타입스크립트란?
타입스크립트는 자바스크립트에 타입을 부여한 언어이다.
자바스크립트에서 확장된 언어이다.
- TypeScript는 MS에 의해 개발/관리되고 있는 오픈소스 프로그래밍 언어이다.
- 대규모 애플리케이션을 개발하는 데 자바스크립트가 어렵고 불편하다는 불만에 대응하기 위해 개발되었다.
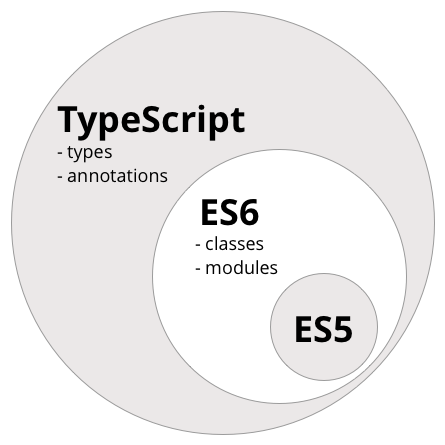
- TypeScript는 ES5의 Superset이므로 기존의 자바스크립트(ES5) 문법을 그대로 사용할 수 있습니다.
- ES6의 새로운 기능들을 사용하기 위해 Babel과 같은 별도 트랜스파일러(Transpiler)를 사용하지 않아도 ES6의 새로운 기능을 기존의 자바스크립트 엔진(현재의 브라우저 또는 Node.js)에서 실행할 수 있습니다.
타입 선언 방법
Type Annotation
TypeScript에서는 변수를 만들어 값을 할당하면 처음 할당된 값의 형식에 따라 그 변수의 형식이 지정되게 된다. 이를 Type Annotation이라고 한다.
- 변수명, 함수명, 객체 속성명 뒤에 : type 을 써서 데이터 타입을 지정한다. (:을 기준으로 왼쪽은 value 오른쪽은 type)
- TypeScript는 JavaScript의 primitive type(number, string, boolean)을 사용 가능하다.
- Type annotation을 사용하여 type 검사를 수행한다.
원시타입
- 불변하면서 객체가 아닌 값을 말한다.
- javascript에서는 타입 추론이 가능하기 때문에 타입 추론을 하는게 좋다.
<종류>
- String
- Number
- Boolean
- BigInt
- Undefined
- Null
- Symbol
<예시>
const str: string = 'STRING'
const num: number = 123
const bool: boolean = true
const big: bigint = 100n객체타입
<잘못된예시>
const obj: object = {
str: 'str',
num: 123,
child: {
str: 'str',
num: 123,
}
}- 타입선언을 object 하나만 선언하는 것은 any와 다른게 없다.
- any는 '어떤 타입이든'이라는 의미로 타입을 엄격하게 검사하고 처리하는 ts에서 any는 치명적인 존재이다.
<좋은 예시>
const obj2: {
str: string,
num: number,
child: {
str: string,
num: number,
}} = {
str: 'str',
num: 123,
child: {
str: 'str',
num: 123,
}
}
console.log(obj2.str)
함수타입
- 매개변수를 받는 부분과 반환 부분 모두 타입을 선언해줘야 한다.
- 반환타입은 타입추론이 잘 되는 편이기에 생략이 가능하다.
/**
* Function Type
*
* //매개변수를 받고 리턴을 하게된다 두가지타입이 필요하다 그래서 타입을 2개 지정해야한다.
*
*
* 1. 매개변수
* 2. 반환
* void는 반환하지 않는다라는 뜻
*/
function func(num: number, str: string): string {
return num + str
}
func(123, 'str')
function func2(num1: number, num2: string) {
return num1 + Number(num2)
}
//반환 타입은 타입추론이 잘되는 편이다
func2(123, '123')
function func3(num1: number, num2: string): void {
console.log(num1 + num2)
}
func3(123, '123')
const func4 = (str1: string, str2: string) => {
return str1 + ' ' + str2
}
//반환 타입은 타입추론이 잘되는 편이다
func4('hello', 'world')
const func5 = (obj: {str1: string, str2: string}) => {
return obj.str1 + ' ' + obj.str2
}
func5({str1: 'hello', str2:'world'})
배열타입
<예시>
const strArr: string[] = ['str', 'str2', 'str3'];
const strArr2: Array<string> = ['str', 'str2', 'str3'];
const numArr: Array<number> = [1, 2, 3];
const boolArr: boolean[] = [false, true, false, true];
strArr.push(1) // error : string으로 넣어야한다.
numArr.push('str') // error : number로 넣어야한다.
boolArr.push(false)- 튜플 타입 사용
const arr = ['str', 123, false];리터럴 타입
- let으로 변수를 선언할 경우 이 변수의 값이 변경될 가능성이 있다.
- const로 변수를 선언하게 되면 TypeScript에게 이 객체는 절대 변경되지 않음을 알린다.
/**
* Literal Type
*/
let letString = 'Hello'
letString = letString + ' World'
console.log(letString)
const constString = 'Hello'
constString
let letNumber = 123
letNumber = letNumber + 123
console.log(letNumber)
const constNumber = 123
constNumber튜플 타입
/**
* Tuple Type
*
* - 길이 고정 & 인덱스 타입이 고정
* - 여러 다른 타입으로 이루어진 배열을 안전하게 관리
* - 배열 타입의 길이 조절
*/
const arr: string[] = ['A', 'B', 'C']
const tuple: [number, string] = [1, 'A']
const tuple0: (string | number)[] = [1, 'A']
const tuple2: [number, ...string[]] = [0, 'A', 'B']
undefined & null
/**
* undefined & null
*
* JavaScript에서와 마찬가지로
* 고유의 특별한 타입으로 인정한다.
*
* 이외에 void, never와 같이 더 세밀한 타입도 제공
*
* strictNullChecks가 핵심
*/
const nu: null = null;
const un: undefined = undefined;
function sayHello(word: string) {
if (word === 'world') {
return 'hello' + word
}
return null
}
function log(message: string | number) {
console.log(message)
}
any
- TypeScript는 any 타입에 대해 엄격하게 검사 또는 체크하지 않기 때문에 개발자의 입장에서는 문제가 없는 코드라고 판단할 수 있지만, 실제로 애플리케이션을 개발하거나 프론트엔드를 개발하면 any 타입 때문에 문제가 발생하는 경우가 종종 있다.
/**
* any
*
* 모든 값(타입)의 집합
* 사용하지 말자
*
* noImplicitAny or strict 옵션 true 권장
*/
function func(anyParam) {
anyParam.trim()
}
func([1,2,3])
unknown
/**
* unknown
*
* 새로운 최상위 타입
* any처럼 모든 값을 허용하지만 상대적으로 엄격하다.
* TS에서 unknown으로 추론하는 경우는 없으니 개발자가 직접 명시해야함
* assertion 혹은 타입 가드와 함께 사용한다.
*/
let num: unknown = 99;
if (typeof num === 'string') {
num.trim();
}
// (num as string).trim();
// function func(x: unknown) {
// let val1: any = x;
// let val2: unknown = x;
// let val3: string = x;
// let val4: boolean = x;
// let val5: number = x;
// let val6: string[] = x;
// let val7: {} = x;
// }void
- void는 자바스크립트에는 없는 키워드로써, 함수에 '이 함수는 아무것도 반환하지 않는다.'라는 의미를 부여한다. 즉, 아무것도 반환하지 않는 함수에 사용하는 타입이다.
