스프링 컨테이너 생성
ApplicationContext applicationContext =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);- ApplicationContext를 스프링 컨테이너라 한다.
- ApplicationContext는 인터페이스이다. 그러므로 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext는 ApplicationContext의 구현체이다.
스프링 컨테이너 생성 과정
1. 스프링 컨테이너 생성

- new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class)를 통해 스프링 컨테이너를 생성한다.
- 스프링 컨테이너를 생성할 때는 구성 정보를 지정해주어야 한다. 여기서 구성정보는 AppConfig.class로 지정하였다.
2. 스프링 빈 등록
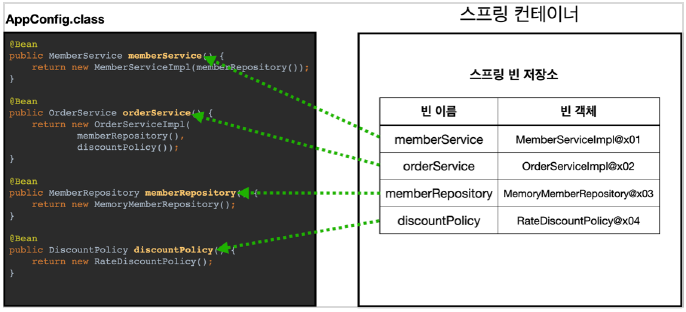
- 스프링 컨테이너에는 구성정보에서 @Bean Annotation이 등록된 메서드를 호출하여 스프링 빈으로 등록한다. 빈 name은 메서드 이름을 Key로 갖고, 빈 객체는 메서드의 반환하는 객체를 빈 객체로 등록한다.
빈 이름
- 빈 이름은 메서드 이름을 사용하며, @Bean(name="사용자 이름 지정") 과 같은 방식으로 이름을 직접 부여해줄 수 도 있다.
주의 : 빈 이름은 항상 다른 이름을 부여해야 한다. 같은 이름을 부여하면, 다른 빈이 무시되거나, 기존 빈을 덮어버리는 등 설정에 따라 오류가 발생한다.
스프링 빈 의존관계 설정
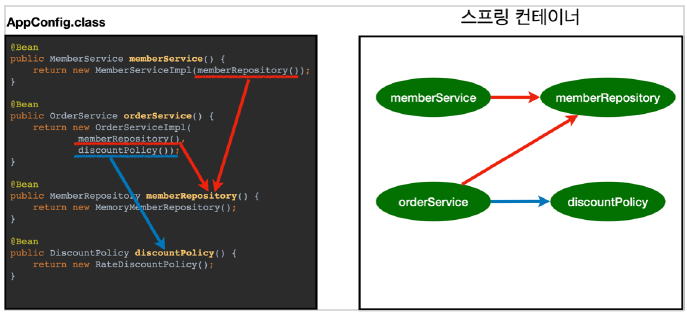
- 스프링 컨테이너는 설정 정보를 참고해서 의존관계를 주입(DI)한다.
- 단순히 자바 코드를 호출하는 것 같지만, 차이가 있다. 이 차이는 뒤에 싱글톤 컨테이너에서 설명한다고 한다.
참고
스프링은 빈을 생성하고, 의존관계를 주입하는 단계가 나누어져 있다. 그런데 이렇게 자바 코드로 스프링 빈을 등록하면 생성자를 호출하면서 의존관계도 한번에 처리된다.
컨테이너에 등록된 모든 빈 조회
스프링 컨테이너에 실제 스프링 빈들이 잘 등록 되었는지 확인해보자.
package hello2.core2.beanfind;
import hello2.core2.AppConfig;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class ApplicationContextInfoTest {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
@Test
@DisplayName("Print All Bean")
void findAllBean() {
String[] beanDefinitionNames = ac.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String beanDefinitionName : beanDefinitionNames) {
Object bean = ac.getBean(beanDefinitionName);
System.out.println("name = " + beanDefinitionName + " object = "
+ bean);
}
}
@Test
@DisplayName("Print ApplicationBean")
void findApplicationBean() {
String[] beanDefinitionNames = ac.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String beanDefinitionName : beanDefinitionNames) {
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = ac.getBeanDefinition(beanDefinitionName);
//ROLE_APPLICATION : 직접 등록한 애플리케이션 빈
//ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE : 스프링이 내부에서 사용하는 빈
if (beanDefinition.getRole() == BeanDefinition.ROLE_APPLICATION) {
Object bean = ac.getBean(beanDefinitionName);
System.out.println("name = " + beanDefinitionName + " object = " + bean);
}
}
}
}- Print All Bean 모든 빈 출력하기
- 실행하면 스프링에 등록된 모든 빈 정보를 출력할 수 있다.
- ac.getBeanDefinitionNames(): 스프링에 등록된 모든 빈 이름을 조회한다.
- ac.getBean(): 빈 이름으로 빈 객체(인스턴스)를 조회한다.
- Print ApplicationBean
- 스프링이 내부에서 사용하는 빈은 getRole()로 구분할 수 있다.
- ROLE_APPLICATION: 사용자가 정의한 빈
- ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE: 스프링이 내부에서 사용하는 빈
스프링 빈 조회 - 기본
스프링 컨테이너에서 스프링 빈을 찾는 가장 기본적인 조회 방법
- ac.getBean(빈이름, 타입)
- ac.getBean(타입)
- 조회 대상 스프링 빈이 없으면 예외 발생
- NoSuchDefinitionException : No bean named 'xxxxx' available
package hello2.core2.beanfind;
import hello2.core2.AppConfig;
import hello2.core2.member.MemberService;
import hello2.core2.member.MemberServiceImpl;
import org.assertj.core.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.*;
public class ApplicationContextBasicFindTest {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
@Test
@DisplayName("Find by bean name")
void findBeanByName(){
MemberService memberService = ac.getBean("memberService", MemberService.class);
assertThat(memberService).isInstanceOf(MemberServiceImpl.class);
}
@Test
@DisplayName("Find by bean Type without name")
void findBeanByType(){
MemberService memberService = ac.getBean(MemberService.class);
assertThat(memberService).isInstanceOf(MemberServiceImpl.class);
}
@Test
@DisplayName("Find by Impl Type")
void findBeanByName2(){
MemberService memberService = ac.getBean(MemberServiceImpl.class);
assertThat(memberService).isInstanceOf(MemberServiceImpl.class);
}
@Test
void findBeanByNameX() {
//ac.getBean("XXXXX", MemberService.class);
org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertThrows(NoSuchBeanDefinitionException.class,
() -> ac.getBean("xxxxx", MemberService.class));
}
}참고 : 구체 타입으로 조회하면 변경 시 유연성이 떨어진다.
스프링 빈 조회 - 동일한 타입이 둘 이상
- 타입으로 조회시 같은 타입의 스프링 빈이 둘 이상이면 오류가 발생한다. 이런 경우 빈 이름을 지정한다.
- ac.getBeansOfType()을 사용하면 해당 타입의 모든 빈을 조회할 수 있다.
package hello2.core2.beanfind;
import hello2.core2.member.Member;
import hello2.core2.member.MemberRepository;
import hello2.core2.member.MemoryMemberRepository;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.Map;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.*;
public class ApplicationContextSameBeanFindTest {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SameBeanConfig.class);
@Test
@DisplayName("If Same Type is found more than 2, Duplicate Error happens")
void findBEanByTypeDuplicate() {
Assertions.assertThrows(NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException.class, () ->
ac.getBean(MemberRepository.class));
}
@Test
void findBeanByName() {
MemberRepository memberRepository = ac.getBean("memberRepository1",
MemberRepository.class);
assertThat(memberRepository).isInstanceOf(MemberRepository.class);
}
@Test
void findAllBeanByType() {
Map<String, MemberRepository> beansOfType = ac.getBeansOfType(MemberRepository.class);
for (String key : beansOfType.keySet()) {
System.out.println("key = " + key + " value = " + beansOfType.get(key));
}
System.out.println("beansOfType = " + beansOfType);
assertThat(beansOfType.size()).isEqualTo(2);
}
@Configuration
static class SameBeanConfig{
@Bean
public MemberRepository memberRepository1() {
return new MemoryMemberRepository();
}
@Bean
MemberRepository memberRepository2() {
return new MemoryMemberRepository();
}
}
}참고 - 인프런 김영한 강사님의 스프링 핵심 원리 기초 강의
