Intro
iOS 앱을 만들다보면 서버와 API 통신을 하게 된다. 우리는 여태 class, struct 를 다루어 보았지 JSON object를 다뤄보지는 않았다. 이 글에서는 어떻게 class, struct instance를 JSON으로 encode 하는지, JSON data를 class, struct instance로 decode 하는지 알아보려고 한다.
Encodable

Encodable은 자기 자신을 외부의 표현 형태로 encode 하는 타입을 나타내는 프로토콜이라고 한다. 여기서 나온 외부의 표현 현태(external representation)은 JSON 이라고 볼 수 있다.
즉, 우리가 앱 안에서 사용하던 class나 struct의 instance를 JSON으로 바꿀 때 사용한다.
Decodable

Decodable은 외부 표현 형태로부터 decode를 하는 프로토콜이라고 한다. 거꾸로 API의 response로 온 JSON data를 앱 안에서 사용할 수 있게 decode 하는 것이다.
Codable
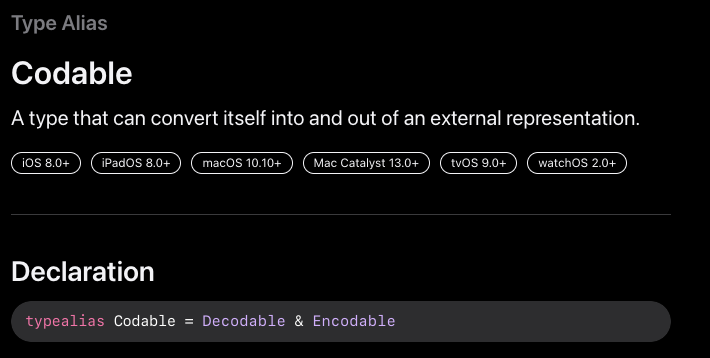
단순히 Encodable과 Decodable protocol을 동시에 따르는 것이다.
가장 단순하게 type을 codable로 만드는 것은 이미 Codable인 type로 property들을 정의하는 것이다. 이런 type으로는 String, Int, Double, Date, Data, URL 등이 있다. Property들이 모두 codable인 경우 해당 type을 Codable이라고 선언해주기만 하면 된다.
예시 struct 만들기(Place)
예시로 Place라는 struct를 만들고 이것을 Codable로 설정해보자. 최대한 실제 상황과 비슷하게 만들기 위해 Identifiable protocol과 id property를 추가하였다(뒤에 Coding key와 관련하여 중요하게 사용될 것이다👻):
import Foundation
struct Place: Identifiable, Codable {
let id = UUID()
let name: String
let latitude: Double
let longitude: Double
}모든 property들이 Codable 하므로 struct를 정의해주고 Codable protocol을 선언해주었다.
JSONEncoder 생성 및 encode
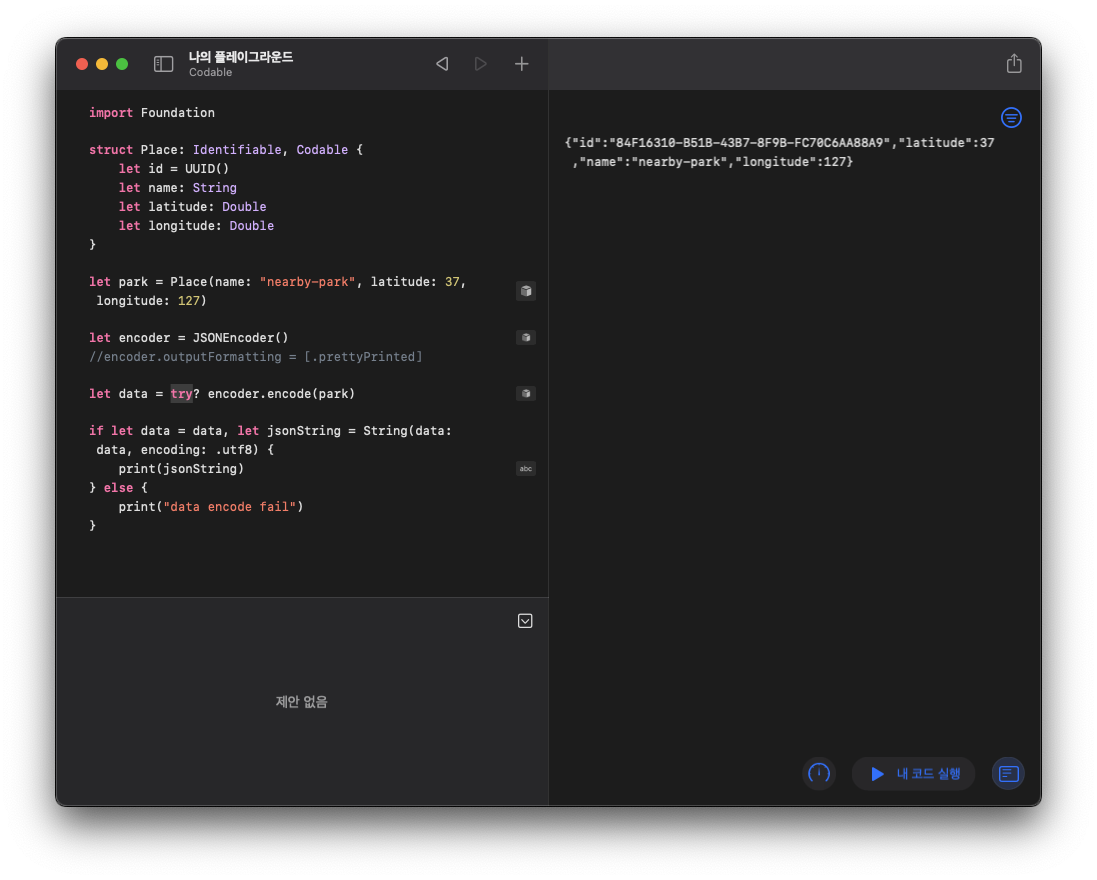
Database에 place를 추가하는 API를 호출하는 상황을 생각해보자. Place instance를 하나 만들고 이것을 request body에 JSON 형태로 담기 위해서 JSONEncoder를 사용한다:
let park = Place(name: "nearby-park", latitude: 37, longitude: 127)
let encoder = JSONEncoder()이제 encoder를 사용하여 park라는 instance를 encoding해보자:
let data = try? encoder.encode(park) // throw 할 수 있는 함수이므로 try와 함께 사용
if let data = data, let jsonString = String(data: data, encoding: .utf8) {
print(jsonString)
} else {
print("data encode fail")
}위의 코드에서 try?를 사용하여 try 문에서 error가 발생하면 data의 값이 nil이 되게 하였다. 그리고 String(data: Data, encoding: String.Encoding)은 failable initializer로 정의되어있어 if let 구문에 같이 사용하여 unwrapping을 해주었다. 이제 제대로 encoding이 되면 if let clause 안에서 제대로 jsonString이 출력되고 encoding에서 error가 발생하는 경우 "data encode fail"이 출력되게 된다.
Playgrounds를 사용하여 진행해보면 아래와 같이 결과가 나온다:
출력물을 조금 더 깔끔하게 보고 싶다면 encoder.outputFormatting을 사용해본다:
encoder.outputFormatting = [.prettyPrinted, .sortedKeys]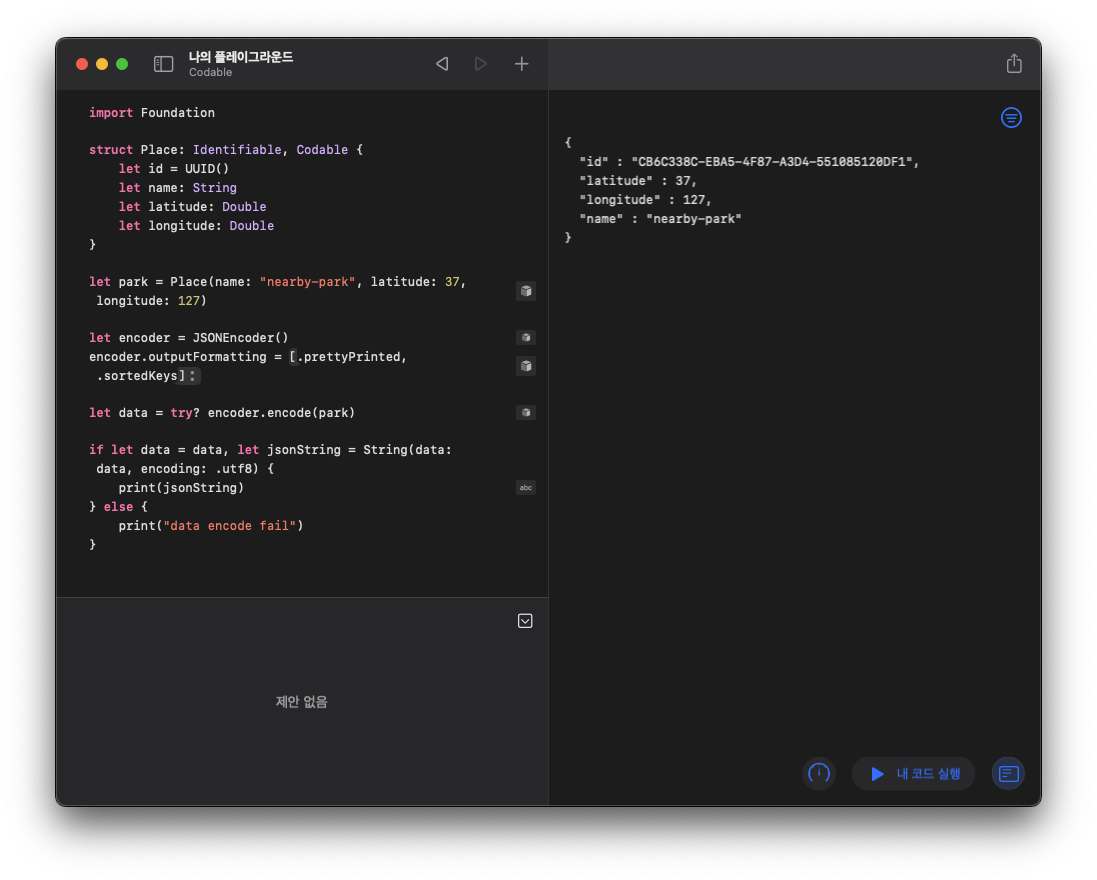
전체 코드는 아래와 같다:
import Foundation
struct Place: Identifiable, Codable {
let id = UUID()
let name: String
let latitude: Double
let longitude: Double
}
let park = Place(name: "nearby-park", latitude: 37, longitude: 127)
let encoder = JSONEncoder()
encoder.outputFormatting = [.prettyPrinted, .sortedKeys]
let data = try? encoder.encode(park)
if let data = data, let jsonString = String(data: data, encoding: .utf8) {
print(jsonString)
} else {
print("data encode fail")
}JSONDecoder 생성 및 decode
이번에는 Database에서 place를 read 해오는 경우를 떠올려보자. HTTP response body로 전달된 json data를 Place struct를 사용해 decode 하여 앱에서 사용한다.
우선은 위에서 출력된 json data를 Data type으로 바꿔준다:
let data = """
{
"id" : "05C2A51A-0FE1-4E07-96C6-A8F7A4C19E53",
"latitude" : 37,
"longitude" : 127,
"name" : "nearby-park"
}
""".data(using: .utf8)!이 형태가 HTTP response data의 형태이다(type: Data).
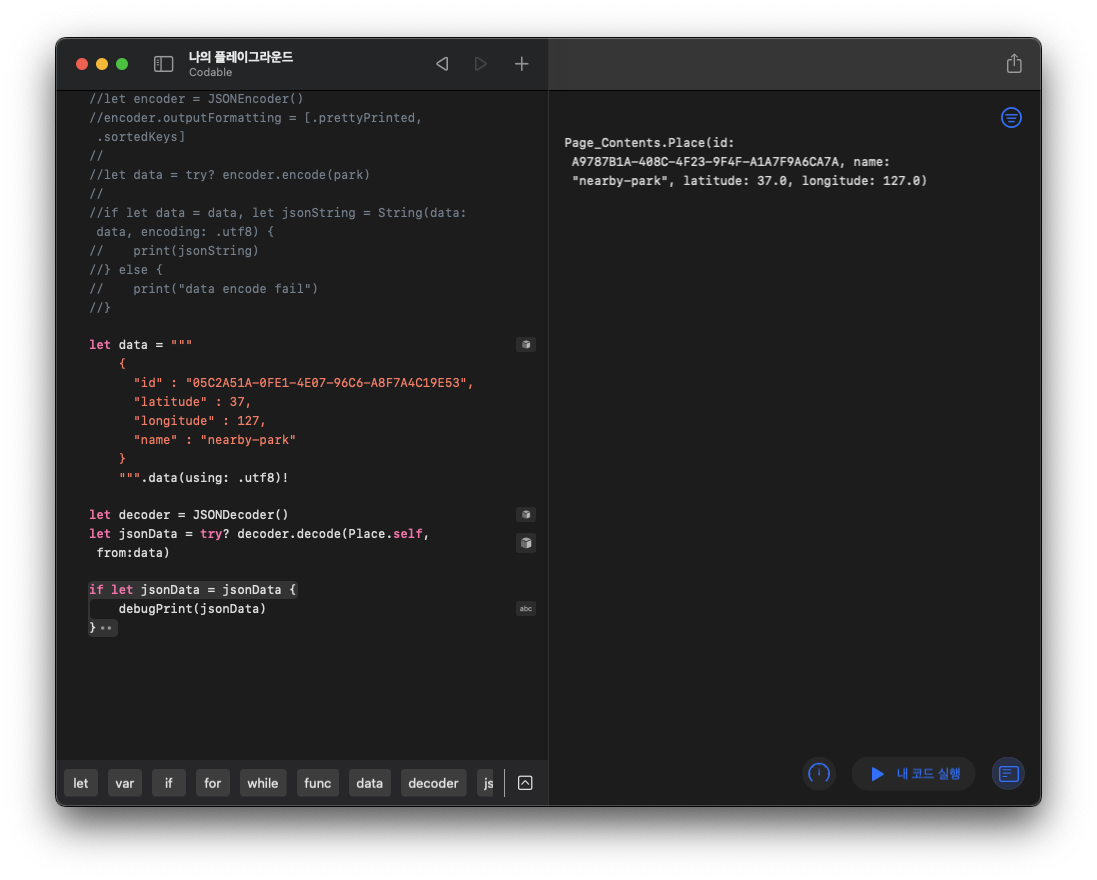
JSONDecoder를 생성하여 위에서 만든 data를 decode 한 뒤 출력해보자:
let decoder = JSONDecoder()
let jsonData = try? decoder.decode(Place.self, from:data)
if let jsonData = jsonData {
debugPrint(jsonData)
}
예시에 사용한 전체 코드
import Foundation
struct Place: Identifiable, Codable {
let id = UUID()
let name: String
let latitude: Double
let longitude: Double
}
//MARK: - encode
//let park = Place(name: "nearby-park", latitude: 37, longitude: 127)
//
//let encoder = JSONEncoder()
//encoder.outputFormatting = [.prettyPrinted, .sortedKeys]
//
//let data = try? encoder.encode(park)
//
//if let data = data, let jsonString = String(data: data, encoding: .utf8) {
// print(jsonString)
//} else {
// print("data encode fail")
//}
//MARK: - decode
let data = """
{
"id" : "05C2A51A-0FE1-4E07-96C6-A8F7A4C19E53",
"latitude" : 37,
"longitude" : 127,
"name" : "nearby-park"
}
""".data(using: .utf8)!
let decoder = JSONDecoder()
let jsonData = try? decoder.decode(Place.self, from:data)
if let jsonData = jsonData {
debugPrint(jsonData)
}