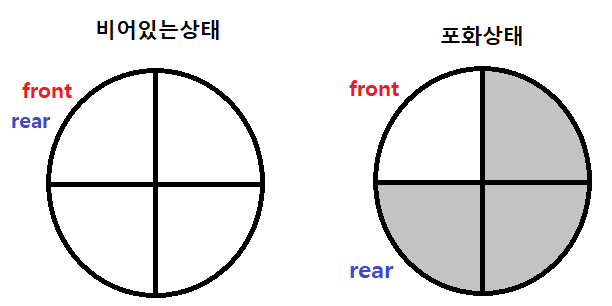
📌 원형 큐 (Circle Queue)
- 선형이 아닌 원형의 방식으로 선형큐와 동일한 FIFO구조
- front변수와 rear변수가 있다
- 선형큐의 문제점을 해결한 방법 -> 선형큐에서는 front와 rear가 계속 이동하여 rear가 가장 마지막 인덱스에 도달했을 때, 앞부분에 데이터를 더이상 삽입할 수 없어서 오버플로우가 터짐
- rear or front가 배열의 끝에 도달하면, 다시 배열의 처음으로 돌아가서 큐 공간을 재사용할 수 있다
->공간을 다시 쓰기 때문에 오버플로우 & 언더플로우 방지- 선형큐에서는 요소를 앞으로 이동시켜야 가능해짐
📌 원형큐에서는 포화상태와 공백상태를 구별하기 위해 한자리는 항상 비워둔다
- front == rear -> 공백상태
- front == rear + 1 -> 포화상태
✅ 클래스에 정의 & 초기화
#include <iostream>
#define SIZE 5
using namespace std;
template <typename T>
// 원형 큐
class CircleQueue
{
private:
int size;
int rear;
int front;
T Container[SIZE];
public:
CircleQueue()
{
size = 0;
rear = SIZE - 1;
front = SIZE - 1;
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++)
{
Container[i] = NULL;
}
}
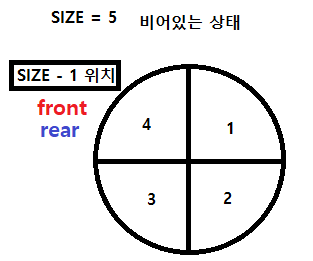
✅ Push( )함수 (데이터 넣기)
4 % 5 = 4
3 % 5 = 3
2 % 5 = 2
1 % 5 = 1
5 % 5 = 0
📌 먼저 rear를 이동시킨 뒤 데이터를 삽입한다
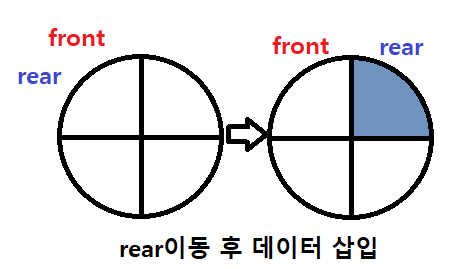
ex) SIZE = 5, front = 4, rear = 3
-> front == (rear + 1) % SIZE
-> 4 % 5 = 4
-> front(4) == 4
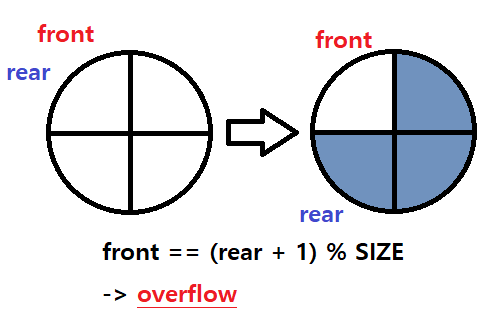
void Push(T data)
{
if (front == (rear + 1) % SIZE)
{
cout << "Circle Queue Overflow" << endl;
}
else
{
rear = (rear + 1) % SIZE;
// 데이터를 넣으면 rear가 이동
Container[rear] = data;
size++;
}
}✅ Pop( )함수 (데이터 빼기)
-
큐가 비어있는지 확인하는 bool형 Empty( )함수
-
큐가 비어있으면 더이상 뺄 데이터가 없다
📌 front가 먼저 이동 후 데이터를 삭제
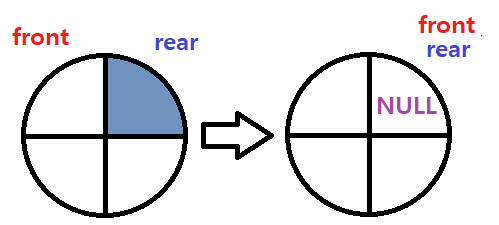
void Pop()
{
if (Empty())
{
cout << "Circle Queue is Empty" << endl;
}
else
{
front = (front + 1) % SIZE;
// 데이터를 빼면 front가 이동
Container[front] = NULL;
size--;
}
}
bool Empty()
{
if (front == rear)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}✅ front & size 값 반환
- front의 위치는 비워두기 때문에 값을 반환할때는 + 1 한 값으로
const T& Front()
{
return Container[(front + 1) % SIZE];
}
const int& Size()
{
return size;
}📌 메인함수
int main()
{
CircleQueue <char> circleQueue;
circleQueue.Push('A');
circleQueue.Push('B');
circleQueue.Push('C');
circleQueue.Push('D');
while (circleQueue.Empty() == false)
{
cout << circleQueue.Front() << endl;
circleQueue.Pop();
}
circleQueue.Push('E');
circleQueue.Push('F');
circleQueue.Push('G');
circleQueue.Push('H');
return 0;
}출력값 :
원형 큐의 시간복잡도
시간복잡도 상수시간 O(1) -> 배열로 접근하기 때문이다