Locust
1. Locust란
Locust: An open source load testing tool(부하 테스트 툴).
-
특정 서버 안에서 여러명의 동시 사용자가 활동했을 때, 서버 성능에 어떤 영향을 미치는지 테스트 하는 툴
-
python 스크립트 코드로 테스트 가능한 어플리케이션
ㄴ python 스크립트 코드를 통해 웹에 어떠한 방식으로 부하를 줄지를 설정 가능
pip install locust #설치
locust -V #정상 설치 여부 확인(버전 확인)2. Locust 사용 process
2.1. 테스트를 위한 스크립트 작성
제공하는 클래스 및 함수들로 테스트 스크립트(user 1명의 요청 작업, 시간에 따른 증감수 등 다양한 커스텀 가능) 작성.
- Locust를 통해 어떤 시나리오의 부하 테스트를 하려하는지 설정 필요
2.2. Locust 웹 접속
스크립트 작성 후 부하 테스트를 위해 작성한 스크립트 실행, 모니터링 할 수 있는 Locust 웹 접속.
- 부하 생성은 Locust 웹에 접속하여 진행
# Locust 웹 실행 명령어(cmd)
locust -f <파일명>.py
# http:/localhost: -.-.-.- 을 통해 Locust 웹 접속2.3. Locust 웹에 아래 4가지 셋팅값 입력 후 웹 내 Start swarming 클릭
2.3.1. Number of users(최대 동시 user 수)
2.3.2. Spawn rate(1 초당 추가 접속할 user 수)
2.3.3. Host(부하 테스트할 서버 주소)
2.3.4. Run time(테스트를 얼마만큼 실행할 것인지) # Advanced options
- Number of users: 100, Spawn rate: 10 입력할 경우,
ㄴ '1초- 10명, 2초- 20명, 3초- 30명 ... 10초- 100명(최대)'
2.4. Locust 웹에서 결과 시각화
-
요청수, 실패 수, 종류별 응답 시간 등 확인
ㄴ Median, Average, Min 등은 각 request에 대한 response 값 -
Locust 웹 내에서 'Number of users', 'Spawn rate' 변경 가능
총 3개의 차트가 보여짐
2.4.1. Total Requests Per Seconds
ㄴ RPS(current Requests Per Seconds), 초당 Failures 시각화
2.4.2. Response Times(ms)
ㄴ Median Response Time, 95% percentile 시각화
2.4.3. Number of Users
ㄴ user 수 증가 추이
3. key point
3.1. User class
: A User class represents one type of user/scenario for your system.
ㄴ Locust에서 지정한 user의 수만큼 User class의 인스턴스가 생성됨, 생성된 각 인스턴스가 요청을 보냄
-
User class: 1명의 user를 의미
User가 3명이면 User class 인스턴스를 3개 생성
ㄴ 이 클래스 안에서 request -> response -> print 등 테스트 스크립가 작성됨 -
User class를 정의할 때 상속 받을 수 인자로는 아래 3가지가 있음
(1) User (2) HttpUser (3) FastHttpUser -
HttpUser는 client 속성이 추가되어 있어, HTTP request로 테스트 가능
ㄴ client 속성은 모든 HTTP methods를 포함 -
FastHttpUser는 HttpUser 보다 높은 코어당 RPS 성능이 높음
ㄴ https://docs.locust.io/en/stable/increase-performance.html#increase-performance -
The self.client attribute makes it possible to make HTTP calls that will be logged by Locust.
For information on how to make other kinds of requests, validate the response, etc, see
ㄴ https://docs.locust.io/en/stable/writing-a-locustfile.html#client-attribute-httpsession
3.1.1. weight
: If you wish to simulate more users of a certain type you can set a weight attribute on those classes.
ㄴ특정한 User class에 가중치를 더 주고 싶을 때 설정
# web users are three times more likely than mobile users
class WebUser(User):
weight = 3
...
class MobileUser(User):
weight = 1
...
3.1.1. wait_time
: method makes it easy to introduce delays after each task execution.
ㄴ몇 초 만큼의 간격을 두고 각 task를 실행할지 설정
ㄴIf no wait_time is specified, the next task will be executed as soon as one finishes.
wait_time = constant(n)
ㄴ constant(n) 각 task마다 고정된 n초 만큼 대기 후 요청을 보낸단 의미
wait_time = between(n, m)
ㄴ between(n, m) 각 task 마다 n초에서 m초 사이의 임의의 값만큼 대기 후 요청을 보낸단 의미
constant_pacing, constant_throughput도 있음
# to make each user wait between 0.5 and 10 seconds between every task execution
class MyUser(User):
@task
def my_task(self):
print("executing my_task")
wait_time = between(0.5, 10)3.2. Task
: 분산 테스트의 업무를 의미. 설정한 User의 수 만큼 User class 인스턴스가 생성되고, User class 인스턴스가 정의된 task들을 실행
: to be able to declare tasks for a User or a TaskSet inline in the class
task 정의 방법(way to add a task)
- task는 가상의 User가 웹에서 행하는 행위를 정의함
3.2.1. @task decorator
- 사용자 정의 함수 위에 ' @task ' 선언
class MyUser(User):
wait_time = constant(1)
@task
def my_task(self):
print("User instance (%r) executing my_task" % self)
class ForumPage(TaskSet):
@task(100)
def read_thread(self):
pass
@task(7)
def create_thread(self):
pass
@task(25)
class ForumThread(TaskSet):
@task
def get_author(self):
pass
@task
def get_created(self):
pass3.2.2. tasks attribute
from locust import User, constant
def my_task(user):
pass
class MyUser(User):
tasks = [my_task]
wait_time = constant(1)3.2.3. weight
: @task takes an optional weight argument that can be used to specify the task’s execution ratio.
# task2 will be twice as likely to be selected as task1:
class MyUser(User):
wait_time = between(5, 15)
@task(3)
def task1(self):
pass
@task(6)
def task2(self):
pass3.2.4. TaskSet
: It is a collection of tasks. If you are performance testing a website that is structured in a hierarchical way, it may be useful to structure your load test the same way.
ㄴ여러 @task를 정의할 수 있는 class
ㄴTaskSet 내 여러 @task들이 정의되어 있는 경우, random하게 진행(순차적이지 않음)
class Testset(TaskSet):
wait_time = constant(1)
@task
def view_thread(self):
pass
@task
def create_thread(self):
pass
@task
def stop(self):
self.interrupt()
3.2.5. SequentialTaskSet
: Works like TaskSet, but task weight is ignored, and all tasks are executed in order.
- '순차적으로 수행되어야 하는 task들(즉, 특정 시나리오)'을 테스트할 때 적합.
ㄴ예) 메인 페이지 → 특정 페이지 접근 → 특정 페이지 내 옵션 클릭
from locust import SequentialTaskSet, HttpUser, constant, task
class SeqTask(SequentialTaskSet):
@task
def get_status(self):
self.client.get("/1")
print("1번째 수행")
@task
def get_500_status(self):
self.client.get("/2")
print("2번째 수행")
class LoadTest(HttpUser):
host = "https://example.co.kr"
tasks = [SeqTask]
wait_time = constant(1)4. 기타 옵션
4.1. name
- name 파라미터를 통해 특정 작업의 명칭을 설정해 줄 수 있으며, 작업들을 그룹핑해 줄 수 있음
@task
def main_page(self):
self.client.get("https://ooooooo.co.kr", name = 'page')
@task
def tech_page(self):
self.client.get("https://ooooooo.co.kr/test", name = 'page')4.2. on_start(), on_stop()
1) Users (and TaskSets) can declare an on_start method and/or on_stop method.
Users
- on_start(): called during when a User
- on_stop(): called during when a User stops running
TaskSet
- on_start(): called during when the TaskSet start executing
- on_stop(): called during when the TaskSet stops executing
2) @task 아래 사용되면 안됨.
3) Locust를 이용한 부하테스트 시, 딱 한 번씩만 실행됨
def on_start(self):
self.client.get('/', name = self.on_start.__name__)
print("START LOCUST")
def on_stop(self):
self.client.get('/', name = self.on_stop.__name__)
print("STOP LOCUST")
# self.client.get('/', name = self.on_stop.__name__)
>> 결과 시각화 시, 해당 작업의 명칭을 sel.on_stop.__name__ 으로 설정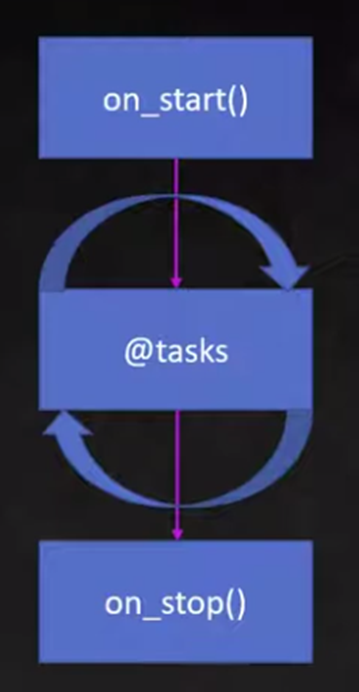
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mEIy2TkuKKM
4. 스크립트 작성
step1: 필요 기능 import
import random; import time # 테스트 스크립트 사용에 흔히 활용
from locust import HttpUser, between, task, constant참고) 결과 해석
동일한 스크립트 코드로 아래 3가지 변수를 변경해 가며 test 가능
=> 어떠한 조건에서 병목 현상이 나타나는지, request -> response가 실패하는지 확인 가능
(1) Number of Total Users, (2) Spawn rate, (3) WaitTime
https://buildabetterworld.tistory.com/124
=====================================
about locust
https://docs.locust.io/en/stable/index.html
https://docs.locust.io/en/stable/quickstart.html
https://docs.locust.io/en/stable/writing-a-locustfile.html
스크립트 작성
https://suen0904.tistory.com/24
https://etloveguitar.tistory.com/145
https://wookkl.tistory.com/67
locust 구버전 -> 신버전 변경점
https://gonigoni.kr/posts/locust-update/
읽어보고 지우기
https://colinch4.github.io/2023-09-07/12-55-47-335253/
https://me2nuk.com/Python-requests-module-example/
