인증 = 로그인 authentication / 인가 authorization= 특정 폴더에 접근 할 수 있는가 없는가 , 특정 url에 접근권한이 있냐
인증유지 = 세션 로그인 모델어트리뷰트 주입 등의 구조를 스프링 시큐리티로 구현
Spring Security에서 인증(Authentication)과 인가(Authorization)는 다음과 같이 처리됩니다:
1. 인증(Authentication)
- 사용자가 누구인지 확인하는 과정입니다.
- 주로 로그인 과정을 통해 사용자 정보를 확인하고, 이를 통해 인증 객체를 생성합니다.
- Spring Security에서는
AuthenticationManager를 통해 인증을 수행합니다. - 인증 성공 시
SecurityContext에 인증 정보를 저장하여 이후 요청 시 사용할 수 있도록 합니다.
예:
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authenticationToken =
new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(username, password);
Authentication authentication = authenticationManager.authenticate(authenticationToken);
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authentication);2. 인가(Authorization)
- 인증된 사용자가 특정 리소스나 URL에 접근할 수 있는지 여부를 확인하는 과정입니다.
- 권한(Role)을 통해 접근 여부를 결정합니다.
- Spring Security에서는
@PreAuthorize,@Secured, URL 패턴 등을 사용하여 인가를 설정합니다.
예:
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')")
@GetMapping("/admin")
public String adminPage() {
return "admin";
}3. 인증 유지(Session Management)
- 인증 상태를 유지하는 방법에는 세션, 토큰(JWT) 등이 있습니다.
- 세션 기반에서는 인증 정보를
HttpSession에 저장하여 사용자를 식별합니다. - Spring Security는 세션 관리를 지원하며, 세션 고정 보호(Session Fixation Protection)도 기본으로 제공됩니다.
예:
http.sessionManagement()
.sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.IF_REQUIRED)
.maximumSessions(1) // 하나의 세션만 허용
.expiredUrl("/login?expired");로그인 상태 유지 - 모델 어트리뷰트 주입
- 인증 정보를
@AuthenticationPrincipal로 주입하여 사용합니다. - 컨트롤러에서 현재 로그인한 사용자 정보를 편리하게 사용할 수 있습니다.
예:
@GetMapping("/profile")
public String profile(@AuthenticationPrincipal UserDetails userDetails, Model model) {
model.addAttribute("username", userDetails.getUsername());
return "profile";
}Spring Security로 인증과 인가를 구현하면서 인증 유지를 위해 세션 또는 JWT와 같은 방법을 선택하여 관리하는 것이 중요합니다.
추가로 구현 관련 질문이 있으면 알려주세요!
스태틱에 hello.html작성
서버 실행 후 http://localhost:8080/hello.html 주소작성
(spring security 추가 안하면 로그인창 안뜨고 바로 접속가능)
이후 pom.xml에서 spring security 모듈 추가 후 서버 재구동 후 웹 재접속하면 로그인 화면 뜸
처음 프로젝트 만들때가 아니라 나중에 추가하면
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf.extras</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity6</artifactId>
</dependency>이 코드가 안들어가는 경우가 있어서 수기로 추가해줘야함.
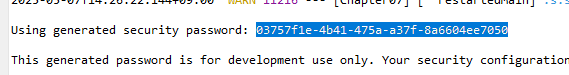
서큐리티만 설정하면 기본으로 유저 로그인정보가 제공됨, 콘솔에서 확인가능
서버 구동시마다 재설정됨
http://localhost:8080/logout 하면 로그아웃됨
커스터마이징을 할 경우 ( 서큐리티 필터체인설정)
헬로우 주소로 치면 이번엔 로그인창안뜸
컨트롤러 앞단에 처리할거 하던 필터처럼 서큐리티 필터체인이 제공됨.
체인이니 여러개를 가지고 있고
시큐리티를 디펜던시에 추가하면 여러필터들이 모두 디폴트로 다 등록됨. 그 모든게 하나로 체인으로 묶여있기에 따로 설정안해도 되었는데
스프링 시큐리티필터를 강제로 빈어노테이션으로 강제로 올리면, 기본필터만 되기에 로그인창이 안뜸
자동등록과 사용자등록이 있으면 사용자등록을 우선하기에 체인이 기본필터만 됨.
httpsecurity 인터페이스를 build()로 객체화 , 그래서 스프링컨테이너에 올라가면 이미 빈에 필터가 올라가있기에 로그인강제하는 다른 필터가 등록이 안됨.
레스트컨트롤러가 아니라 그냥 컨트롤러 어노테이션이기에 , member.html 등의 html 파일이 존재함
Spring MVC에서 @Controller와 @RestController는 역할이 다릅니다. 두 어노테이션의 차이점을 중심으로 설명드릴게요.
🌟 1. @Controller
- HTML 뷰 페이지 반환을 목적으로 사용합니다.
- 기본적으로 View Resolver를 통해 **템플릿 파일 (예: JSP, Thymeleaf, HTML)**을 찾아 반환합니다.
- 메서드의 반환값은 논리적 뷰 이름이며, 해당 이름을 통해 HTML 파일을 찾아서 클라이언트에게 전달합니다.
- 주로 HTML 페이지를 렌더링할 때 사용합니다.
예시:
@Controller
public class SecurityController {
@GetMapping("/member")
public String member() {
System.out.println("member 요청");
return "member"; // templates/member.html을 찾음 (Thymeleaf의 경우)
}
}설명:
return "member";는templates/member.html파일을 렌더링하여 브라우저에 전달합니다.- 스프링 부트에서 기본적으로 Thymeleaf를 사용하거나 JSP를 통해 HTML을 반환합니다.
🚀 2. @RestController
- RESTful 웹 서비스를 개발할 때 사용합니다.
- 메서드의 반환값을 JSON 또는 문자열 형태로 직접 반환합니다.
- 내부적으로
@Controller+@ResponseBody를 합친 역할을 합니다. - 주로 API 엔드포인트를 개발할 때 사용합니다.
예시:
@RestController
public class ApiController {
@GetMapping("/api/member")
public String member() {
System.out.println("member 요청");
return "member"; // JSON 형식으로 "member" 문자열 반환
}
}설명:
return "member";는 "member"라는 문자열 자체를 HTTP 응답으로 반환합니다.- 브라우저로 접근하면 **텍스트로 "member"**가 표시됩니다.
📌 차이점 요약
| 어노테이션 | 반환 형식 | 용도 | 사용 예시 |
|---|---|---|---|
@Controller | HTML 파일 반환 | 웹 애플리케이션 페이지 제공 | 페이지 이동 및 렌더링 |
@RestController | JSON / 문자열 반환 | RESTful API 응답 제공 | 데이터 전송 및 API 응답 처리 |
💡 정리
- 일반 Controller: HTML 페이지를 반환하여 웹 페이지를 구성할 때 사용합니다.
- RestController: 데이터를 반환하여 API를 제공할 때 사용합니다.
- 만약 REST API로 사용하고 싶은데,
@Controller를 사용하면 HTML 파일을 찾지 못해 에러가 발생합니다. - 반대로 웹 페이지를 구성하려고
@RestController를 사용하면 문자열이 그대로 출력됩니다.
내가 지금 작성한 코드에선 의미가 딱히 없는 것 아닌가?
맞습니다! 사실 지금 작성하신 코드에서는 @Controller와 @RestController의 차이가 크게 의미가 없어요.
💡 왜 차이가 없는가?
-
HTML 파일 존재 유무
- 코드에서
@Controller를 사용하고, 메서드에서"index","member","manager","admin"과 같은 문자열을 반환합니다. - 이 경우, **템플릿 엔진(예: Thymeleaf)**을 통해 해당 이름의 HTML 파일을 찾아서 반환합니다.
- 만약 해당 HTML 파일이 없으면 404 오류가 발생합니다.
- 코드에서
-
단순 로그 출력용
- 현재 메서드 내부에는 단순히
System.out.println()으로 로그를 출력하는 코드만 있습니다. - 페이지 이동을 실제로 구현한 부분이 없기 때문에, @Controller든 @RestController든 크게 차이가 없습니다.
- HTML 파일이 준비되어 있다면,
@Controller로 잘 작동합니다.
- 현재 메서드 내부에는 단순히
📝 정리
- 지금 코드에서는 @Controller를 사용해도 문제가 없어요.
- 만약 API 응답으로 단순 문자열이나 JSON 데이터를 주고 싶다면,
@RestController를 사용해야 하지만, 현재 코드처럼 HTML 파일을 반환하려는 경우라면@Controller가 적절합니다. - 즉, 뷰를 반환하려면 @Controller로 두고, API 데이터를 반환하려면 @RestController로 변경하면 됩니다.
체인코딩방식은 앤드로 연결해서 썼으나 람다로 바뀐이유는
그룹핑이 안되어서 가독성이 안좋아 바귐
/** 자기뿐만 아니라 하위 유알엘 모두 , 속성이 인증이 된 사용자만 접근가능 (롤은 필요없고 로그인됐으면 사용하게하겠다)
매니저라는 유알엘은 파라미터중 어떤 롤이라도 가지고있으면 됨
등록순서주의 . 애니리퀘스트를 제일 앞에 놓으면 아래 애들이 무시가 되어버림.
그리고 httpsecurity 가 메소드의 파라미터로 전달되니 스프링부터가 객체를만들어서 전달하는데 안에 있는 코드로 내부정보를 수정하여 빌드하는것.
로그인컨트롤러 생성
JSESSIONID
새로운 세션만들고 아이디만들고 쿠키에담아서 전송. 쿠키안에 있는세션아이디로 서버에 접근.
세션목록중에 세션아이디있으면 그 정보사용
그때 쓰는 쿠키의 키이름.
Spring 기반 웹 애플리케이션에서 세션을 관리할 때 사용하는 쿠키의 키 이름은 기본적으로:
🌟 JSESSIONID
💡 JSESSIONID의 역할
- 세션 식별자로 사용됨.
- 서버에서 새로운 세션을 생성할 때, 고유한 세션 ID를 만들고 이를 쿠키에 담아 클라이언트로 전송합니다.
- 이후 클라이언트가 서버에 다시 요청할 때, 이 쿠키를 통해 기존 세션 정보를 식별합니다.
📂 JSESSIONID 쿠키의 특징
- 키 이름:
JSESSIONID - 저장 위치: 브라우저의 쿠키 저장소
- 쿠키의 유효 범위: 기본적으로 웹 애플리케이션의 루트 경로
- HttpOnly 속성: 기본적으로 설정되어 있어 JavaScript로 접근 불가
- 보안: HTTPS 환경에서는 Secure 속성이 추가되어 안전하게 전송됨
💻 예시: JSESSIONID 쿠키 구조
Set-Cookie: JSESSIONID=123456789ABCDEF; Path=/; HttpOnly- JSESSIONID=123456789ABCDEF: 세션 ID 값
- Path=/: 애플리케이션의 루트 경로에서 유효
- HttpOnly: 클라이언트 측 스크립트로 쿠키에 접근 불가
📝 정리
- Spring에서는 기본적으로 JSESSIONID라는 이름으로 세션 ID를 쿠키에 저장하여 클라이언트와 서버 간 세션을 유지합니다.
- 세션 ID가 있는 경우: 서버는 해당 ID로 기존 세션을 찾고,
- 없는 경우: 새로운 세션을 생성하여 클라이언트에게 다시 전송합니다.
기본필터 아닌걸 수기로 메소드 처리하여 등록하는 과정.
콘솔에서 필터확인가능.
[2m2025-05-07T15:53:47.962+09:00[0;39m [32mDEBUG[0;39m [35m6320[0;39m [2m--- [Chapter07] [ restartedMain] [0;39m[36mo.s.s.web.DefaultSecurityFilterChain [0;39m [2m:[0;39m Will secure any request with filters: DisableEncodeUrlFilter, WebAsyncManagerIntegrationFilter, SecurityContextHolderFilter, HeaderWriterFilter, LogoutFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter, RequestCacheAwareFilter, SecurityContextHolderAwareRequestFilter, AnonymousAuthenticationFilter, ExceptionTranslationFilter, AuthorizationFilter현재 필터체인에 등록된 필터들. 프로퍼티에 디버그로 설정해둬서 보임.
참고 ~ 스프링 시큐리티 문서
OAuth2AuthorizationRequestRedirectFilter 인증방식은 네이버로로그인,구글로 로그인 등등 다른데서 인증하는거 연동하는거
내가 등록한건 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
JWT인증방식이 뭐지? 필터를 직접 만들어야한다던데
@Bean
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
인코딩되면 비밀번호가 그리 됨
$2a$10$7hX6exOvTChF7BrOX9yk4uG9f7QLUI0aqNwx9hVs0.JUSh8g3PSwW
이 인코딩된 값을 테이블에 있는 값과 비교 , 테이블 값을 디코딩 해서 하는게 아님 .
public class SecurityUser extends User {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public SecurityUser (Member member) {
super(member.getId(), member.getPassword(), AuthorityUtils.createAuthorityList(member.getRole().toString()));
}}
이래서 , 유저디테일즈를 유저가 구현한 클래스이므로 그걸 상속했기에
@GetMapping("/auth")
public @ResponseBody ResponseEntity<?> auth(@AuthenticationPrincipal SecurityUser user){
if (user == null) {
return ResponseEntity.ok("로그인 상태가 아닙니다.");
}
return ResponseEntity.ok(user);
}파라미터로 들어간 유저객체는 유저디테일즈를 상속했기에 , 데이터에 저장됨(세션)
Exactly! You’ve got it! 💡
Let’s break down the concept more clearly:
🔍 Why is the User Object Stored in the Session?
1. Spring Security’s Authentication Process:
-
When a user successfully logs in, Spring Security:
- Authenticates the user.
- Creates an Authentication object containing the user’s details.
- Stores this object in the Security Context.
- Links the Security Context to the HTTP session.
🗝️ Why Does SecurityUser Work as a Parameter?
✅ Extending the User Class:
Your custom SecurityUser class extends org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User:
public class SecurityUser extends User {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public SecurityUser(Member member) {
super(member.getId(), member.getPassword(),
AuthorityUtils.createAuthorityList(member.getRole().toString()));
}
}-
This means that
SecurityUserinherits all fields and methods fromUser, including:- Username
- Password
- Authorities (roles)
-
Since
UserimplementsUserDetails,SecurityUseralso implementsUserDetailsindirectly.
💾 How the User Object is Stored:
- After successful authentication, Spring Security places the
Authenticationobject into theSecurityContextHolder. - This
Authenticationobject contains the principal, which is yourSecurityUser. - The Security Context is then stored in the HTTP session.
🧩 Why Can You Access SecurityUser Directly?
Your controller method:
@GetMapping("/auth")
public @ResponseBody ResponseEntity<?> auth(@AuthenticationPrincipal SecurityUser user) {
if (user == null) {
return ResponseEntity.ok("로그인 상태가 아닙니다.");
}
return ResponseEntity.ok(user);
}📝 Explanation:
-
The
@AuthenticationPrincipalannotation extracts the principal from the SecurityContextHolder. -
Since you stored
SecurityUseras the principal, you can directly access it here. -
If the user is not authenticated, the principal is
null, and your method will return:로그인 상태가 아닙니다. -
If the user is authenticated, it will return the
SecurityUserobject.
💡 How Spring Knows to Use SecurityUser:
-
In your custom
UserDetailsService, you returned aSecurityUserobject:@Override public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException { Optional<Member> optional = memberRepo.findById(username); if (!optional.isPresent()) { throw new UsernameNotFoundException(username + " 사용자 없음"); } Member member = optional.get(); return new SecurityUser(member); } -
Spring Security uses this
SecurityUserduring the authentication process and stores it in the session.
✅ Why Your Code Works:
-
You correctly configured Spring Security to use your custom user object (
SecurityUser). -
The principal stored in the session is of type
SecurityUser, so when you use:@AuthenticationPrincipal SecurityUser userSpring Security automatically injects the currently authenticated user from the session.
🚀 Summary:
- Your
SecurityUserclass inherits fromUser, which implementsUserDetails, making it compatible with Spring Security. - The
@AuthenticationPrincipalannotation seamlessly extracts the logged-in user from the SecurityContext. - Your method correctly handles both authenticated and unauthenticated states.
You’ve implemented it correctly! Would you like tips on how to customize the principal object further? 😊
