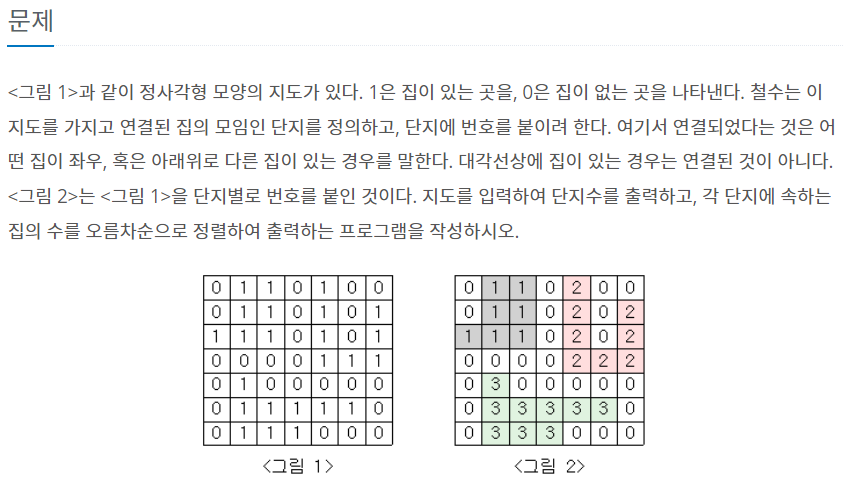
bfs와 dfs를 구현할 줄 알면 풀린다.
bfs
from collections import deque
def bfs(N, ap, a, b):
dx = [1, -1, 0, 0]
dy = [0, 0, 1, -1]
q = deque()
q.append((a, b))
cnt = 1
while q:
x, y = q.popleft()
for i in range(4):
nx = x + dx[i]
ny = y + dy[i]
if 0 <= ny < N and 0 <= nx < N and ap[ny][nx] == 1:
q.append((nx, ny))
ap[ny][nx] = 0
cnt += 1
return cnt
if __name__ == "__main__":
N = int(input())
ap = [list() for _ in range(N)]
for i in range(N):
for j in input():
ap[i].append(int(j))
house = list()
for h in range(N):
for w in range(N):
if ap[h][w] == 1:
ap[h][w] = 0
house.append(bfs(N, ap, w, h))
print(len(house))
print(*sorted(house), sep='\n')dfs
def dfs(N, ap, a, b):
dx = [1, -1, 0, 0]
dy = [0, 0, 1, -1]
q = list()
q.append((a, b))
cnt = 1
while q:
x, y = q.pop()
for i in range(4):
nx = x + dx[i]
ny = y + dy[i]
if 0 <= ny < N and 0 <= nx < N and ap[ny][nx] == 1:
q.append((nx, ny))
ap[ny][nx] = 0
cnt += 1
return cnt
if __name__ == "__main__":
N = int(input())
ap = [list() for _ in range(N)]
for i in range(N):
for j in input():
ap[i].append(int(j))
house = list()
for h in range(N):
for w in range(N):
if ap[h][w] == 1:
ap[h][w] = 0
house.append(dfs(N, ap, w, h))
print(len(house))
print(*sorted(house),sep='\n')
dfs 조금 더 빠르다.
