🎯 2차원 배열 - 특정 조건을 만족하는 최소 값 구하기
📌 백준 7576번 토마토
public class Exam7576_토마토 {
private static int N, M, empty;
private static int[][] tomatoes;
private static int[][] dirs = {{1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
static class Site {
public int row;
public int col;
Site(int row, int col){
this.row = row;
this.col = col;
}
}
static int BFS(Queue<Site> queue){
int day = 0; // 날짜
int ripened = 0; // 익은 토마토의 수
int size = queue.size();
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[N][M];
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
if(size <= 0) {
day++;
size = queue.size();
}
Site site = queue.poll();
if(!visited[site.row][site.col] && tomatoes[site.row][site.col] == 1){
visited[site.row][site.col] = true;
ripened++;
for(int dir[] : dirs){
int row2 = site.row + dir[0];
int col2 = site.col + dir[1];
if((row2 >= 0 && row2 < N) && (col2 >= 0 && col2 < M)){
if(tomatoes[row2][col2] == 0){
tomatoes[row2][col2] = 1;
queue.add(new Site(row2, col2));
}
}
}
}
size--;
}
return (ripened == (N * M - empty)) ? day : -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
Queue<Site> queue = new LinkedList<>();
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 가로칸의 수
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 세로칸의 수
tomatoes = new int[N][M];
empty = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i){
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for(int j = 0; j < M; ++j){
tomatoes[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
if(tomatoes[i][j] == 1){ // 토마토를 발견하면
queue.add(new Site(i, j)); // 좌표를 Site 인스턴스로 만들어 큐에 삽입
} else if(tomatoes[i][j] == -1){ // 토마토가 들어있지 않은 칸을 발견하면
empty++; // 빈 칸의 수 상승
}
}
}
System.out.println(BFS(queue));
br.close();
}
}이 문제는 다음과 같이 전형적인 BFS 문제의 유형을 하고 있습니다.
- DFS로 풀기엔 M, N의 최대값이 1,000 * 1,000으로 크다
- 문제의 답에 '최소'라는 단어가 들어간다.
- Queue를 사용해서 노드(Site)를 삽입하고 그 노드를 poll()해서 반복문을 통해 인접노드를 Queue에 다시 추가하는 형태
하지만 구해야 하는 값이 토마토가 모두 익을 때 까지 최소 날짜를 구해야 하므로 하나의 아이디어가 추가됩니다.
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
if(size <= 0) {
day++;
size = queue.size();
}
Site site = queue.poll();
...
size--;
}
반복문으로 구현한 BFS는 특정 단계를 식별하기 어렵다는 단점이 있습니다. 그래서 size라는 변수를 선언해서 그 단계에 있는 노드 갯수, 즉 Queue의 크기로 초기화해줍니다.
size만큼 노드들을 전부 poll()하고 인접노드를 Queue에 전부 추가했다면 해당 단계가 끝났다는 것을 뜻하므로 구하고자 하는 날짜 day를 상승시키고 다시 size 변수를 초기화해줍니다. 이것을 Queue가 빌 때까지 반복해줍니다.
📌 프로그래머스 67259 경주로 건설
public class 경주로건설 {
static class Solution {
int N;
int[][][] cBoard;
int[] dr = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
int[] dc = {0, -1, 0, 1};
class Node {
// bfs에서 필요하다면 매 케이스마다 생성되는 인스턴스에 상태정보를 담아놓자
public int row;
public int col;
public int cost; // 해당 노드에서 건설 요금
public int dir; // 이동 방향
Node(int row, int col, int cost, int dir){
this.row = row;
this.col = col;
this.cost = cost;
this.dir = dir;
}
}
public int solution(int[][] board) {
N = board.length;
cBoard = new int[4][N][N];
for(int i = 0; i < cBoard.length; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < cBoard[0].length; ++j) {
// 최솟값을 구하기 위해 최댓값으로 초기화
Arrays.fill(cBoard[i][j], Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
}
bfs(board);
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i){ // 모든 방향에서 최소 비용 비교하여 반환
min = Math.min(min, cBoard[i][N - 1][N - 1]);
}
return min;
}
public void bfs(int[][] board){
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) queue.add(new Node(0, 0, 0, i));
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
Node node = queue.poll();
// >=이 아니라 > 쓰면 시간 초과!!
if(node.cost >= cBoard[node.dir][node.row][node.col]) continue;
int r = node.row;
int c = node.col;
if(board[r][c] == 1) continue;
// 최소 값이라면 변경
cBoard[node.dir][r][c] = Math.min(cBoard[node.dir][r][c], node.cost);
for(int i = 0; i < dr.length; ++i){
int nr = r + dr[i];
int nc = c + dc[i];
int fee = 100;
if(nr >= 0 && nr < N && nc >= 0 && nc < N) {
// 전에 이동했던 방향과 달라지면
if((node.dir % 2 == 0 && dr[i] == 0) || (node.dir % 2 == 1 && dc[i] == 0)){
fee += 500;
}
queue.add(new Node(nr, nc, node.cost + fee, i));
}
}
}
}
}
}이 문제는 도착점 cBoard[N - 1][N - 1]까지 경주로를 건설하는 최소 비용을 계산하기 위해 각 행열에 위치 했을때 최소값을 업데이트 하여 재사용하는 메모이제이션 방식을 사용해야 합니다.
따라서 solution 메서드에 주어지는 2차원 배열 board[][]를 기반으로 같은 크기를 갖는 cBoard[][](테스트 케이스 추가 되고 나서는 방향도 고려해야하므로 3차원 배열 cBoard[][][]) 를 선언합시다.
BFS와 메모이제이션을 통해 최소값을 구하는 문제의 핵심은 다음과 같습니다.
- 인접노드로 뻗어가는 매 케이스마다 새로 생성하는 인스턴스에 상태 정보를 저장할 수 있도록 클래스에 속성을 선언합니다.
- 같은 크기의 다른 배열에 최소값을 저장해서 재사용하기 때문에 방문 배열이 필요하지 않습니다.
- 따라서 목표점에 도착(
if(r == N - 1 && c == N - 1))했다고 별도의 연산을 안해주어도 됩니다.
// >=이 아니라 > 쓰면 시간 초과!!
if(node.cost >= cBoard[node.dir][node.row][node.col]) continue;특정 노드에 도착했을 때 해당 케이스가 최소값이어야지만 통과시키도록 해야 시간초과가 일어나지 않습니다.
📌 프로그래머스 72415 카드 짝 맞추기
public class 카드짝맞추기 {
private static final int LEN = 4;
static int[] dr = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
static int[] dc = {0, 0, -1, 1};
static class Vertex {
public int row;
public int col;
public int press;
Vertex(int row, int col) {
this.row = row;
this.col = col;
}
Vertex(int row, int col, int press) {
this.row = row;
this.col = col;
this.press = press;
}
}
static class Solution {
ArrayList<int[]> orders;
public int solution(int[][] board, int r, int c) {
int answer = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int n = 0; // 카드 짝 갯수
for (int i = 0; i < LEN; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < LEN; ++j) {
if (board[i][j] != 0) n++;
}
}
n /= 2;
int[] temp = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
temp[i] = i + 1;
}
orders = new ArrayList<>();
permutation(n, n, new int[n], temp, 0, 0);
for (int[] order : orders) { // order = 순열 배열
int total = 0;
Vertex point = new Vertex(r, c); //최초 커서위치 (r,c)
int[][] cBoard = deepCopy(board);
for (int card : order) { // 순열 요소 한가지 씩
int cnt = 0;
//목표 카드 찾기
cnt += bfs(cBoard, card, point) + 1; // enter키 입력
//목표 카드 선택
cBoard[point.row][point.col] = 0;
//카드 짝 찾기
cnt += bfs(cBoard, card, point) + 1; // enter키 입력
//짝 찾기 성공
cBoard[point.row][point.col] = 0;
total += cnt;
}
answer = Math.min(total, answer);
}
return answer;
}
private int bfs(int[][] board, int target, Vertex point) {
Queue<Vertex> queue = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[LEN][LEN];
queue.add(new Vertex(point.row, point.col, 0));
visited[point.row][point.col] = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Vertex p = queue.poll();
if (board[p.row][p.col] == target) {
point.row = p.row;
point.col = p.col;
return p.press;
}
//4방 탐색
for (int d = 0; d < LEN; d++) {
int nr = p.row + dr[d];
int nc = p.col + dc[d];
if (nr >= 0 && nr < LEN && nc >= 0 && nc < LEN && !visited[nr][nc]) {
visited[nr][nc] = true;
queue.add(new Vertex(nr, nc, p.press + 1));
}
}
//ctrl + 4방 탐색
for (int d = 0; d < 4; d++) {
Vertex result = findCard(board, p.row, p.col, d);
if ((result.row != p.row || result.col != p.col) && !visited[result.row][result.col]) {
visited[result.row][result.col] = true;
queue.add(new Vertex(result.row, result.col, p.press + 1));
}
}
}
return 0;
}
private Vertex findCard(int[][] board, int row, int col, int d) {
row += dr[d];
col += dc[d];
while (row >= 0 && row < LEN && col >= 0 && col < LEN) {
if (board[row][col] != 0) {
return new Vertex(row, col);
}
row += dr[d];
col += dc[d];
}
return new Vertex(row - dr[d], col - dc[d]);
}
public int[][] deepCopy(int[][] board) {
int[][] result = new int[LEN][LEN];
for (int i = 0; i < LEN; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < LEN; ++j) {
result[i][j] = board[i][j];
}
}
return result;
}
private void permutation(int n, int r, int[] perms, int[] input, int depth, int flag) {
if (depth == r) {
int[] temp = new int[n];
System.arraycopy(perms, 0, temp, 0, n);
orders.add(temp); // orders.ArrayList에 순서 순열 저장
String[] str = new String[10];
String str1 = Arrays.toString(str);
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if ((flag & (1 << i)) == 0) {
perms[depth] = input[i];
permutation(n, r, perms, input, depth + 1, flag | (1 << i));
}
}
}
}
}모든 카드를 제거하기 위한 키 조작 횟수의 최솟값을 구하는 문제입니다.
- 주어진
board[][]2차원 배열을 선형 탐색하여 카드의 갯수를 구하고 2로 나누어 카드 짝의 갯수를 구해 변수 n을 초기화 합니다. - 1부터 n까지의 정수로 초기화된 1차원 배열로
permutation함수를 이용해 순열 배열을 만들어ArrayList<int[]> orders에 모두 추가해줍니다. ArrayList<int[]> orders와order[]를 이용한 2중 forEach문을 통해 카드 짝을 고를 수 있는 모든 경우의 수 → 순열로 BFS를 실행합니다.- [Ctrl] 키를 누른 상태에서 방향키 ←, ↑, ↓, → 중 하나를 누르면, 누른 키 방향에 있는 가장 가까운 카드로 한번에 이동하기 때문에 4방 탐색 외에도
findCard를 통해 Ctrl + 방향키를 눌렀을 때도 고려하여Vertex인스턴스의press(입력 횟수) 값을 업데이트 해줍니다. - BFS 함수가 종료되었다면 입력수를 카운트하는 변수 cnt에 결과값을 더해주고 row, col 값이 업데이트 된
Vertex point로 한번 더 bfs 함수를 실행합니다. - 순열 루프마다
total변수에 cnt 값을 더 해주고 기존 최소값인answer와 비교해줘서 작으면 업데이트 해줍니다. - 최소 입력값이 저장된
answer를 반환합니다.
이 문제도 경주로 건설 문제 처럼 인접노드로 뻗어가는 매 케이스마다 새로 생성하는 인스턴스에 여태까지 키보드를 입력한 횟수를 저장할 수 있도록 클래스에 press 속성 변수를 선언한 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
🎯 그래프 구조 - 경로
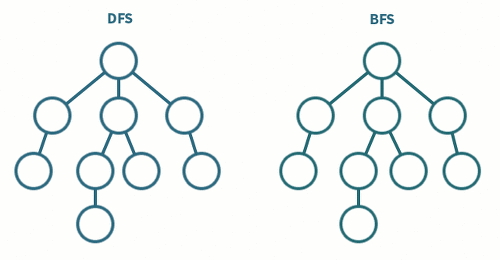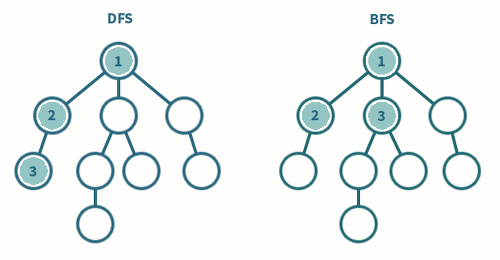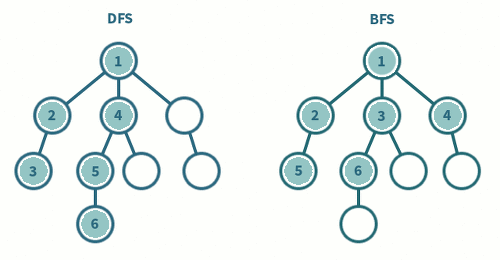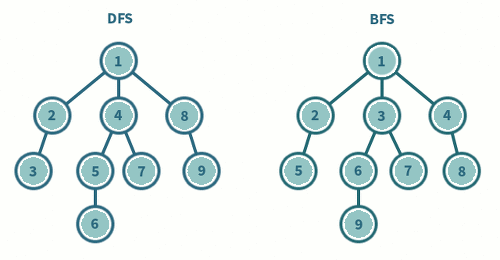
📌 백준 1260번 DFS와 BFS
public class Exam1260_DFS와BFS_2 {
static int N, M, V, cnt;
static boolean visited[];
static class Graph {
int N;
LinkedList<Integer>[] edgeList; // 인접노드 리스트
Graph(int n){
N = n;
edgeList = new LinkedList[N + 1];
for(int i = 0; i <= N; ++i){ // edgeList[0]은 0의 인접노드들이 들어있음
edgeList[i] = new LinkedList<>();
}
}
void addEdge(int start, int end){
edgeList[start].add(end);
}
void sortEdgeList(){
for(LinkedList<Integer> list : edgeList) {
Collections.sort(list);
}
}
void DFS(int now){
if(cnt == N) return;
else if(visited[now]) return;
else {
System.out.print(now + " ");
visited[now] = true;
cnt++;
for(int next : edgeList[now]){
DFS(next);
}
}
}
void BFS(int s){
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(s);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
if(cnt == N) break;
int now = queue.poll();
if(!visited[now]){
visited[now] = true;
System.out.print(now + " ");
while(!edgeList[now].isEmpty()){
queue.add(edgeList[now].poll());
}
cnt++;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
V = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
Graph g = new Graph(N);
for(int i = 0; i < M; ++i){
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int start = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int end = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
g.addEdge(start, end);
g.addEdge(end, start);
}
cnt = 0;
visited = new boolean[N + 1];
g.sortEdgeList();
g.DFS(V);
System.out.println();
cnt = 0;
visited = new boolean[N + 1];
g.sortEdgeList();
g.BFS(V);
System.out.println();
br.close();
}
}