2022.01.05.Wed.
✍ 복습
hashCode()와 equals()
package com.icia.java2;
public class Example1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TV tv1 = new TV();
TV tv2 = new TV();
// 메인을 실행하면
// 참조 변수 2개와 객체 2개가 만들어진다
System.out.println(tv1.hashCode());
System.out.println(tv2.hashCode());
// ==를 객체를 비교하면 hashCode를 비교한다
System.out.println(tv1==tv2);
System.out.println(tv1==tv1);
// 객체의 값을 비교하는 equals 메소드가 준비되어 있다
// equals도 hashCode를 비교한다
// -> 프로그래머가 커스터마이즈할 수 있다(override)
System.out.println(tv1.equals(tv2));
System.out.println(tv1.equals(tv1));
}
}
클래스의 구성 멤버 : 필드, 생성자, 메소드
package com.icia.java2;
public class Monitor {
// 클래스의 멤버인 값 -> field
private int size;
private int bright;
// 생성자(constructor) : 객체 생성 전용 메소드
// - 객체 초기화. 공장초기화 목적으로 사용할 수 없다
// 생성자는 객체를 만들 때 사용하며 임의로 호출할 수 없다
// vs 생성자는 호출이 불가능한다
// 생성자의 이름 : 클래스 이름과 같다
// 리턴값은 존재하지 않는다(void가 아니라 그런 거 없다)
// 패키지 필수
// -> 지정하지 않으면 소스를 저장한 현재 폴더가 패키지가 된다
// 생성자는 필수 -> 안만들면 자바가 파라미터없는 생성자(기본 생성자)만들어준다
public Monitor() {
}
// 메소드 - 필드를 읽고(getter) 쓰는(setter) 메소드
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
public int getBright() {
return bright;
}
public void increaseBright() {
bright+=5;
}
public void decreaseBright() {
bright-=5;
}
}@Test
Private인 필드에 접근해서 @Test를 돌리기 위해서 getter 생성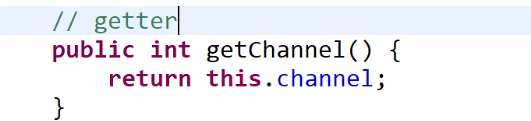
package com.icia.java2;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
public class MonitorTest {
@Test
public void 생성자test() {
Monitor m = new Monitor();
}
}
@Test는 병렬수행되기 때문에 주석처리 후 Test할 부분만 Test...
Overload

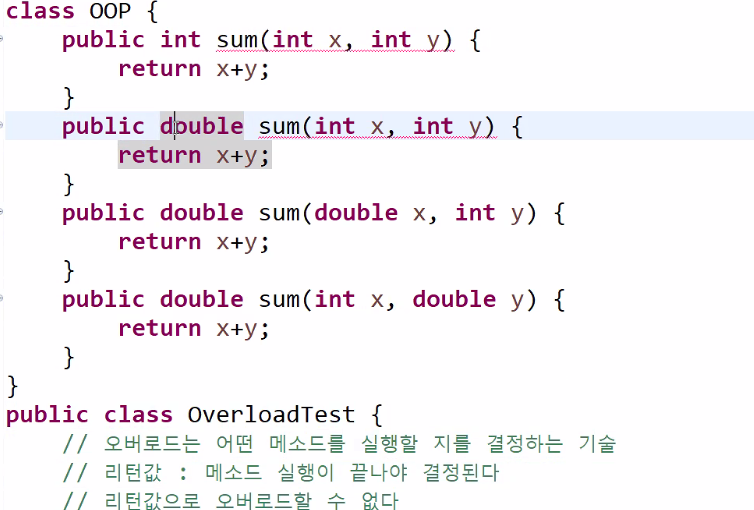
Java 계좌 예제
package com.icia.java2;
public class TV {
// 객체가 가진 값 : 필드
private int volume;
private int channel;
private final int MAX_VOLUME=32;
private final int MIN_VOLUME = 0;
private final int MAX_CHANNEL = 999;
private final int MIN_CHANNEL = 0;
// 필드를 변경하는 메소드
public void volumeUp() {
if(this.volume<this.MAX_VOLUME)
this.volume++;
}
public void voluemDown() {
if(this.volume>this.MIN_VOLUME)
this.volume--;
}
public void channelUp() {
if(this.channel<this.MAX_CHANNEL)
this.channel++;
}
public void channelDown() {
if(this.channel>this.MIN_CHANNEL)
this.channel--;
}
public void powerOn() {
this.channel = 0;
this.volume = 15;
}
// getter
public int getChannel() {
return this.channel;
}
public int getVolume() {
return this.volume;
}
}계좌 @Test
package com.icia.java2;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
public class 계좌Test {
@Test
public void 입금Test() {
계좌 account = new 계좌();
assertEquals(true, account.deposit(1000));
assertEquals(1000, account.checkBalance());
}
@Test
public void 출금Test() {
계좌 account = new 계좌();
// 테스트할 때는 실패같이 테스트해야 한다
assertEquals(false, account.withdraw(500));
assertEquals(true, account.deposit(10000));
assertEquals(true, account.withdraw(500));
assertEquals(9500, account.checkBalance());
}
