Motivation
-
fine-tuning은 all the parameters of the pre-trained model을 update한다.
-
large model을 pre-train하기에, 모든 model parameter들을 retraining하는 full fine-tuning은 less feasible해지고 있다.
-
GPT-3 175B를 예로 들면, 각 175B parameter의 independent한 fine-tunde model의 instance를 deploy하는 것은 매우매우매우 비싸다.
-
많은 이전의 연구들은, new task를위해,
약간의 parameter를 adapting하거나,
external modules를 learning하는 방법을 사용했다.- 장점
- 이 방법은 적은 수의 task-specific parameters만 store하고 load하면 되기에, efficient하다.
- 단점
- 하지만, inference latency를 늘린다.
- model depth를 키우거나 model의 usable sequence length를 줄이기 때문.
- efficiency와 module quality 간의 trade-off 가짐.
- 하지만, inference latency를 늘린다.
- 장점
-
inspiration
-
학습된 over-parametrized 모델들이 실제로 낮은 intrinsic dimension에 위치한다는 것을 보인 연구를 토대로,
-
model adaptation 과정에서 발생하는 weight 변화 또한 낮은 "intrinsic rank"를 가질 것이라고 가설을 세움.
-
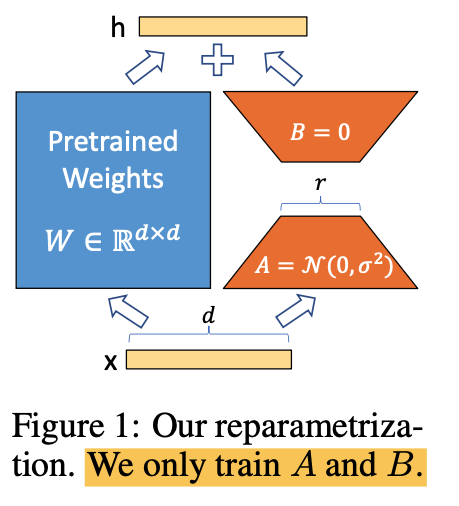
LoRA를 사용하면 neural network의 일부 dense layer들을 indirect하게 학습 가능.
-
pre-trained weight들을 frozen 상태로 유지하면서,
-
adaptation 과정에서 dense layer의 변화를 rank decomposition matrix(low-rank matrix)들을 optimize하는 방식
-
-
-
Apporach
-
LoRA는 pretrained model weight를 freeze하고,
trainalbe rank decomposition matrices를 각 Transformer의 layer에 inject한다.
➡️ downstream task를 위한 trainable parameter 개수를 크게 줄임.-
Adam으로 fine-tuned된 GPT-3 175B와 비교해서,
trainable paramter를 10,000배 줄이고
GPU memory requirment를 3배 줄임. -
no additional inference latency
-
Problem Statement (Full fine-tuning)
-
full-fine tuning 과정에 대해 살펴 보면,
-
pre-trained (auto-regresive) language model 는 parametrized by
-
Each downstream task는
training dataset of context-target pairs: 으로 표현됨.-
: sequence of tokens,
: sequence of tokens -
ex) in NL2SQL,
: natural language query
: corresponding SQL commdands -
ex) for summarization,
: content of article
: its summary
-
-
full-finetuning 동안,
-
model은 pre-trained weight 로 intialized.
-
그리고 로 updated됨.
- 아래 conditional LM objective를 maximize하도록, 반복적으로 gradient를 따라 update됨.
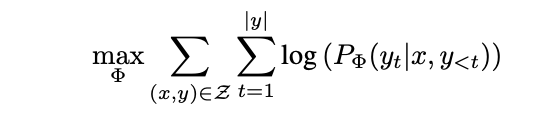
-
-
full-finetuing의 main drawback
-
각 downstream task에 대해, 각기 다른 parameter set 을 학습해야 한다는 점.
-
-
따라서, pre-trained model이 크다면, 각 independent한 fined-tuned model들의 instance를 stroing하고 deploy하는 것은 challenging 함.
-
-
LoRA
-
parameter-efficient approach
-
task-specific parameter incerement 는 low-rank representation을 사용해서,
훨씬 작은 parameters set 로 encode한다. -
-
를 찾는 task에서,
를 optimize하는 task로 바뀜. -
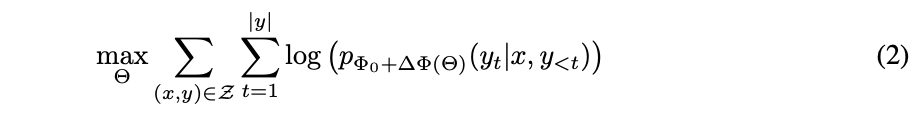
-
기존 Solution들의 한계
-
efficient adaptation의 두 가지 주요 전략
- 1.adapter layers 추가
- 2.input layer activation들의 form을 optimize(prompt optimize)
-
1.Adapter Layers
-
각 Transformer block마다 두 개의 adapter layer를 추가하거나,
adapter layer와 추가적인 LayerNorm 사용하는 연구 등. -
단점: 매우 작은 bottleneck dimension을 사용하더라도 adapter를 사용할 때 latency가 눈에 띄게 증가
- sequential하게 adapter layers가 processed돼야 하기 때문.
-
-
2.Optimizing the Prompt
-
대표적인 예인 Prefix tuning은 optimize하기 어려움.
-
trainable parameter 수에 따른 성능 변화가 예측 불가능함.
-
adaptation을 위해 sequence length의 일부를 사용함으로써 downstream task를 위한 유효 sequence length가 줄어드는 trade-off가 존재.
Method
Low-rank parametrized update matrices
-
layer의 weight matrix들은 주로 full-rank를 갖는다.
-
Intrinsic Dimensionality Explains the Effectiveness of Language Model Fine-Tuning(Aghajanyan et al, 2020) 연구는
specific task에 adapting할 때, pre-trained language model들이 낮은 "intrinsic dimension"을 가지고 있으며,
smaller subspace로의 random projection에도 불구하고 여전히 efficient하게 learning 할 수 있다는 것을 보임.- claude 3.5 설명 첨부
- Intrinsic dimension은 pre-trained language model의 parameter 공간에서 실제로 중요한 변화가 일어나는 차원의 수를 의미함.
- 대규모 language model이 겉보기에는 매우 많은 parameter를 가지고 있지만, 실제로는 훨씬 더 작은 차원의 subspace에서 대부분의 중요한 learning과 adaptation이 일어난다는 것을 시사함.
- claude 3.5 설명 첨부
-
위 연구에 inspired 받아,
저자는 adaptation 동안 weight에 대한 update도 낮은 "intrinsic rank"를 가질 것이라고 hypothesize함. -
pre-trained weight matrix 에 대해,
의 update 를 low-rank decomposition로 제한한다(constrain)where , ,
rank -
training 동안,
- 는 frozen ❄️. graident updates ❌
- 와 는 trainable parameters를 가짐.
- 와 는 동일한 input에 곱해지고,
각각의 output vector들은 coordinate-wise로 sum한다. - 에 대해, LoRA forward pass는
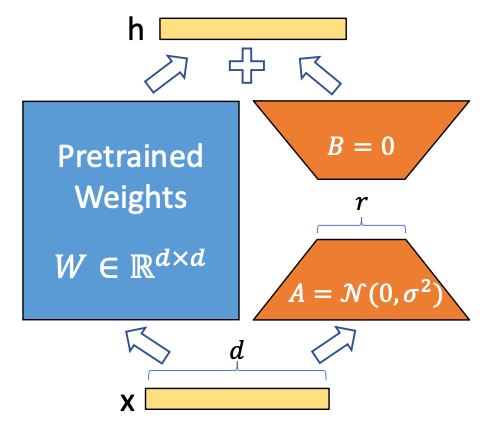
- training 시작 시에,
- 는 random Gaussian initialization을 사용
- 는 zero
- 는 zero로 시작.
- training 시작 시에,
-
를 로 scaling
- 는 고정된 상수(constant)이고, 은 rank
- 로 scaling함으로써, 이 변할 때 전체 update의 크기가 크게 변하지 않도록.
- 즉, low-rank 업데이트의 크기를 조절하는 역할.
- Adam optimizer와의 관계
- Adam에서는 learning rate가 update의 크기를 조절
- 로 scaling하는 것은 실질적으로 learning rate를 조절하는 효과.
- 이러한 방식으로 를 설정하면, 을 변경할 때마다 learning rate나 다른 hyperparameter를 재조정할 필요가 줄어듦.
-
No Additional Inference Latency
- Production 환경에 deploy할 때, 를 계산하고 저장하여 일반적인 방식으로 inference를 수행 가능.
- 와 모두 dimension임에 주목.
- 다른 downstream task로 전환해야 할 때, 를 빼고 다른 를 사용하면 됨.
- 이는 매우 적은 memory overhead로 빠르게 수행할 수 있는 연산.
- inference 동안 어떠한 추가적인 latency도 발생시키지 않음을 보장.
Applying LoRA to Transformer
-
LoRA는 어떤 weight matrix들의 subset에도 적용해서, trainable parameter를 줄일 수 있음.
-
Tranformer 구조에선, self-attention module에 4개의 weight matrix들 ()과 MLP module에 2개의 matrix가 존재.
-
LoRA는 (또는 )를 dimension의 single matrix로 취급함.
이는 output dimension이 일반적으로 attention head들로 나눠지더라도 마찬가지. -
simplicity와 parameter-efficiency를 위해 downstream task에서
attention weight 🔥만을 adapt하고 MLP module은 freeze ❄️
(즉, MLP module은 training되지 않음) -
MLP layers, LayerNorm layers, 나머지 parameter들의 adapting에 관한 empirical investigation은 future work로 남김.
Praticial Benefit & Limitation
-
Benefit
-
memory와 storage usage의 reduction
-
Adam으로 train된 large Transformer의 경우, 이면 frozen parameter에 대한 optimizer state를 store할 필요가 없음
➡️ VRAM usage 까지 감소- r은 LoRA의 rank를, 은 원래 모델의 dimension을 나타냄.
- r이 보다 훨씬 작다는 것은 학습해야 할 parameter 수가 크게 줄어든다는 의미.
- Adam은 각 parameter에 대해 first moment(평균)와 second moment(분산) 등의 state를 유지.
- 이 state들은 각 parameter마다 저장되어야 하므로, parameter 수만큼의 추가 memory가 필요.
- Frozen parameter는 update되지 않으므로, 이에 대한 optimizer state를 유지할 필요가 없음.
- LoRA에서는 대부분의 원래 parameter가 frozen 상태이므로, 이에 대한 optimizer state를 store할 필요가 없음.
-
r = 4이고 query와 value projection matrix만 adapt할 경우,
➡️ checkpoint size가 약 10,000배 감소(350GB에서 35MB로).
➡️ 훨씬 적은 수의 GPU로 train할 수 있고 I/O bottleneck을 피할 수 있음. -
LoRA가 전체 model weight를 저장하지 않고, 작은 rank의 update만을 저장하기 때문에 가능
-
또한 모든 layer가 아닌 query와 value projection matrix만 adapt하는 것도 size 감소에 기여
-
deployed 상태에서 모든 parameter가 아닌 LoRA weight만 swap함으로써 훨씬 낮은 cost로 task를 switch 가능.
-
-
limitation
-
각 input마다 다른 weight: 를 사용해야 하므로,
기존의 batch matrix multiplication을 직접 적용할 수 없음. -
이로 인해, 단일 task에 대한 inference는 빨라지지만,
여러 task의 input을 동시에 효율적으로 처리하는 것은 복잡해짐.
-
Understanding the Low-rank updates
-
empirical studies to answer the follwing questions
-
1) Given a parameter budget constraint, which subset of weight matrices in a pre-trained Transformer should we adapt to maximize downstream performance?
-
Limited parameter budget (18M, 약 35MB)에서 어떤 weight를 adapt해야 downstream task에서 최고의 성능을 얻을 수 있는지 조사.
-
Self-attention module의 weight matrix만 고려.
-
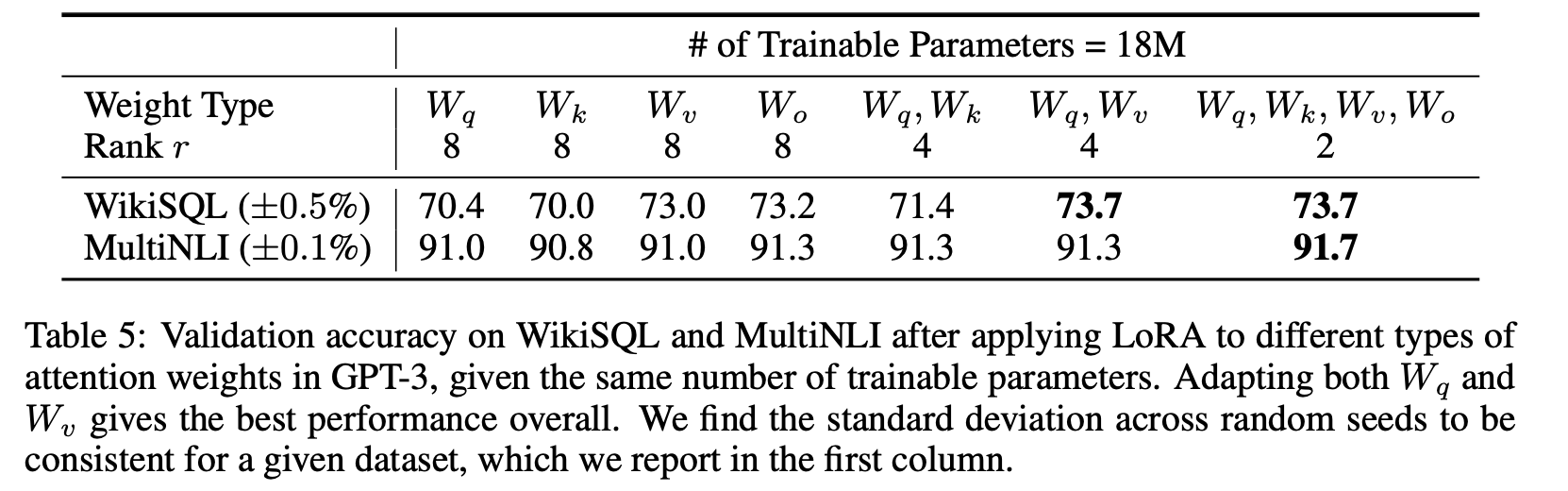
- 실험 결과
- Wq나 Wk만 adapt ➡️ 성능이 상대적으로 낮음.
- Wq와 Wv를 함께 adapt ➡️ 가장 좋은 성능.
- 모든 attention weight (Wq, Wk, Wv, Wo)를 함께 adapt하는 것도 좋은 성능을 보이지만,
parameter 효율성 측면에서는 Wq와 Wv만 adapt하는 것이 더 효과적
- 실험 결과
-
주요 발견
-
rank가 4로 낮아도 의 충분한 information을 capture 가능.
-
단일 type의 weight를 높은 rank로 adapt하는 것보다 여러 weight matrix를 낮은 rank로 adapt하는 것이 더 효과적.
-
-
-
2) Is the "optimal" adaptation matrix really rank-deficient?
If so, what is a good rank to use in practice?-
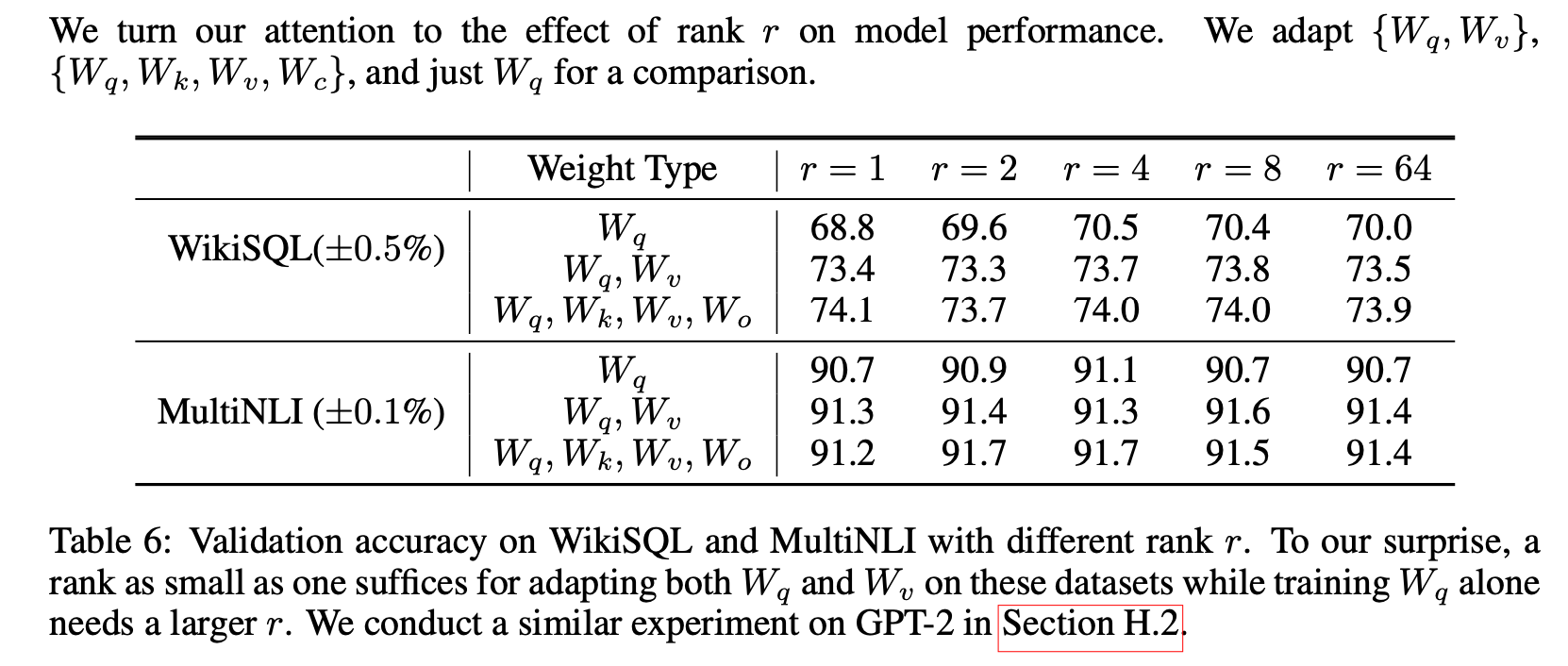
-
Table 6은 놀랍게도 LoRA가 매우 작은 로도 이미 competitive한 performance를 보인다는 것을 보여줌
(Wq만 adapt하는 것보다 {Wq,Wv}에서 더 좋음). -
이는 update matrix 가 매우 작은 "intrinsic rank"를 가질 수 있음을 suggest함.
-
이 finding을 further support하기 위해, 서로 다른 값과 다른 random seed에 의해 학습된 subspace들의 overlap을 check.
-
r을 증가시키는 것이 더 meaningful한 subspace를 cover하지 않는다고 주장,
이는 low-rank adaptation matrix가 sufficient하다는 것을 suggest.
-
-
subspace similarity between different
-
rank 이 다른 두 adaptation matrix 간의 subspace similarity를 분석.
-
구체적으로는, 과 의 adaptation matrix 사이에 어떤 singular vector가 얼마나 겹치는지를 조사
-
이를 위해 두 rank에 대한 singular value decomposition을 수행하고, right-singular unitary matrices 와 의 similarity를 비교함.
-
이 유사성을 측정하기 위해, Grassmann distance 기반의 정규화된 subspace similarity를 사용.
-
에서 상위 개의 singular vectors가 에서 상위 개의 singular vectors와 얼마나 겹치는지를 평가
-
-
⭐ 실험 결과
-
과 에서 상위 singular vector directions는 상당히 겹치지만, 나머지 방향들은 그렇지 않다는 점을 발견
-
즉, r이 작은 경우에도 상위 singular vectors는 중요한 정보를 담고 있으며,
조차도 다운스트림 작업에서 효과적인 이유를 설명 가능. -
이 커질수록 유용한 정보는 증가하지만,
많은 singular directions는 noise에 가깝다는 결론에 도달
-
-
이 분석은 LoRA의 adaptation matrix가 매우 낮은 rank에서도 유용한 정보를 충분히 캡처할 수 있다는 것을 강조.
-
-
Subspace similarity between different random seeds
-
random seeds를 다르게 설정한 두 번의 rank r = 64로 학습한 결과들 간의 subspace similarity를 분석.
-
이를 통해, 동일한 rank r = 64로 학습했을 때, ∆Wq와 ∆Wv의 차이점을 관찰 가능.
-
실험 결과
-
∆Wq는 ∆Wv보다 더 높은 "intrinsic rank"를 가지고 있는 것으로 나타남.
- 이는 ∆Wq가 두 random seeds 간에 더 많은 공통적인 singular value directions를 학습했다는 의미.
- 이러한 결과는 Table 6에서 관찰된 실험적 결과와 일치하며, ∆Wq의 rank가 ∆Wv보다 상대적으로 더 높다는 것.
-
또한, 두 개의 random Gaussian matrices를 비교했을 때,
이들 사이에는 공통된 singular value directions가 거의 없다는 사실이 도출됨.- 이는 random Gaussian matrices 간의 subspace similarity가 매우 낮다는 것.
-
이 실험을 통해, ∆Wq가 ∆Wv보다 더 중요한 singular directions를 학습하며,
rank가 높을수록 유의미한 sub-space가 더 잘 포착된다는 것을 확인.
-
-
-
-
3) What is the connection between and ?
Does highly correlate with ?
How large is comparing to ?- ∆W가 W와 얼마나 높은 상관관계를 가지는지
그리고 ∆W가 W의 상위 singular directions에 주로 포함되는지를 조사 - Frobenius norm을 사용해 Wq의 subspace에 투영된 ∆Wq와 Wq를 비교하는 방식.
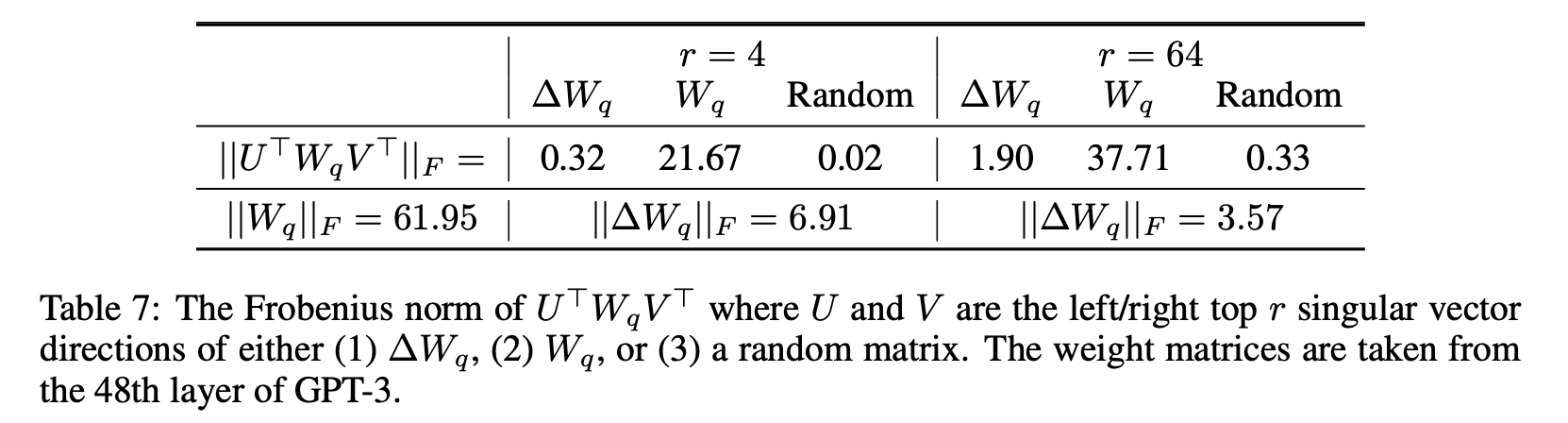
- 실험 결과
- ∆W는 W와 무작위 행렬(random matrix)과 비교했을 때 더 높은 상관관계를 가지며,
∆W는 W에 이미 존재하는 일부 특성을 증폭(amplify)하는 역할을 한다는 사실을 발견 - 또한, ∆W는 W의 상위 singular directions를 반복하는 것이
아니라 W에서 강조되지 않은 방향들만 증폭한다는 점을 발견 - r = 4인 경우 amplification factor가 21.5에 달하는데, 이는 ∆Wq가 Wq의 특정 중요한 특성들을 매우 크게 증폭함을 나타냄.
- ∆W는 W와 무작위 행렬(random matrix)과 비교했을 때 더 높은 상관관계를 가지며,
- ∆W가 W와 얼마나 높은 상관관계를 가지는지
Future Works
-
LoRA는 다른 효율적인 적응 방법과 결합될 수 있으며, 이로 인해 orthogonal improvement(서로 독립적인 성능 향상)을 이끌어낼 가능성.
-
LoRA 또는 fine-tuning의 메커니즘은 아직 명확하지 않음.
pre-trianing 중에 학습된 특성들이 어떻게 downstream task에 잘 적용되는지에 대한 이해가 부족.
LoRA는 full fine-tuning보다 이러한 질문에 답을 제시하는 데 더 효과적일 것으로 보임. -
현재는 LoRA를 적용할 weight matrices를 선택하는 데 있어 주로 경험적인 방법(heuristics)에 의존.
이를 더 원칙적인 방법으로 개선할 수 있는지에 대한 연구 필요. -
∆W의 rank-deficiency는 W 또한 rank-deficient 할 수 있다는 점을 시사.