- 논문은 학습된 over-parameterized model이 실제로 낮은 low intrinsic dimension에 있다는 아래 두 논문에 영감을 받았음
- Measuring the Intrinsic Dimension of Objective Landscapes Li et al., 2018a
- Intrinsic Dimensionality Explains the Effectiveness of Language Model Fine-Tuning Aghajanyan et al., 2020
- LoRA : Low-Rank Adaptation
- LoRA 를 사용하면?
- Pretrained weight 를 고정된 상태로 유지하면서
Adaptation 중 dense layer의 변화에 대한 rank decomposition matrices를 최적화 - 이를 통해 신경망의 일부 dense layer를 간접적으로 훈련시키는 것이 가능
LoRA는 trainable parameter의 수가 적고 학습 처리량이 높으며 inference latency가 이전 연구 대비 적음 - 그럼에도 불구하고 RoBERTa, DeBERTa, GPT-2, GPT-3에서 fine-tuning 보다 같거나 더 나은 성능을 보여줌
기존에 solutions 들은 아래와 같은 문제점을 가짐
1. adapter layers introduce inference latency
2. Directly optimizing the prompt is hard
LoRA 는
- LoRA는 모든 dense layer에 적용 가능
- Neural Network 는 Matrix multiplicatio을 수행하는 많은 dense layer를 포함
이 matrices의 weights는 일반적으로 full-rank - Intrinsic Dimensionality Explains the Effectiveness of Language Model Fine-Tuning. (2020) (Meta AI)
- PLM은 low intrinsic dimension 을 가짐 (보통 over-parameterized model 이 가지는 특징이라고 함)
- 더 작은 subspace에 대한 random projection 에도 불구하고 여전히 효율적으로 학습할 수 있음을 보임
- 특히 RoBERTa의 경우 only 200 trainable parameters 로 90%의 performance를 달성했다고 주장

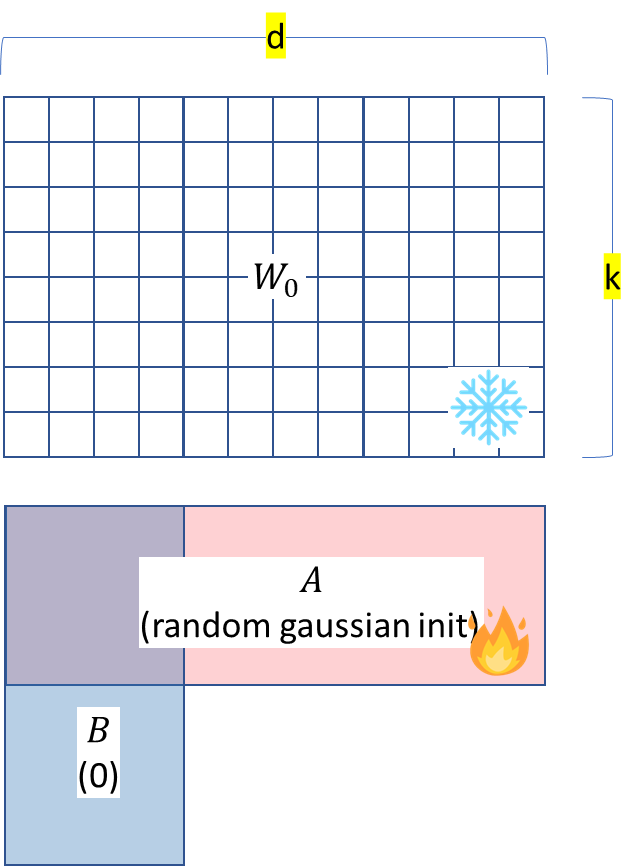
아래에서 W0은 gradient update❌
BA는 gradient update✅

따라서
- 메모리 효율
- 추가적인 계산 X
- 학습할 param 선택할 수 있음
참고한 사이트
https://kimjy99.github.io/%EB%85%BC%EB%AC%B8%EB%A6%AC%EB%B7%B0/lora/
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BJqwmDpa0wM&t=1565s
