그래프란?
그래프는 정점과 그 정점을 연결하는 간선으로 구성된 한정된 자료구조를 의미
정점(Vertex)과 간선(Edge)

- 각 노드들이 각각의 정점이다
- 이 정점들을 연결하는 선(변)들이 간선이다
방향 그래프와 무방향 그래프
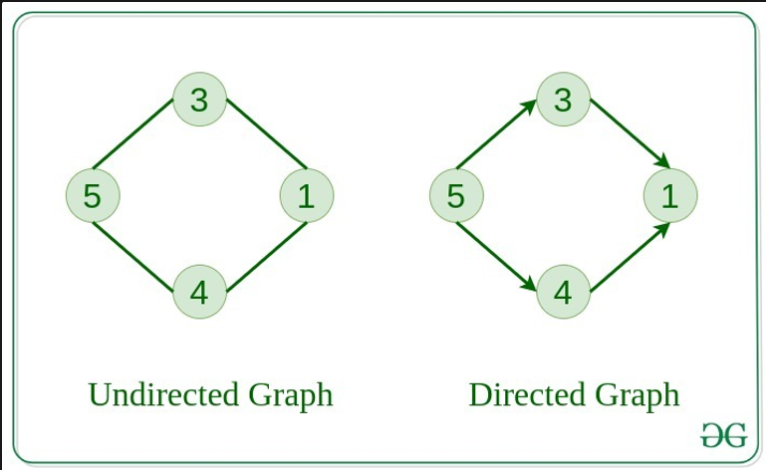
- 무방향 그래프 - 간선에 방향이 없는 그래프, 간선을 정의할 때 정점 간에 순서가 존재하지 않는다
- 방향 그래프 - 간선에 방향이 존재하는 그래프, 간선을 정의할 때 정점 간에 순서가 존재
그래프의 표현
주어진 input이 아래와 같을 때
// 정점, 간선의 수
3 3
// 간선의 관계
1 2
1 0
2 0
인접 행렬로 무방향 그래프 표현
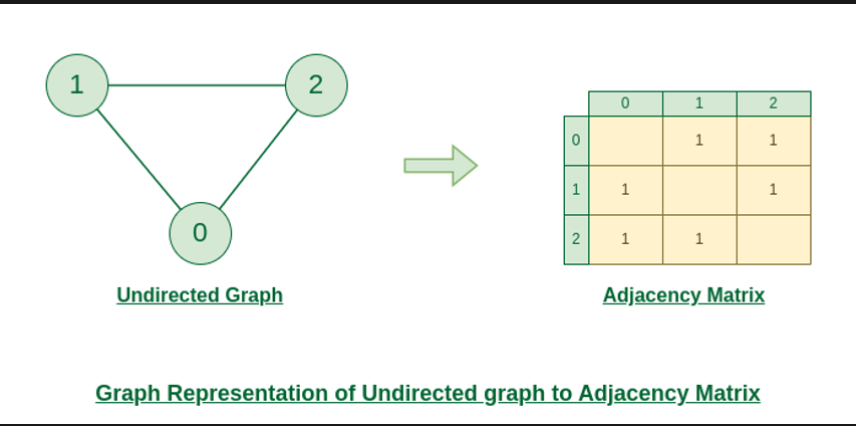
public static void undirectedGraphUsingAdjacencyMatrix() {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = s.nextInt(); // 정점 개수
int M = s.nextInt(); // 간선 개수
int[][] matrix = new int[N+1][N+1];
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int v1 = s.nextInt();
int v2 = s.nextInt();
matrix[v1][v2] = 1;
matrix[v2][v1] = 1;
}
printGraphByMatrix(matrix);
}인접 리스트로 무방향 그래프 표현
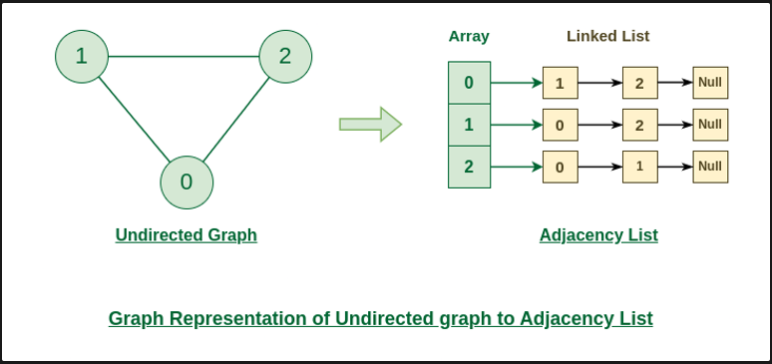
public static void undirectedGraphUsingAdjacencyList() {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = s.nextInt(); // 정점 개수
int M = s.nextInt(); // 간선 개수
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> nodeList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++) {
nodeList.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int v1 = s.nextInt();
int v2 = s.nextInt();
nodeList.get(v1).add(v2);
nodeList.get(v2).add(v1);
}
printGraphByList(nodeList);
}인접 행렬로 방향 그래프 표현
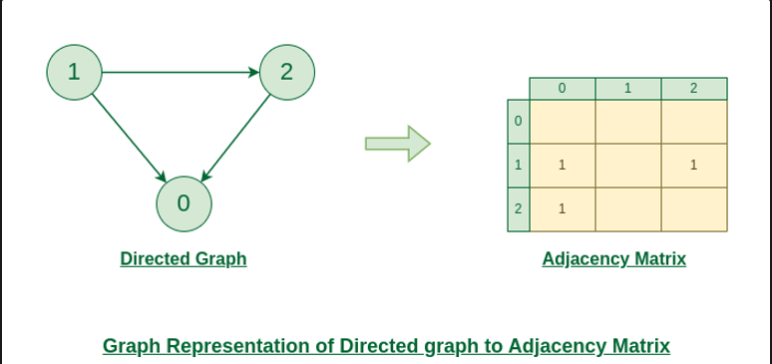
public static void directedGraphUsingAdjacencyMatrix() {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = s.nextInt(); // 정점 개수
int M = s.nextInt(); // 간선 개수
int[][] matrix = new int[N+1][N+1];
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int from = s.nextInt();
int to = s.nextInt();
matrix[from][to] = 1;
}
printGraphByMatrix(matrix);
}인접 리스트로 방향 그래프 표현
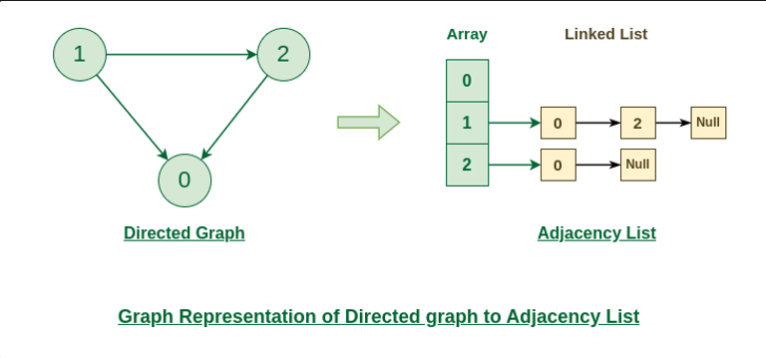
public static void directedGraphUsingAdjacencyList() {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = s.nextInt(); // 정점 개수
int M = s.nextInt(); // 간선 개수
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> nodeList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++) {
nodeList.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int from = s.nextInt();
int to = s.nextInt();
nodeList.get(from).add(to);
}
printGraphByList(nodeList);
}출력
public static void printGraphByMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
for (int[] row : matrix) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(row));
}
}
public static void printGraphByList(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> list) {
for (int from=0; from<list.size(); from++) {
System.out.print("정점 " + from + "의 인접리스트: ");
for (int to=0; to<list.get(from).size(); to++) {
System.out.print(" " + list.get(from).get(to));
}
System.out.println();
}
}