1. with~as문
with~as문을 이용하면 파일 닫기(close)를 생략할 수 있다.
with~as문을 사용하면 파일을 열고 작업을 수행한 후에 파일을 자동으로 닫아준다. 이것은 파일 관리를 보다 효율적으로 처리할 수 있도록 도와준다.
with open('파일명', '모드') as 파일별칭: # 파일에 대한 작업 수행 # 파일은 이 블록을 벗어나면 자동으로 닫힘
여기서 open() 함수는 파일을 열고, as 키워드를 사용하여 파일에 대한 별칭을 만든다. 이후 with 블록 내에서 파일 작업을 수행하고, 블록을 빠져나오면 파일이 자동으로 닫힌다. 이것은 코드를 보다 깔끔하고 오류가 발생할 가능성을 줄여준다.
with~as문을 쓰지 않는 경우:
# 파일 쓰기
url = '/Users/kimye/Downloads/pythonTxt/'
file = open(url + '5_037.txt', 'a')
file.write('study python')
file.close()
# 파일 읽기
file = open(url + '5_037.txt', 'r')
print(file.read())
file.close()with~as문을 쓰는 경우:
# 파일 쓰기
with open(url + '5_037.txt', 'a') as f:
f.write('study python')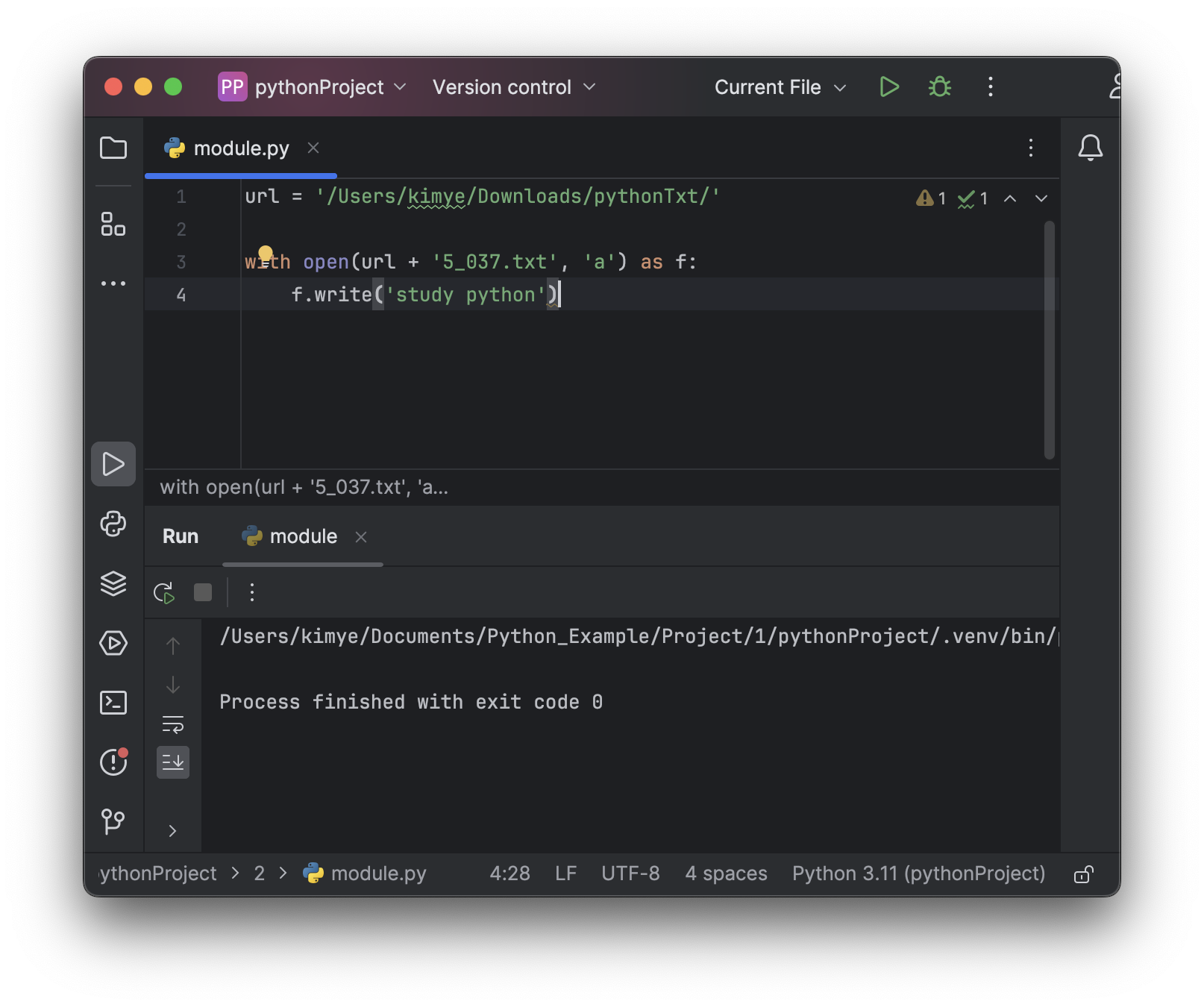
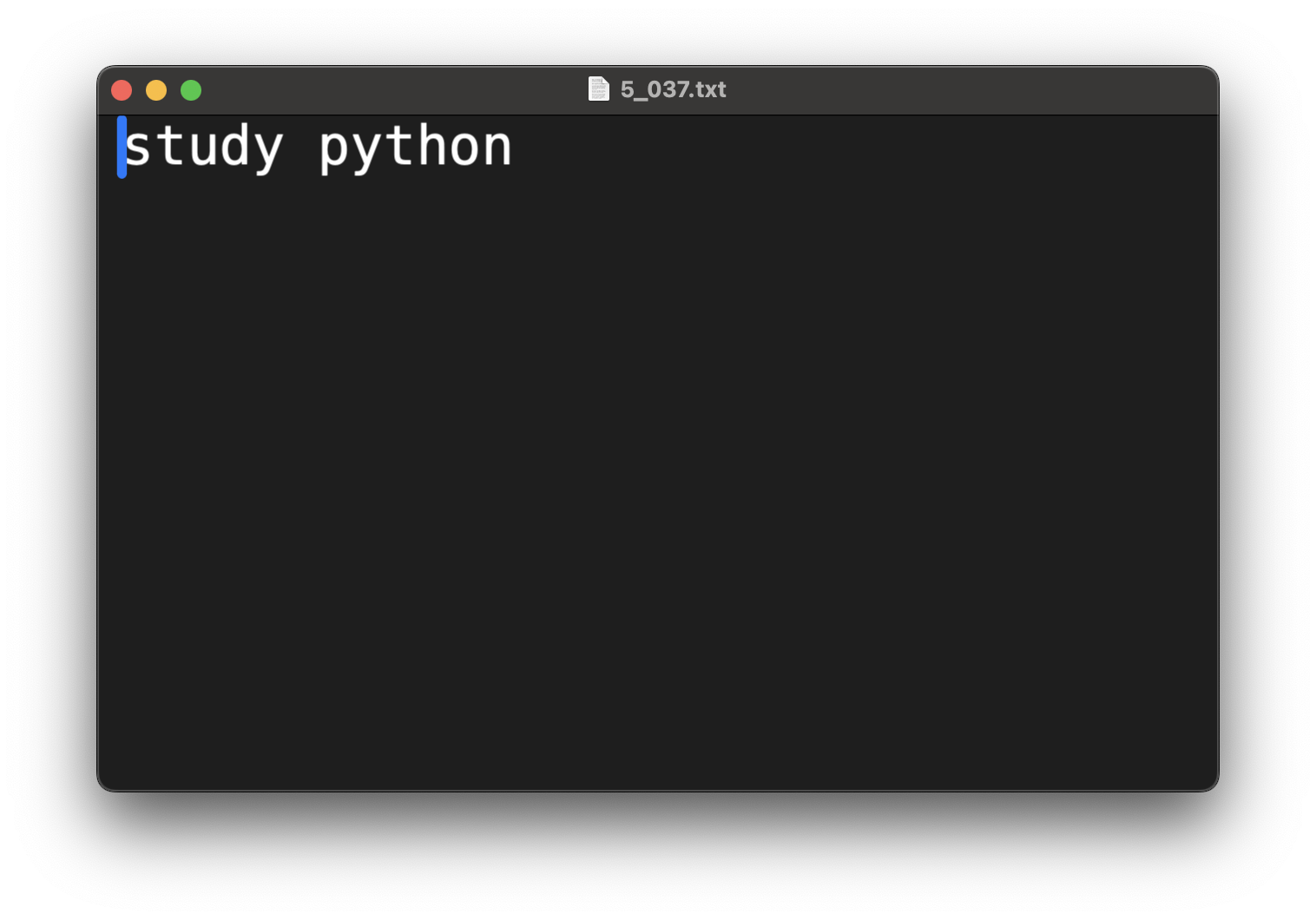
# 파일 읽기
with open(url + '5_037.txt', 'r') as f:
print(f.read())
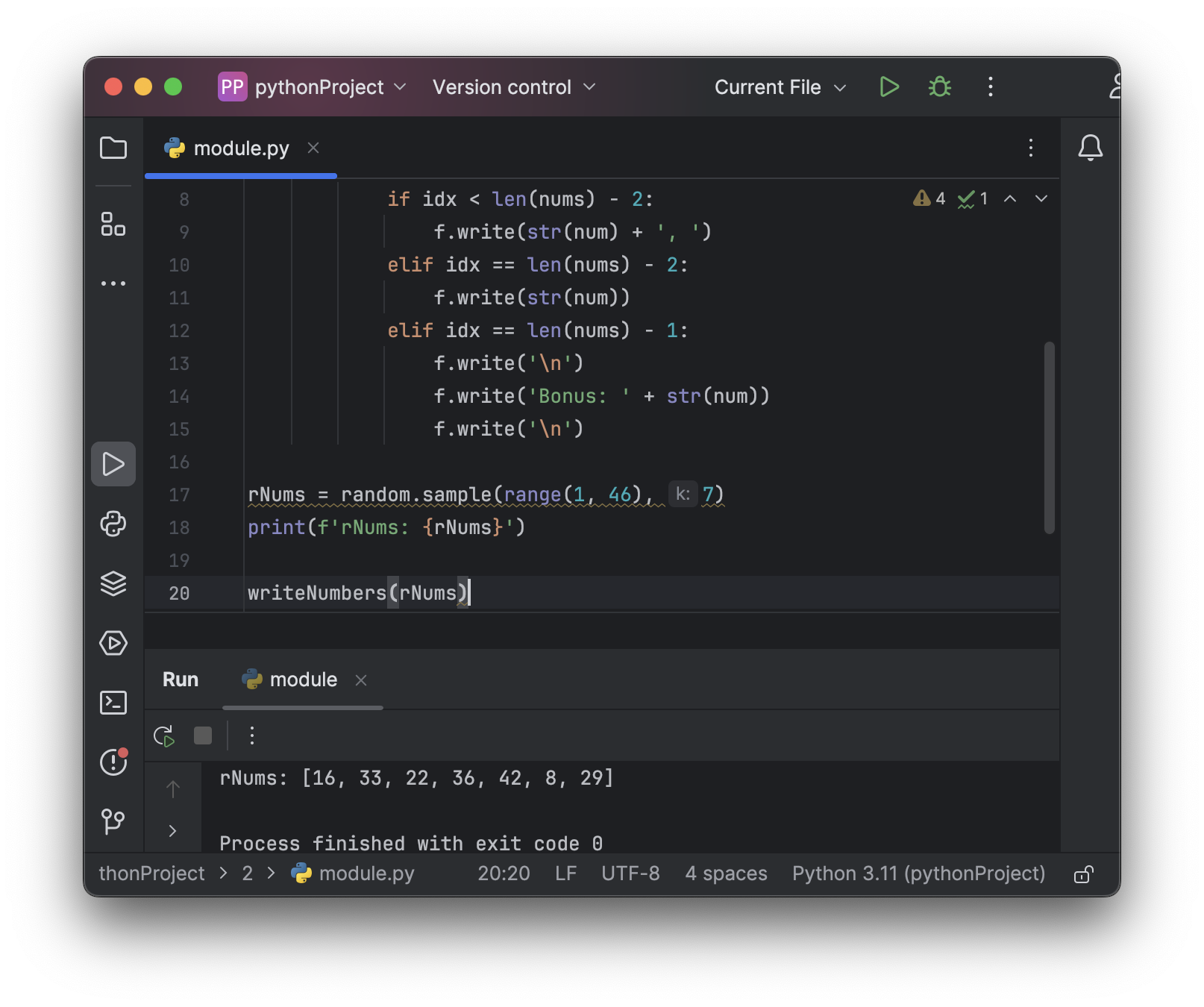
Example: 로또 번호 생성기 프로그램을 만들고 파일에 번호 출력하기
import random
url = '/Users/kimye/Downloads/pythonTxt/'
def writeNumbers(nums):
for idx, num in enumerate(nums):
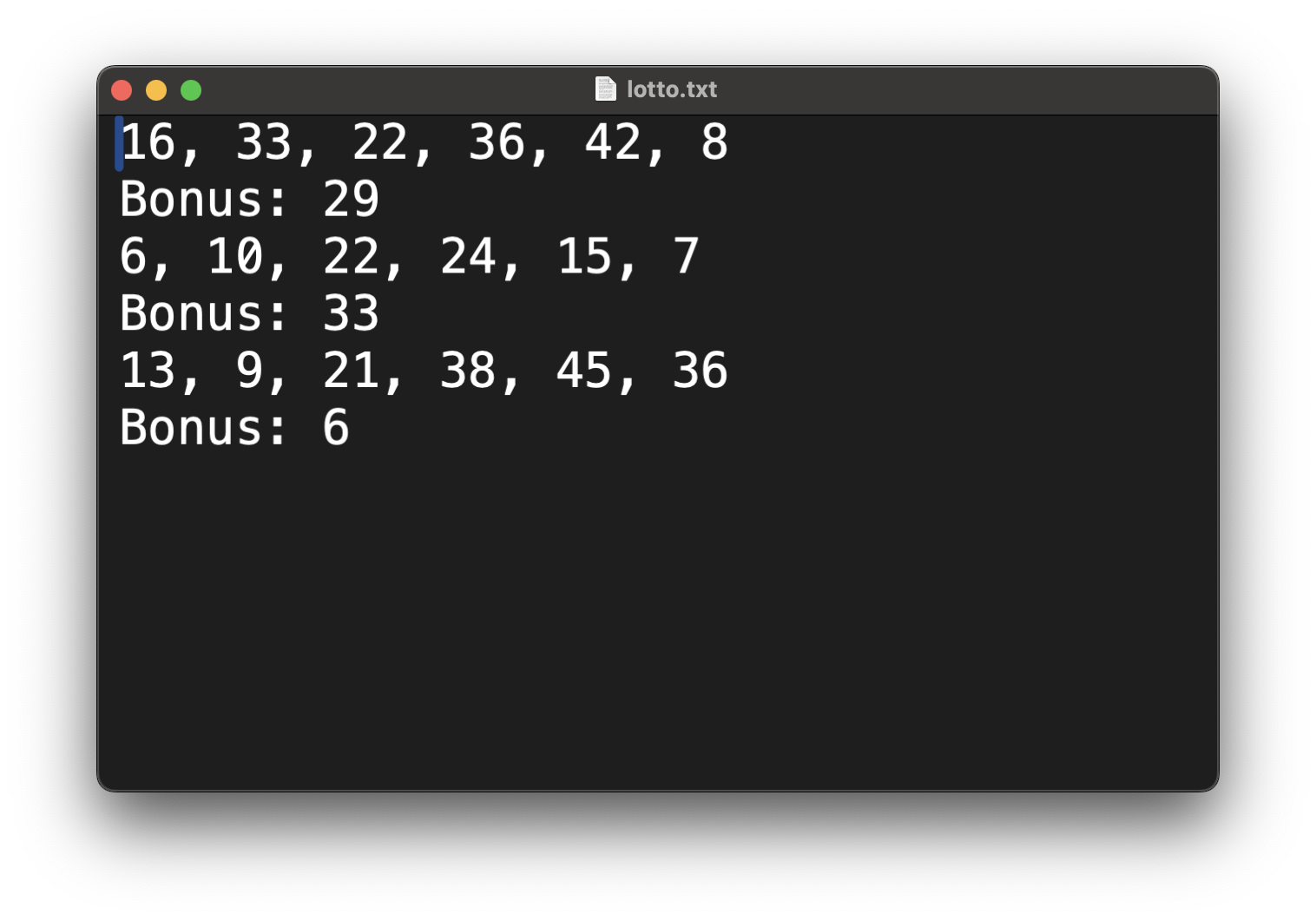
with open(url + 'lotto.txt', 'a') as f:
if idx < len(nums) - 2:
f.write(str(num) + ', ')
elif idx == len(nums) - 2:
f.write(str(num))
elif idx == len(nums) - 1:
f.write('\n')
f.write('Bonus: ' + str(num))
f.write('\n')
rNums = random.sample(range(1, 46), 7)
print(f'rNums: {rNums}')
writeNumbers(rNums)