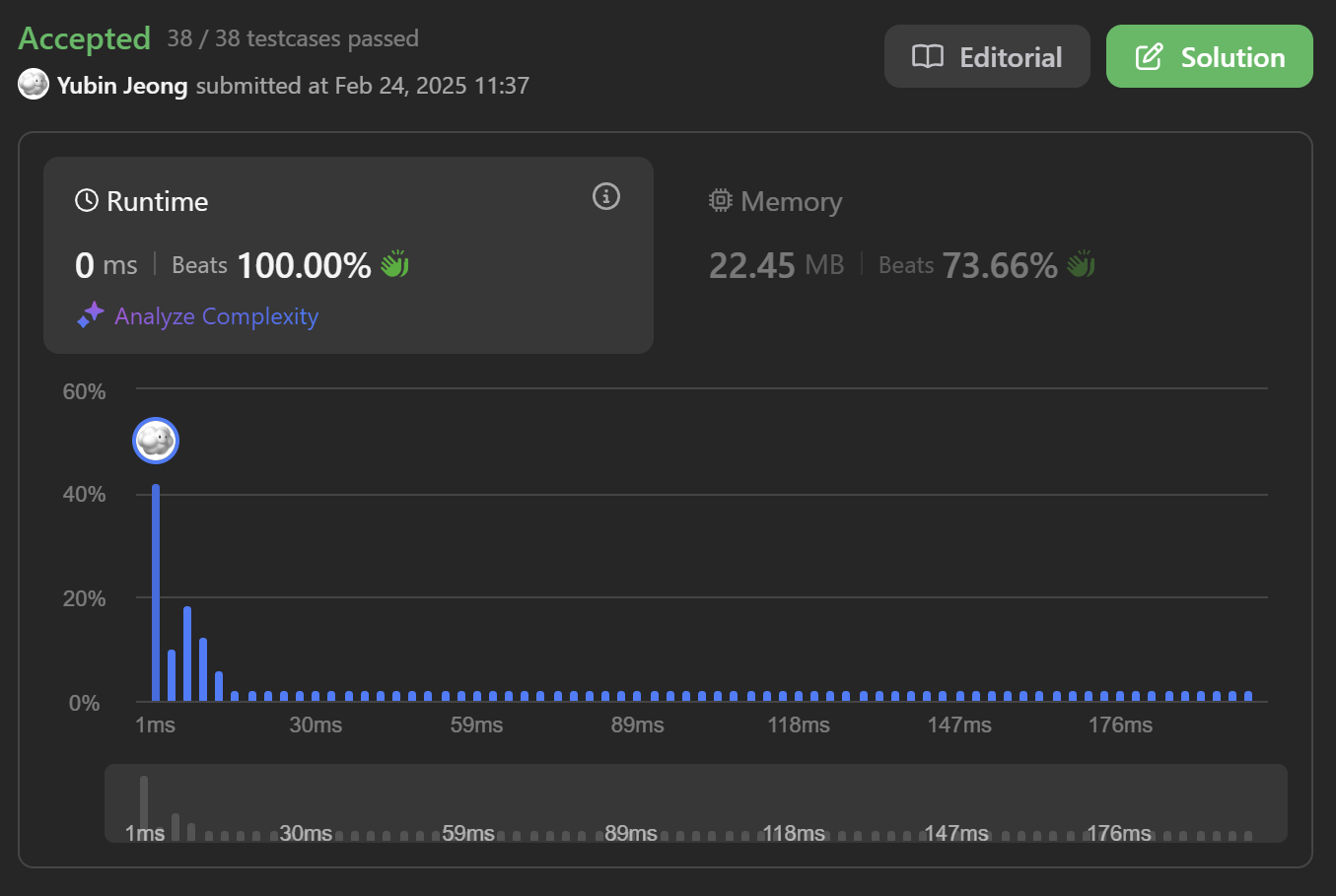
Top Interview 150
189. Rotate Array
Medium
Given an integer array nums, rotate the array to the right by k steps, where k is non-negative.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], k = 3 Output: [5,6,7,1,2,3,4] Explanation: rotate 1 steps to the right: [7,1,2,3,4,5,6] rotate 2 steps to the right: [6,7,1,2,3,4,5] rotate 3 steps to the right: [5,6,7,1,2,3,4]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [-1,-100,3,99], k = 2 Output: [3,99,-1,-100] Explanation: rotate 1 steps to the right: [99,-1,-100,3] rotate 2 steps to the right: [3,99,-1,-100]
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 105-231 <= nums[i] <= 231 - 10 <= k <= 105
Follow up:
- Try to come up with as many solutions as you can. There are at least three different ways to solve this problem.
- Could you do it in-place with
O(1)extra space?
Code
trial 1
for i in range(k):
nums.insert(0, nums.pop())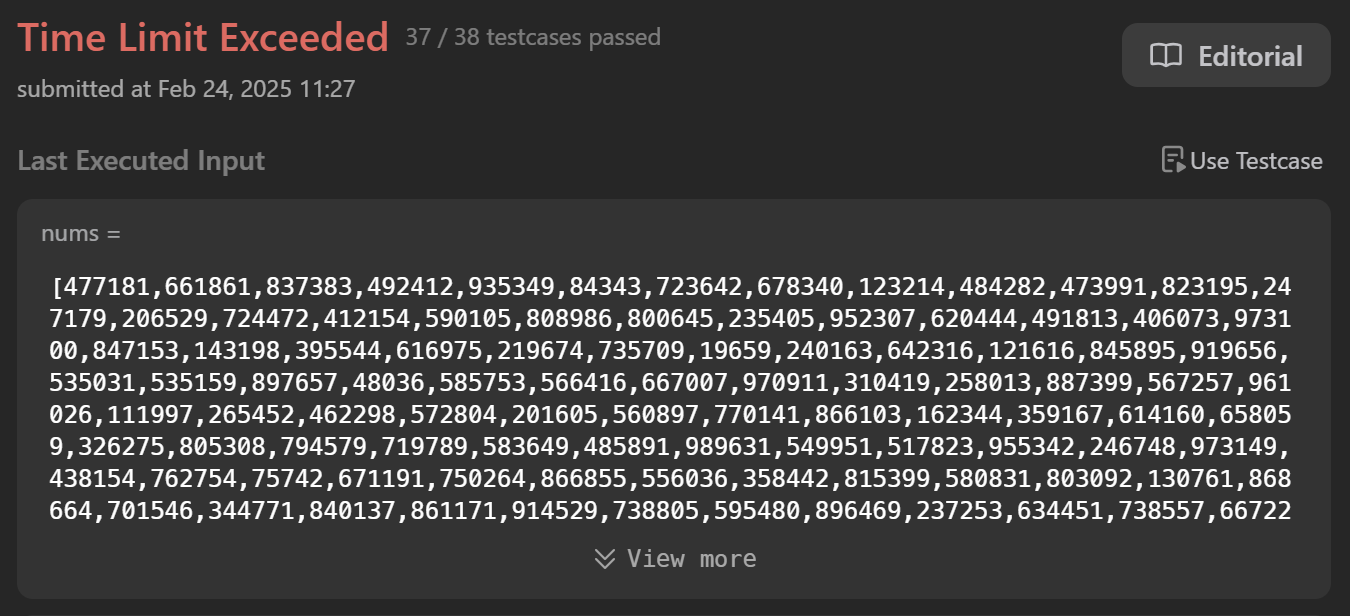
처음에는 맨 뒤의 원소를 꺼내 맨 앞으로 삽입하는 코드로 작성하였는데, 시간초과가 났다.
trial 2
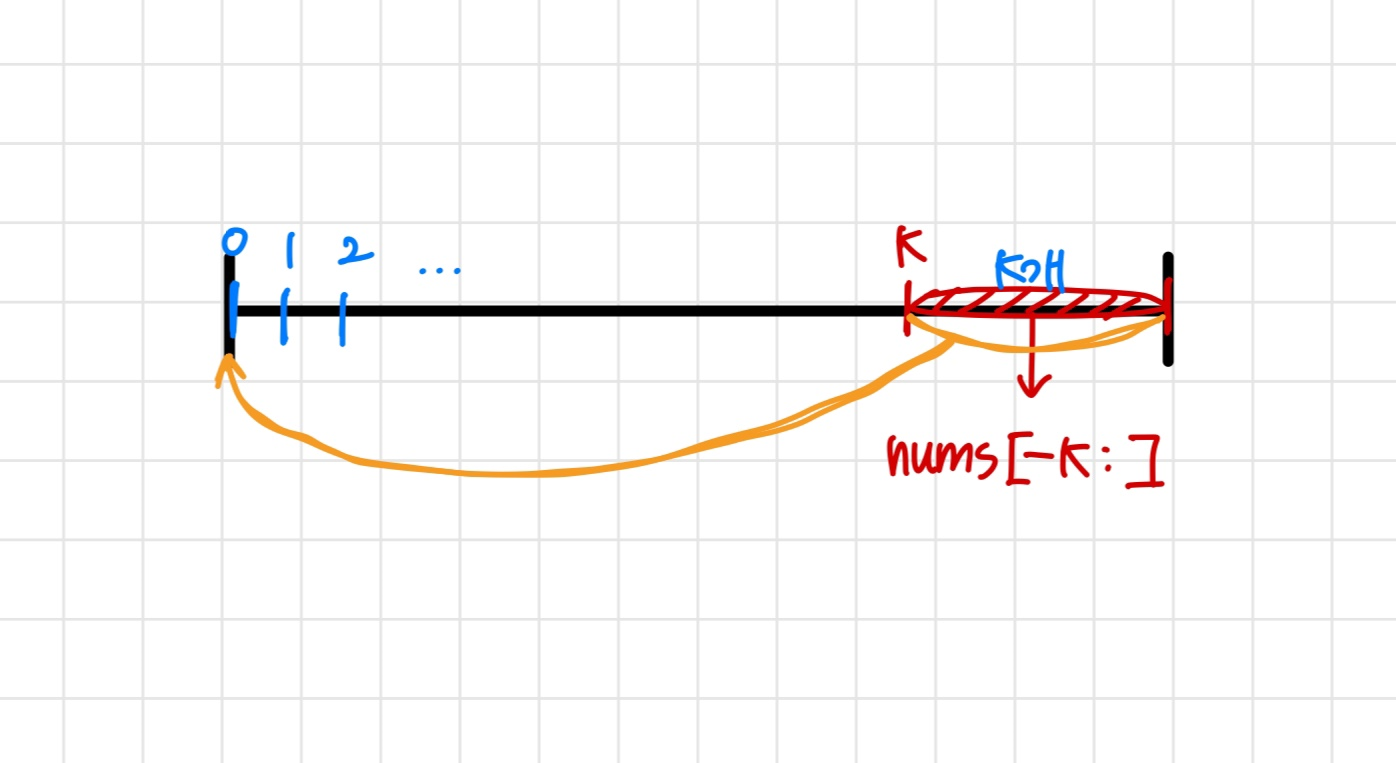
shift = nums[:-k]
del nums[:-k]
nums.extend(shift)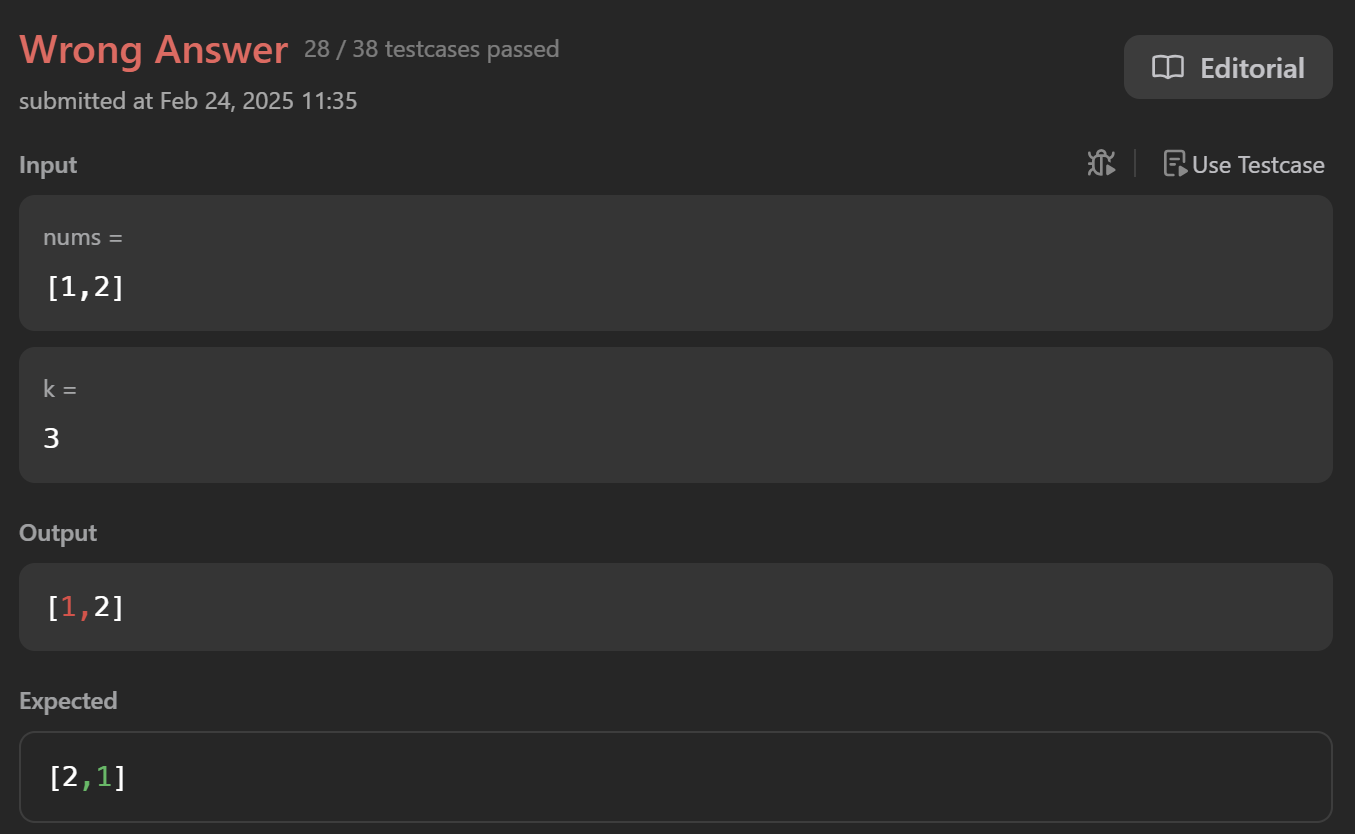
nums[-k:]만큼을 nums의 맨 앞으로 이동시키는 코드이다.
다만, 생각지 못했던 부분이 있었다.
k가 len(nums)보다 큰 경우도 생각해주어야 한다. 그래서 k %= len(nums) 코드를 추가해주었더니 통과했다.
Right Code
class Solution(object):
def rotate(self, nums, k):
k %= len(nums)
shift = nums[:-k]
del nums[:-k]
nums.extend(shift)Time Complexity
k %= len(nums):shift = nums[:-k]:del nums[:-k]:nums.extend(shift):