[Java] OOp
오브젝트를 생성하는 방법들
- New
- newInstance()
- clone()
- deserialization (역직열화)
- factory method
Anonymous object
- 참조가 없는 객체를 익명 객체
- 오브젝트를 한번 사용할때 익명오브젝트가 좋은 접근이다.
class Calculation{
void fact(int n){
int fact=1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
fact=fact*i;
}
System.out.println("factorial is "+fact);
}
public static void main(String args[]){
new Calculation().fact(5);//calling method with anonymous object
}
} Copy Constructor
- 생성자
- 한 객체의 값을 다른 객체에 할당함으로써
- clone() 메서드를 사용하여
- 생성자는 현재 클레스 인스턴스를 리턴한다
Static
-
The static keyword in Java is used for memory management mainly. We can apply static keyword with variables, methods, blocks and nested classes.
-
Advantages of static variable
It makes your program memory efficient (i.e., it saves memory). -
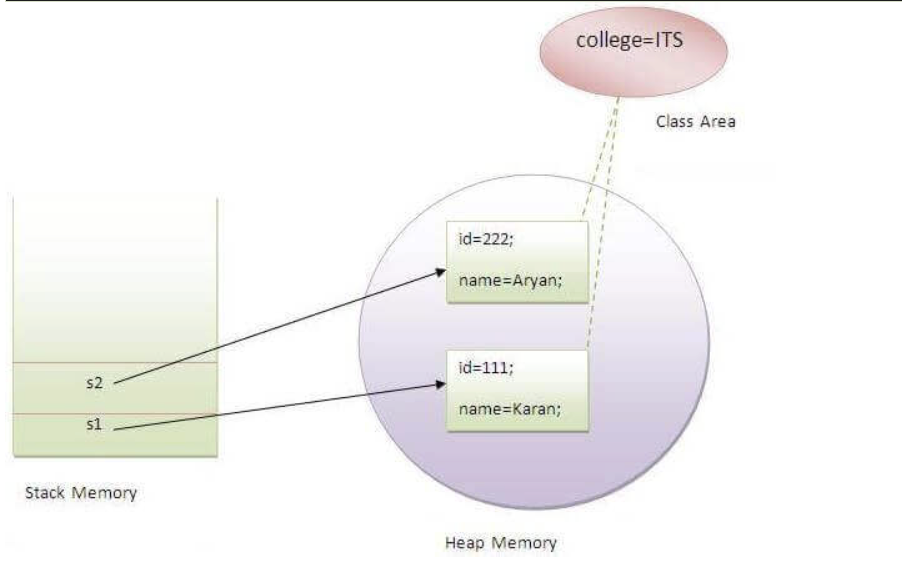
Java static property is shared to all objects.
//Java Program to demonstrate the use of static variable
class Student{
int rollno;//instance variable
String name;
static String college ="ITS";//static variable
//constructor
Student(int r, String n){
rollno = r;
name = n;
}
//method to display the values
void display (){System.out.println(rollno+" "+name+" "+college);}
}
//Test class to show the values of objects
public class TestStaticVariable1{
public static void main(String args[]){
Student s1 = new Student(111,"Karan");
Student s2 = new Student(222,"Aryan");
//we can change the college of all objects by the single line of code
//Student.college="BBDIT";
s1.display();
s2.display();
}
} -> 111 Karan ITS
111 Karan ITS
-
A static method can access static data member and can change the value of it.
-
There are two main restrictions for the static method. They are:
The static method can not use non static data member or call non-static method directly.
this and super cannot be used in static context.
- Java static block
Is used to initialize the static data member.
It is executed before the main method at the time of classloading.
class A2{
static{System.out.println("static block is invoked");}
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println("Hello main");
}
} Output : static block is invoked
Hello main
This
-
this is a reference variable that refers to the current object.
-
If there is ambiguity between the instance variables and parameters, this keyword resolves the problem of ambiguity.
-
this() : to invoke current class constructor
class Student{
int rollno;
String name,course;
float fee;
Student(int rollno,String name,String course){
this.rollno=rollno;
this.name=name;
this.course=course;
}
Student(int rollno,String name,String course,float fee){
this(rollno,name,course);//reusing constructor
this.fee=fee;
}
void display(){System.out.println(rollno+" "+name+" "+course+" "+fee);}
}
class TestThis7{
public static void main(String args[]){
Student s1=new Student(111,"ankit","java");
Student s2=new Student(112,"sumit","java",6000f);
s1.display();
s2.display();
}} 111 ankit java 0.0
112 sumit java 6000.0
-
Rule: Call to this() must be the first statement in constructor.
-
4) this: to pass as an argument in the method
class S2{
void m(S2 obj){
System.out.println("method is invoked");
}
void p(){
m(this);
}
public static void main(String args[]){
S2 s1 = new S2();
s1.p();
}
} method is invoked
-
Application of this that can be passed as an argument:
In event handling (or) in a situation where we have to provide reference of a class to another one. It is used to reuse one object in many methods. -
5) this: to pass as argument in the constructor call
We can pass the this keyword in the constructor also. It is useful if we have to use one object in multiple classes. Let's see the example:
class B{
A4 obj;
B(A4 obj){
this.obj=obj;
}
void display(){
System.out.println(obj.data);//using data member of A4 class
}
}
class A4{
int data=10;
A4(){
B b=new B(this);
b.display();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
A4 a=new A4();
}
} 10
- 6) this keyword can be used to return current class instance
We can return this keyword as an statement from the method. In such case, return type of the method must be the class type (non-primitive). Let's see the example:
class A{
A getA(){
return this;
}
void msg(){System.out.println("Hello java");}
}
class Test1{
public static void main(String args[]){
new A().getA().msg();
}
}Hello java
Inheritance
- Inheritance represents the IS-A relationship which is also known as a parent-child relationship.
-Class: A class is a group of objects which have common properties. It is a template or blueprint from which objects are created
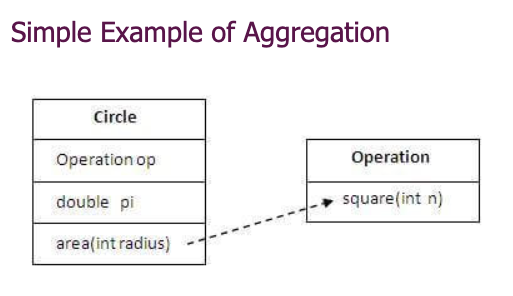
Aggregation
- If a class have an entity reference, it is known as Aggregation. Aggregation represents HAS-A relationship.
class Employee{
int id;
String name;
Address address;//Address is a class
...
} 
- When use Aggregation?
Code reuse is also best achieved by aggregation when there is no is-a relationship.
Inheritance should be used only if the relationship is-a is maintained throughout the lifetime of the objects involved; otherwise, aggregation is the best choice.e
Method Overriding
-
Rules for Java Method Overriding
The method must have the same name as in the parent class
The method must have the same parameter as in the parent class.
There must be an IS-A relationship (inheritance). -
Can we override static method?
No, a static method cannot be overridden. It can be proved by runtime polymorphism, so we will learn it later.
Covariant Return Type
-
The covariant return type specifies that the return type may vary in the same direction as the subclass.
-
Advantages of Covariant Return Type
Following are the advantages of the covariant return type.
1) Covariant return type assists to stay away from the confusing type casts in the class hierarchy and makes the code more usable, readable, and maintainable.
2) In the method overriding, the covariant return type provides the liberty to have more to the point return types.
3) Covariant return type helps in preventing the run-time ClassCastExceptions on returns.
Let's take an example to understand the advantages of the covariant return type.
Super
-
The super keyword in Java is a reference variable which is used to refer immediate parent class object.
-
Usage of Java super Keyword
super can be used to refer immediate parent class instance variable.
super can be used to invoke immediate parent class method.
super() can be used to invoke immediate parent class constructor.
class Animal{
Animal(){System.out.println("animal is created");}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
Dog(){
System.out.println("dog is created");
}
}
class TestSuper4{
public static void main(String args[]){
Dog d=new Dog();
}} - As we know well that default constructor is provided by compiler automatically if there is no constructor. But, it also adds super() as the first statement.
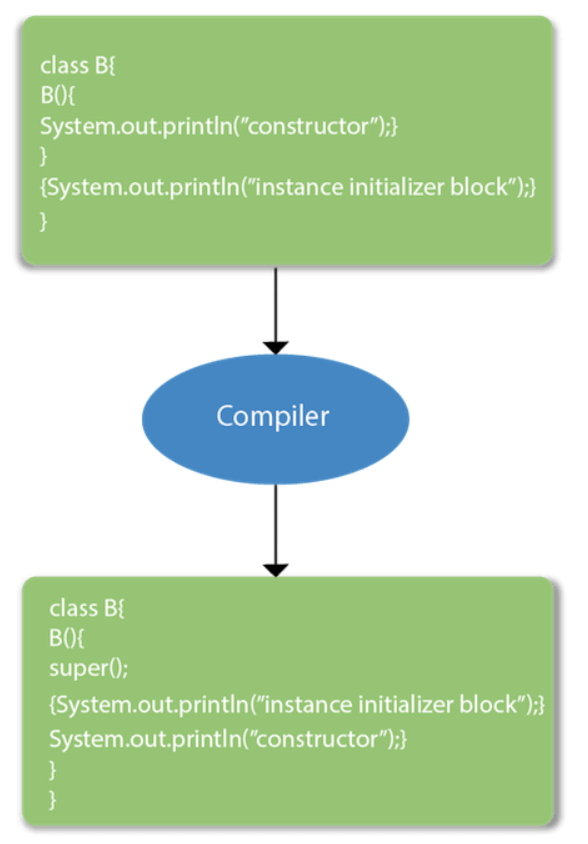
Instance initializer block
class Bike8{
int speed;
Bike8(){System.out.println("constructor is invoked");}
{System.out.println("instance initializer block invoked");}
public static void main(String args[]){
Bike8 b1=new Bike8();
Bike8 b2=new Bike8();
}
} instance initializer block invoked
constructor is invoked
instance initializer block invoked
constructor is invoked
In the above example, it seems that instanc
-
In the above example, it seems that instance initializer block is firstly invoked but NO. Instance intializer block is invoked at the time of object creation. The java compiler copies the instance initializer block in the constructor after the first statement super(). So firstly, constructor is invoked. Let's understand it by the figure given below:
-
Rules for instance initializer block :
There are mainly three rules for the instance initializer block. They are as follows:
The instance initializer block is created when instance of the class is created.
The instance initializer block is invoked after the parent class constructor is invoked (i.e. after super() constructor call).
The instance initializer block comes in the order in which they appear.
Final keyword
-
1) Java final variable
If you make any variable as final, you cannot change the value of final variable(It will be constant). -
2) Java final method
If you make any method as final, you cannot override it. -
3) Java final class
If you make any class as final, you cannot extend it. -
Que) Can we initialize blank final variable?
Yes, but only in constructor. For example:
static blank final variable
-
A static final variable that is not initialized at the time of declaration is known as static blank final variable. It can be initialized only in static block.
-
Example of static blank final variable
class A{
static final int data;//static blank final variable
static{ data=50;}
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println(A.data);
}
} Q) What is final parameter?
- If you declare any parameter as final, you cannot change the value of it.
class Bike11{
int cube(final int n){
n=n+2;//can't be changed as n is final
n*n*n;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Bike11 b=new Bike11();
b.cube(5);
}
} Compile Time error
