테스트 하나에 오랜 시간 거의 반나절 쩔쩔 거렸던 것을 공유하고자 한다......

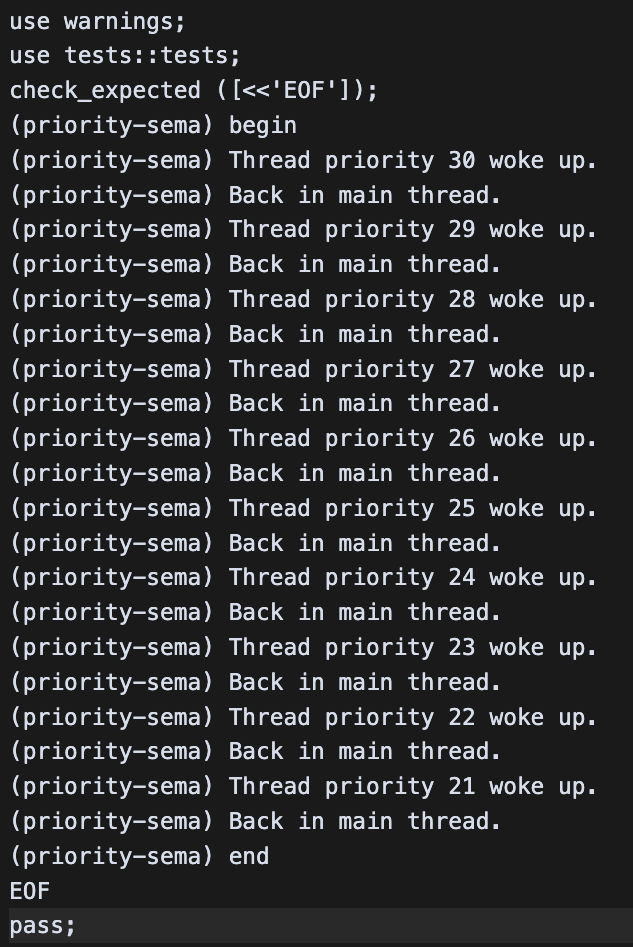
테스트 케이스 ⬆️
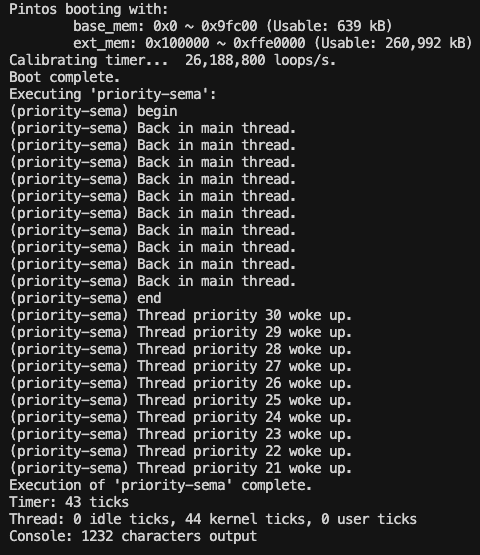
내 결과....

도대체 문제가 무엇일까?
static thread_func priority_sema_thread;
static struct semaphore sema;
void
test_priority_sema (void)
{
int i;
/* This test does not work with the MLFQS. */
ASSERT (!thread_mlfqs);
sema_init (&sema, 0);
thread_set_priority (PRI_MIN);
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
int priority = PRI_DEFAULT - (i + 3) % 10 - 1;
char name[16];
snprintf (name, sizeof name, "priority %d", priority);
thread_create (name, priority, priority_sema_thread, NULL);
}
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
sema_up (&sema);
msg ("Back in main thread.");
}
}
static void
priority_sema_thread (void *aux UNUSED)
{
sema_down (&sema);
msg ("Thread %s woke up.", thread_name ());
}let's look at the code!
thread_create가 호출될 때, priority_sema_thread 함수가 실행된다.
이 함수에선 sema_down을 호출한다.
void
sema_down (struct semaphore *sema) {
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (sema != NULL);
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
old_level = intr_disable ();
while (sema->value == 0) {
/* list_insert_ordered 추가 */
list_insert_ordered(&sema->waiters, &thread_current()->elem, compare_priorities, NULL);
thread_block ();
}
sema->value--;
intr_set_level (old_level);
}sema_down 함수는 interrupt를 비활성화 하고,
sema->value가 0이면, sema->waiters에 현재 element를 insert 한다.
sema_init (&sema, 0);
이 코드를 보면 init 자체를 0으로 초기화한다.
semaphore는 value가 0일 때,
다른 스레드가 접근하지 못하게 동기화를 제공하는 역할을 하는게 sema_down(),
value를 1로 만들어, 다시 접근할 수 있게 만드는게 sema_up() 이다.
어찌됬든 테스트 설명으로 들어가보자.
thread_create() -> priority_sema_thread() -> sema_up()
크게 작업을 보면 이렇게 볼 수 있다.
tid_t /* 시작 지점 */
thread_create (const char *name, int priority,
thread_func *function, void *aux) {
...
...
...
/* Add to run queue. */
thread_unblock (t);
if (t->priority > thread_get_priority()) {
thread_yield();
}
return tid;
}thread_create()가 호출 되었을 때, 한 스레드 씩 작업을 하게 만들면 되는거 아니야?라는 생각으로 계속 아직 완벽히 이해하지 못한, lock()을 사용해 보기도 하고, semaphore를 계속 이 사이에 넣어보면서 테스트 해보았는데
결과는?
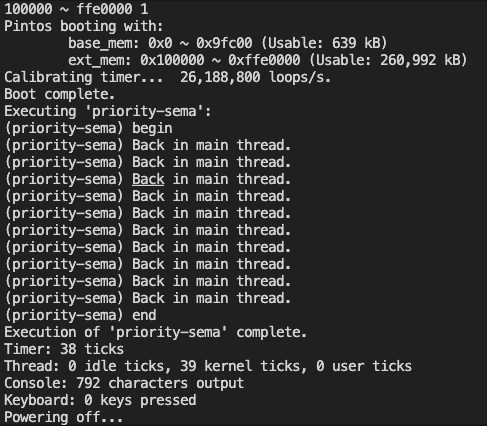
다를게 없잖아...
혼자서 계속 끙끙거리다 도저히 안되겠다는 심정으로
우리 팀의 gosu 양00에게 어떻게 해결할 수 있을까?
물어봤다.
2가지 조언을 해주었다.
1. ready_list가 안들어 가져 있거나
2. 재스케줄링이 되지 않았거나
이렇게 2가지를 얘기했다.
1번은 틀리지 않음을 확신했다.
왜냐하면 코드를 다 확인 해보았다 ^___^
그래서 스케줄링 후 우선순위 재정렬을 보자.
스케줄링 이후 실행되는 것은 sema_up()
thread_create() 함수를 실행할 때, thread_yield()를 통해 스케줄링을 처리한다.
void
sema_up (struct semaphore *sema) {
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (sema != NULL);
old_level = intr_disable ();
if (!list_empty (&sema->waiters)) {
/* 정렬 후 priority가 가장 큰 값을 불러온다. */
list_sort(&sema->waiters, compare_elements, NULL);
struct thread *unblock_thread = list_entry (list_pop_front (&sema->waiters),
struct thread, elem);
thread_unblock (unblock_thread);
}
sema->value++;
intr_set_level (old_level);
}스케줄링 처리를 하기 위해서 interrupt가 활성화 되어 있어야 한다.
그렇다면 intr_set_level(old_level) 이후 코드를 추가하면 될 것이라 생각했다.
void
sema_up (struct semaphore *sema) {
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (sema != NULL);
old_level = intr_disable ();
struct thread *unblock_thread;
if (!list_empty (&sema->waiters)) {
/* 정렬 후 priority가 가장 큰 값을 불러온다. */
list_sort(&sema->waiters, compare_priorities, NULL);
unblock_thread = list_entry (list_pop_front (&sema->waiters),
struct thread, elem);
thread_unblock(unblock_thread);
}
sema->value++;
intr_set_level (old_level);
// /* running thread의 우선 순위보다 높은 thread일 경우 reschedule */
thread_yield();
}마지막 2줄, 최종적으로 현재 실행중인 thread 보다 ready_list로 들어온 thread의 priority가 높다면, 재스케줄 해라!
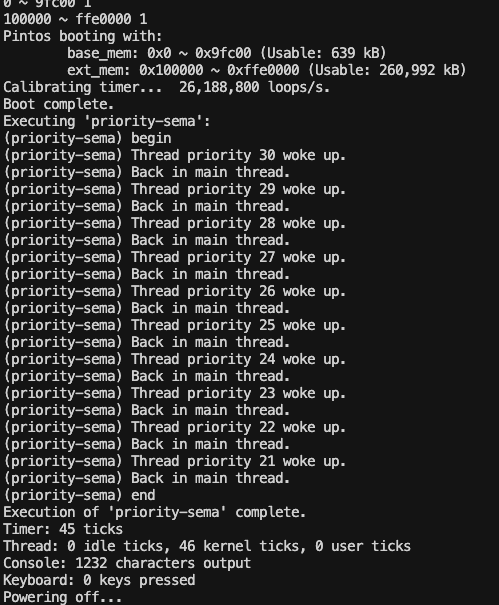
이렇게 문제를 해결했다.
재스케줄 하는 이유는
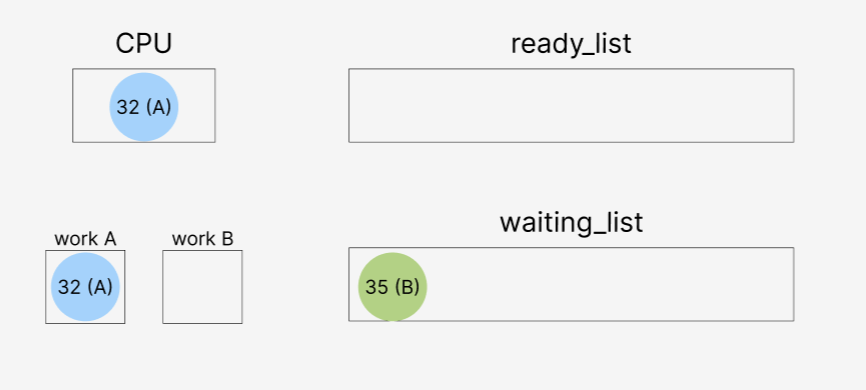
A를 작업중인 우선순위 32가 있었는데, sema_up() 호출로 인하여
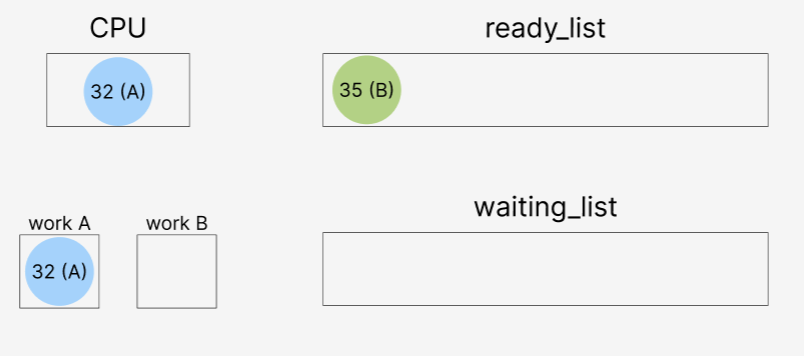
35가 ready_list로 이동한 후,
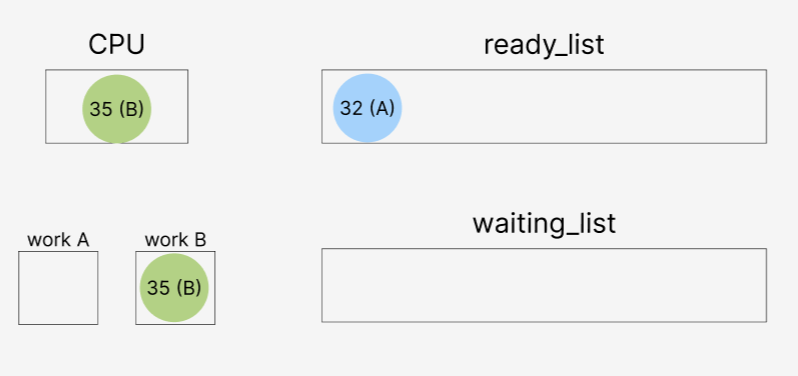
35가 더 높은 우선순위를 갖고 있기 때문에 현재 thread를 35로 바꾸어주는 작업이다.
이 하나의 테스트에 참 많은 시간을 쏟았다니...
다음 문제, 다음 주 project들이 기대된다.
하하하하하하


