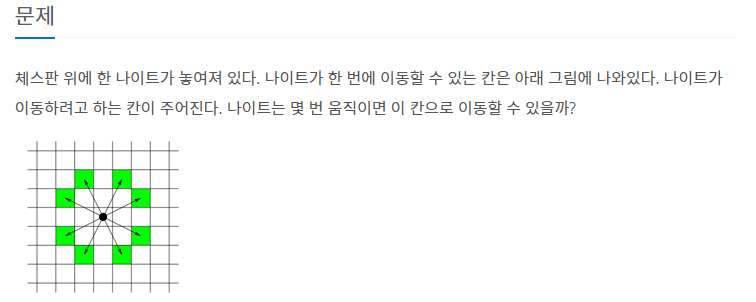
너비 우선 탐색을 이용한다... 이유는 넓게 퍼져가면서 최소를 찾아야 하기 때문
bfs 한 단계 마다 +1을 해준다. 먼저 도착하면 출력
from collections import deque
def bfs(x, y, tmp):
visited[x][y] = False
q = deque()
q.append([x, y, tmp])
while q:
x, y, tmp = q.popleft()
if [x, y] == goal:
print(tmp)
break
for dx, dy in dxy:
nx = dx + x
ny = dy + y
if 0 <= nx < n and 0 <= ny < n:
if visited[nx][ny]:
visited[nx][ny] = False
q.append([nx, ny, tmp+1])
l = int(input())
dxy = [[-2, -1], [-2, 1], [-1, -2], [-1, 2], [1, -2], [1, 2], [2, -1], [2, 1]]
for _ in range(l):
n = int(input())
now = list(map(int, input().split()))
goal = list(map(int, input().split()))
a = [[0] * n for _ in range(n)]
visited = [[True] * n for _ in range(n)]
bfs(now[0], now[1], 0)