📌 문제 링크

1. 문제 이해

문제를 이해하는데 조금 헤맨 문제이다.
테스트 케이스1을 예시로 이해해보면 다음과 같다.
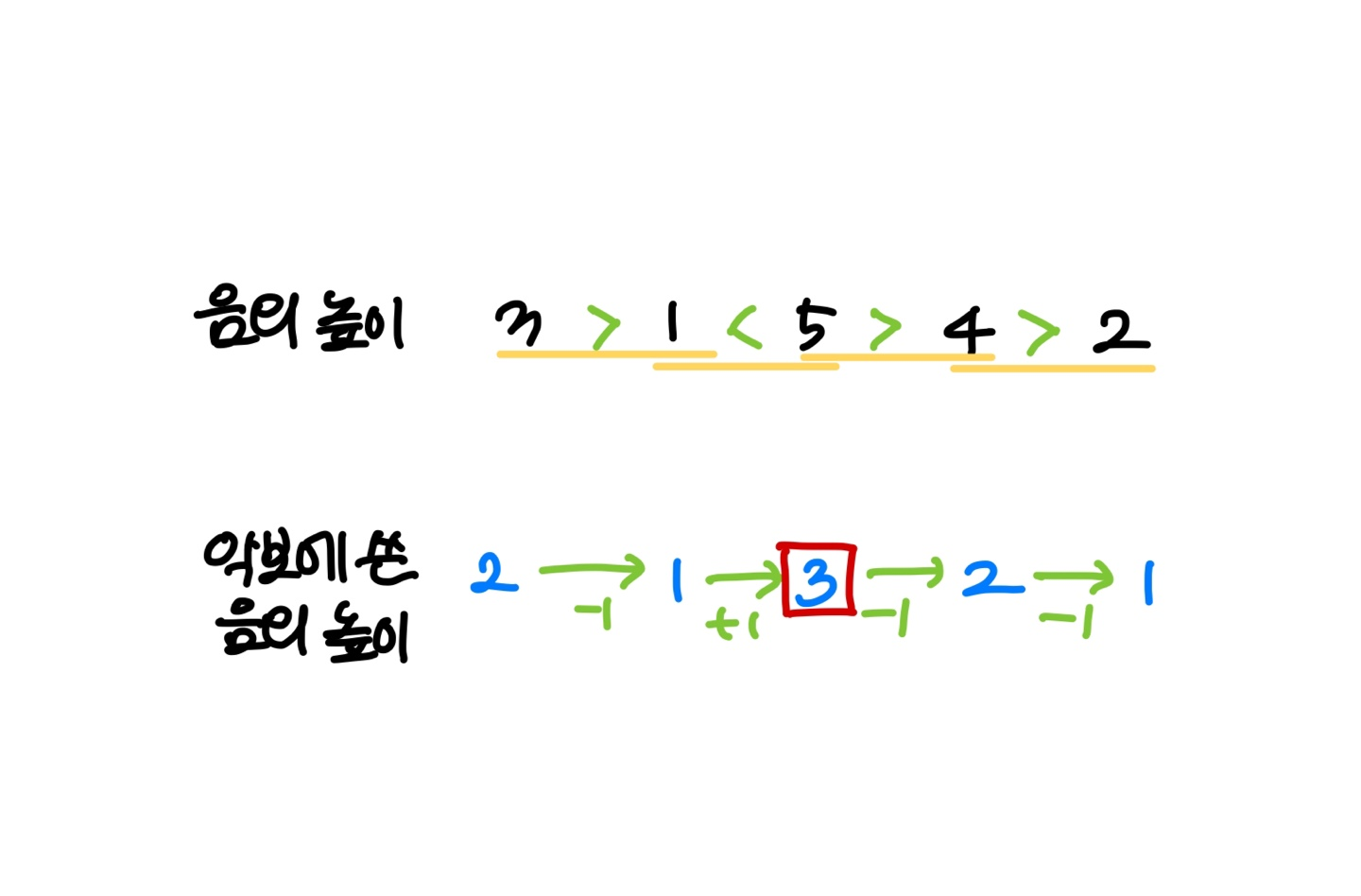
Input
- 음의 개수
- 음의 높이들
Output
악보에 작성한 음의 높이의 최솟값
2. 해결 전략
우리는 가장 높은 음의 높이의 최솟값을 구해야 한다.
즉, 음의 높이들을 악보에 작성하는 음의 높이로 바꾸면서 +1, -1, +0의 변화를 거치게 된다. 이 과정에서 가장 높은 음의 높이의 최솟값은 연속적으로 증가 혹은 감소한 값의 최댓값과 같다.
3. 코드 분석
input = open(0).readline
n = int(input())
std_up, std_down, max_ans = 0, 0, 0
notes = list(map(int, input().split()))음의 개수를 n에, 음의 종류들을 notes에 입력받는다.
std_up : 직전의 음의 높이보다 할 예정인 음의 높이가 높아 +1해주는 변수
std_down : 직전의 음의 높이보다 할 예정인 음의 높이가 낮아 -1해주는 변수
max_ans : 연속적으로 증가 혹은 감소하는 값의 최댓값 저장하는 변수
for i in range(n-1):
if notes[i] < notes[i+1] and std_up != 0:
std_up += 1
elif notes[i] < notes[i+1] and std_up == 0:
max_ans = max(std_down, max_ans)
std_down = 0
std_up = 1
elif notes[i] > notes[i+1] and std_down != 0:
std_down += 1
elif notes[i] > notes[i+1] and std_down == 0:
max_ans = max(std_up, max_ans)
std_up = 0
std_down = 1 직전 음의 높이 < 할 예정 음의 높이+ std_up의 연속과정- std_up 1 추가
직전 음의 높이 < 할 예정 음의 높이+ std_up의 이제 시작(그 전까지는 std_down진행중이었음)- std_down로 max_ans 갱신
- std_down = 0
- std_up = 1
직전 음의 높이 > 할 예정 음의 높이+ std_down의 연속과정- std_down 1 추가
직전 음의 높이 > 할 예정 음의 높이+ std_down의 이제 시작(그 전까지는 std_up진행중이었음)- std_up로 max_ans 갱신
- std_up = 0
- std_down = 1
max_ans = max(std_up, max_ans)
max_ans = max(std_down, max_ans)
print(max_ans+1)마지막으로, max_ans를 std_up과 std_down으로 갱신해주고 max_ans + 1을 출력해준다.
값이 max_ans + 1인 이유는, 음의 높이는 1 이상이기 때문이다.
4. 전체 코드
input = open(0).readline
ans = 1
n = int(input())
std_up, std_down, max_ans = 0, 0, 0
notes = list(map(int, input().split()))
for i in range(n-1):
if notes[i] > notes[i+1] and std_up != 0:
std_up += 1
elif notes[i] > notes[i+1] and std_up == 0:
max_ans = max(std_down, max_ans)
std_down = 0
std_up = 1
elif notes[i] < notes[i+1] and std_down != 0:
std_down += 1
elif notes[i] < notes[i+1] and std_down == 0:
max_ans = max(std_up, max_ans)
std_up = 0
std_down = 1
max_ans = max(std_up, max_ans)
max_ans = max(std_down, max_ans)
print(max_ans+1)