What the heck is the event loop anyway?
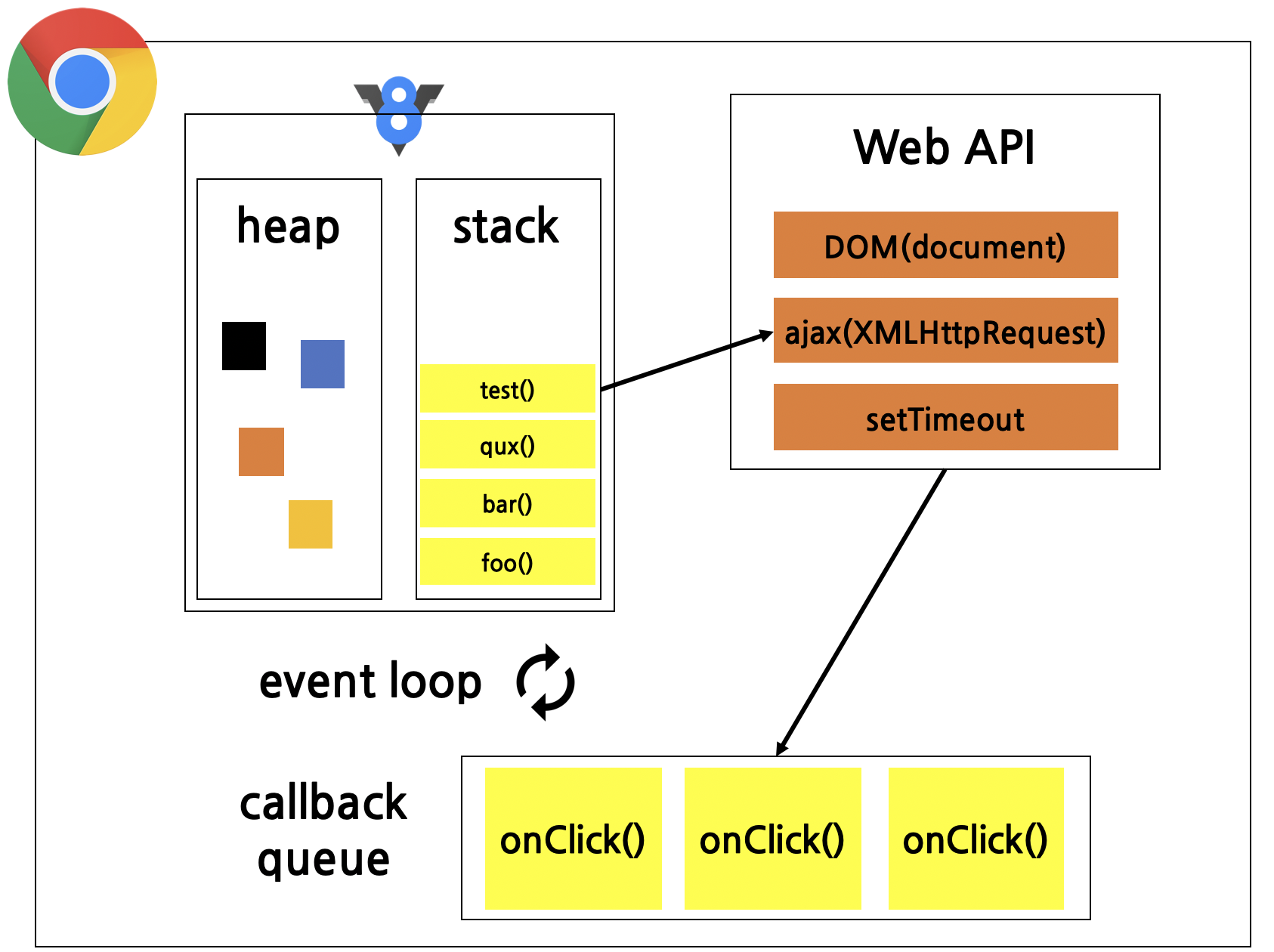
자바스크립트는 싱글 쓰레드 기반 non-blocking 방식의 비동기적인 동시성 언어이며 콜 스택, 이벤트 루프와 콜백 큐 그리고 여러가지 다른 API들을 가지고 있다.
하나의 쓰레드 = 하나의 콜 스택 = 한번에 하나의 작업
JS가 싱글 쓰레드 기반임에도 불구하고 동시성 언어라고 부르는 이유는 웹 브라우저가 제공하는 API를 통해 동시에 작업을 할 수 있기 때문이다.
-
JS runtime engine(여기서는 V8 엔진)은 Call Stack과 memory heap을 담당한다.
-
Call Stack에서 호출된 Web API 함수는(node.js 의 경우 C/C++ APIs) 비동기 콜백이 있을 경우 해당 함수를 Callback Queue에 밀어 넣는다. 비동기 콜백을 사용하는 webapi 함수로는 DOM event, fetch, setTimeout 같은 것들이 있다.
call stack
함수가 실행되면 쌓이는 공간. 먼저 호출된 함수가 가장 아래에 위치.
callback queue
callback 함수들의 대기열.
event loop
event loop 는 call stack의 함수들이 다 실행되면 callback queue에 있는 콜백함수를 하나씩 꺼내서 스택에 집어넣는다.
sync callback vs async callback
콜백이라고 해서 모두가 비동기로 처리되는 것은 아니다.
// Synchronous
[1,2,3,4].forEach((i) => {
console.log(i);
});
// Asynchronous
[1,2,3,4].forEach((i) => {
setTimeout(()=> {
console.log(i);
}, 0);
});둘 다 forEach 의 콜백함수지만 다음과 같은 일이 벌어진다.
-
sync
console.log()를 스택으로 바로 집어넣고 실행하기 때문에 스택에서 forEach가 가장 마지막에 사라진다. -
async
console.log()가 콜백큐로 가고 forEach가 사라지고 난 후에야 비로소console.log()가 하나씩 실행된다.
async 는 왜 필요한가
메인 스레드를 막지 않고 긴 시간이 걸리는 network request 를 처리할 수 있다.
callback queue 의 종류
callback queue 에는 2가지 종류의 큐가 있다.
- Message Queue for task
- Job Queue for micro task
Job queue 는 ES6 에서 promise 와 함께 나온 개념으로 micro task 를 위한 큐이다.
Job queue 는 Message queue 보다 우선권을 가진다. promise 로 처리하는 것들이 바로 이 Job queue 에 해당한다.
예시 1
// callstack
console.log('Script start');
setTimeout(() => {
// Message queue
console.log('setTimeout');
}, 0);
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// Job queue
resolve('Promise resolved');
}).then(res => console.log(res))
.catch(err => console.log(err));
// callstack
console.log('Script End');Script start
Script End
Promise resolved
setTimeout예시 2
console.log('Script start');
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('setTimeout 1');
}, 0);
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('setTimeout 2');
}, 0);
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('Promise 1 resolved');
}).then(res => console.log(res))
.catch(err => console.log(err));
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('Promise 2 resolved');
}).then(res => console.log(res))
.catch(err => console.log(err));
console.log('Script End');Script start
Script End
Promise 1 resolved
Promise 2 resolved
setTimeout 1
setTimeout 2예시 3
console.log('Script start');
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('setTimeout');
}, 0);
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('Promise 1 resolved');
}).then(res => console.log(res));
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('Promise 2 resolved');
}).then(res => {
console.log(res);
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('Promise 3 resolved');
})
}).then(res => console.log(res));
console.log('Script End');Script start
Script End
Promise 1 resolved
Promise 2 resolved
Promise 3 resolved
setTimeout