템플릿 매칭(Template matching)
입력 영상에서 부분 영상 위치를 찾는 방법이다.
템플릿: 전체 영상 내에서 찾고자 하는 작은 이미지
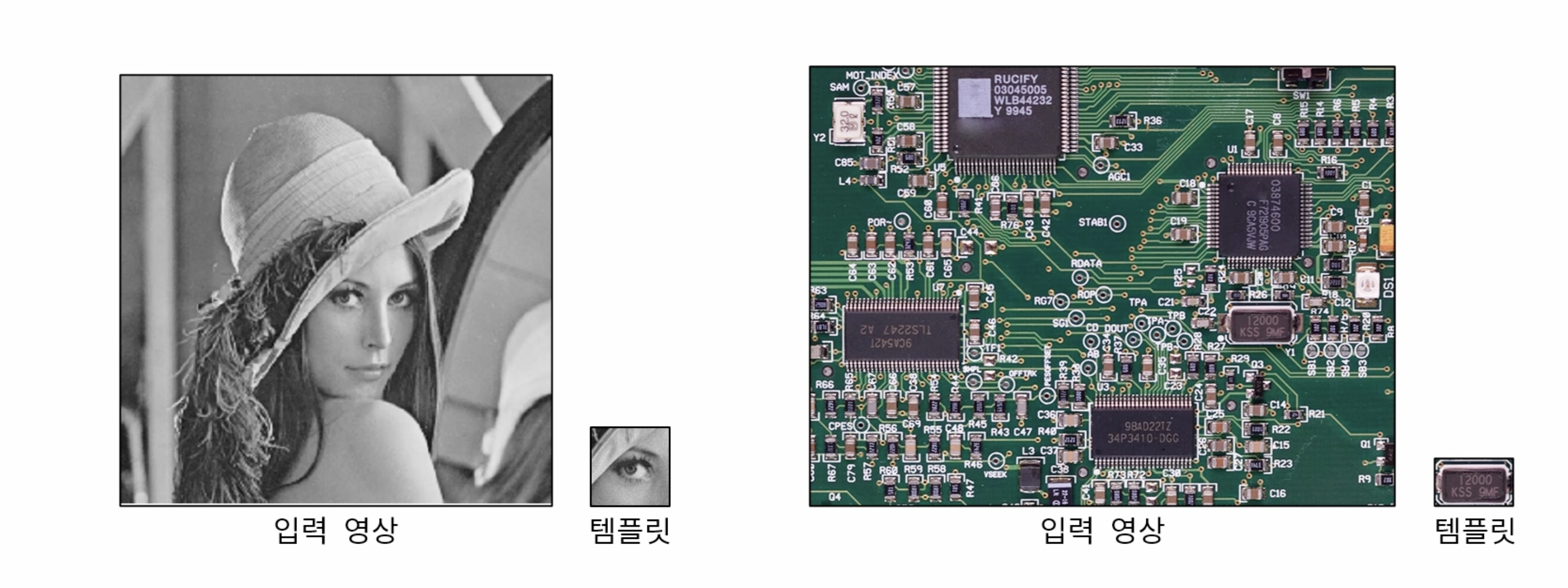

원본 영상 위를 템플리 이미지를 가지고 슬라이딩 하면서 유사도 혹은 비유사도를 구한다. 템플릿 이미지의 중심이 원본 영상과의 유사도가 되고 이미지로 표현하면 우상단의 이미지와 같다. 영상 전체에 대해서 유사도를 구했다면 그 중에서 가장 큰 값 혹은 작은 값의 위치가 해당 템플릿과 일치하는 부분이 된다.
알고리즘 특성상 크기 변환이나 회전에 대해서는 안좋은 결과를 보여준다.



void ex_processing(){
Mat src = imread("../data/circuit.bmp", IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
Mat tmpl = imread("../data/crystal.bmp", IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
#if 0
src = imread("wheres_wally.jpg", IMREAD_GRAYSCALE); // IMREAD_COLOR
tmpl = imread("wally.bmp", IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
#endif
if (src.empty() || tmpl.empty()) {
cerr << "Image load failed!" << endl;
return ;
}
#if 1
src = src + 50;
// 밝기 증가
Mat noise(src.size(), CV_32S);
// singned 타입이기 때문에 음수 형태의 잡음도 생성이 됨
randn(noise, 0, 10); // 10, 50, 100
add(src, noise, src, noArray(), CV_8U);
// 표준 편차가 10인 잡음을 추가
#endif
#if 0 // 노이즈 제거를 위한 가우시안 필터
GaussianBlur(src, src, Size(), 1);
GaussianBlur(tmpl, tmpl, Size(), 1);
#endif
#if 0 // 이미지 크기 조절
resize(src, src, Size(), 0.9, 0.9); // 0.8, 0.7
#endif
#if 0 // 반시계 방향으로 10도 회전시키는 코드
Point2f cp(src.cols / 2.f, src.rows / 2.f);
Mat rot = getRotationMatrix2D(cp, 10, 1); // 20, 30
warpAffine(src, src, rot, src.size());
#endif
Mat res, res_norm;
matchTemplate(src, tmpl, res, TM_CCOEFF_NORMED);
normalize(res, res_norm, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX, CV_8U);
double maxv;
Point maxloc;
minMaxLoc(res, 0, &maxv, 0, &maxloc);
cout << "maxv: " << maxv << endl;
cout << "maxloc: " << maxloc << endl;
Mat dst;
cvtColor(src, dst, COLOR_GRAY2BGR);
rectangle(dst, Rect(maxloc.x, maxloc.y, tmpl.cols, tmpl.rows), Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2);
imshow("src", src);
imshow("tmpl", tmpl);
imshow("res_norm", res_norm);
imshow("dst", dst);
waitKey();
}

여러개의 템플릿을 찾는 경우




레이블링 방법을 통해서 6개의 영역을 찾고 해당 영역에 대해서 최대값을 찾는 방법으로 여러 객체에 대해서 템플릿 매칭을 수행할 수 있다.
void ex_processing(){
Mat src = imread("../data/cookierun.png");
Mat tmpl = imread("../data/item.png");
if (src.empty() || tmpl.empty()) {
cerr << "Image load failed!" << endl;
return ;
}
Mat res, res_norm;
matchTemplate(src, tmpl, res, TM_CCOEFF_NORMED);
normalize(res, res_norm, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX, CV_8UC1);
Mat local_max = res_norm > 220;
Mat labels;
int num = connectedComponents(local_max, labels);
Mat dst = src.clone();
for (int i = 1; i < num; i++) {
Point max_loc;
Mat mask = (labels == i);
// 원본 이미지와 동일한 크기의 마스크로 배경은 0, 연결된 픽셀들 간에는 고유의 아이디로 표현된 마스크
minMaxLoc(res, 0, 0, 0, &max_loc, mask);
cout << max_loc.x << ", " << max_loc.y << endl;
Rect b_rect = Rect(max_loc.x, max_loc.y, tmpl.cols, tmpl.rows);
rectangle(dst, b_rect, Scalar(0, 255, 255), 2);
}
// imshow("src", src);
// imshow("templ", templ);
// imshow("res_norm", res_norm);
imshow("local_max", local_max);
imshow("dst", dst);
waitKey();
}

서브픽셀 에지 위치 검출하기
주행 영상에서 차선의 안과 밖의 서브픽셀 위치를 구한다.
서브픽셀 이란? 이미지의 픽셀의 위치는 정수를 기준으로 구성된다. 하지만 주변 픽셀들 간의 높이 차이를 통해 실수 영역에서의 픽셀 위치를 구할 수 있다. 실수 영역의 픽셀의 위치를 서브픽셀이라고 한다.

차선 인식은 ROI 설정 -> x축 미분 -> 최대와 최소 지점을 구하는 순서로 이루어진다.

위에서 구한 극점의 앞과 뒤를 이용해서 2차 방방정식으로 근사 시킨다. 이때 함수의 미분이 0이되는 지점을 이용한다.
코드
#define GETFPOINT(x,y,z) ((x-z) / ( (2.f*x)-(4.f*y)+(2.f*z) ))
float get_float_point(Mat roi, Point loc){
float x, y, z;
x = roi.at<float>(loc.x-1);
y = roi.at<float>(loc.x);
z = roi.at<float>(loc.x+1);
return loc.x + GETFPOINT(x,y,z);
}
const Point p1(300, 600), p2(500, 600);
const Point p3(800, 600), p4(1000, 600);
vector<Point2f> find_edges(const Mat& img);
void drawCross(Mat& img, Point pt, Scalar color);
void ex_processing(){
Mat src = imread("../data/lane01.bmp", IMREAD_COLOR);
if (src.empty()) {
cerr << "Image laod failed!" << endl;
return ;
}
Mat gray;
cvtColor(src, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
Rect rc1(p1 + Point(0, -10), p2 + Point(0, 10));
Rect rc2(p3 + Point(0, -10), p4 + Point(0, 10));
vector<Point2f> pts1 = find_edges(gray(rc1));
vector<Point2f> pts2 = find_edges(gray(rc2));
Mat dst = src.clone();
line(dst, p1, p4, Scalar(0, 255, 128), 1, LINE_AA);
rectangle(dst, rc1, Scalar(255,0,0), 1, LINE_AA);
rectangle(dst, rc2, Scalar(255,0,0), 1, LINE_AA);
drawCross(dst, Point(cvRound(p1.x + pts1[0].x), p1.y), Scalar(255, 0, 0));
drawCross(dst, Point(cvRound(p1.x + pts1[1].x), p1.y), Scalar(0, 0, 255));
putText(dst, format("(%4.3f, %d)", p1.x + pts1[0].x, p1.y),
Point(p1.x + pts1[0].x - 50, p1.y - 20),
FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, Scalar(255, 0, 0), 1, LINE_AA);
putText(dst, format("(%4.3f, %d)", p1.x + pts1[1].x, p1.y),
Point(p1.x + pts1[1].x - 20, p1.y + 30),
FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 1, LINE_AA);
drawCross(dst, Point(cvRound(p3.x + pts2[0].x), p3.y), Scalar(255, 0, 0));
drawCross(dst, Point(cvRound(p3.x + pts2[1].x), p3.y), Scalar(0, 0, 255));
putText(dst, format("(%4.3f, %d)", p3.x + pts2[0].x, p3.y),
Point(p3.x + pts1[0].x - 50, p3.y - 20),
FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, Scalar(255, 0, 0), 1, LINE_AA);
putText(dst, format("(%4.3f, %d)", p3.x + pts2[1].x, p3.y),
Point(p3.x + pts1[1].x - 20, p3.y + 30),
FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 1, LINE_AA);
imshow("dst", dst);
waitKey();
}
vector<Point2f> find_edges(const Mat& img)
{
Mat fimg, blr, dx;
img.convertTo(fimg, CV_32F);
GaussianBlur(fimg, blr, Size(), 1.);
Sobel(blr, dx, CV_32F, 1, 0);
double minv, maxv;
Point minloc, maxloc;
int y2 = img.rows / 2;
Mat roi = dx.row(y2);
minMaxLoc(roi, &minv, &maxv, &minloc, &maxloc);
// cout << maxloc << " " << maxv << endl;
// cout << img.rows << endl;
// cout << roi.colRange(maxloc.x-1, maxloc.x+2) << endl;
// cout << roi.at<float>(maxloc.x) << endl;
#if 0
vector<Point2f> pts;
pts.push_back(Point2f(maxloc.x, y2));
pts.push_back(Point2f(minloc.x, y2));
#else
vector<Point2f> pts;
pts.push_back(Point2f(get_float_point(roi, maxloc), y2));
pts.push_back(Point2f(get_float_point(roi, minloc), y2));
// pts.push_back(Point2f(minloc.x + hat, y2));
#endif
return pts;
}
void drawCross(Mat& img, Point pt, Scalar color)
{
int span = 5;
line(img, pt + Point(-span, -span), pt + Point(span, span), color, 1, LINE_AA);
line(img, pt + Point(-span, span), pt + Point(span, -span), color, 1, LINE_AA);
}
결과


