기 위해 아래 그림처럼 코드를 짜야 한다.
else
{
tail.Next = newNode; // tail의 Next 노드가 newNode를 가리킨다.(가리키기 위해 nextNode의 주소를 tail의 Next에게 넘겨야 한다.
newNode.Prev = tail; // newNode의 Prev 노드가 tail을 가리킨다. (가리키기 위해 tail의 주소를 newNode의 Prev에게 넘겨야 한다.
}⭐ 2. 양 방향으로 연결이 끝났으면 tail이 NewNode를 가리켜야 한다. (tail은 항상 마지막 노드여야 한다)
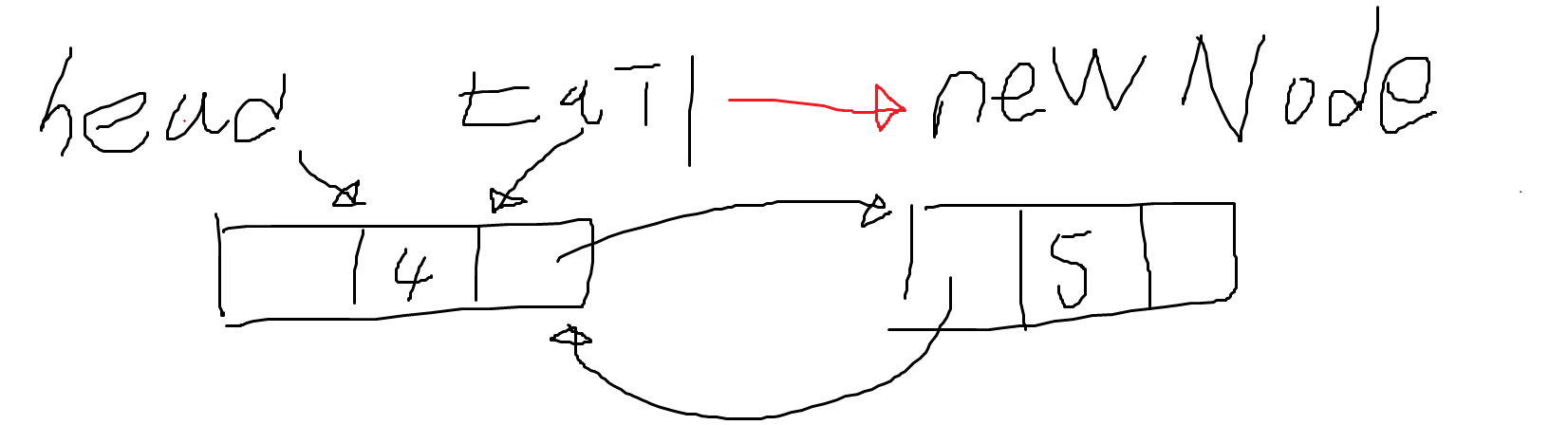
tail = newNode; //tail이 newNode를 가리켜야 한다.(가리키기 위해 newNode의 주소를 tail에게 넘겨야 한다.)- 최종 결과 사진이다.
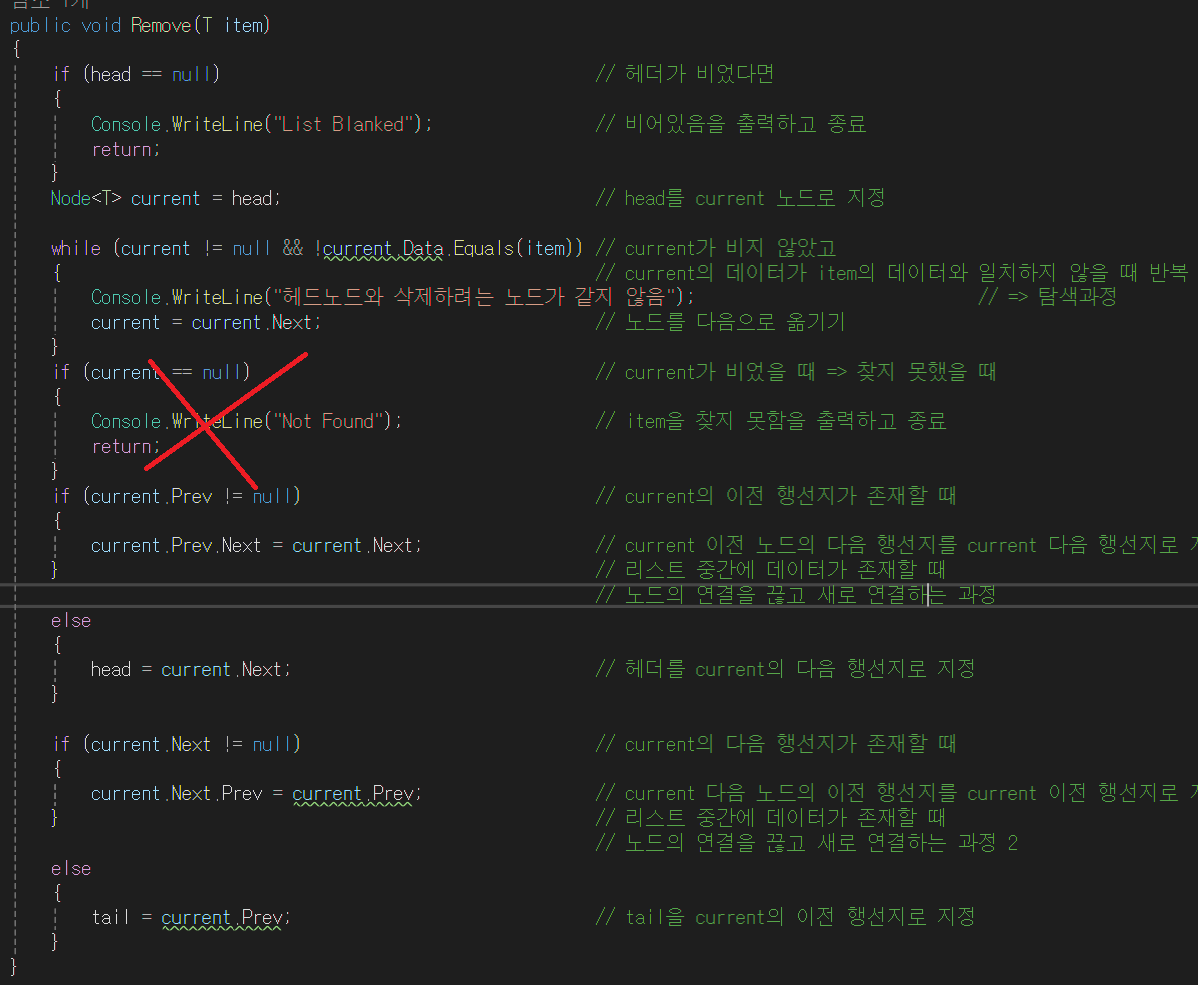
⭐⭐ 데이터를 삭제하기
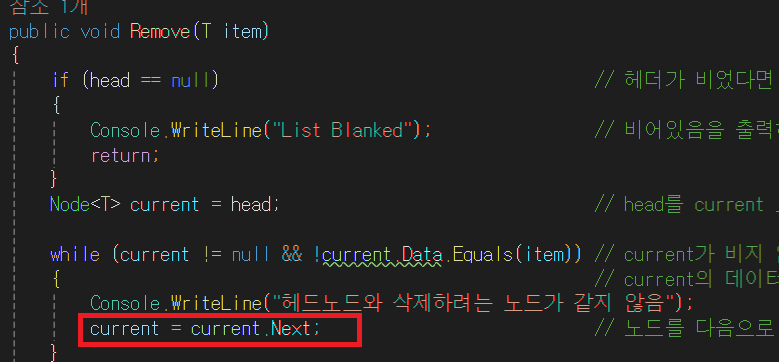
- 만약 head 노드가 존재하지 않다면 빈 리스트이므로, 삭제할 것이 없으므로 return한다
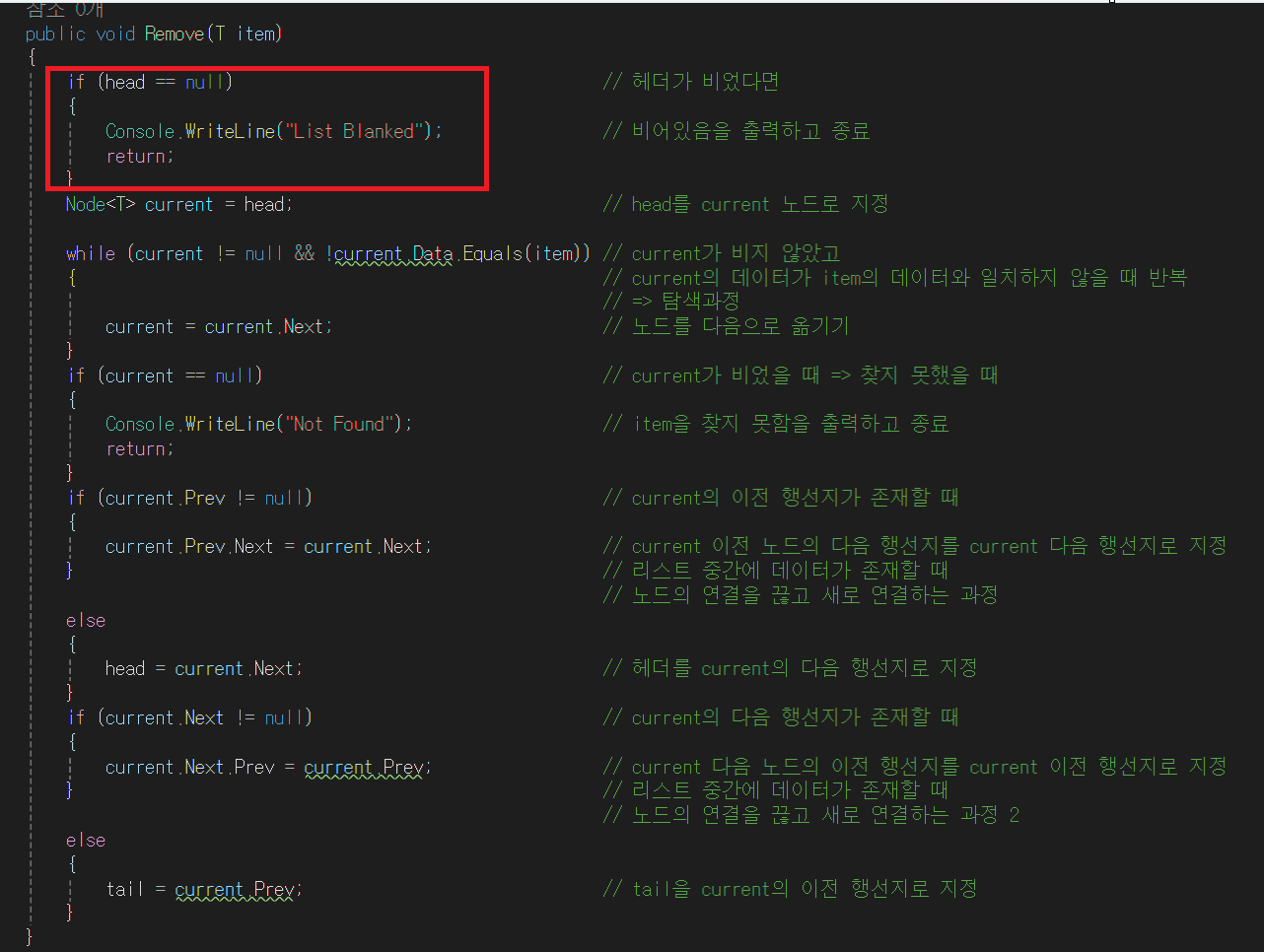
- 만약 head 노드가 존재하지 않다면 빈 리스트이므로, 삭제할 것이 없으므로 return한다
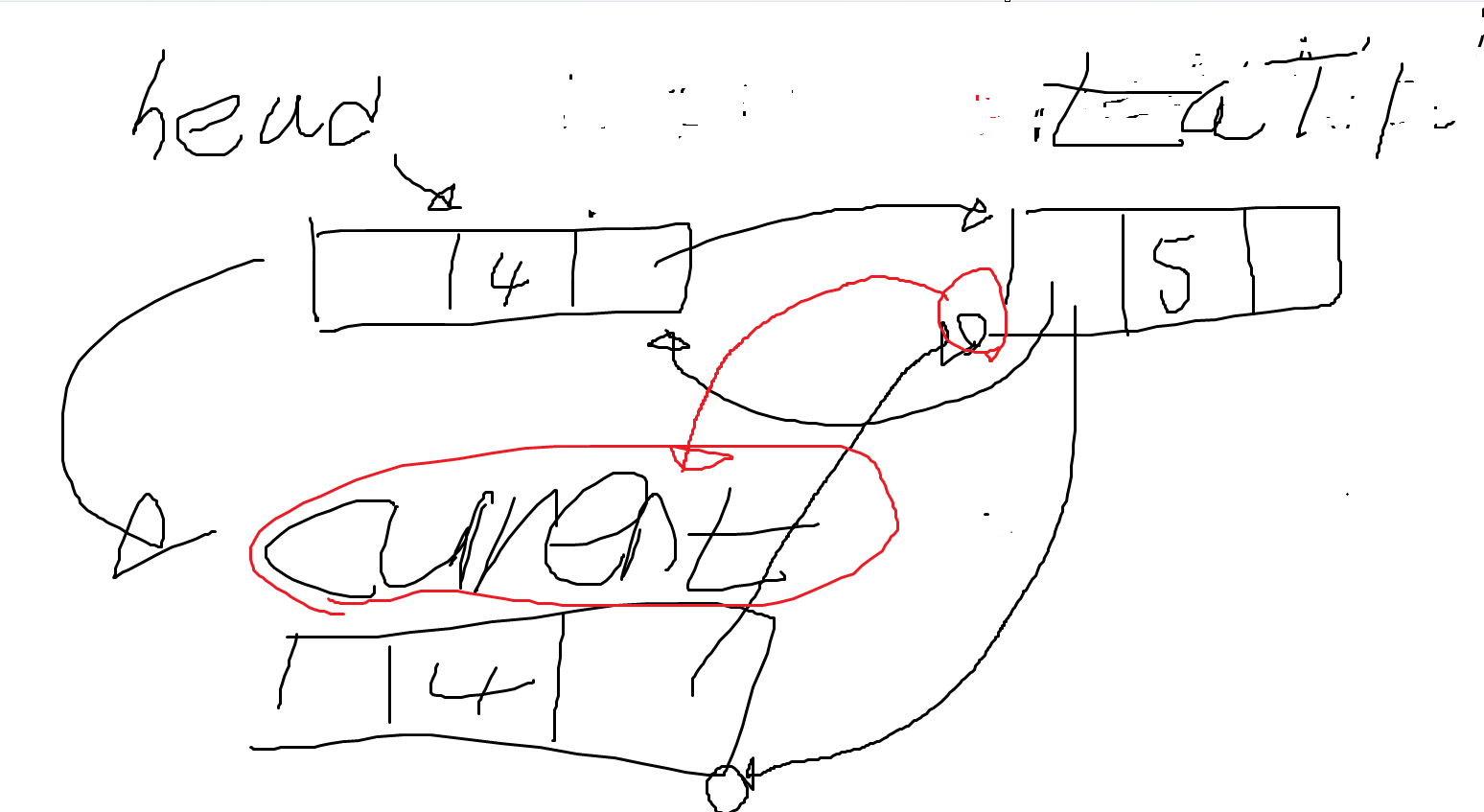
- head의 주소를 current 에게 넘긴다. 즉, current는 이전의 head 노드가 무엇을 가리키고 있었는지 알고 있다. current는 head의 주소를 알고 있다.
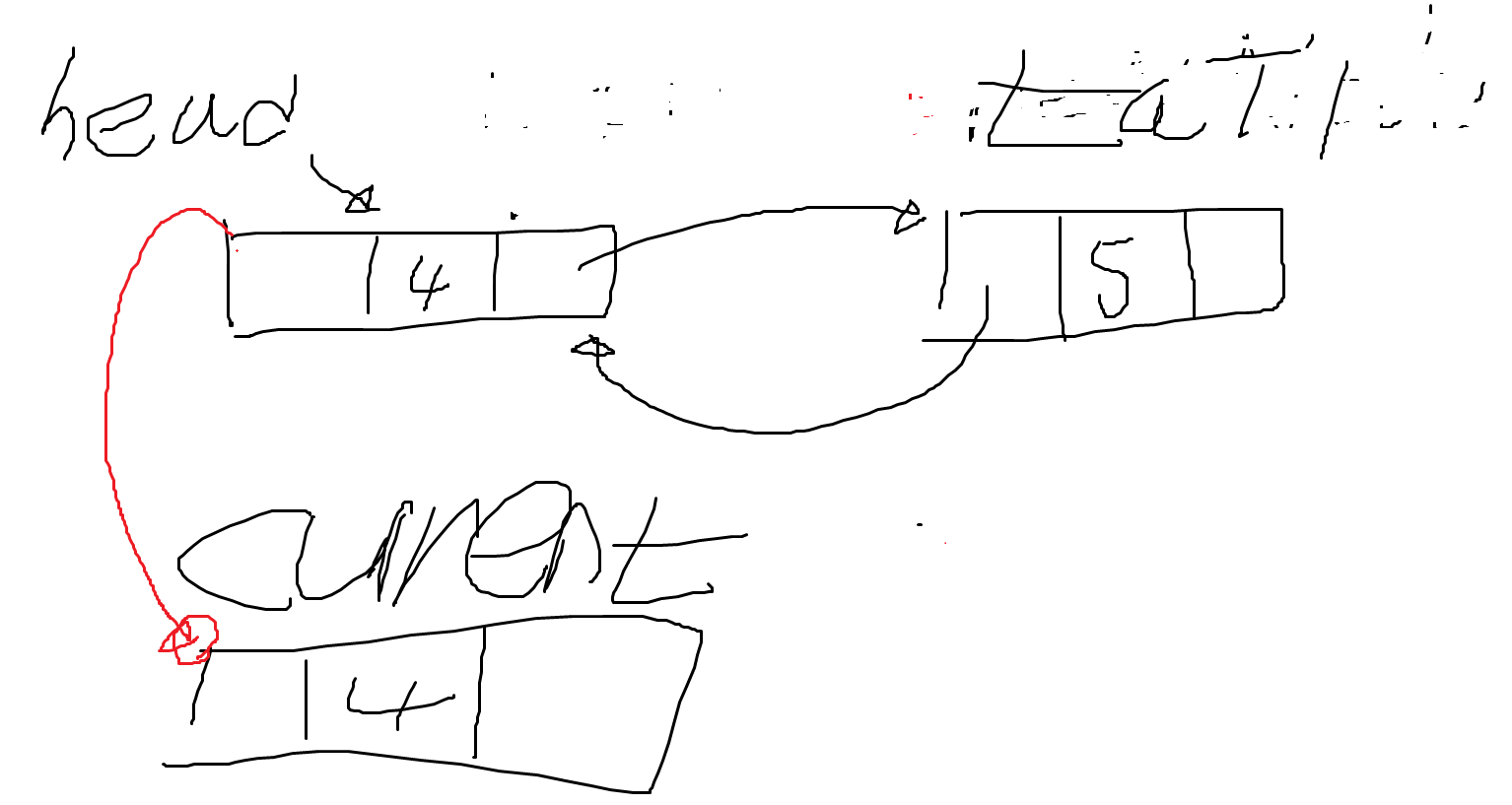
- head의 주소를 current 에게 넘긴다. 즉, current는 이전의 head 노드가 무엇을 가리키고 있었는지 알고 있다. current는 head의 주소를 알고 있다.
- while문의 조건이 true가 된다. 그 이유는 현재 current는 null이 아니며, 삭제하려는 것은 4 헤드 노드의 값은 4 값이 같으므로 while문의 조건은 true가 된다.
- while문의 조건이 true가 된다. 그 이유는 현재 current는 null이 아니며, 삭제하려는 것은 4 헤드 노드의 값은 4 값이 같으므로 while문의 조건은 true가 된다.
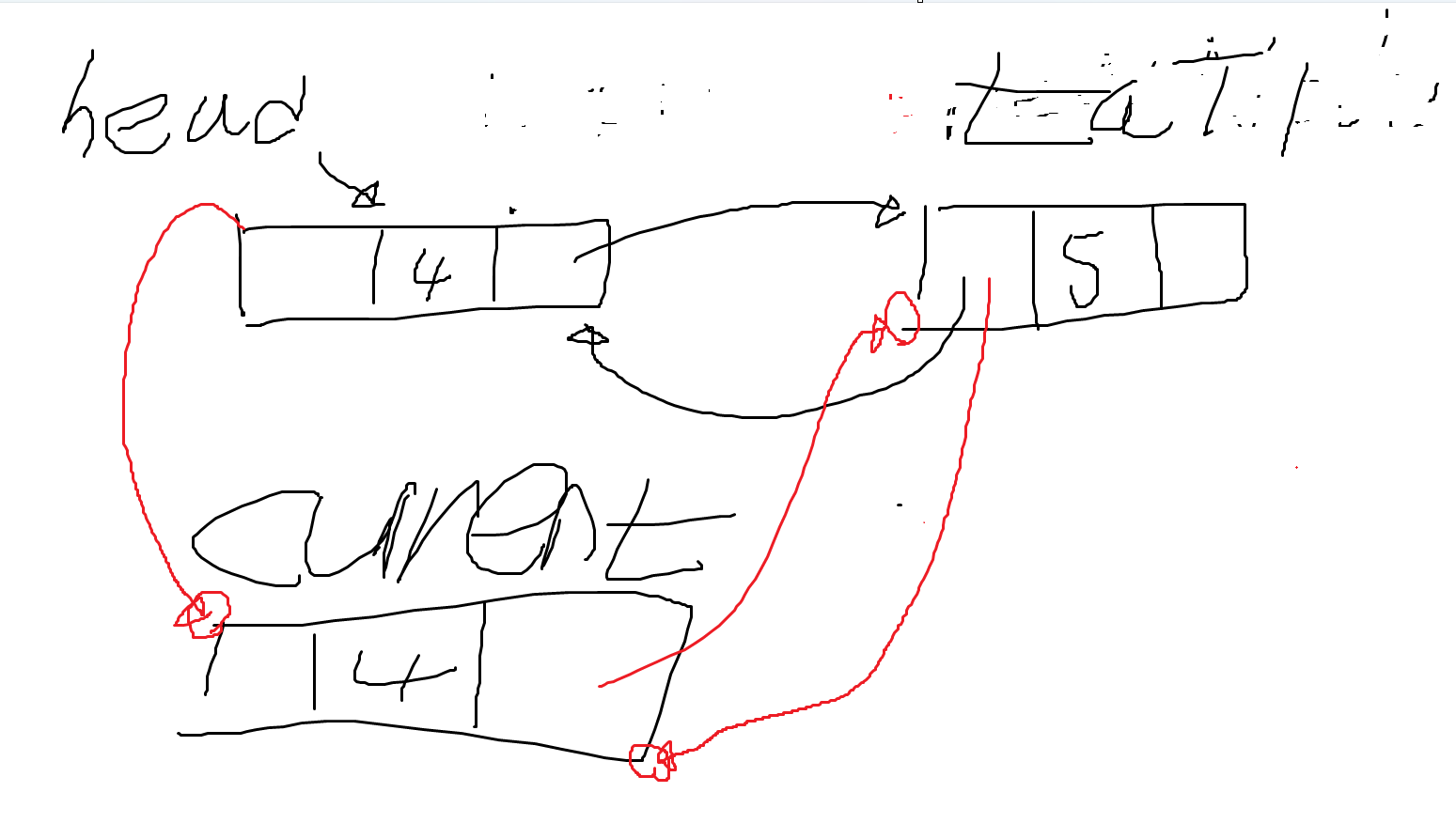
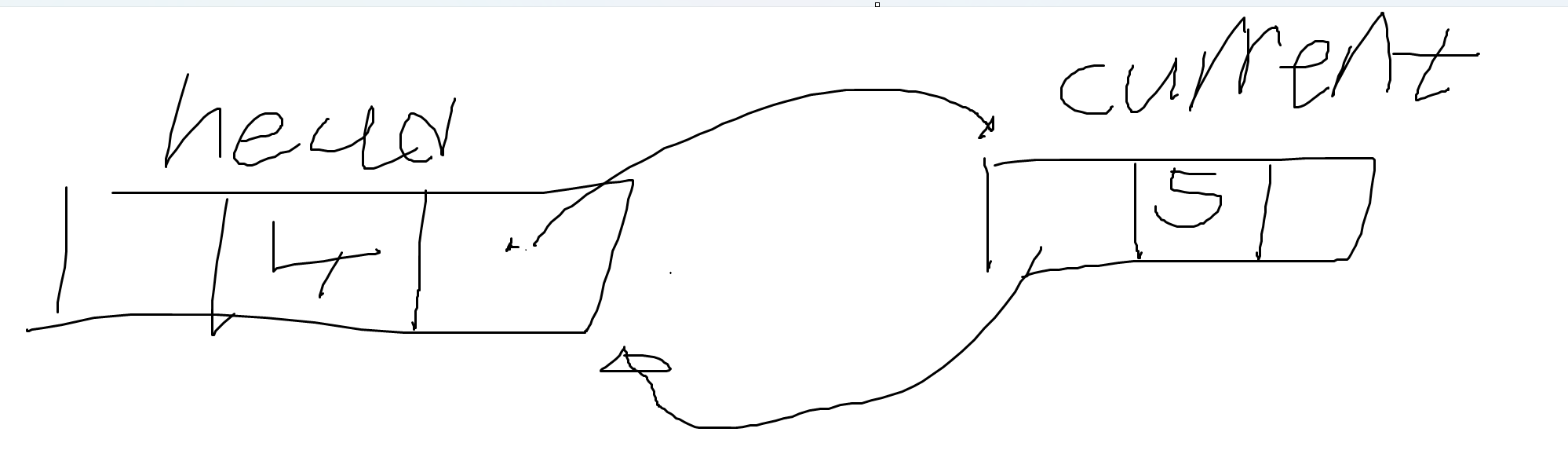
- current.Next는 tail을 현재 가리키고 있다.
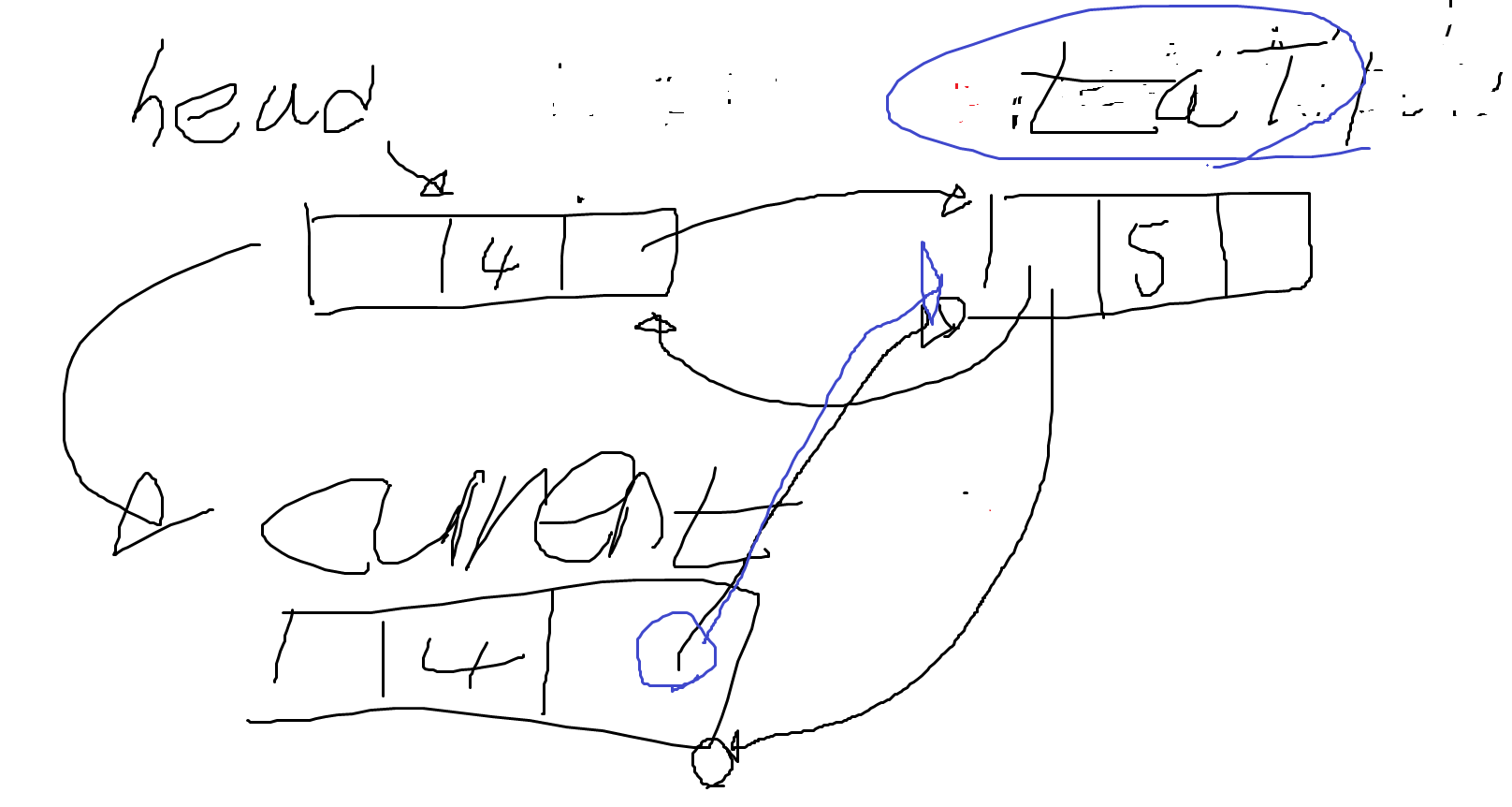
- current.Next는 tail을 현재 가리키고 있다.
- 즉, current.Next는 tail을 의미한다. current = tail; 로 해석이 가능하다. tail의 주소를 current로 넘긴다.
- 아래 그림처럼 될 것이다.
- 아래 if문은 거짓이 된다. 현재 current는 null이 아니다. null일 경우 return한다. while문의 조건이 거짓이면 current 는 null이므로 데이터가 존재하지 않는다는 말이다. (이전에 current = head; 과정이 있었다. head가 null이라는 것인데 head가 null이라면, 데이터가 존재하지 않는다는 뜻이다)
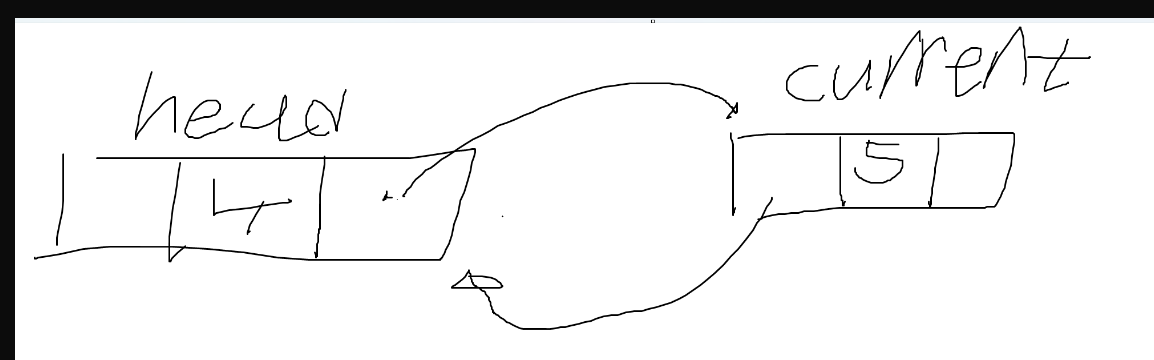
- 아래 if문은 거짓이 된다. 현재 current는 null이 아니다. null일 경우 return한다. while문의 조건이 거짓이면 current 는 null이므로 데이터가 존재하지 않는다는 말이다. (이전에 current = head; 과정이 있었다. head가 null이라는 것인데 head가 null이라면, 데이터가 존재하지 않는다는 뜻이다)
- 아래 if문은 참이 된다. current.Prev는 null이 아니다. head 노드를 가리키고 있다.
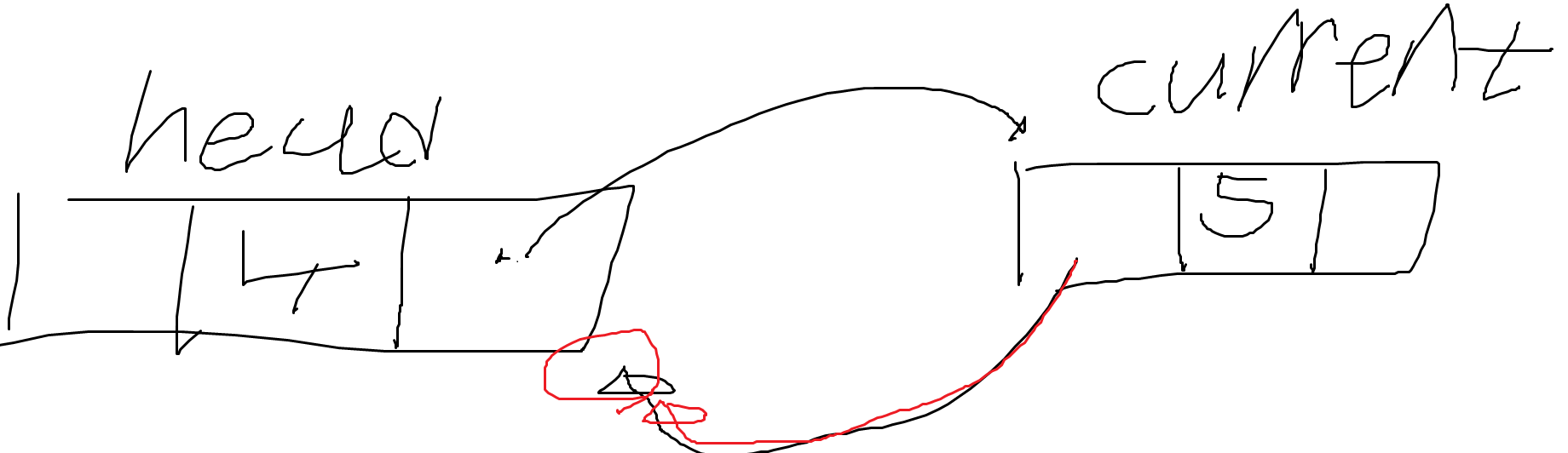
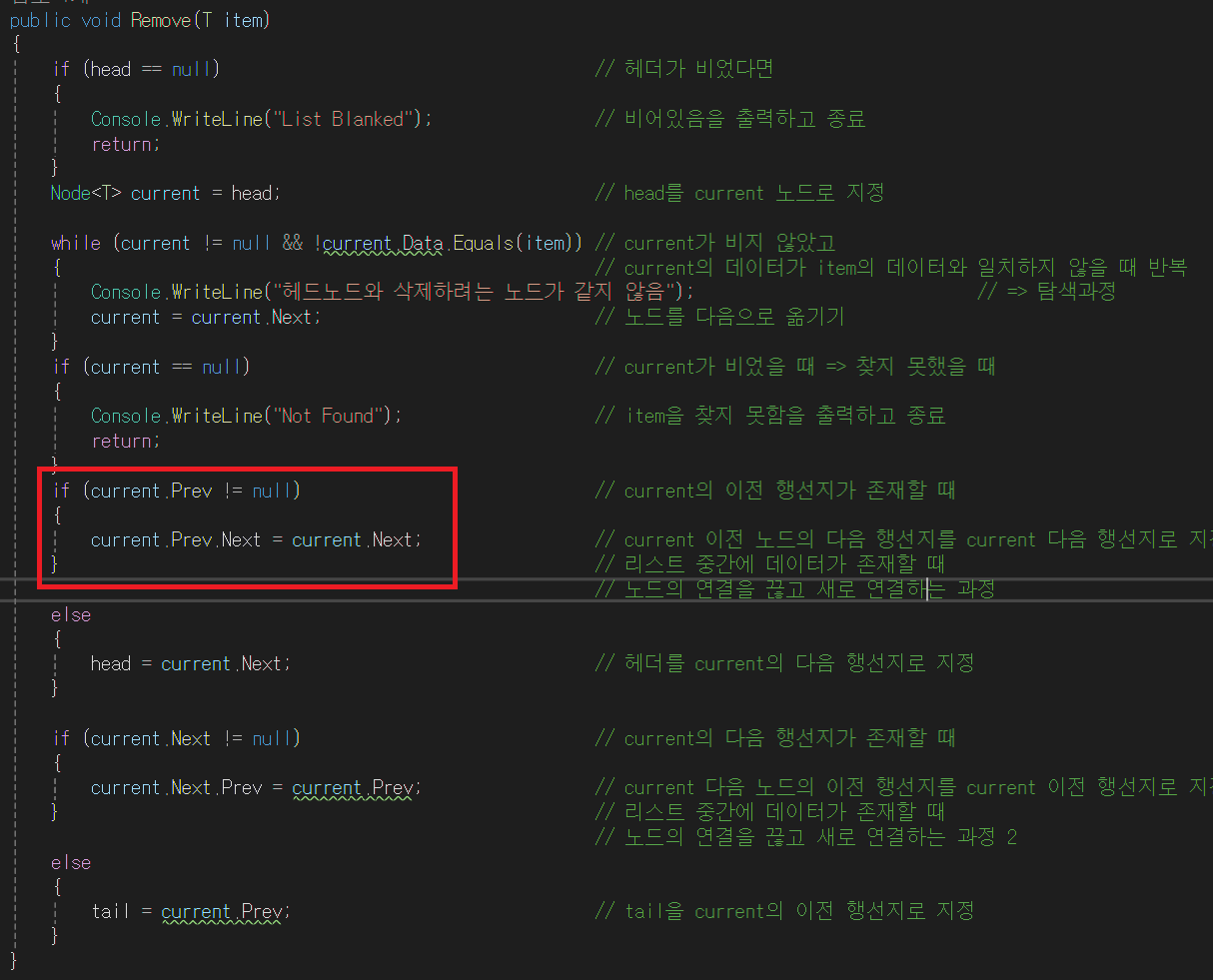

- 아래 if문은 참이 된다. current.Prev는 null이 아니다. head 노드를 가리키고 있다.
- current.Next는 현재 null인 상태이다. current.Prev.Next
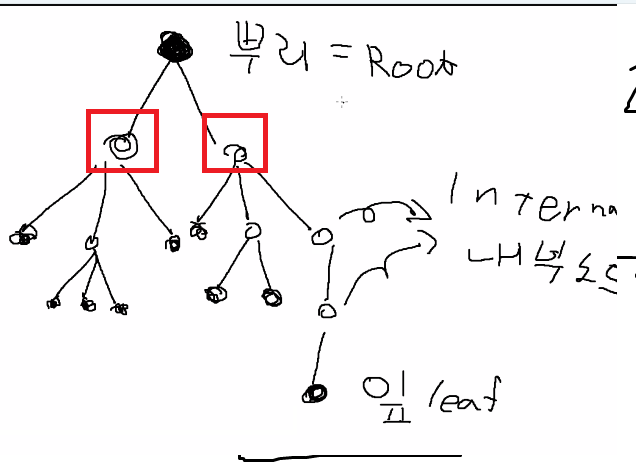
트리구조
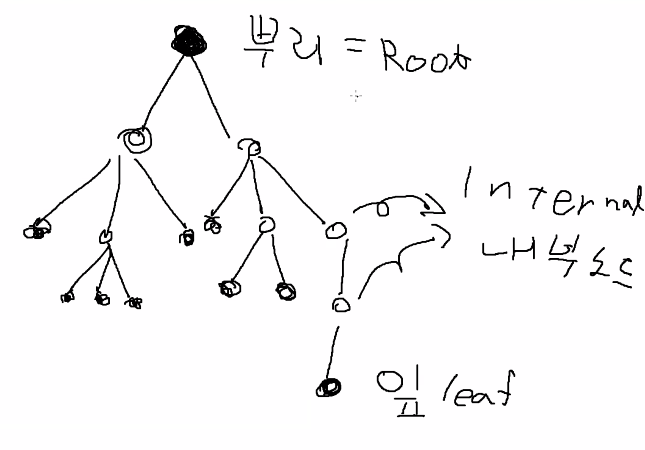
- 자식 중 세모가 없는 자식은 leaf이다.세모가 있는자식은 내부 노드이다.
- 부모가 없는 노드를 뿌리라고 한다. 자식을 가지는 노드를 내부노드이고, 자식을 가지지 않는다면 잎이다.
- 부모가 같다면, 해당 두 노드는 형제이다.
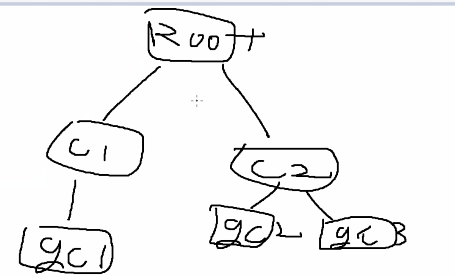
호출
using LionStudy_00;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
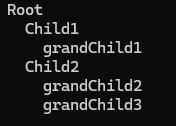
Tree<string> tree = new Tree<string>("Root");
TreeNode<string> child1 = tree.Root.AddChild(new TreeNode<string>("Child1"));
TreeNode<string> child2 = tree.Root.AddChild(new TreeNode<string>("Child2"));
child1.AddChild(new TreeNode<string>("grandChild1"));
child2.AddChild(new TreeNode<string>("grandChild2"));
child2.AddChild(new TreeNode<string>("grandChild3"));
}
} 로직
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace LionStudy_00
{
public class TreeNode<T>
{
//트리는 Data와 자식이 들어있다.
public T Data; //
public List<TreeNode<T>> Children; //자식
public TreeNode(T data)
{
Data = data;
Children = new List<TreeNode<T>>();
}
public TreeNode<T> AddChild(TreeNode<T> child)
{
Children.Add(child);
return child;
}
}
public class Tree<T>
{
public TreeNode<T> Root; //트리는 무조건 Root가 있어야함
public Tree(T rootData)
{
Root = new TreeNode<T>(rootData); //매개변수 rootData를 Root에 저장
}
}
}
- 위 코드로 인해 아래처럼 되었다.
정렬 알고리즘
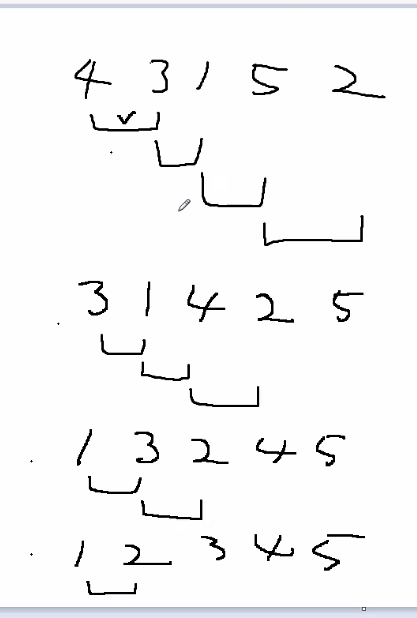
- 5개의 데이터가 있다. 4,3,1,5,2 가 있고, 큰 수가 뒤로 갈 수 있게끔 정렬한다.
- 4번 정렬 -> 3번 정렬 -> 2번 정렬 -> 1번 정렬 = 정렬 완료
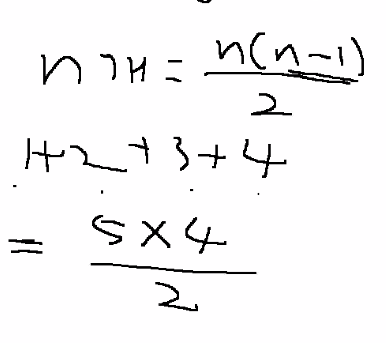
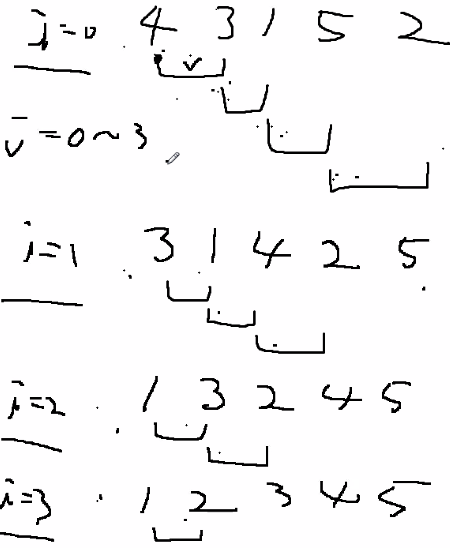
분할 정복
- 큰 문제를 작은 문제로 나누는 것