: 어떻게 모든 component와 code module들을 관리할까?
Monolithic Kernels
→ basic
- 전 운영체제를 하나로 커널모드에서 실행
1) 장점
-
cost of module interactions is low
∵ call instruction 한번만 → 빠르게 요청 가능 -
good performance
—> function / 전역변수로 process사이의 정보교환 쉬움
2) 단점
- hard to understrand
- hard to modify
- unreliable (no isolation between system modules)
- hard to maintain
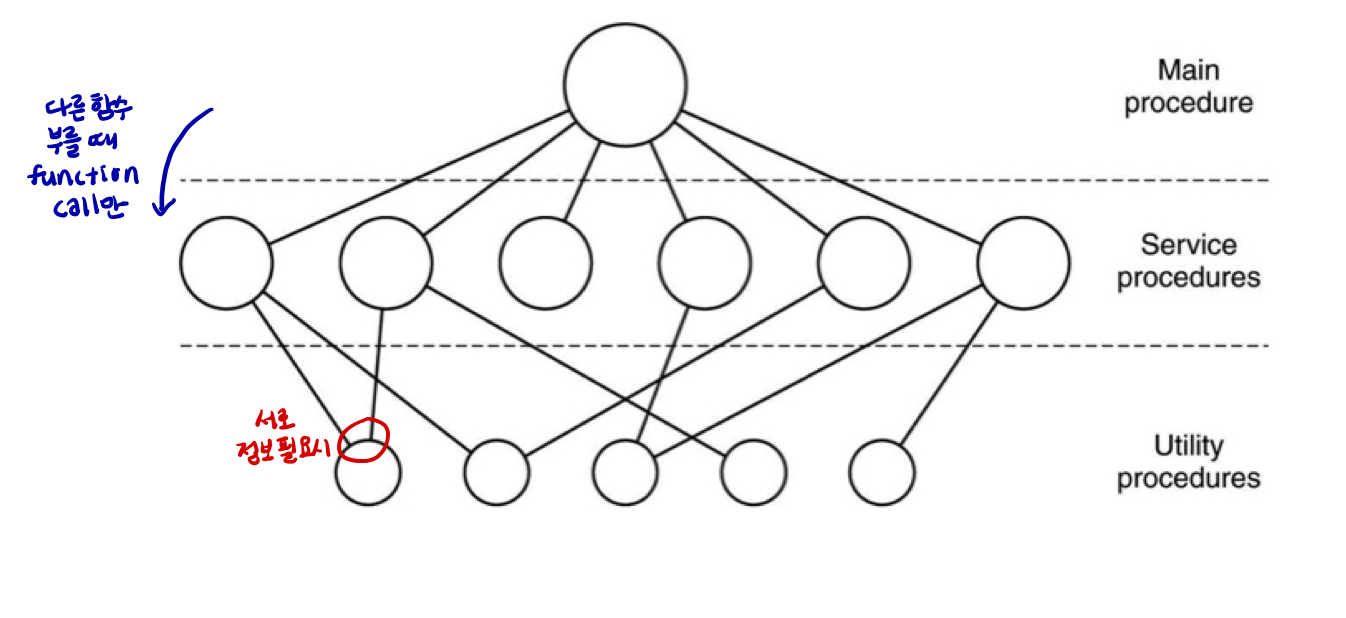
Layering
- OS를 set of layers로 구현
→ 각 layer는 위 layer의 virtual machine으로
e.g.
L0 : hardware
L1 : CPU scheduling
L2 : memory management (virtual processors)
L3 : console devices (VM segments)
L4 : I/O device buffering (virtual console)
L5 : user programs (virtual I/O drivers)
→ 직접 부르는게 아니라 위 레이어 거쳐서 approach
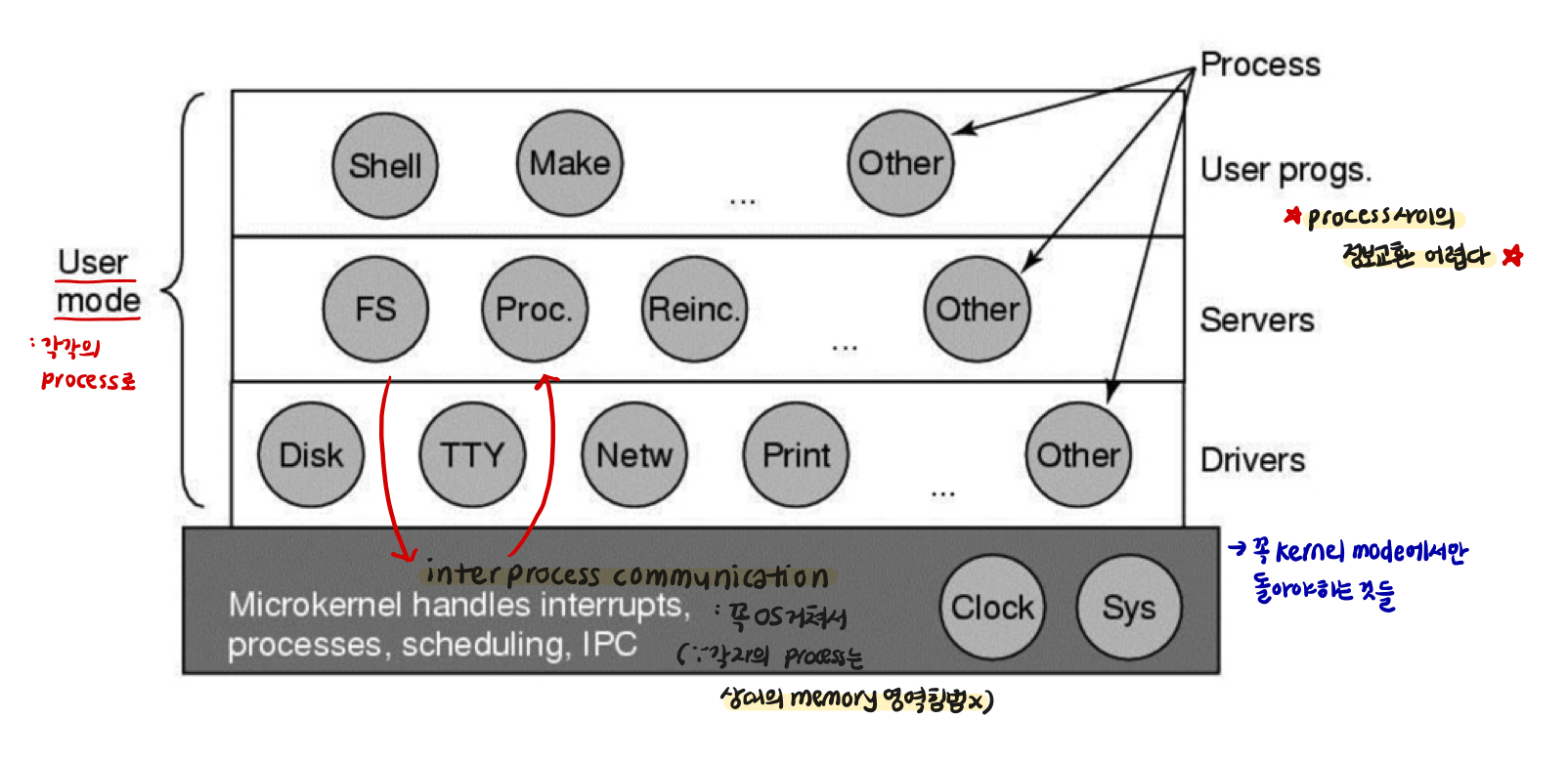
Microkernels
←→ monolithic : os의 전체가 커널 → 속도가 중요한 부분에서
-
80s 후반 ~ 90s 초반에 유행
-
Goal : minimize what goes in kernel
∵ communication의 비용 줄이기→ assembler로 짜진 부분은 많지 x ∵ 위의 단은 알고리즘적
→ 굳이 커널모드에서 돌 필요 없음
→ 나머지 OS를 user-level processes -
This results in
-
better reliability
∵ isolation between components -
ease of extension and customization
-
poor performance
-
-
file system, process manage가 따로있어 정보교환의 방법 x
→ file 입출력으로 ?
: file access는 os에서 disk access 등등 시간 오래걸림
→ I/O 안거치고 memory 사용 방법 제공하는데 오래걸림
1) 장점
-
kernel mode에 적은 OS
→ code ⬇️, kernel bug ⬇️ -
새로운 file system 장착 가능 → flexivity
-
process 죽어도 OS 계속 동작
2) 단점
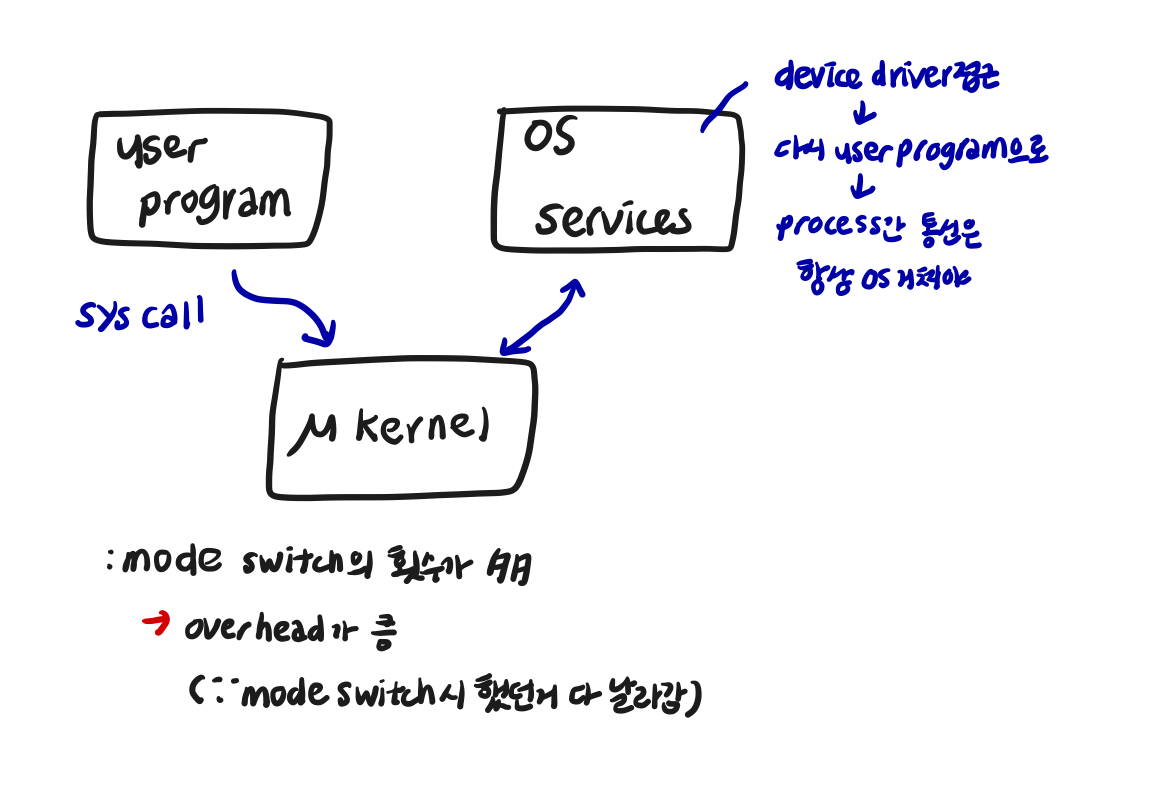
-
inefficient
∵ boundary crossing -
inconvenient to share data between kernel and services → 성능 ⬇️
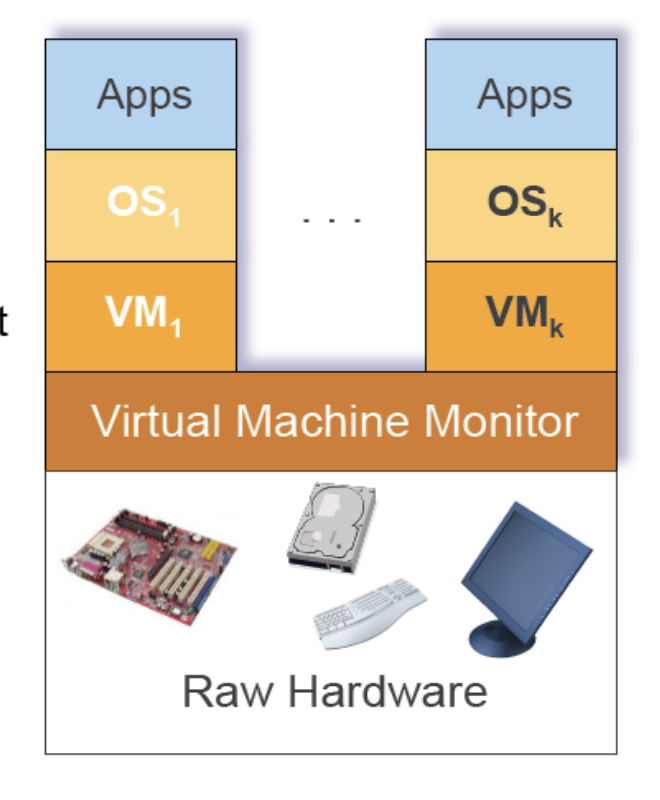
Virtual Machine
-
multiprogramming 제공 & raw HW보다 훨씬 편리한 인터페이스의 기계
→ multiprogramming과 abstraction분리 -
virtual machine monitor
: HW의 가상화
→ multiple instances of 'raw' hw로서 노출e.g.