해당 구현 내용은, 프로그래밍 언어에 대한 기초가 있어야 이해 가능합니다.
reference variable (비슷한 개념으로는 pointer 가 있음), 반복자 등의 개념 설명은 따로 하지 않습니다.
Java 1.5 이상 문법을 이용하여 작성한 것으로,
Iterable, Iterator, Generic 등을 이용하여 구현하였습니다.
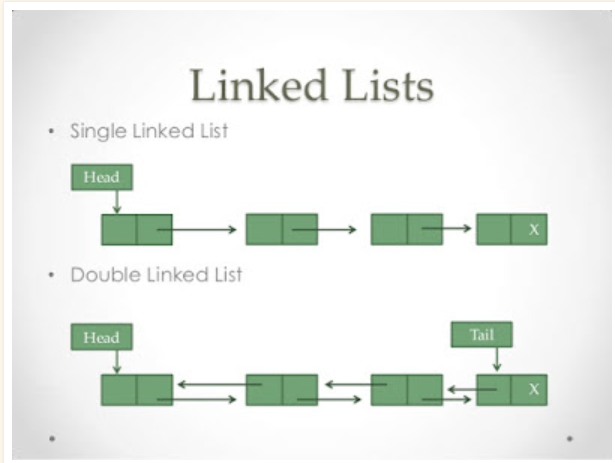
🔗 LinkedList란?
간단하게 설명하자면, 같은 형태의 데이터가 담겨져 있고,
다음 데이터를 포인터로 가리키는 자료구조를 말한다.
목차
1. 배열과의 차이점은?
2. 자료구조 설계할 때 유의점
3. LinkedList의 시간복잡도
4. 구현 코드 설명
5. 구현 코드
1. 배열과의 차이점은?
- 배열은 생성부터 크기를 지정해야하고, -> 크기를 지정하지 않는다.
- 연속된 메모리 공간을 사용한다. -> Node라는 클래스의 next 포인터로 연결하므로 연속된 메모리 공간은 아니다.
- 그렇기 때문에 배열의 추가 및 삭제는 실질적으로 불가능하다 (가능은 하지만 해당 인덱스를 null이나 0으로 초기화 하는 수 밖에 없다.) -> 추가는 tail의 next를 연결하는 방법으로 가능하다. 삭제는 해당 index 또는 해당 value를 비교하여 이 전 Node의 next를 해당 index 또는 value의 Node의 next로 바꿔주며 삭제한다. (garbage collection 이 처리)
- 한번 선언된 길이는 변경할 수 없다. -> 크기를 지정하지 않는다.
2. 자료구조 설계할 때 유의점
- 자료 구조가 비어 있을 때
- 요소가 하나만 있을 때
- 시작점의 요소 추가 / 제거
- 끝 점의 요소 추가 / 제거
- 중간의 요소에 대한 작업
3. LinkedList의 시간복잡도
- 데이터의 추가
O(1)
1. 처음과 끝 추가O(1)
2. 중간 요소 추가O(n)
- 데이터의 삭제
1. 처음과 끝 삭제O(1)
2. 중간 요소 삭제O(n)
4. 구현 코드 설명
구현해본 LinkedList 는,
Node 라는 class 를 작성한다.
Node의 field에는 data 와 next 라는 포인터를 가진다.
LinkedList의 field에는
head, tail 이 존재하고, 해당 field 모두 Node 의 포인터 역할을 한다.
head는
자료구조가 비어 있을 때 (head == null),
하나만 있을 때, (head != null),
시작점의 요소 추가 / 제거 ( head != null) 등에서 사용할 것이다.
tail은
하나만 있을 때, (head == tail),
끝점의 요소 추가 / 제거 등에 사용할 것이다.
5. 구현 코드
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
public class LinkedList<E> implements ListI<E>,Iterable<E>{
@Override
public Iterator iterator() {
return new IteratorHelper();
}
class IteratorHelper implements Iterator<E>{
Node<E> index;
public IteratorHelper(){
index = head;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return index != null;
}
@Override
public E next() {
if (!hasNext()){
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
E val = index.data;
index = index.next;
return val;
}
}
class Node<E>{
E data;
Node<E> next;
public Node(E obj){
this.data = obj;
this.next = null;
}
}
private Node<E> head;
private Node<E> tail;
private int currentSize;
public LinkedList(){
this.head = null;
currentSize = 0;
}
// 맨 앞에 추가할 때
public void addFirst(E obj){
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(obj);
if (head == null){
head = tail = node;
currentSize++;
return;
}
node.next = head;
head = node;
currentSize++;
}
// 맨 뒤에 추가할 때
public void addLast(E obj){
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(obj);
// 요소가 비어 있을 때
if (head == null){
head = tail = node;
currentSize++;
return;
}
// O(n) 방식
/* Node<E> tmp = head;
// next 포인터가 null일 때까지 tmp를 갱신한다.
while (tmp.next != null){
tmp = tmp.next;
}
tmp.next = node;*/
tail.next = node;
tail = node;
currentSize++;
}
public void add(E obj){
addLast(obj);
}
public E removeFirst(){
if (head == null){
return null;
}
// head와 tail의 포인터가 같을시
// 요소가 한개 있다는 말이 되므로
// head와 tail을 null로 초기화한다.
Node<E> tmp = head;
if (head == tail)
head = tail = null;
else
head = head.next;
currentSize--;
return tmp.data;
}
public E removeLast(){
if (head == null){
return null;
}
// current
// previous
if (head == tail)
return removeFirst();
Node<E> current = head;
Node<E> previous = null;
// tail과 current 포인터가 같으면
// current는 tail과 같고,
// previous는 이 전 노드를 가리키게 됨.
while (tail != current) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
// tail까지 왔으면, tail 이전 previous.next를 null
// garbage collector 가 제어해준다.
previous.next = null;
tail = previous;
currentSize--;
return current.data;
}
public E remove(E obj){
if (head == null){
return null;
}
Node<E> current = head, previous = null;
// head 부터 current 가 null 일 때까지 반복하여
while (current != null){
// 매 번 두 객체를 비교하여, argument obj 와 current.data를 비교했을 때
// compareTo가 0을 return 한다면, 요소가 같다는 것이기 때문에
// head 와 tail pointer 를 비교하여 바로 삭제한다.
if (contains(obj)){
// current 가 head 와 pointer 가 같다면,
if (current == head){
return removeFirst();
}
// current 가 tail 과 같다면,
if (current == tail){
return removeLast();
}
// 만약 head 와 tail 이 아니라면,
// current.next 를 previous.next 포인터에 참조 시킨다.
// 원래 previous.next 가 가리키고 있던 current 는
// garbage collector 가 처리한다.
currentSize--;
previous.next = current.next;
return current.data;
}
// previous 에 current 를 참조시키고,
// current 는 current.next 를 참조한다.
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
return null;
}
public boolean contains(E obj){
Node<E> current = head;
while (current != null){
if (((Comparable<E>)obj).compareTo(current.data) == 0){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public E peekFirst(){
if (head == null){
return null;
}
return head.data;
}
public E peekLast(){
if (tail == null){
return null;
}
return tail.data;
}
public Node<E> getHead() {
return head;
}
public Node<E> getTail() {
return tail;
}
public String toString(){
Node<E> tmp = head;
String s = "";
while (tmp.next != null){
s += tmp.data + " ";
tmp = tmp.next;
}
s += tmp.data;
return s;
}
}
구현을 마치며
- 다음 자료구조 포스팅에서는 구현된
LikedList를 이용하여Hash Table을 구현할 예정이다. - 막상 직접 구현하려니 어려웠다🤣
혹시라도 틀린게 있거나 불편한거 있으시면 댓글 달아주세요!!
