Python 기초 4.
01.복합연산자
- 할당(대입) 연산자
: 코딩에서 '='은 오른쪽 값이 왼쪽에 대입(할당)된다는 뜻
num1 = 10
- 복합 연산자
| 복합연산자 | 예시 |
|---|
| += | 덧셈 연산 후 할당 |
| -= | 뺄셈 연산 후 할당 |
| *= | 곱셈 연산 후 할당 |
| /= | 나눗셈 연산 후 할당 |
| %= | 나머지 연산 후 할당 |
| //= | 몫 연산 후 할당 |
| **= | 거듭제곱 연산 후 할당 |
num1 = num1 +5
num1 += 5
02.비교연산자
- 숫자 비교
:연산 결과는 bool(true/false)로 나옴.
num1 = 10
num2 = 4
result = num1 > num2
print('num1 > num2 :{}' .format(result)) #[result] true
result = num1 != num2
print('num1 != num2 :{}' .format(result))
- 문자 비교
- 아스키 코드를 이용한 비교연산
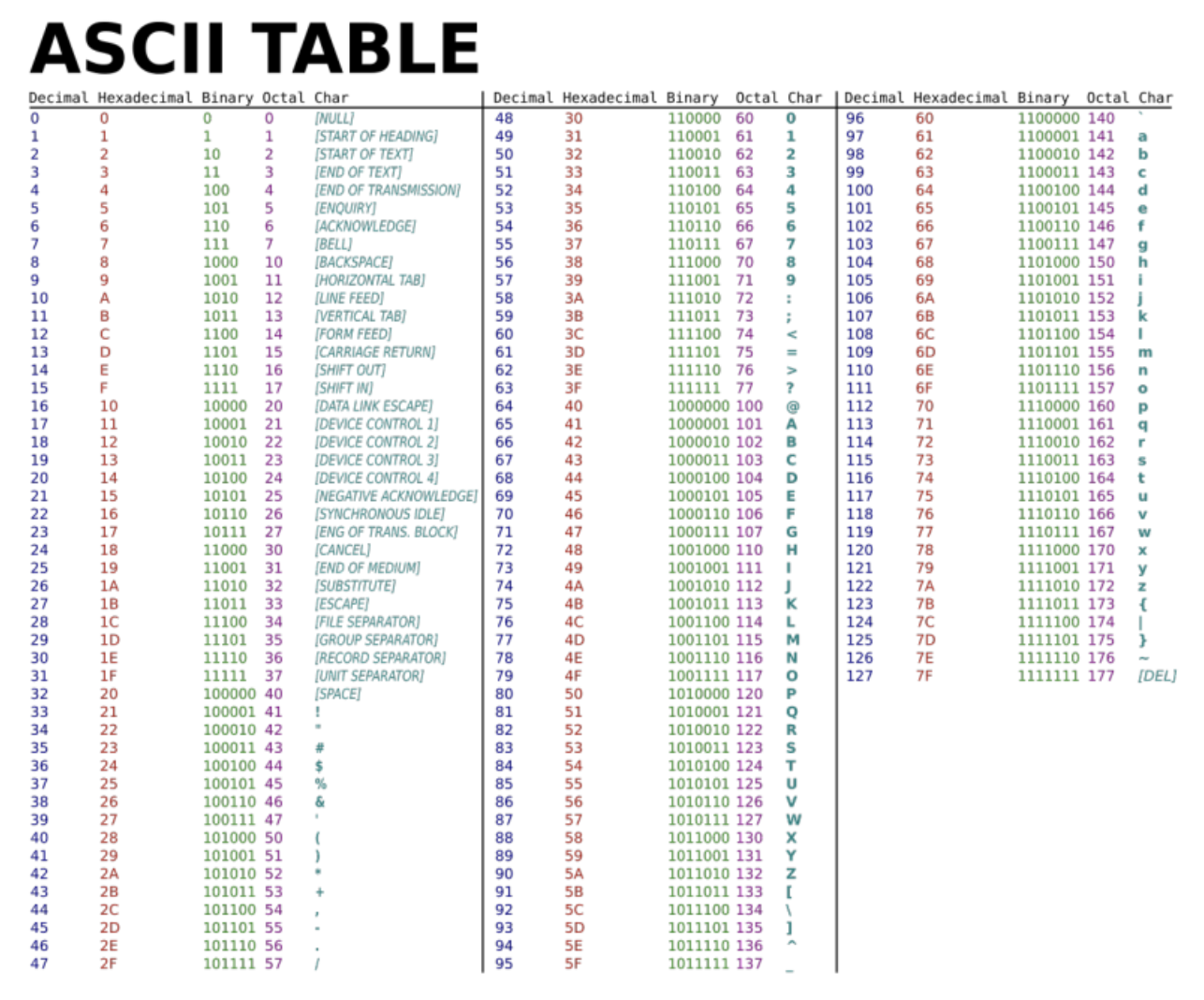
char1 = 'A' #65
char2 = 'S' #83
print('{} > {} : {}'.format(char1,char2,(char1 > char2)))
print('{} >= {} : {}'.format(char1,char2,(char1 >= char2)))
#알파벳 입력시 아스키 코드 출력하는 코드
userInputAlphabet = input('알파벳 입력: ')
print('{} : {}'. format(userInputAlphabet, ord(userInputAlphabet)))
#알파벳 입력시 문자를 출력하는 코드
userInputASCII = int(input('아스키 코드 입력: '))
print('{} : {}'. format(userInputASCII, chr(userInputASCII)))
print('\'A\' -> {}'.format(ord('A')))
print('\'S\' -> {}'.format(ord('S')))
print('65 -> {}'.format(chr(65)))
print('83 -> {}'.format(chr(83)))
3.문자열 비교 : 문자열 자체 비교
: ==(같다) 와 !=(같지않다) 만 가능
print('{} == {} : {}'.format(str1,str2,str1 == str2))
#[result] Hello == hello : False
03.논리연산자
: 피연산자의 논리(True,False)를 이용한 연산. (and,or,not)
- and 연산자
: A and B = A와 B 모두 True인 경우에만 결과값으로 True
�print('{} and {} : {}' . format(True, True, (True and True))) #[result] True
print('{} and {} : {}' . format(True, True, (True and False))) #[result] False
print('{} and {} : {}' . format(True, True, (False and False))) #[result] False
- or 연산자
: A or B = A와 B 중 어느 하나만 True인 경우에 결과값으로 True_
�print('{} or {} : {}' . format(True, True, (True and True))) #[result] True
print('{} or {} : {}' . format(True, True, (True and False))) #[result] True
print('{} and {} : {}' . format(True, True, (False and False))) #[result] False
- not 연산자
: not A = A의 상태를 부정하는 결과를 나타냄.
print('not {} : {}'.format(True, (not True))) #[result] not True : False
print('not {} : {}'.format(False, (not False))) #[result] not False : True
04.Operator 모듈
- 산수 연산자
| 연산자 | operator 함수 |
|---|
| + | operator.add() |
| - | operator.sub() |
| * | operator.mul() |
| / | operator.truediv() |
| % | operator.mod() |
| // | operator.floordiv() |
| ** | operator.pow() |
import operator
num1 = 9
num2 = 10
print('{} + {} : {}'.format(num1,num2,operator.add(num1,num2)))
- 비교 연산자
| 연산자 | operator 함수 |
|---|
| == | operator.eq() |
| != | operator.ne() |
| > | operator.gt() |
| >= | operator.ge() |
| < | operator.lt() |
| <= | operator.le() |
import operator
num1 = 9
num2 = 10
print('{} >= {} : {}'.format(num1,num2,operator.ge(num1,num2)))
- 논리 연산자
| 연산자 | operator 함수 |
|---|
| and | operator.and_() |
| or | operator.or_() |
| not | operator.not_() |
import operator
flag1 = True
flag2 = False
print('{} and {} : {}'.format(flag1,flag2,operator.and_(flag1,flag2)))
Reference
- 이글은 제로베이스 데이터 취업 스쿨의 강의자료 일부를 발췌하여 작성되었음.

