1. ex01 : print_groups
https://neul-carpediem.tistory.com/78
https://blog.naver.com/whdgml1996/222036754903
1. 문제의 조건은 FT_USER 에 포함된 login 가 포함된 그룹을 list 형식으로 해봐라.
cat print_groups.sh### id -Gn $FT_USER | tr ' ' ',' | tr -d '\n'쉘 변수와 환경 변수
자주 필요한 정보를 저장하여 사용자가 사용하기 편리하게 해주는 것, 프로세스가 컴퓨터에서 동작하는 방식에 영향을 미치는 동적인 값들의 모임이다.
환경변수는 설정을 export FT_USER='dsfsdf" 이런식으로 한다.
export FT_USER='daemon'id : 현재 사용자의 실제 id와 유효 사용자 id, 그룹 id를 출력
man id 를 보면 -G , -n 인자가 있다.
-G (--groups) 추가 그룹의 ID 를 출력
Display the different group IDs (effective, real and supplementary) as white-space separated numbers, in no particular order.
-n : Display the name of the user or group ID for the -G, -g and -u options instead of the number. If any of the ID numbers cannot be mapped into names, the number will be displayed as usual.
하지만 , 형식과 '\n'을 지워야함.
tr을 이용 tr [a][b] : a를 b 로 translate 하라.
NAME:
tr - translate or delete characters
SYNOPSIS:
tr [OPTION]... SET1 [SET2]
DESCRIPTION:
Translate, squeeze, and/or delete characters from standard input, writing to
standard output.
-d, --delete
delete characters in SET1, do not translate
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/38206797/comma-separated-list-from-ft-user2. ex02 find_sh
cat find_sh.shfind . -type f -name "*.sh" | xargs -I{} basename {} | rev | cut -c 4- | rev
find 명령어 . -> 현재 디렉토리, 하위 디렉토리, 타입은 file
name 은 .sh 로 끝나야함.
xargs 는 입력값을 받아서 명령어를 실행함. basename 은 경로를 받아서, 순수파일명 만을 출력해줌.
rev 는 역순으로 하는 명령어
cut -c 4- 는 4번째 자리부터 끝까지만을 남긴다는 의미
다시 역순으로 해주면 .sh 가 제거된 것을 확인할 수 있다.
cf ) sed 도 알아놓기
3. ex03 count_files
https://devconnected.com/how-to-count-files-in-directory-on-linux/
http://minsone.github.io/shell/shell-dev-null
cat count_files.shfind . 2> /dev/null | wc -l | tr -d ' '3.문제의 조건 : 1. .를 포함시키자. 2. 현재 하위 디렉토리, 파일 2 개수
wc -l : wordline character을 줄(개행문자)의 수로 표시한다. -> 파일 또는 디렉토리의 개수. '..' 를 제외한 수이다.
~~_WC(1) User Commands WC(1)
NAME
wc - print newline, word, and byte counts for each file
SYNOPSIS
wc [OPTION]... [FILE]...
wc [OPTION]... --files0-from=F
DESCRIPTION
Print newline, word, and byte counts for each FILE, and a total line if more
than one FILE is specified. A word is a non-zero-length sequence of characters
delimited by white space.
With no FILE, or when FILE is -, read standard input.
The options below may be used to select which counts are printed, always in the
following order: newline, word, character, byte, maximum line length.
-c, --bytes
print the byte counts
-m, --chars
print the character counts
-l, --lines
print the newline counts_~~2> /dev/null => 추가적이기는 한데, 만약 오류가 발생했을 때 제거해주는 것
2 : 오류라는 뜻임. 정상적으로 흐름이 진행되면 당연히 오류가 안생기겠지? 혹시 몰라서..
When recursively counting files in a directory, you might not be authorized to explore every single subentry, thus having permission denied errors in your console.
permission denied folder linux
In order for the error messages to be redirected, you can use “output redirection” and have messages redirected to “/dev/null”.
Count Files Recursively using find
In order to count files recursively on Linux, you have to use the “find” command and pipe it with the “wc” command in order to count the number of files.
$ find -type f | wc -l
As a reminder, the “find” command is used in order to search for files on your system.
When used with the “-f” option, you are targeting ony files.
4. ex04 MAC
// mac 환경이어서 다시 봐야 할거같은데..
1. 문제의조건 : MAC address!
cat MAC.shifconfig -a | grep 'ether ' | awk ' { print $2 }
https://cets.seas.upenn.edu/answers/find-mac-address.htmlman ifconfig 를 봐보자-> ifconfig -a : 모든 네트워크 인터페이스 구성 확인.
ifconfig -- configure network interface parameters
SYNOPSIS
ifconfig [-L] [-m] [-r] interface [create] [address_family] [address [dest_address]] [parameters]
ifconfig interface destroy
ifconfig -a [-L] [-d] [-m] [-r] [-u] [-v] [address_family]
ifconfig -l [-d] [-u] [address_family]
ifconfig [-L] [-d] [-m] [-r] [-u] [-v] [-C]
ifconfig interface vlan vlan-tag vlandev iface
ifconfig interface -vlandev iface
ifconfig interface bonddev iface
ifconfig interface -bonddev iface
ifconfig interface bondmode lacp | static
DESCRIPTION
The ifconfig utility is used to assign an address to a network interface and/or configure network interface parameters.grep : 입력으로 전달된 파일의 내용에서 특정 문자열을 찾고자할 때 사용하는 명령어
grep이 파일의 문자열을 검색할 때, 단순 문자열 매칭이 아니라, 정규 표현식(Regular Expression)에 의한 패턴 매칭(Pattern Matching) 방식을 사용하기 때문입니다.
매칭되는 PATTERN이 존재하지 않는 라인 선택 grep -v "STR" [FILE]
grep 사용 예 명령어 옵션
대상 파일에서 문자열 검색 grep "STR" [FILE]
현재 디렉토리 모든 파일에서 문자열 검색 grep "STR" *
특정 확장자를 가진 모든 파일에서 문자열 검색 grep "STR" *.ext
대소문자 구분하지 않고 문자열 검색 grep -i "STR" [FILE]
매칭되는 PATTERN이 존재하지 않는 라인 선택 grep -v "STR" [FILE]
단어(Word) 단위로 문자열 검색 grep -w "STR" [FILE]
검색된 문자열이 포함된 라인 번호 출력 grep -n "STR" [FILE]
하위 디렉토리를 포함한 모든 파일에서 문자열 검색 grep -r "STR" *
최대 검색 결과 갯수 제한 grep -m 100 "STR" FILE
검색 결과 앞에 파일 이름 표시 grep -H "STR" *
문자열 A로 시작하여 문자열 B로 끝나는 패턴 찾기 grep "A.*B" *
0-9 사이 숫자만 변경되는 패턴 찾기 grep "STR[0-9]" *
문자열 패턴 전체를 정규 표현식 메타 문자가 아닌
일반 문자로 검색하기 grep -F "*[]?..." [FILE]
정규 표현식 메타 문자를 일반 문자로 검색하기 grep "\*" [FILE]
문자열 라인 처음 시작 패턴 검색하기 grep "^STR" [FILE]
문자열 라인 마지막 종료 패턴 검색하기 grep "$STR" [FILE]https://recipes4dev.tistory.com/157
두번째 필드인 것만 출력해라 : AWK-> 액션 : print 필드 : $2 -> 두번째의 필드를 선택해라.
awk는 파일로부터 레코드(record)를 선택하고, 선택된 레코드에 포함된 값을 조작하거나 데이터화하는 것을 목적으로 사용하는 프로그램입니다.
awk [OPTION...] [awk program] [ARGUMENT...]
OPTION
-F : 필드 구분 문자 지정.
-f : awk program 파일 경로 지정.
-v : awk program에서 사용될 특정 variable값 지정.
awk program
-f 옵션이 사용되지 않은 경우, awk가 실행할 awk program 코드 지정.
ARGUMENT
입력 파일 지정 또는 variable 값 지정.pattern과 action은 모두 생략이 가능한데, pattern이 생략되는 경우, 매칭 여부를 검사할 문자열 패턴 정보가 없기 때문에 모든 레코드가 선택되고, action을 생략하면, 기본 액션인 print가 실행되는 것입니다.
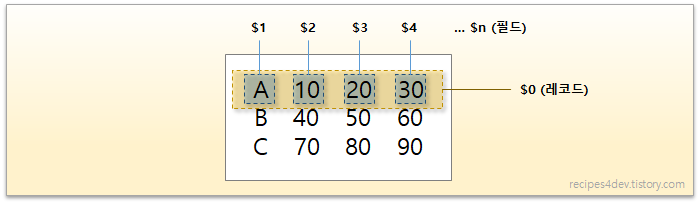
https://recipes4dev.tistory.com/171
5. ex05 Can you create it
1. 조건 : 2바이트 개행문자 출력 x , escape character 을 알아? 특수문자를 잘 처리해 줘야해, 시간하고 권한도 혹시 모르니까 맞춰주자
1)
touch \\?$\*\'MaRViN\'\*\$?\\\" echo -n "42" > \"\\\?\$\*\'MaRViN\'\*\$\?\\\"각각의 특수 문자 마다 \ 를 붙여준다.
기본적으로 쉘에서는 개행문자를 같이 출력.. ->에코에 -n 인자
따라서 3바이트가 되는데 문제에서는 2바이트로 맞추라고 했으므로, 다음과 같이 에코에 -n 인자를 통해 해결하였다.
https://unix.stackexchange.com/questions/412835/append-text-with-echo-without-new-line
-n Do not print the trailing newline character. This may also be achieved by appending `\c' to the end of the
string, as is done by iBCS2 compatible systems. Note that this option as well as the effect of `\c' are imple-
mentation-defined in IEEE Std 1003.1-2001 (``POSIX.1'') as amended by Cor. 1-2002. Applications aiming for
maximum portability are strongly encouraged to use printf(1) to suppress the newline character.2) -> 특수문자는 escape character 를 통해 해결하였다.
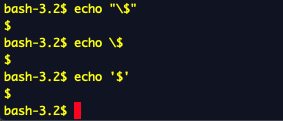
3) touch -t "10021221" \"\?*\'MaRViN\'*\?\"
6. ex06
cat skip.shls -l | awk 'NR %2 ==1'awk 명령의 입력
으로 파일로부터 데이터를 분류한 다음 분류된 텍스트 데이터를 바탕으로 패턴 매칭 여부를 검사하거나 데이터 조작 및 연산 등을 수행하고 그 결과를 출력한다.
NR 변수 : 각 레코드들의 번호는 awk의 빌트인 변수 NR에 저장된다. 레코드가 저장된 다음 NR의 값은 하나씩 증가한다.
레코드와 필드
레코드
awk는 입력 데이터를 볼 수 없지만 포맷 또는 구조는 볼 수 있다. 레코드라고 불리는 각 라인은 newline으로 분리.
$ awk '{print NR, $0}' awkfile
>
1 홍 길동 3324 5/11/96 50354
2 임 꺽정 5246 15/9/66 287650
3 이 성계 7654 6/20/58 60000
4 정 약용 8683 9/40/48 365000
필드
각 레코드는 디폴트로 공백이나 탭으로 분리된 필드라는 워드로 구성된다. NF에 필드의 수를 유지하며 라인당 100개의 필드를 가질 수 있다
$ awk '{print $1, $2, $5, NF}' awkfile
>
홍 길동 50354 5
임 꺽정 287650 5
이 성계 60000 5
정 약용 365000 51. awk 'NR%2==0{ print $0 }'
2. awk 'NR%2'
3. awk '0 '
4. awk '"0"'
5. awk 'NR>5&&NR<10'
6. awk "$0 = NR" "$0"
1번은 짝수줄 NR%2==0이면 출력하라 { print $0 }는 뜻이다.
2번은 홀수줄이면 출력하라는 뜻이다. 왜냐하면 NR이 홀수줄이면 NR%2가 0이 아니므로 드폴트 액션인 { print $0 }이 출력되기 때문이다. 여기서 NR%2의 값은 0 또는 1인데 0은 false를 뜻하고 0이 아닌 숫자는 true를 뜻한다.
3번은 아무 줄도 출력하지 않느다. 왜냐하면 항상 0, false이기 때문이다.
4번은 항상 출력한다. "0"은 문자열이기 때문에 항상 참이다.
5번은 6,7,8,9 줄을 출력한다.
6번은 줄 앞에 줄번호를 붙인다. $0은 현재 레코드인데 $0 = NR" "$0은 $0에 NR" "$0을 대입하라는 의미이다. 중간에 " "은 단지 줄번호(NR)과 레코드($0) 사이에 공간을 두기 위해 붙인 문자열에 지나지 않는다.7. ex07
cat r_dwssap.shexport FT_LINE1=7
export FT_LINE2=15 cat /etc/passwd | grep -v '^#' | awk 'NR%2==0' | cut -f 1 -d ':' | rev | sort -r | sed -n "${FT_LINE1},${FT_LINE2}p" | tr '\n' ',' | sed 's/,/, /g' | sed 's/, $/./' | tr -d '\n'grep 에 관련된 명령어
https://recipes4dev.tistory.com/157
https://pdseulpace.tistory.com/17
매칭되는 PATTERN이 존재하지 않는 라인 선택 grep -v "STR" [FILE] -> patter ^ : 시작을 의미
awk -> 짝수 줄만 출력 !
cut -f 1 -d ':' : -f ( 필드인자) 1 첫번째 필드 -d ':' (delimiter : 구분자 ':' 를 기준으로 구분한다)
rev : 거꾸로 뒤집는다.
sort -r 알파벳 역순으로 정렬 !
sed -n, p 는 붙어다님, -n sed 로 작업한 부분만 억제하여 출력, p는 출력을 뜻함.
tr '\n' 로 바꿈
sed , 를 , (스페이스) 로 바꿈 , global 하게
sed , (스페이스) 마지막 꺼만 .로 바꿈
\n 를 삭제함.
sed 설명 ! : https://jhnyang.tistory.com/287
8. ex08
cat add_chelou.sh echo $FT_NBR2 + $FT_NBR1 | tr 'mrdoc' '01234' | tr '\\\"\?\!' '1234' | tr "\'" "0" | xargs echo 'obase=13; ibase=5;' | bc | tr 0123456789ABC 'gtaio luSnemf'export FT_NBR1=\\\'\?\"\\\"\'\\
export FT_NBR2=rcrdmdddexport FT_NBR1=\\\"\\\"\!\\\"\\\"\!\\\"\\\"\!\\\"\\\"\!\\\"\\\"\!\\\"\\\"
export FT_NBR2=dcrcmcmooododmrrrmorcmcrmomo작은따옴표로 감사진 문자열은 변화 없이 그대로 출력.
큰따옴표 안에 넣으면 변수가 실제값으로 치환된 후 출력
xargs : 두 개 이상의 명령어를 조합할 때 사용. 앞 명령어의 결과를 다음 명령어의 입력으로 넘겨주는 파이프와 함께 사용. 앞 명령어의 출력값을 다음 명령어의 인자로 넘김.
xargs echo echo "obase=13; ibase=5"의 결과를 #### xargs 명령어로 다음 명령으로 연결(파이프)
ibase는 input base로 입력값이 무슨 진수인지 지정
obase는 output base로 출력값을 무슨 진수로 표시할 것인지 지정.
bc : 리눅스 계산기 명령어 연산기호를 자동으로 인식하여 처리. bc 계산하여 처리.
https://freewin.tistory.com/240
ibase, obase 를 둘다 설정할 경우 obase 가 먼저 나와야 한다.
예제
덧셈
echo '12+34' | bc
나눗셈
echo 'scale=2;12/34' | bc
* scale 소수점 x자리 표시, 하지 않으면 정수 범위에서 계산
거듭제곱
echo '4^4^4' | bc