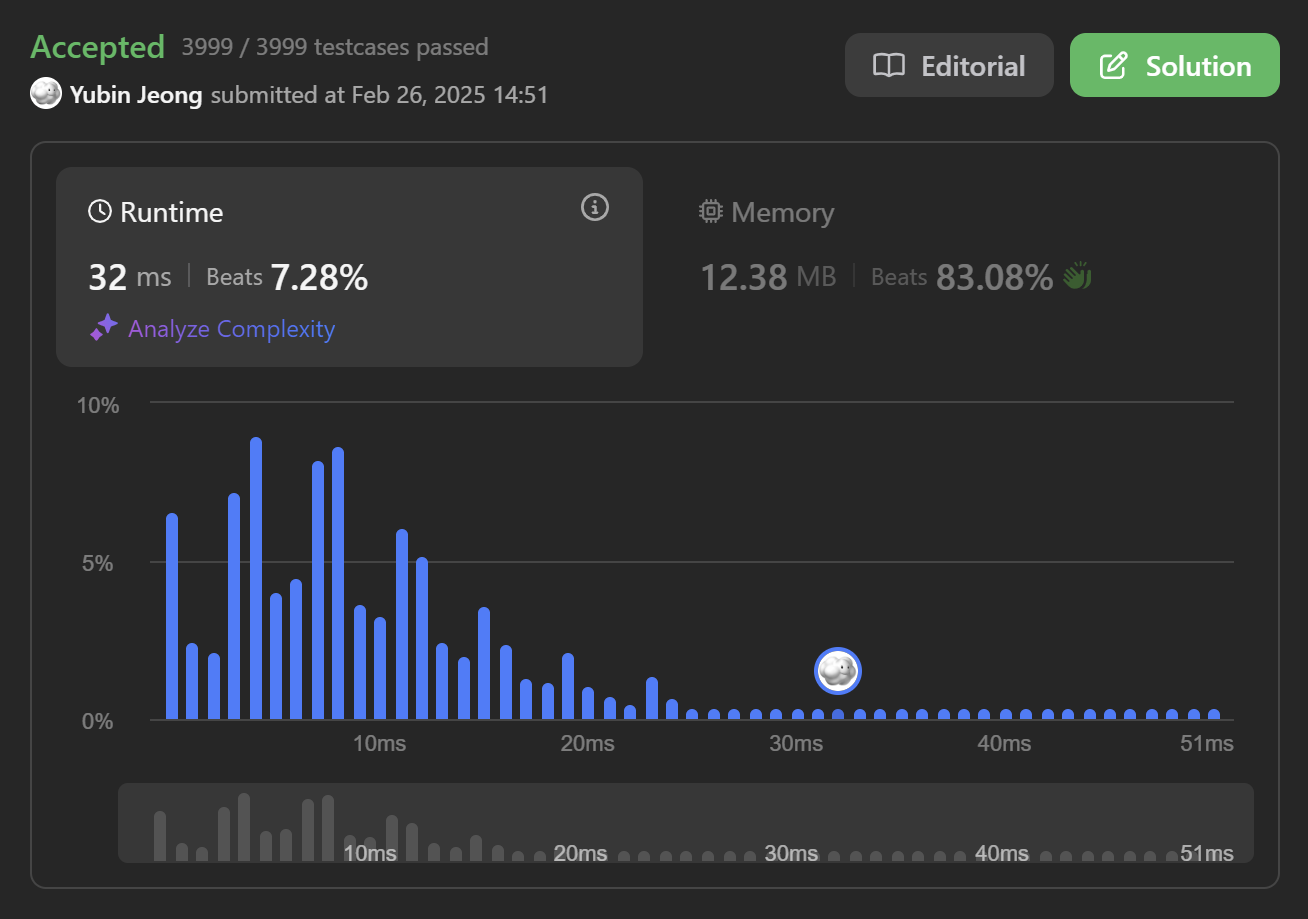
Top Interview 150
12. Integer to Roman
Medium
Seven different symbols represent Roman numerals with the following values:
| Symbol | Value |
|---|---|
| I | 1 |
| V | 5 |
| X | 10 |
| L | 50 |
| C | 100 |
| D | 500 |
| M | 1000 |
Roman numerals are formed by appending the conversions of decimal place values from highest to lowest. Converting a decimal place value into a Roman numeral has the following rules:
- If the value does not start with 4 or 9, select the symbol of the maximal value that can be subtracted from the input, append that symbol to the result, subtract its value, and convert the remainder to a Roman numeral.
- If the value starts with 4 or 9 use the subtractive form representing one symbol subtracted from the following symbol, for example, 4 is 1 (
I) less than 5 (V):IVand 9 is 1 (I) less than 10 (X):IX. Only the following subtractive forms are used: 4 (IV), 9 (IX), 40 (XL), 90 (XC), 400 (CD) and 900 (CM). - Only powers of 10 (
I,X,C,M) can be appended consecutively at most 3 times to represent multiples of 10. You cannot append 5 (V), 50 (L), or 500 (D) multiple times. If you need to append a symbol 4 times use the subtractive form.
Given an integer, convert it to a Roman numeral.
Example 1:
Input: num = 3749
Output: "MMMDCCXLIX"
Explanation:
3000 = MMM as 1000 (M) + 1000 (M) + 1000 (M) 700 = DCC as 500 (D) + 100 (C) + 100 (C) 40 = XL as 10 (X) less of 50 (L) 9 = IX as 1 (I) less of 10 (X) Note: 49 is not 1 (I) less of 50 (L) because the conversion is based on decimal places
Example 2:
Input: num = 58
Output: "LVIII"
Explanation:
50 = L 8 = VIII
Example 3:
Input: num = 1994
Output: "MCMXCIV"
Explanation:
1000 = M 900 = CM 90 = XC 4 = IV
Constraints:
1 <= num <= 3999
Code
class Solution(object):
def intToRoman(self, num):
global roman_num
roman = {1: 'I', 5: 'V', 10: 'X', 50: 'L', 100: 'C', 500: 'D', 1000: 'M'}
n_list = list(reversed(list(map(int, str(num)))))
roman_num = ""
digits = sorted(list(roman.keys()))
def func(n):
global roman_num
if n_list[n] == 1:
roman_num += roman[digits[n*2]]
elif n_list[n] == 2:
roman_num += (roman[digits[n*2]] * 2)
elif n_list[n] == 3:
roman_num += (roman[digits[(n*2)]] * 3)
elif n_list[n] == 4:
roman_num += (roman[digits[(n*2)+1]] + roman[digits[n*2]])
elif n_list[n] == 5:
roman_num += roman[digits[(n*2)+1]]
elif n_list[n] == 6:
roman_num += (roman[digits[n*2]] + roman[digits[(n*2)+1]])
elif n_list[n] == 7:
roman_num += (roman[digits[n*2]] * 2 + roman[digits[(n*2)+1]])
elif n_list[n] == 8:
roman_num += (roman[digits[n*2]] * 3 + roman[digits[(n*2)+1]])
elif n_list[n] == 9:
roman_num += (roman[digits[(n*2)+2]] + roman[digits[n*2]])
for n in range(len(n_list)):
if n == 3:
roman_num += ('M' * n_list[n])
else:
func(n)
return ''.join(reversed(roman_num))무식하게 푼 방법이다.
예를 들어, 3749를 생각해보면, XILXCCDMMM이 나와야 한다.
내가 푼 방법은 n_list = [9, 4, 7, 3]로 역순으로 바꾼 리스트를 일일이 확인해주면서 dictionary에서 값을 찾아 적용해주었다.