[백준/7420] [Java] 맹독 방벽
문제
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/7420
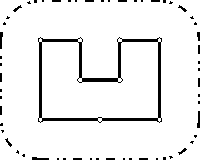
틀렸던 문제여서 오답노트 용으로 씁니다.
풀이
맹독 방벽을 지을 때 가능한 적게 지어야 하므로 건물들의 외곽선을 구하는 볼록 껍질 유형의 문제입니다. 각 건물에서 맹독 방벽이 L이상 거리를 유지해야 하므로 외곽 건물들을 중심으로 반지름이 L인 원들을 끈으로 둘러싼 형태로 방벽을 만듭니다.
그림으로 표현하면 다음과 같습니다.
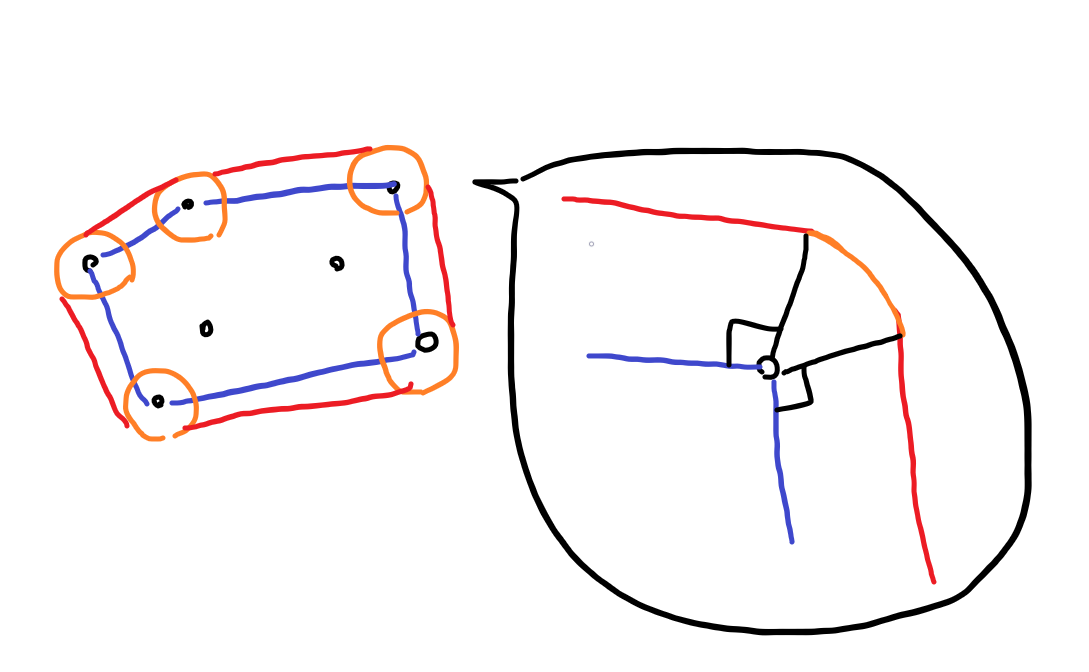
맹독 방벽의 길이는 빨간 선(=파랑 선)과 주황 선 길이의 합입니다.
1. 볼록 껍질
외곽 건물을 알아내기 위해 그라함 스캔(Graham's scan) 알고리즘을 사용합니다.
이 알고리즘은 간략하게 다음과 같습니다.
1.모든 정점을 가장 아래, 그 중 가장 왼쪽 정점을 기준으로 시계 반대 방향으로 정렬
2.정점들을 이으며 다각형의 변을 만드는데 다음 정점을 이어 변을 만들었을 때 볼록하지 않으면 이전에 연결했던 정점들을 조건을 만족할 때 까지 삭제해 줍니다.
볼록 여부는 ccw 알고리즘을 통해 구합니다.
볼록 껍질을 통해 파란 선 길이를 구할 수 있고 이는 빨간 선과 길이가 같습니다.
2. 호 길이 구하기
방벽의 각 모서리는 반지름의 길이가 L인 원의 일부, 호의 형태입니다. 호의 길이는 원의 둘레 x 호의 각 / 360 °이고 호의 각은 360 ° - 볼록 껍질 모서리의 각도 - 180 °이므로 각 볼록 껍질 모서리의 각도를 통해 구할 수 있습니다.
모서리의 각도는 벡터의 내적을 사용해 구했습니다.
int inner = v1[0]*v2[0] + v1[1]*v2[1];
double theta = Math.acos(inner / (sizeOfVector(v1) * sizeOfVector(v2)));
answer += 2 * Math.PI * l * (theta / (2 * Math.PI));전체 코드
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class BJ_7420_맹독방벽 {
static int n, l;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(in.readLine());
n = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
l = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int[][] vertice = new int[n][2];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(in.readLine());
vertice[i][0] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
vertice[i][1] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
int idx = 0;
//가장 y좌표가 작은 점 찾기. y좌표가 같다면 x좌표가 가장 작은 값.
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if((vertice[i][1] < vertice[idx][1]) ||
(vertice[i][1] == vertice[idx][1] && vertice[i][0] < vertice[idx][0])) {
idx = i;
}
}
int tx = vertice[idx][0];
int ty = vertice[idx][1];
vertice[idx][0] = vertice[0][0];
vertice[idx][1] = vertice[0][1];
vertice[0][0] = tx;
vertice[0][1] = ty;
//기준점을 중심으로 시계 반대 방향으로 정렬
Arrays.sort(vertice, (Comparator<int[]>) (int[] v1, int[] v2) -> {
int val = ccw(vertice[0], v1, v2);
if(val == 0) {
return (v1[0]-vertice[0][0])*(v1[0]-vertice[0][0]) + (v1[1]-vertice[0][1])*(v1[1]-vertice[0][1])
- (v2[0]-vertice[0][0])*(v2[0]-vertice[0][0]) - (v2[1]-vertice[0][1])*(v2[1]-vertice[0][1]);
}
return -val;
});
//그라함 스캔 알고리즘
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.add(0);
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
while(stack.size() >= 2) {
int v1 = stack.pop();
int v0 = stack.peek();
int val = ccw(vertice[v0], vertice[v1], vertice[i]);
if(val == 0) {
break;
}
else if(val < 0) {
continue;
} else {
stack.add(v1);
break;
}
}
stack.add(i);
}
// 외곽점들 집합
int[] shell = new int[stack.size()];
for(int i = shell.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
shell[i] = stack.pop();
}
double answer = 0;
// 방벽은 각 외곽점을 중심으로 반지름이 L인 원들을 둘러싼 모양.
// = 각 원 사이의 거리 + 원들의 일부. 원의 일부, 즉 호는 각도 계산으로 구함.
for(int i = 0; i < shell.length; i++) {
int next = shell[(i + 1) % shell.length];
int here = shell[i];
int nnext = shell[(i + 2) % shell.length];
int v1[] = new int[] {vertice[next][0]-vertice[here][0], vertice[next][1]-vertice[here][1]};
int v2[] = new int[] {vertice[nnext][0]-vertice[next][0], vertice[nnext][1]-vertice[next][1]};
answer += sizeOfVector(v1);
int inner = v1[0]*v2[0] + v1[1] * v2[1];
double theta = Math.acos(inner / (sizeOfVector(v1) * sizeOfVector(v2)));
answer += 2 * Math.PI * l * (theta / (2 * Math.PI));
}
System.out.println(Math.round(answer));
}
static double sizeOfVector(int[] v) {
return Math.sqrt(Math.pow(v[0], 2) + Math.pow(v[1], 2));
}
static int ccw(int[] v0, int[] v1, int[] v2) {
return (v1[0]-v0[0]) * (v2[1]-v1[1]) - (v1[1]-v0[1])*(v2[0]-v1[0]);
}
}
