- JavaScript Algorithms and Data Structures Masterclass(Udemy Course)
- 다익스트라의 알고리즘 : 가중치가 있는 그래프를 기반으로 최단 경로를 찾는 알고리즘
가중치가 있는 그래프
const WeightedGraph = {
init: function () {
this.adjacencyList = {};
this.length = 0;
},
addVertex: function (vertex) {
if (!this.adjacencyList.hasOwnProperty(vertex)) {
this.adjacencyList[vertex] = {};
this.length++;
}
},
addEdge: function (vertex1, vertex2, weight) {
this.addVertex(vertex1);
this.addVertex(vertex2);
this.adjacencyList[vertex1][vertex2] = weight;
// 지향성 그래프를 만들고자 한다면 아래 작업을 생략하면 된다.
this.adjacencyList[vertex2][vertex1] = weight;
return this.adjacencyList;
},
removeEdge: function (vertex1, vertex2) {
if (!this.adjacencyList.hasOwnProperty(vertex1)) {
return `There's no ${vertex1}`;
}
if (!this.adjacencyList.hasOwnProperty(vertex2)) {
return `There's no ${vertex2}`;
}
function removeHelper(v1, v2) {
if (!this.adjacencyList[v1].hasOwnProperty(v2)) {
return `There's no edge between ${v1} and ${v2}`;
}
delete this.adjacencyList[v1][v2];
if (Object.keys(this.adjacencyList[v1]).length == 0) {
delete this.adjacencyList[v1];
this.length--;
}
}
removeHelper.call(this, vertex1, vertex2);
removeHelper.call(this, vertex2, vertex1);
return this.adjacencyList;
},
removeVertex: function (vertex) {
if (!this.adjacencyList.hasOwnProperty(vertex)) {
return `There's no ${vertex}`;
}
const edges = this.adjacencyList[vertex];
for (const key in edges) {
this.removeEdge(key, vertex);
}
return this.adjacencyList;
},
};
const wg = Object.create(WeightedGraph);
wg.init();
wg.addEdge("한국", "미국", 3);
wg.addEdge("한국", "중국", 2);
wg.addEdge("한국", "일본", 1);우선순위 큐 적용 이전에 스스로 만들어본 풀이
const WeightedGraph = {
// 생략
findShortestRoute: function (start, end) {
if (!start || !end) {
throw Error("출발지와 도착지를 모두 입력해야 합니다.");
}
// 초기화
const reference = {};
const previous = {};
for (const key in this.adjacencyList) {
const node = key == start ? start : key;
const distance = key == start ? 0 : Infinity;
reference[node] = distance;
previous[key] = null;
}
const visited = {};
while (true) {
// current 선별 로직
let current;
let min = Infinity;
for (const key in reference) {
if (visited.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
continue;
}
const distance = reference[key];
if (min > distance) {
min = distance;
current = key;
}
}
if (current == end) {
break;
}
// current 인접 노드 거리 계산 후 업데이트
const neighbors = this.adjacencyList[current];
for (const key in neighbors) {
const distFromCurrent = reference[current] + neighbors[key];
if (distFromCurrent < reference[key]) {
reference[key] = distFromCurrent;
previous[key] = current;
}
}
visited[current] = true;
}
let node = end;
const route = [];
while (node) {
route.unshift(node);
node = previous[node];
}
return route;
},
};
const wg = Object.create(WeightedGraph);
wg.init();
wg.addEdge("A", "B", 4);
wg.addEdge("A", "C", 2);
wg.addEdge("B", "E", 3);
wg.addEdge("C", "D", 2);
wg.addEdge("C", "F", 4);
wg.addEdge("D", "E", 3);
wg.addEdge("D", "F", 1);
wg.addEdge("E", "F", 1);
wg.findShortestRoute("A", "E");- 우선순위 큐를 사용할 생각을 못해 current를 뽑아내는데 애를 먹었다.
우선순위 큐 적용 이후 풀이
// 우선순위 큐 자료구조는 생략('힙'포스팅에 있음)
const WeightedGraph = {
// 생략
findShortestRoute: function (start, end) {
if (!start || !end) {
throw Error("출발지와 도착지를 모두 입력해야 합니다.");
}
// 초기화
const distance = {};
const previous = {};
const pq = Object.create(PriorityQueue);
pq.init();
pq.enqueue(start, 0);
const visited = {};
const hashOfVertex = this.adjacencyList;
for (const vertexName in hashOfVertex) {
const priority = vertexName == start ? 0 : Infinity;
distance[vertexName] = priority;
previous[vertexName] = null;
}
while (true) {
let current = pq.dequeue();
current = current.val;
if (current == end) {
break;
}
const neighbors = hashOfVertex[current];
for (const vertexName in neighbors) {
if (visited.hasOwnProperty(vertexName)) {
continue;
}
const distFromStart = distance[current] + neighbors[vertexName];
if (distFromStart < distance[vertexName]) {
pq.enqueue(vertexName, distFromStart);
distance[vertexName] = distFromStart;
previous[vertexName] = current;
}
debugger;
}
visited[current] = true;
}
let node = end;
const route = [];
while (node) {
route.unshift(node);
node = previous[node];
}
return route;
},
};
const wg = Object.create(WeightedGraph);
wg.init();
wg.addEdge("A", "B", 4);
wg.addEdge("A", "C", 2);
wg.addEdge("B", "E", 3);
wg.addEdge("C", "D", 2);
wg.addEdge("C", "F", 4);
wg.addEdge("D", "E", 3);
wg.addEdge("D", "F", 1);
wg.addEdge("E", "F", 1);
wg.findShortestRoute("A", "E");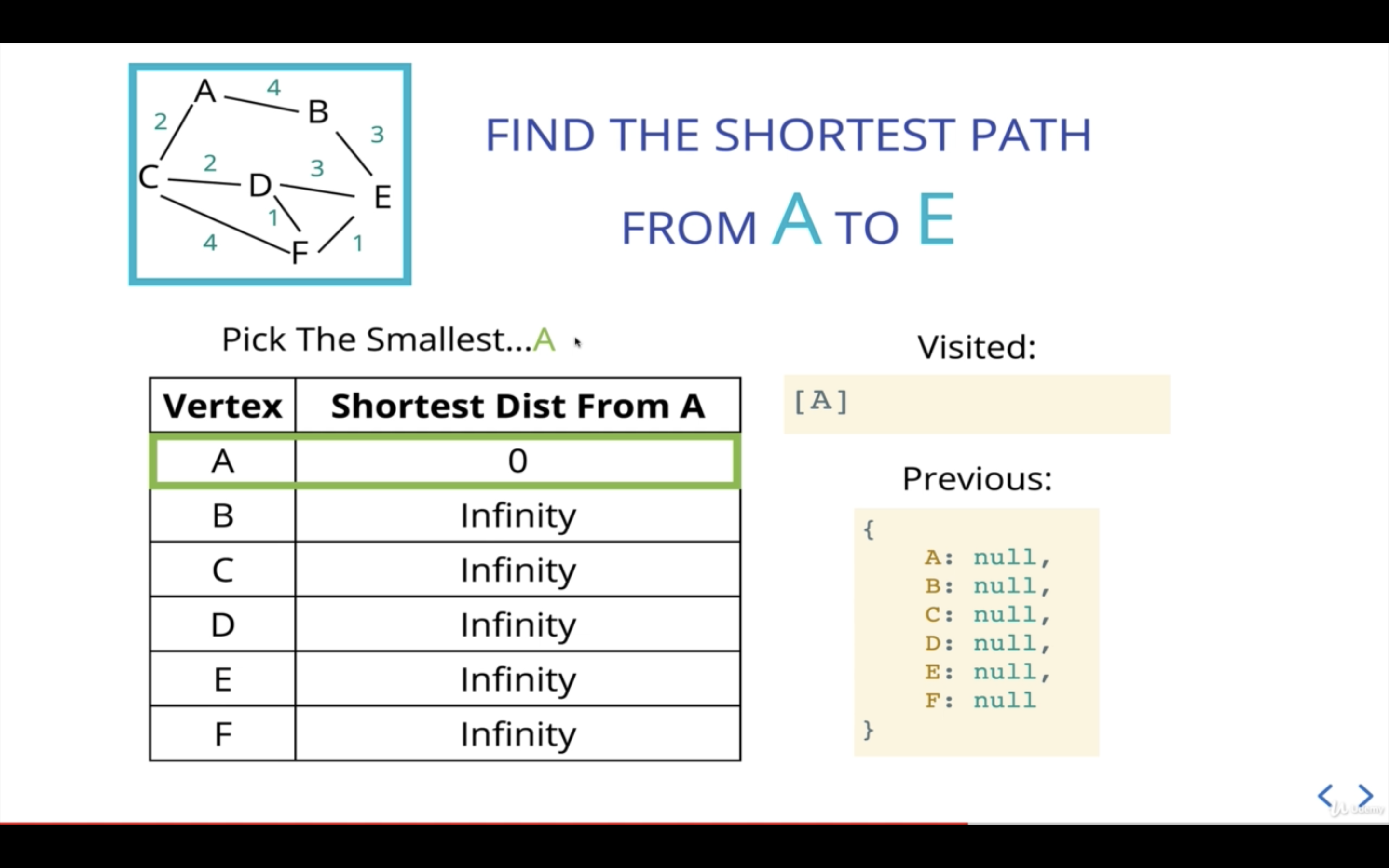
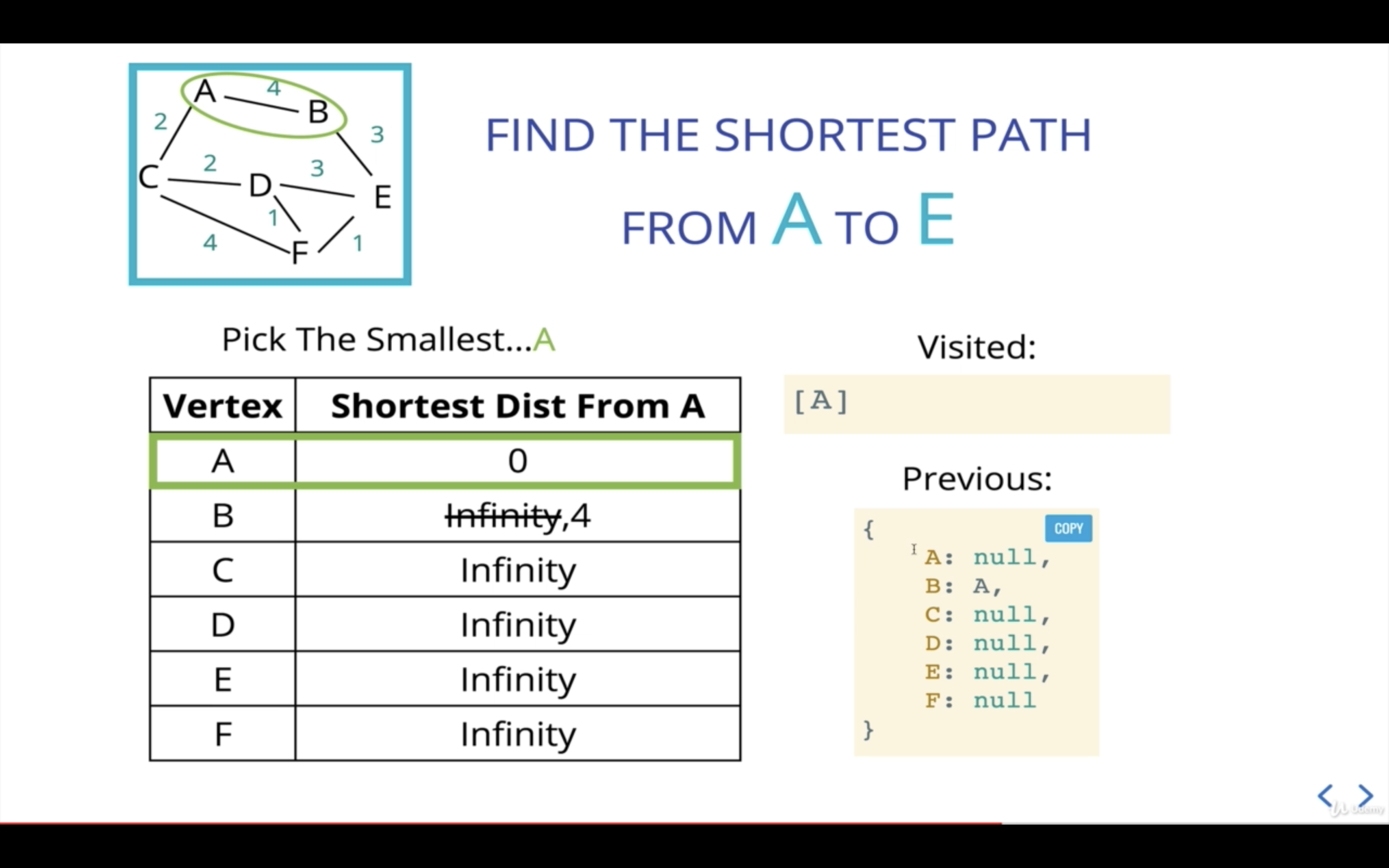
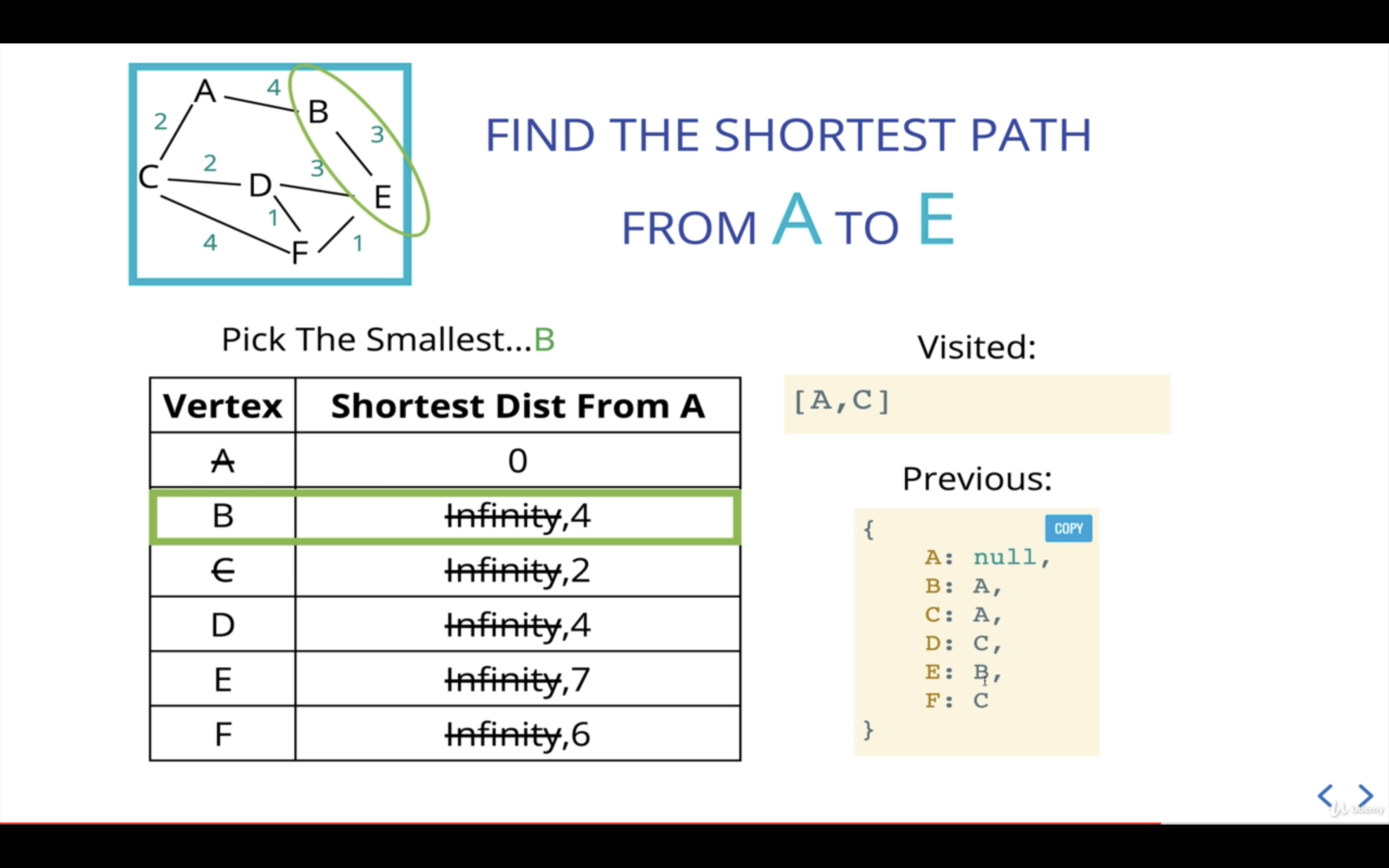
- 현재 기준점(current)은 A로부터의 거리가 가장 작은 노드(A 자신)를 고른다.
(여기에서 우선순위 큐가 필요한 것)
-
current의 인접 노드인 neighbors중 B에 대한 처리이다.
-
A에서 B까지의 거리가 4이고, 이는 B의 이전 거리인 Infinity보다 작기 때문에 B의 거리를 4로 업데이트해준다.
-
B는 A노드로부터 온 것이므로 previous값을 업데이트해준다.
-
또한, 다음 current를 산출할 수 있도록 우선순위 큐에 노드B를 넣어준다.

-
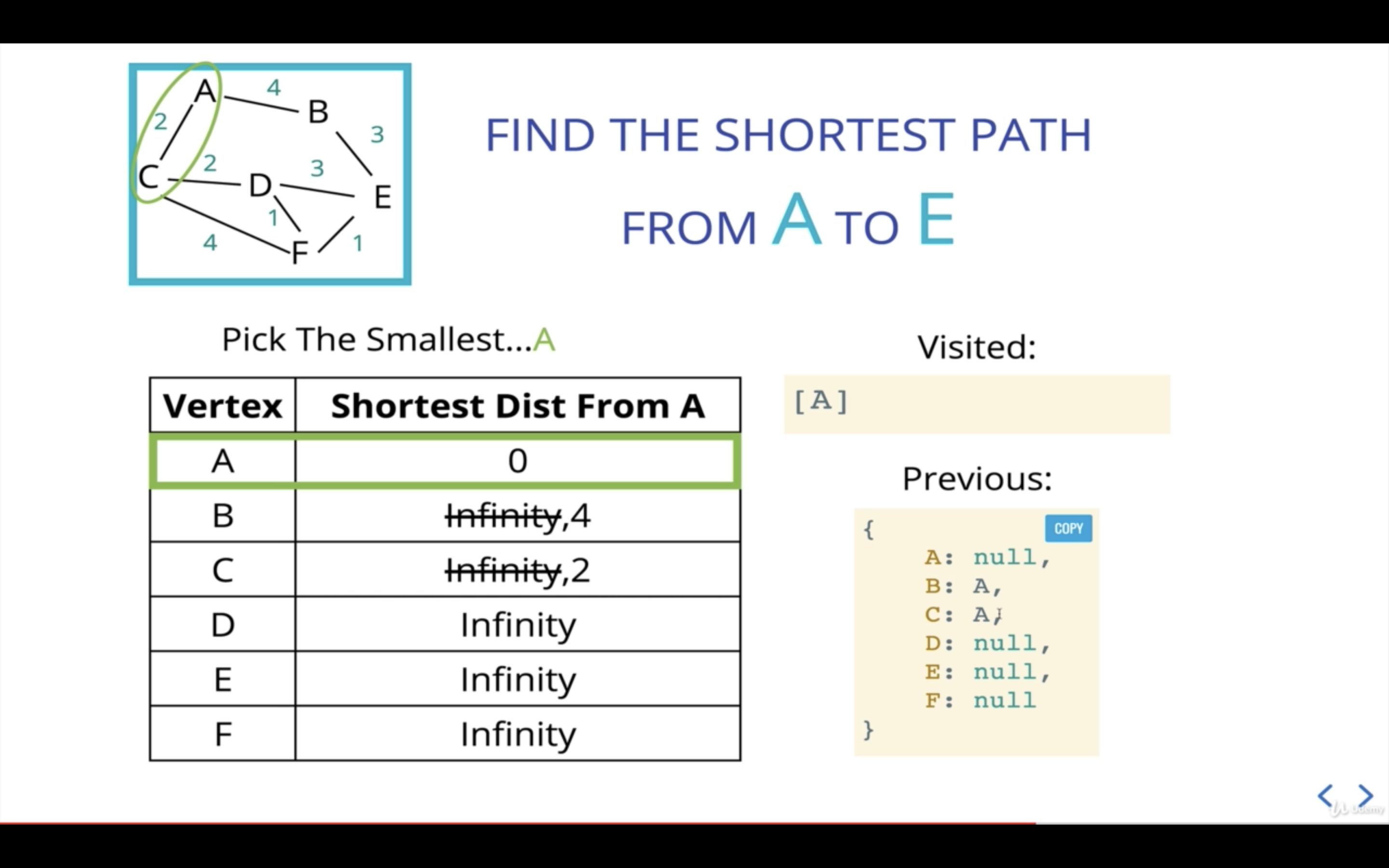
A의 다음 인접 노드인 C에 대한 처리이다.
-
A에서 C까지의 거리가 2이고, 이는 C의 이전 거리인 Infinity보다 작기 때문에 C의 거리를 2로 업데이트해준다.
-
C는 A노드로부터 온 것이므로 previous값을 업데이트해준다.
-
또한, 다음 current를 산출할 수 있도록 우선순위 큐에 노드B를 넣어준다.
-
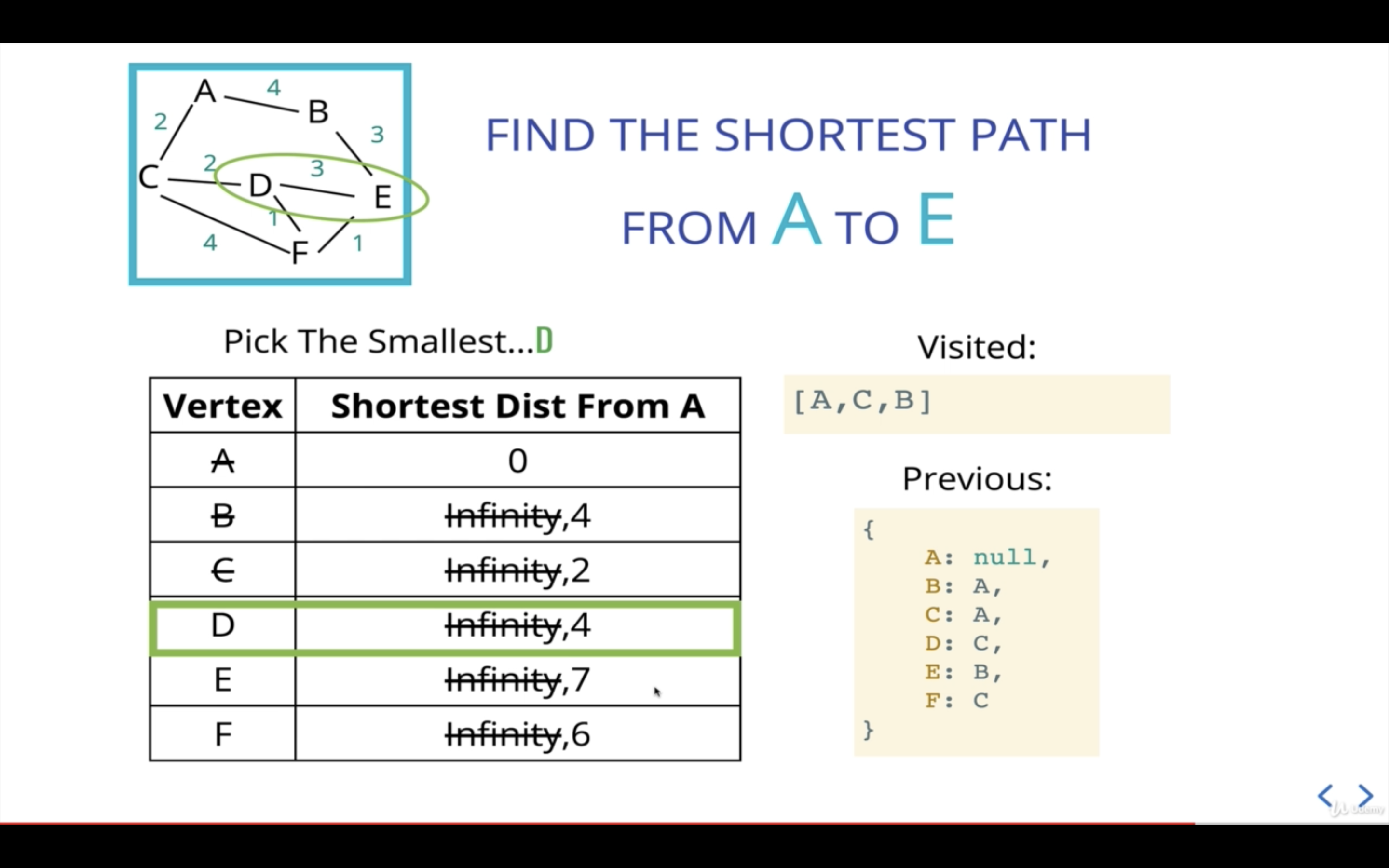
A의 인접 노드를 모두 살펴봤으니, 다음 current로 넘어가게 되는데 현재 우선순위 큐에 따르면 C가 다음 current가 된다.
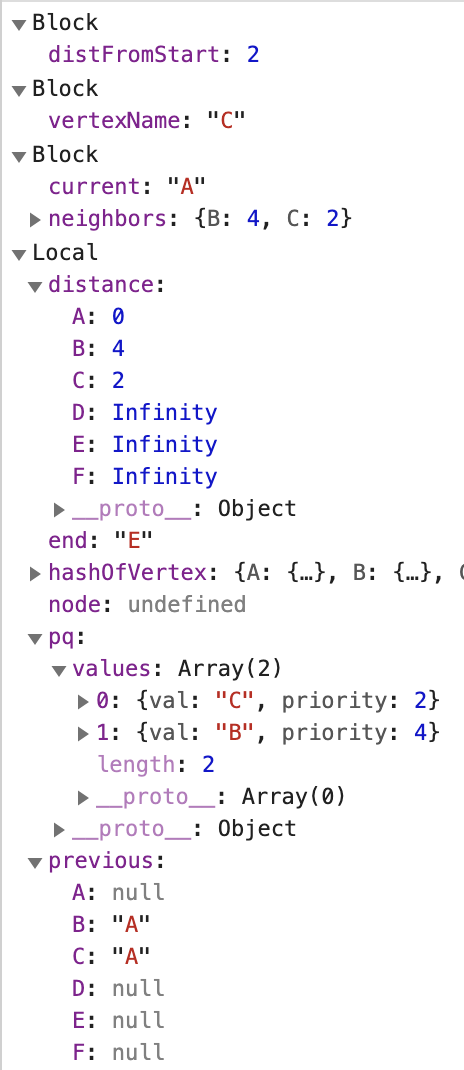
-
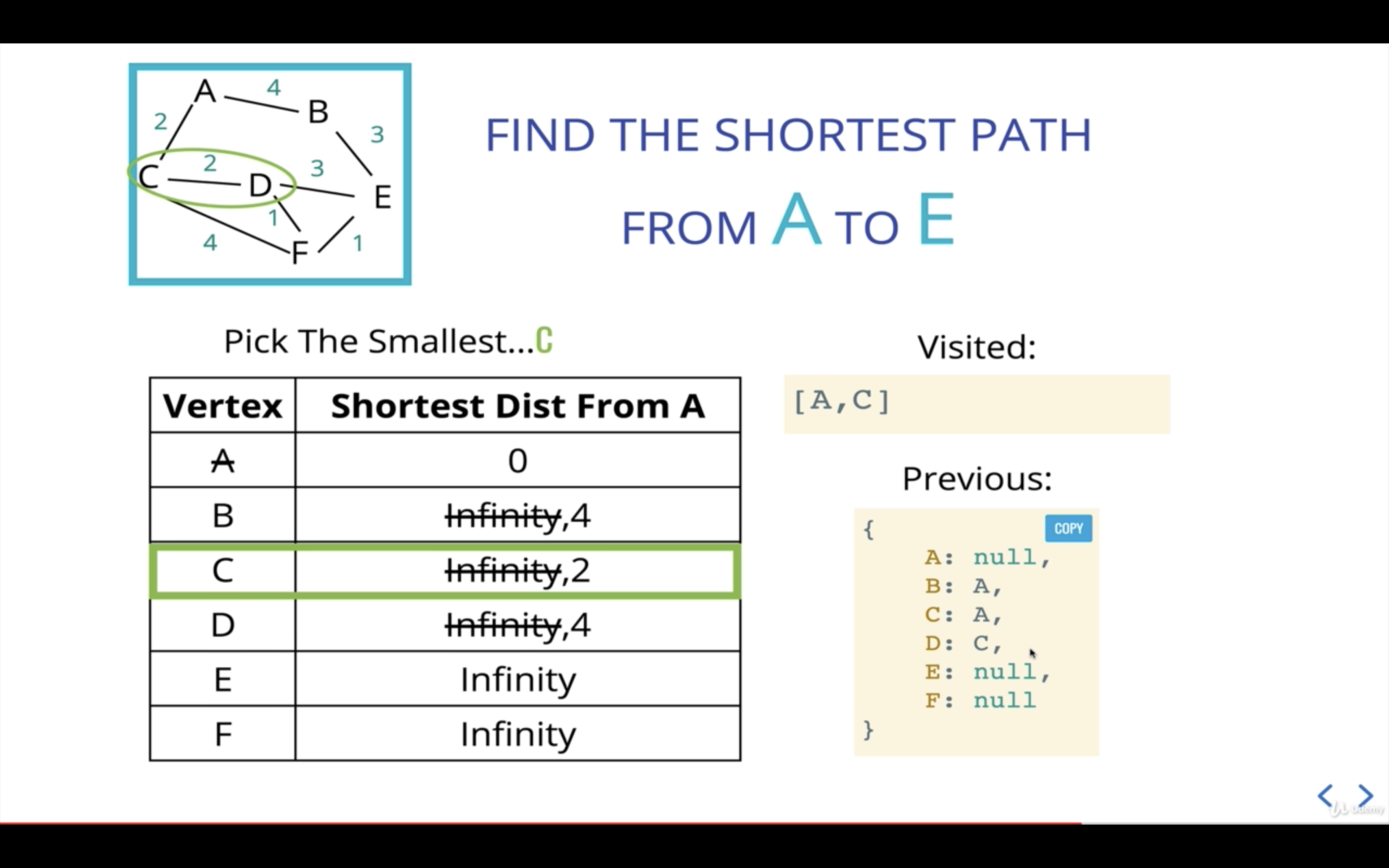
새 current인 C를 기준으로 인접 노드를 살펴본다.
-
첫번째 인접 노드인 A는 경로 탐색을 끝낸 visited이므로, 다음 인접 노드인 D를 본다.
-
A에서 D까지의 거리는 현재 기준점인 C가 A로부터 걸리는 거리(2)에 C에서 D까지의 거리(2)를 더해 산출한다.
-
A에서 D까지의 거리가 4이므로 D의 이전 거리인 Infinity보다 작으니, D의 거리를 4로 업데이트해준다.
-
D는 C로부터 왔으니 previous값도 업데이트해준다.
-
다음 current산출을 위해 우선순위 큐에 D를 추가해준다.

-
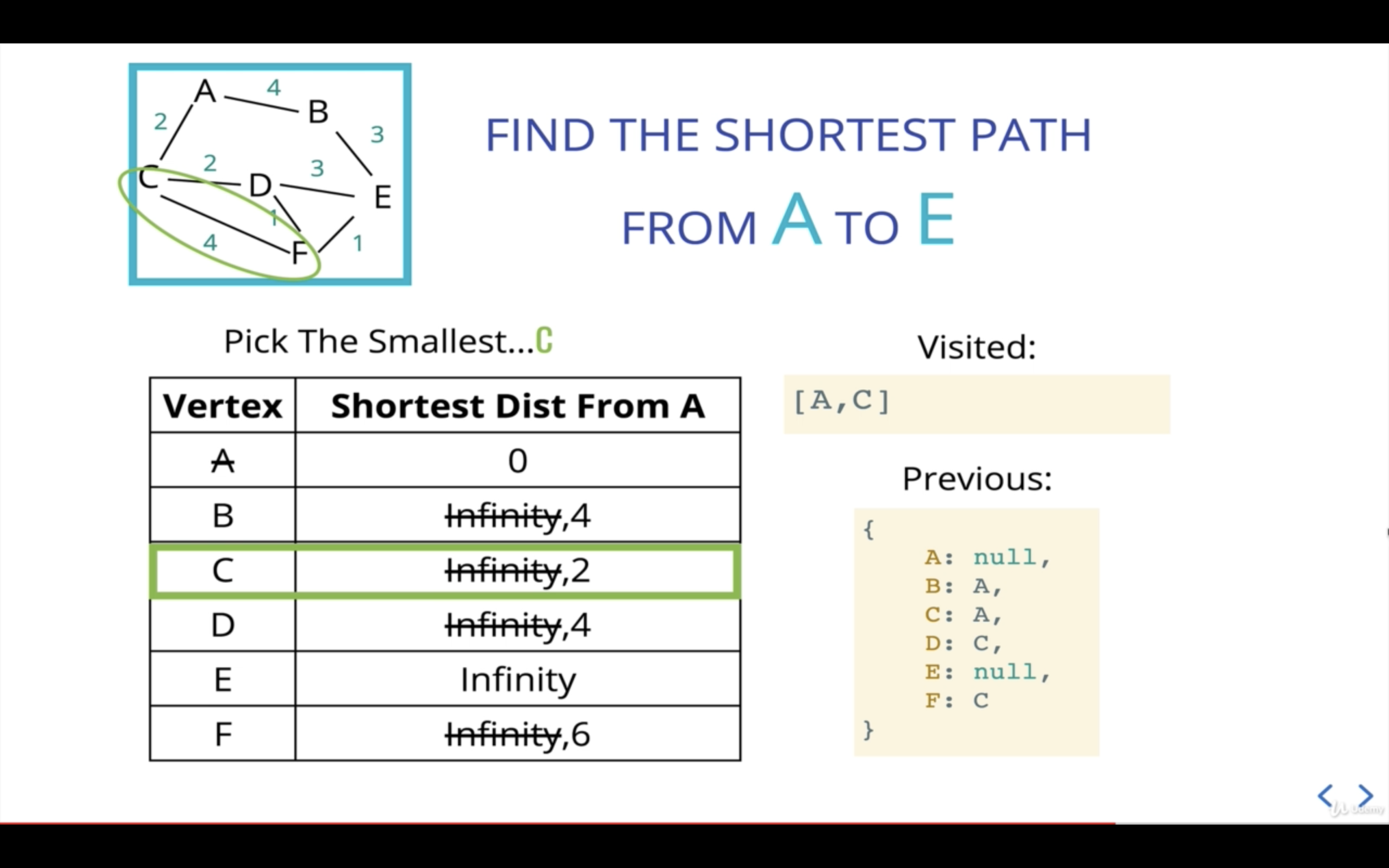
C의 다음 인접 노드인 F를 본다.
-
A에서 F까지의 거리는 현재 기준점인 C가 A로부터 걸리는 거리(2)에 C에서 F까지의 거리(4)를 더해 산출한다.
-
A에서 F까지의 거리가 6이므로 F의 이전 거리인 Infinity보다 작으니, F의 거리를 6으로 업데이트해준다.
-
F는 C로부터 왔으니 previous값도 업데이트해준다.
-
다음 current산출을 위해 우선순위 큐에 F를 추가해준다.
-
C의 인접 노드를 모두 살펴봤으므로, 다음 current를 산출한다.
-
현재 우선순위 큐에 있는 것 중 가장 우선순위가 작은 것은 B와 D인데, 우선순위가 같으므로 어느 것을 먼저 선택해도 무방하다
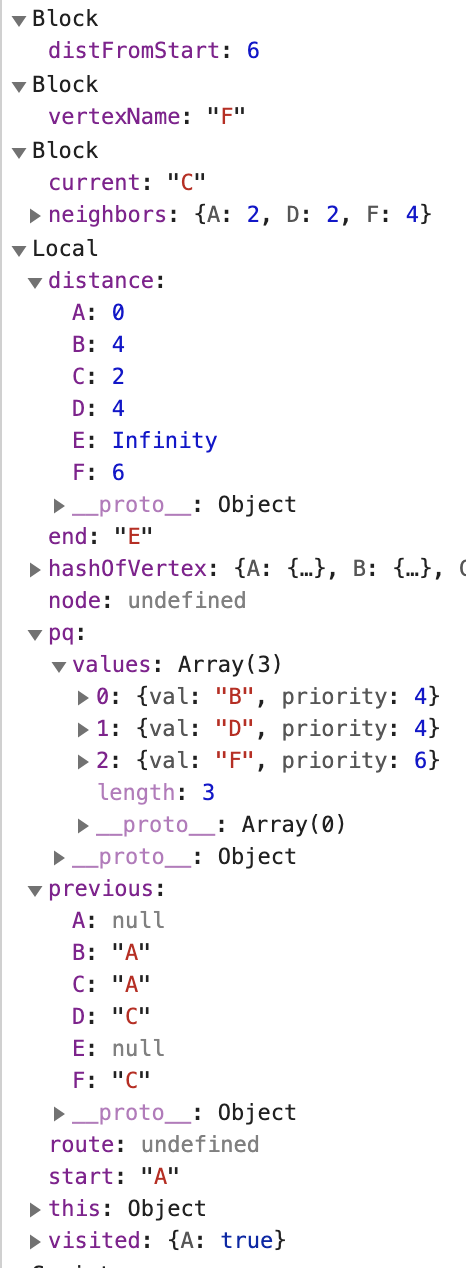
-
새로운 current인 B를 기준으로 인접 노드를 살펴본다.
-
B의 인접 노드 중 A는 이미 visited에 속한 노드이므로 넘어가고, E를 본다.
-
A에서 E까지의 거리는 현재 기준점인 B가 A로부터 걸리는 거리(4)에 B에서 E까지의 거리(3)를 더해 산출한다.
-
A에서 E까지의 거리가 7이므로 E의 이전 거리인 Infinity보다 작으니, E의 거리를 7로 업데이트해준다.
-
E는 B로부터 왔으니 previous값도 업데이트해준다.
-
다음 current산출을 위해 우선순위 큐에 E를 추가해준다.
-
B의 인접 노드를 모두 살펴봤으므로, 다음 current를 산출한다.
-
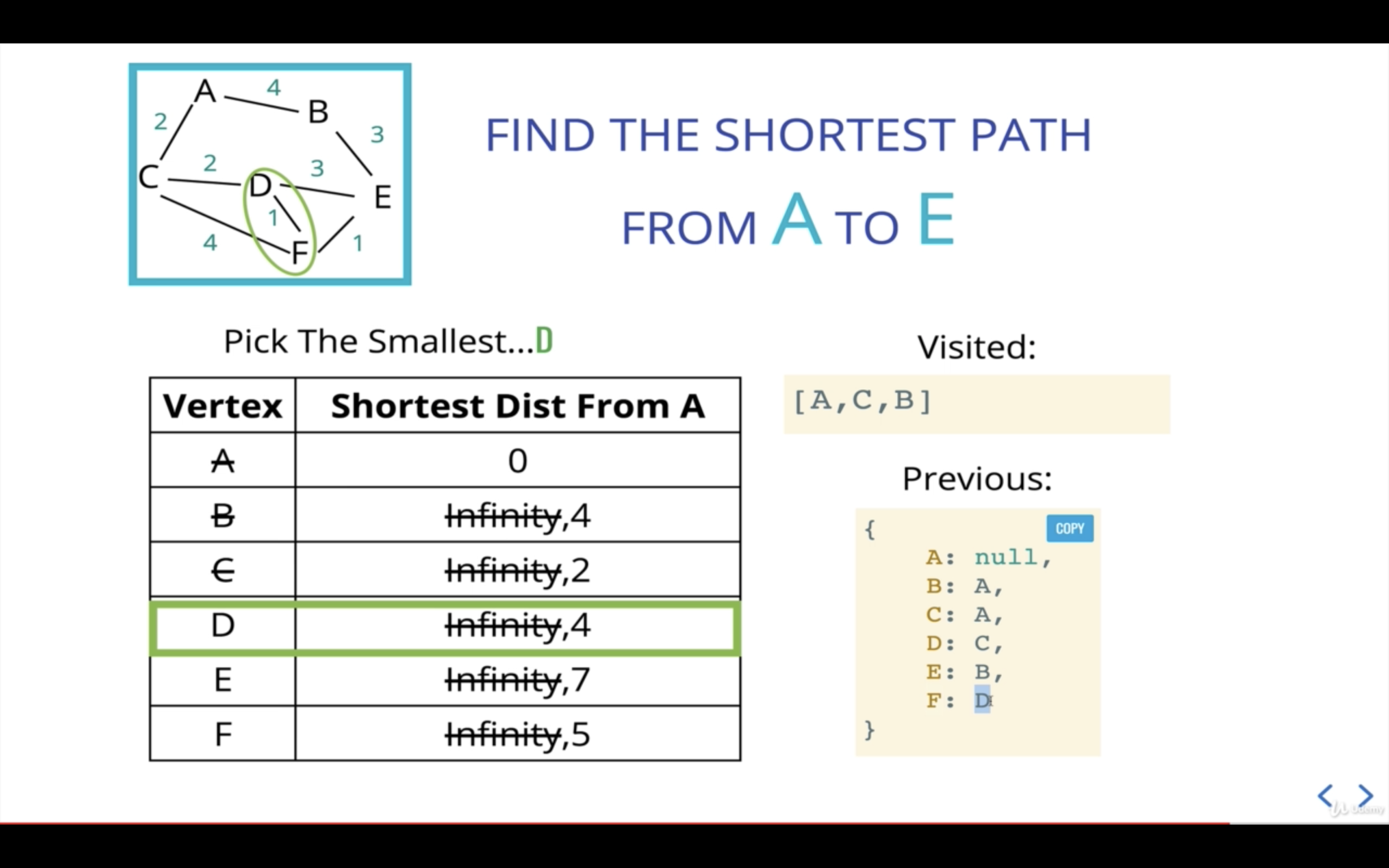
현재 우선순위 큐에 있는 것 중 가장 우선순위가 작은 것은 D이다.

-
새로운 current인 D를 기준으로 인접 노드를 살펴본다.
-
D의 인접 노드 중 C는 이미 visited에 속한 노드이므로 넘어가고, E를 본다.
-
A에서 E까지의 거리는 현재 기준점인 D가 A로부터 걸리는 거리(4)에 D에서 E까지의 거리(3)를 더해 산출한다.
-
A에서 E까지의 거리가 7이므로 E의 이전 거리인 7과 같으니 별도의 처리 없이 넘어간다.

-
D의 다음 인접 노드인 F를 살펴본다.
-
A에서 F까지의 거리는 현재 기준점인 D가 A로부터 걸리는 거리(4)에 D에서 F까지의 거리(1)를 더해 산출한다.
-
A에서 F까지의 거리가 5이므로 F의 이전 거리인 6보다 작으니, F의 거리를 5로 업데이트해준다.
-
F는 D로부터 왔으니 previous값도 업데이트해준다.
-
다음 current산출을 위해 우선순위 큐에 F를 추가해준다.
-
D의 인접 노드를 모두 살펴봤으므로, 다음 current를 산출한다.
-
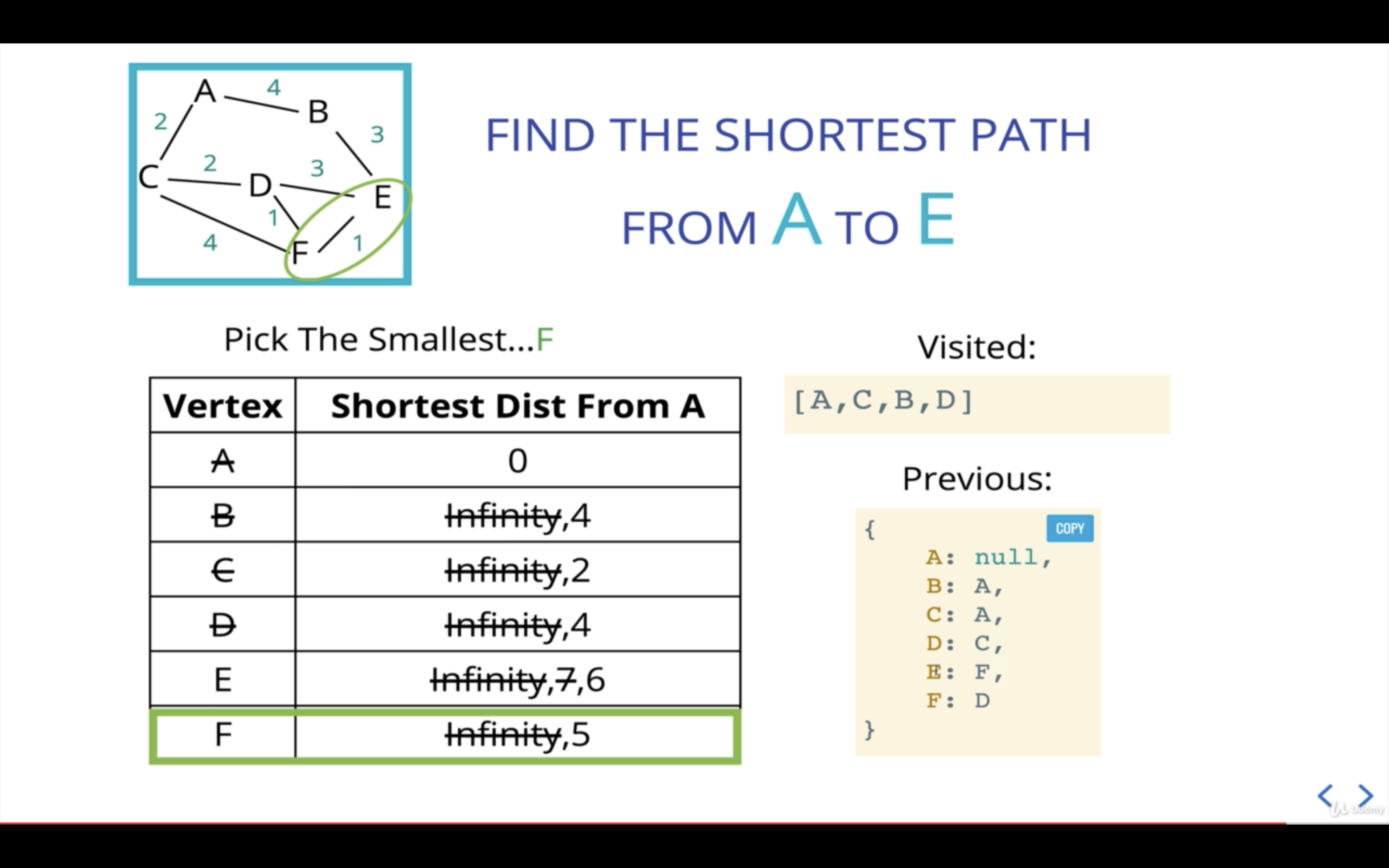
현재 우선순위 큐에 있는 것 중 가장 우선순위가 작은 것은 F이다.

-
새로운 current인 F를 기준으로 인접 노드를 살펴본다.
-
F의 인접 노드 중 C와 D는 이미 visited에 속한 노드이므로 넘어가고, E를 본다.
-
A에서 E까지의 거리는 현재 기준점인 F가 A로부터 걸리는 거리(5)에 F에서 E까지의 거리(1)를 더해 산출한다.
-
A에서 E까지의 거리가 6이므로 E의 이전 거리인 7보다 작으니, E의 거리를 6으로 업데이트해준다.
-
E는 F로부터 왔으니 previous값도 업데이트해준다.
-
다음 current산출을 위해 우선순위 큐에 E를 추가해준다.
-
F의 인접 노드를 모두 살펴봤으므로, 다음 current를 산출한다.
-
현재 우선순위 큐에 있는 것 중 가장 우선순위가 작은 것은 우선순위가 6인 E와 F이다.
-
F를 선택하면, F의 인접 노드가 모두 이미 방문 노드이므로 E로 넘어가고
-
E가 current가 되면 반복문에서 빠져나온다.
-
반복문에서 빠져나온 이후엔 도착지인 E를 기준으로 previous값을 되짚어 가면서 최단 경로를 배열의 형태로 산출해 반환한다.

전체 코드
const Node = {
init: function (val, priority) {
this.val = val;
this.priority = priority;
},
};
const PriorityQueue = {
init: function () {
this.values = [];
},
enqueue: function (val, priority) {
const newNode = Object.create(Node);
newNode.init(val, priority);
this.values.push(newNode);
let idxOfNewNode = this.values.length - 1;
while (idxOfNewNode > 0) {
const idxOfParentNode = Math.floor((idxOfNewNode - 1) / 2);
const parentNode = this.values[idxOfParentNode];
if (priority < parentNode.priority) {
this.values[idxOfParentNode] = newNode;
this.values[idxOfNewNode] = parentNode;
idxOfNewNode = idxOfParentNode;
// debugger;
continue;
}
break;
}
return this.values;
},
dequeue: function () {
if (this.values.length == 0) {
return;
}
const dequeued = this.values.shift();
const lastItem = this.values.pop();
if (!lastItem) {
// debugger;
return dequeued;
}
this.values.unshift(lastItem);
let idxOfTarget = 0;
while (true) {
let idxOfLeftChild = idxOfTarget * 2 + 1;
let idxOfRightChild = idxOfTarget * 2 + 2;
let leftChild = this.values[idxOfLeftChild];
let rightChild = this.values[idxOfRightChild];
function swap(direction) {
const idxOfChild =
direction == "left" ? idxOfLeftChild : idxOfRightChild;
const child = direction == "left" ? leftChild : rightChild;
this.values[idxOfChild] = this.values[idxOfTarget];
this.values[idxOfTarget] = child;
idxOfTarget = idxOfChild;
}
// 자식이 없을 때
if (!leftChild) {
// 자식이 추가될 때는 왼쪽 자식부터 추가되는 힙의 구조상 왼쪽 자식이 없다는 건,
// 오른쪽 자식도 없다는 것이다.
// 따라서 더 이상 내려갈 수 없다.
// debugger;
return dequeued;
}
// 오른쪽 자식이 없을 때
if (!rightChild) {
if (leftChild.priority < lastItem.priority) {
swap.call(this, "left");
// debugger;
continue;
}
// debugger;
return dequeued;
}
// 두 자식이 모두 존재하면서, 두 자식의 우선순위가 같을 때
// 최소 힙의 구조상 bubbleDown되는 노드가 어느 쪽에서 올라왔든,
// 두 자식 모두의 우선순위보다 높을(작을) 수는 없다
// 그런데 두 자식의 우선순위가 같다는 것은,
// bubbleDown되는 노드의 우선순위가 두 자식의 우선순위보다 낮다는(크다는) 것이므로,
// 왼쪽이든 오른쪽이든 내려가야 한다.
if (leftChild.priority == rightChild.priority) {
swap.call(this, "left");
// debugger;
continue;
}
if (
leftChild.priority < rightChild.priority &&
leftChild.priority < lastItem.priority
) {
// 두 자식이 모두 존재할 때 && 왼쪽으로 swap할 때
swap.call(this, "left");
// debugger;
continue;
}
// 두 자식이 모두 존재할 때 && 오른쪽으로 swap할 때
if (
rightChild.priority < leftChild.priority &&
rightChild.priority < lastItem.priority
) {
swap.call(this, "right");
// debugger;
continue;
}
}
},
};
const WeightedGraph = {
init: function () {
this.adjacencyList = {};
this.length = 0;
},
addVertex: function (vertex) {
if (!this.adjacencyList.hasOwnProperty(vertex)) {
this.adjacencyList[vertex] = {};
this.length++;
}
},
addEdge: function (vertex1, vertex2, weight) {
this.addVertex(vertex1);
this.addVertex(vertex2);
this.adjacencyList[vertex1][vertex2] = weight;
// 지향성 그래프를 만들고자 한다면 아래 작업을 생략하면 된다.
this.adjacencyList[vertex2][vertex1] = weight;
return this.adjacencyList;
},
removeEdge: function (vertex1, vertex2) {
if (!this.adjacencyList.hasOwnProperty(vertex1)) {
return `There's no ${vertex1}`;
}
if (!this.adjacencyList.hasOwnProperty(vertex2)) {
return `There's no ${vertex2}`;
}
function removeHelper(v1, v2) {
if (!this.adjacencyList.hasOwnProperty(v1)) {
return `There's no edge between ${v1} and ${v2}`;
}
delete this.adjacencyList[v1][v2];
if (Object.keys(this.adjacencyList[v1]).length == 0) {
delete this.adjacencyList[v1];
}
}
removeHelper.call(this, vertex1, vertex2);
removeHelper.call(this, vertex2, vertex1);
return this.adjacencyList;
},
removeVertex: function (vertex) {
if (!this.adjacencyList.hasOwnProperty(vertex)) {
return `There's no ${vertex}`;
}
const edges = this.adjacencyList[vertex];
for (const key in edges) {
this.removeEdge(key, vertex);
}
return this.adjacencyList;
},
findShortestRoute: function (start, end) {
if (!start || !end) {
throw Error("출발지와 도착지를 모두 입력해야 합니다.");
}
// 초기화
const distance = {};
const previous = {};
const pq = Object.create(PriorityQueue);
pq.init();
pq.enqueue(start, 0);
const visited = {};
const hashOfVertex = this.adjacencyList;
for (const vertexName in hashOfVertex) {
const priority = vertexName == start ? 0 : Infinity;
distance[vertexName] = priority;
previous[vertexName] = null;
}
while (true) {
let current = pq.dequeue();
current = current.val;
if (current == end) {
break;
}
const neighbors = hashOfVertex[current];
for (const vertexName in neighbors) {
if (visited.hasOwnProperty(vertexName)) {
continue;
}
const distFromStart = distance[current] + neighbors[vertexName];
if (distFromStart < distance[vertexName]) {
pq.enqueue(vertexName, distFromStart);
distance[vertexName] = distFromStart;
previous[vertexName] = current;
}
debugger;
}
visited[current] = true;
}
let node = end;
const route = [];
while (node) {
route.unshift(node);
node = previous[node];
}
return route;
},
};
const wg = Object.create(WeightedGraph);
wg.init();
wg.addEdge("A", "B", 4);
wg.addEdge("A", "C", 2);
wg.addEdge("B", "E", 3);
wg.addEdge("C", "D", 2);
wg.addEdge("C", "F", 4);
wg.addEdge("D", "E", 3);
wg.addEdge("D", "F", 1);
wg.addEdge("E", "F", 1);
wg.findShortestRoute("A", "E");