Bash Redirection
Redirection이란?
- File Descriptor의 조작!
- 명령어 실행 전, shell의 특별한 Notation을 통해 I/O가 redirect될 수 있음
- 명령어의 file이 복제, 열기, 닫기 등의 기능을 할 수 있게 제공
Three Standard File Descriptors
Bash 시작시, 3개의 Standard File Descriptor가 열린다.
- stdin (File Descriptor 0)
- stdout (File Descriptor 1)
- stderr (File Descriptor 2)
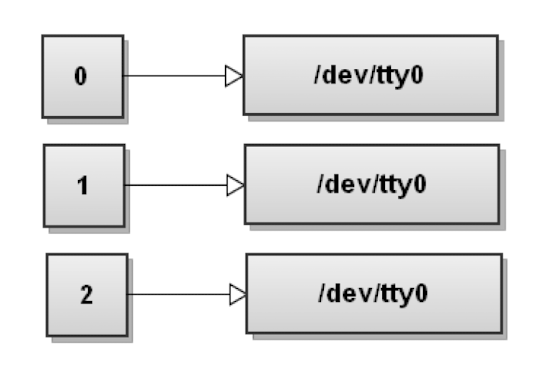
초기 상태는 위와 같이 terminal device를 가리킨다.
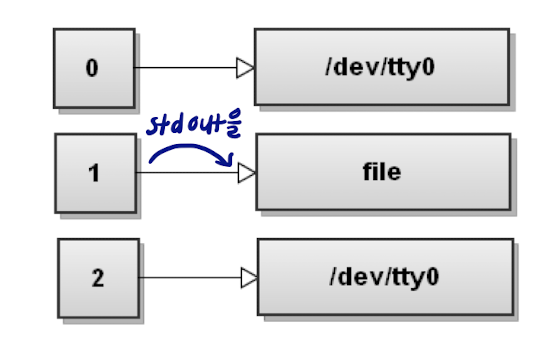
> : output redirection
-
$ command > file
: 명령어의 stdout을 file에 담기 ($ command 1> file와 같음)
이 명령어를 수행하면, stdout이 file에 연결된다.
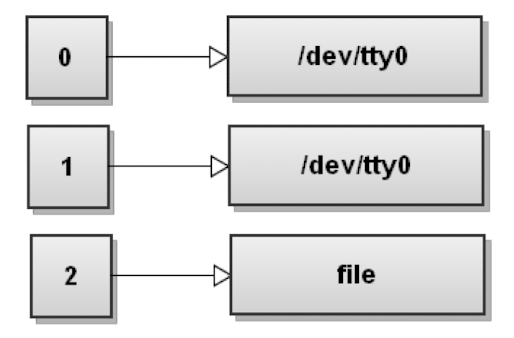
->$ command n> file: file descriptor n을 file에 연결 -
$ command 2> file
: 명령어의 stderr을 file에 담기
이 명령어를 수행하면, stderr이 file에 연결되고, 해당 명령어의 에러 메세지가 file에 이어서 써진다.
> : appending output
$ command >> file
: 명령어의 stdout을 file에 append ($ command 1>> file와 같음)
이 명령어를 수행하면, stdout이 file에 연결되고, 해당 명령어의 output이 file에 이어서 써진다.
&> : stdout과 stderr 한번에 연결
$ command &> file
: 명령어의 stdout과 stderr이 file에 연결된다.
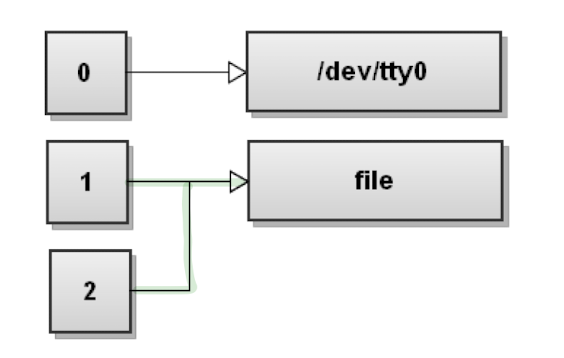
-> $ command > file 2>&1 와 같다. 여기서 >&는 file descriptor 2가 file descriptor 1의 연결을 copy한다는 의미
-> $ command &>> file는 append mode로 stdout, stderr을 연결
Redirection의 순서
Redirection시 순서가 중요하다.
예를 들어,
-
$ command > file 2>&1은 다음과 같은 결과를 가진다.
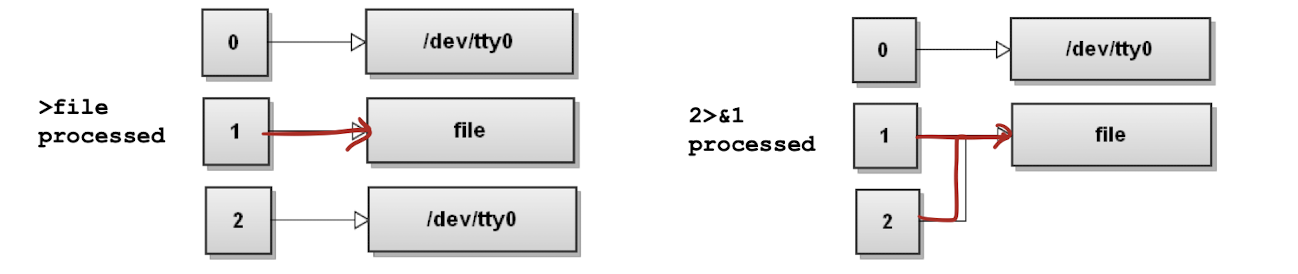
-
반면
$ command 2>&1 > file은 다음과 같은 결과를 가진다.
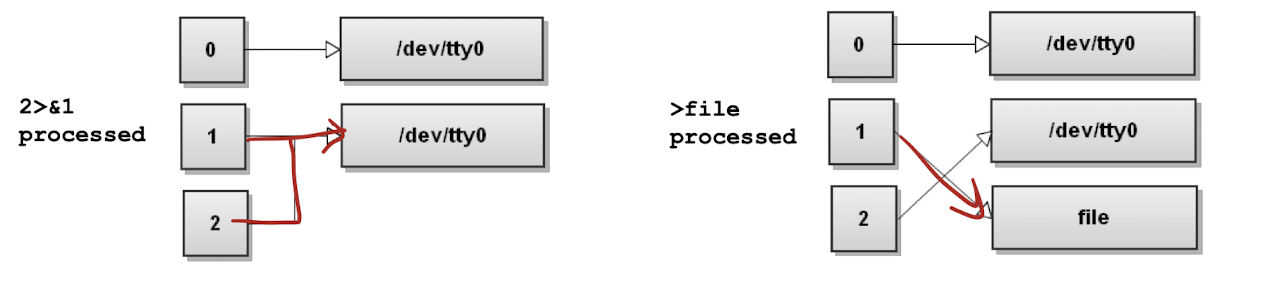
null로 redirect
output이 필요없는 경우, 다음과 같이 /dev/null에 fd를 연결한다.
$ command > /dev/null
: special file인/dev/null에 연결시, 해당 파일에 써지는 모든 데이터가 무시된다.- stdout과 stderr을 동시에 무시하는 방법은 다음과 같다.
$ command &> /dev/null,$ command > /dev/null 2&>1
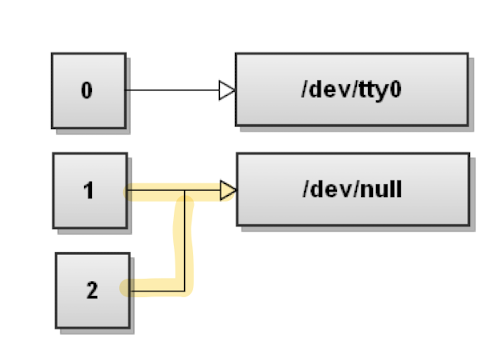
< : input redirection
$ command < file: file의 내용을 stdin에 redirect
예를 들어,

<< cmd : Here Document
여러줄의 input을 stdin에 redirect한다.
$ command << {cmd} : {cmd}를 만나기 전까지의 여러 줄의 input이 stdin과 redirect된다.
$ command << EOL file
your
multi-line
text goes
here
EOL
- Here String: 한줄의 text를 stdin에 redirect
$ command <<< {a single line of cmd}
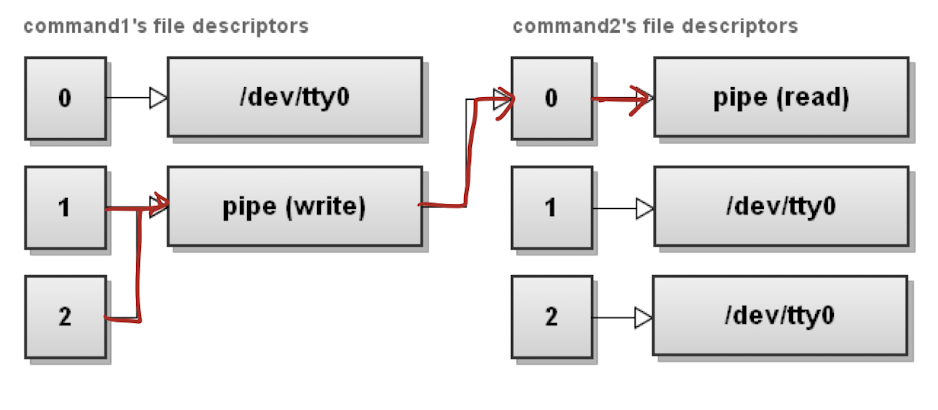
| : Pipe
: 한 process의 stdout을 다른 process의 stdin으로 연결
$ command1 | command2
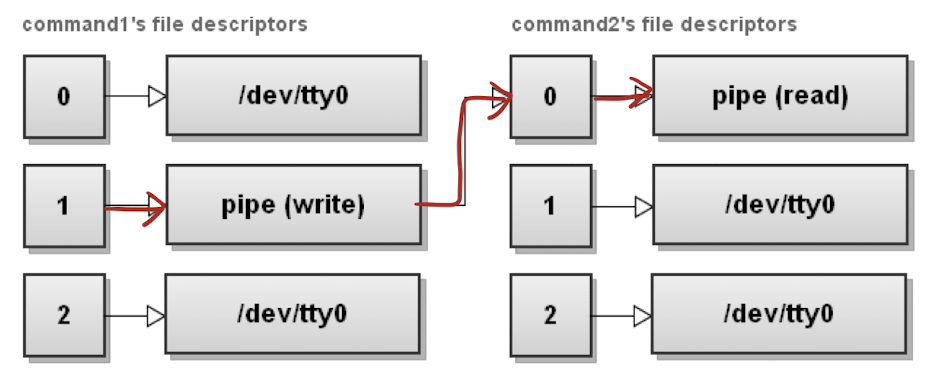
|& : stdout, stderr를 stdin으로
$ command1 |& command2: command1의 stdout, stderr을 command2의 stdin으로
->$ command1 2>&1 | command2과 같은 동작
<> : fd를 read&write로 열기
$ command n <> file: file을 fd n에 대해서 reading, writing으로 열기
-> 해당 command 내에서 fd n이 file을 의미한다.
file descriptor 복제하기
$ command 4<&3: input file descriptor 4가 3을 복사$ command 4>&3: output file descriptor 4가 3을 복사
-> file descriptor 4와 3이 같은 file/device를 가리킴
file descriptor 옮기기
$ command 4<&3-: input file descriptor인 3을 4에 옮기고 3은 닫기$ command 4>&3-: output file descriptor인 3을 4에 옮기고 3은 닫기
