🤔 궁금점
Queue를 사용할 때 자주 사용하는 구현체로 ArrayDeque와 LinkedList를 사용하는데 언제 어떻게 사용하면 좋을까?
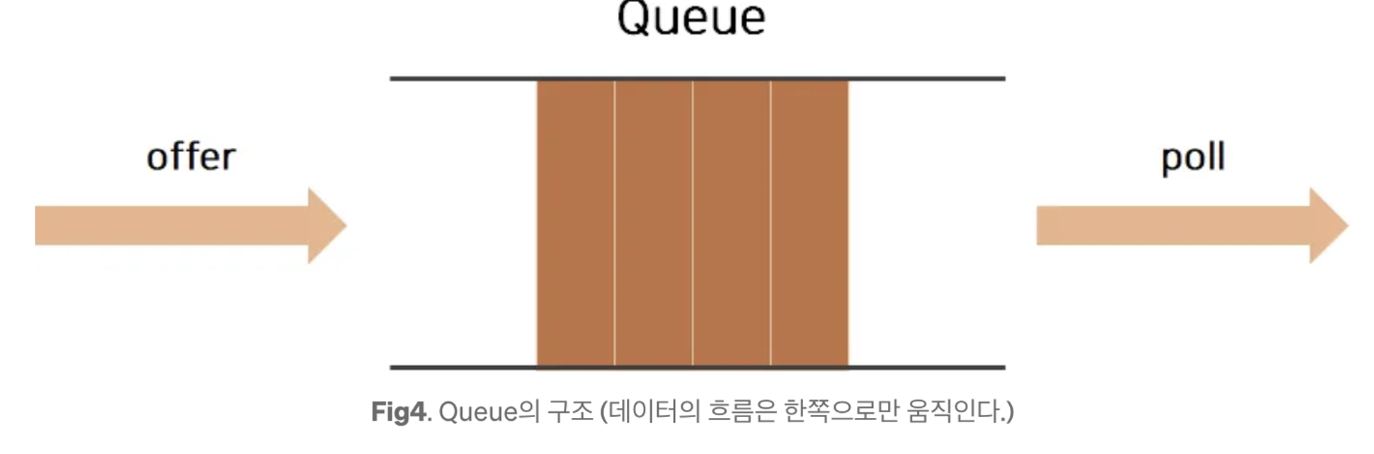
우선 Queue의 대표적인 특징은 선입선출 방식이에요.
Queue 대기열에 데이터를 추가하는 것을 Enqueue, 데이터를 꺼내는 것을 Dequeue라고 하지만, java에서는 추가는 두 메서드 add()와 offer() 존재하며 , 꺼내는 메서드는 poll() 메서드가 존재한다.
출처: https://medium.com/depayse/kotlin-data-structure-collections-4-stack-queue-deque-4c383efebee9
1️⃣ Array(Deque) 기반 Queue
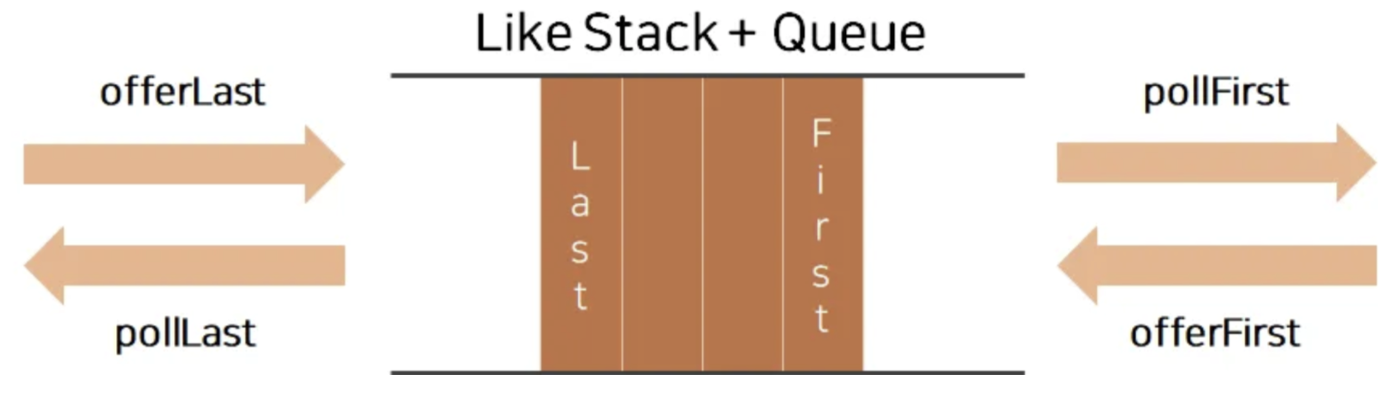
ArrayDeque는 Queue의 서브인터페이스인 Deque의 구현체이며, 배열의 특성을 가지고 있어요.
그리고 데이터 삽입 및 삭제가 큐의 앞, 뒤 모두에서 가능해요.
출처: https://medium.com/depayse/kotlin-data-structure-collections-4-stack-queue-deque-4c383efebee9
📕 메서드

☀︎ 특징
- Array(Deque)로 구현된 Queue는 고정된 크기의 배열을 사용하여 요소를 저장합니다.
- 큐의 앞(head)과 뒤(tail)를 가리키는 포인터를 사용하여 요소를 삽입 및 제거합니다.
- 크기가 제한되어 있는 배열을 활용하기 때문에 크기가 가득차면 크기를 조정해야 합니다. 이 때는 resize에 대한 비용이 듭니다.
- 요소의 추가 및 삭제가 빈번하게 발생하며, 크기의 확장 및 축소가 크게 문제되지 않는 경우에 적합합니다.
- null 참조가 불가합니다.
- Thread-safe하지 않습니다.
- 외부 동기화의 부제로, 다양한 쓰레드의 동시 접근을 지원하지 않습니다.
resize는 어떻게 진행될까?
우선 ArrayDeque를 기본생성자를 통해 생성하면 16개의 공간이 만들어져요.
public ArrayDeque() {
elements = new Object[16];
}그리고 값을 추가 할 때, 기존의 큐의 크기를 초과하게 되면 resize가 다음과 같은 순서로 이루어져요.
public void addFirst(E e) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
final Object[] es = elements;
es[head = dec(head, es.length)] = e;
if (head == tail)
grow(1); // resize 관련된 부분
}grow() 함수를 보면 다음과 같이 진행되고 있어요.
- 현재 큐의 길이를 구한 후
- 길이가 2^6 보다 작다면 기존의 길이의 + 2를 추가한 값을 기존의 길이에 더하고, 크다면 비트 시프트 연산을 통해 50% 크기를 증가시켜요.
ex) oldCapacity = 16 이면? newCapacity = 16 + (16 + 2) → 34
ex) oldCapacity = 64 이면? newCapacity = 64 + (64 / 2) → 100 - 기존 배열을 복사하여 새로운 배열을 이전에 계산했던 크기만큼 만들어요.
private void grow(int needed) {
// overflow-conscious code
final int oldCapacity = elements.length;
int newCapacity;
// Double capacity if small; else grow by 50%
int jump = (oldCapacity < 64) ? (oldCapacity + 2) : (oldCapacity >> 1);
// 여기서 newCapacity에 값 할당이 이루어집니다.
if (jump < needed
|| (newCapacity = (oldCapacity + jump)) - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = newCapacity(needed, jump);
final Object[] es = elements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, newCapacity);
// Exceptionally, here tail == head needs to be disambiguated
if (tail < head || (tail == head && es[head] != null)) {
// wrap around; slide first leg forward to end of array
int newSpace = newCapacity - oldCapacity;
System.arraycopy(es, head,
es, head + newSpace,
oldCapacity - head);
for (int i = head, to = (head += newSpace); i < to; i++)
es[i] = null;
}
}
// newCapacity를 다시 계산하는 이유는 배열 크기가 MAX_ARRAY_SIZE를 초과할 수 없기 때문입니다.
private int newCapacity(int needed, int jump) {
final int oldCapacity = elements.length, minCapacity;
if ((minCapacity = oldCapacity + needed) - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) {
if (minCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException("Sorry, deque too big");
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
if (needed > jump)
return minCapacity;
return (oldCapacity + jump - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE < 0)
? oldCapacity + jump
: MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}2️⃣ Linked-list(기반) Queue
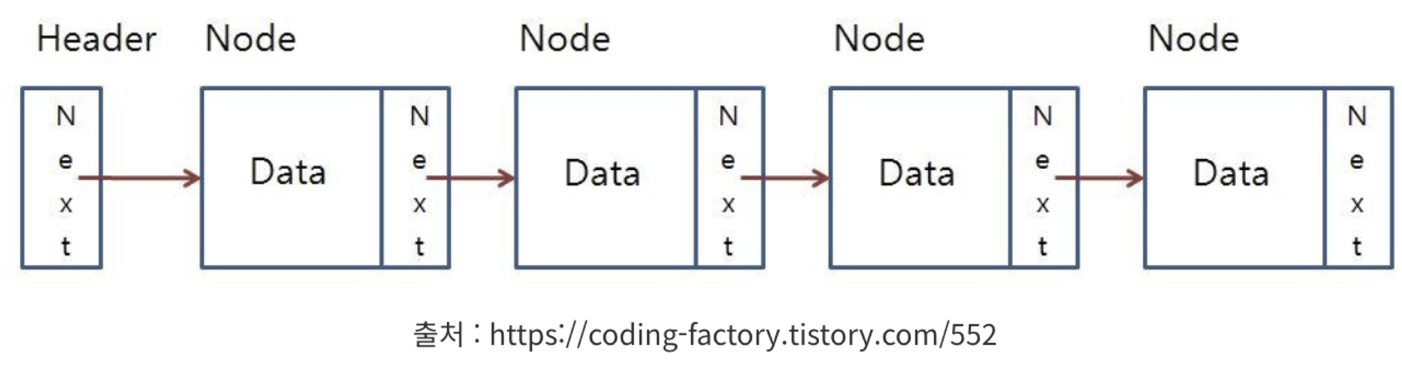
LinkedList는 List와 Queue의 구현체에요. 따라서 LinkedList는 List의 특징을 가지고 있고, 다음 그림을 통해 자신의 노드와 다음 데이터를 참조하는 데이터를 갖고 있어요.
📕 메서드

☀︎ 특징
- Linked-list로 구현된 Queue는 각 요소를 노드로 표현하고, 노드들을 연결하여 큐를 구성합니다.
- 요소의 추가는 큐의 맨 뒤(tail)에 노드를 추가하고, 요소의 삭제는 큐의 맨 앞(front)에서 노드를 제거하는 방식으로 동작합니다.
- 크기의 확장이나 축소가 필요하지 않으며, 크기 제한이 없다는 장점이 있습니다.
- 하지만 포인터로 노드를 연결하므로 메모리 오버헤드가 발생할 수 있고, 개별적인 메모리 할당으로 인해 메모리 관리에 대한 오버헤드가 발생할 수도 있습니다.
- null 참조가 가능합니다.
테스트
테스트 하고 있는 환경은 다음과 같아요.
- M1 Air, RAM 16GB
- java 17
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayDeque<Event> arrayDeque = new ArrayDeque<>();
int size = 변경되는 크기 부분
long dequeStart = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
arrayDeque.offer(new Event("test", i));
}
long dequeEnd = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.printf("Array Deque Times: %dms\n", dequeEnd - dequeStart);
Queue<Event> linkedListQue = new LinkedList<>();
long linkedListStart = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
linkedListQue.offer(new Event("test", i));
}
long linkedListEnd = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.printf("LinkedList Que Times: %dms\n", linkedListEnd - linkedListStart);
}데이터를 추가하는 상황만 테스트 해보았어요. Deque resize를 자주 하기 때문에 성능이 더 안좋을 것이라고 생각했는데, 300,000 번 부터는 Deque가 성능이 더 좋았어요.
Deque에 값을 넣을 때는 단순히 값을 넣지만, LinkedList Que는 새로운 노드 추가 뿐만 아니라다음 노드에 대한 메모리도 참조해야 하기에 더 많은 연산이 필요해서 그런 것 같아요.
- 100,000번 데이터 추가
- Array Deque Times: 14ms
- LinkedList Que Times: 5ms
- 300,000번 데이터 추가
- Array Deque Times: 22ms
- LinkedList Que Times: 58ms
- 1,000,000번 데이터 추가
- Array Deque Times: 75ms
- LinkedList Que Times: 130ms
- 10,000,000번 데이터 추가
- Array Deque Times: 385ms
- LinkedList Que Times: 1565ms
다음은 추가와 삭제가 빈번한 상황을 테스트하려고 해요. 이전 테스트와 큰 차이가 없네요.
- 100,000번 데이터 추가와 50,000번 데이터 삭제
- Array Deque Times: 15ms
- LinkedList Que Times: 6ms
- 300,000번 데이터 추가와 150,000번 데이터 삭제
- Array Deque Times: 26ms
- LinkedList Que Times: 53ms
- 1,000,000번 데이터 추가와 500,000번 데이터 삭제
- Array Deque Times: 69ms
- LinkedList Que Times: 135ms
- 10,000,000번 데이터 추가와 5,000,000번 데이터 삭제
- Array Deque Times: 384ms
- LinkedList Que Times: 1441ms
정리
자바 공식문서에 다음과 같이 설명이 되어 있어요.
This class is likely to be faster than
Stackwhen used as a stack, and faster thanLinkedListwhen used as a queue.
위의 공식문서를 토대로 다음과 같은 결론을 내렸어요.
- ArrayDeque는 Array에 의해 지원되고 Array는 LinkList보다
cache locality-friendly하다.- 메모리에서 데이터를 읽고 쓸 때 캐시의 효과를 최대한 누릴 수 있도록 설계되었다.
- 많은 데이터가 삽입, 삭제가 빈번하게 발생할 때에도 ArrayDeque가 LinkedList보다 성능적으로도 메모리적으로도 효율적이다.
정리하다보니 다음과 같은 생각도 하게 되었어요.
ArrayList vs ArrayDeque vs LinkedList: which one is best?
- 인덱스로 데이터에 접근하고 끝에 삽입, 삭제만 할 경우에는 ArrayList를 사용하자.
- stack, queue 혹은 deque로 사용한다면 ArrayDeque를 사용하자.
- 리스트를 순회할때 삽입, 삭제 빈번하다면 LinkedList를 사용하자.
