생성자
객체가 생성될 때 자기가 받은 파라미터 값을 멤버변수에 넣는게 생성자의 역할
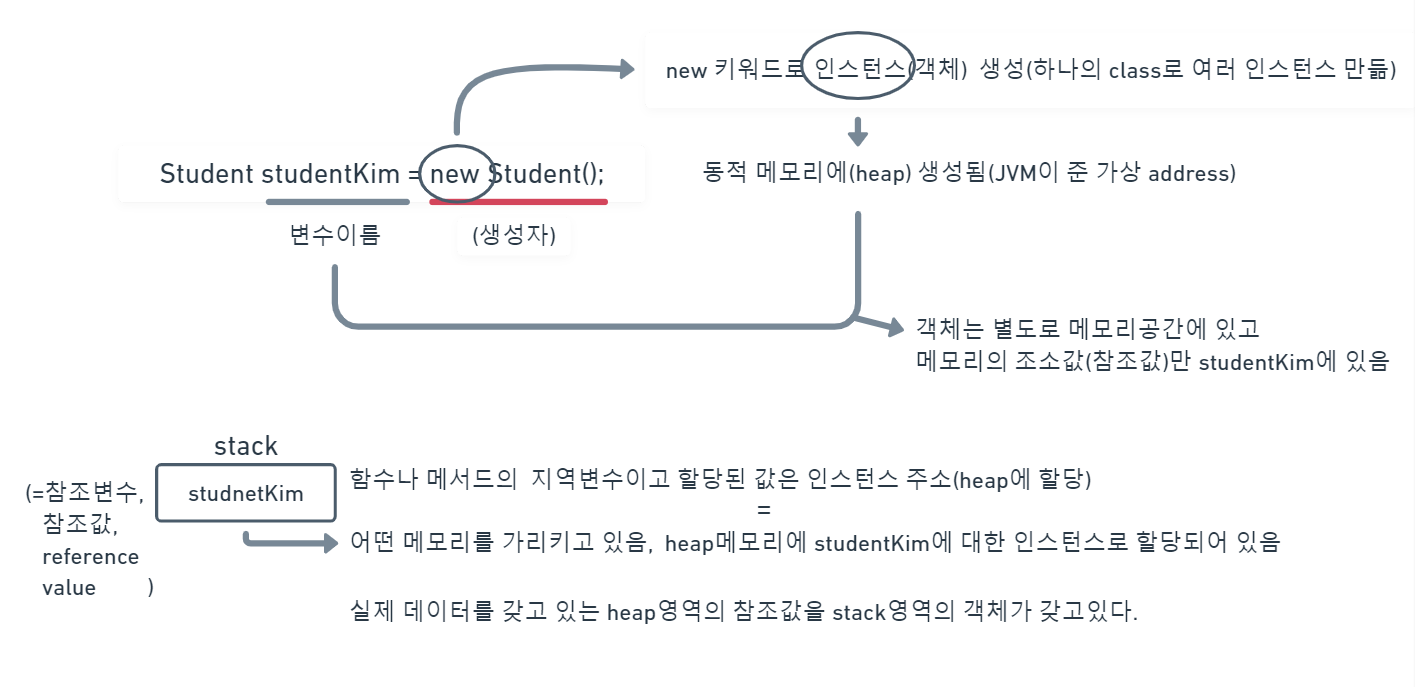
- 객체를 생성할 때 new 키워드와 함께 사용(new Student)
- 생성자는 일반 함수처럼 기능을 호출하는 것이 아니고 객체를 생성하기 위해 new와 함께 호출됨
- 객체가 생성될 때 변수나 상수를 초기화 하거나 다른 초기화 기능을 수행하는 메서드 호출함
- 생성자는 반환 값이 없고, 클래스의 이름과 동일
- 대부분의 생성자는 외부에서 접근 가능하지만, 필요에 의해 private 으로 선언되는 경우도 있음
기본 생성자(default constructor)
· 클래스에는 반드시 적어도 하나 이상의 생성자가 존재
· 클래스에 생성자를 구현하지 않아도 new 키워드와 함께 생성자를 호출할 수 있음
· 클래스에 생성자가 하나도 없는 경우 컴파일러가 생성자 코드를 넣어줌
· 매개 변수가 없음, 구현부가 없음
public class Student {
public int studentNumber;
public String studentName;
public int grade;
public Student() {}
public Student(int studentNumber,String studentName,int grade){
this.studentNumber = studentNumber;
//변수 이름 같게하면 가독성이 좋아짐
this.studentName = studentName;
this.grade = grade;
}
public String showStudentInfo() {
return studentNumber + "학생의 학번은 " + studentNumber +
"이고, " + grade + "학년 입니다.";
}
}
public class StudentTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student studentLee = new Student();
studentLee.grade = 1;
System.out.println(studentLee.showStudentInfo());
Student studentKim = new Student(123456,"Kim",3);
System.out.println(studentKim.showStudentInfo());
}this가 하는일
- 인스턴스 자신의 메모리를 가리킴
public static void main(String[] args){
BirdthDay day = new BirthDay();
day.setYear(2000);public void setYear(int year){
this.year = year;
}setYear()와 day는 stack에 쌓이고 heap의 메모리를 가리킨다.
그래서 this.year는 heap메모리의 값이다. 그래서 꼭 this를 써주어야하고 this를 안써주실 시에는 대입되는 year가 year에 대입되는 모양이 되어버린다.
-
생성자에서 또 다른 생성자를 호출하는 this
(생성자는 원한다고 아무때나 호출되는 메소드와 다르다.
생성자는 객체가 생성될 때 호출된다.(new될 때 호출된다)
그러나 생성자에서 또 다른 생성자를 호출할 때 사용할 수 있는데
이 때 this를 사용한다.) -
자신의 주소(참조값)을 반환함
public class Person{
String name;
int age;
public Person(){
ex) int num = 10; (x)
this("이름없음",1); //(아무이름이 없을 때 초기화해두고 싶음)
ex) name = "aaa"; (o)
// 생성자의 역할은 인스턴스를 초기화하는 것
// 여기서 this를 호출할 때 String ,int와 매핑되는
// 똑같은 데이터 매개변수를 가진 construct를 찾는데
// 아래의 생성자와 매핑되여 호출되는데
// 아래의 생성자의 호출이 끝나야 인스턴스 생성이 끝나는 것
// 여기서 호출될 때는 인스턴스가 아직 생성이 다 된게 아니기 때문에
// 이것의 이전에 다른 코드를 집어 넣으면 오류발생
}
public Person(String name, int age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Person getPerson(){
return this; // 여기에서 반환된 this인 person2하고 같은 값임
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Person person = new Person(); //여기에 person하고
System.out.println(person);
// Person@1175e2db;
Person person2 = person.getPerson();
System.out.println(person2);
// Person@1175e2db;
}- 클래스에 생성자가 여러 개 인 경우, this를 이용하여 생성자에서 다른 생성자를 호출할 수 있음
- 생성자에서 다른 생성자를 호출하는 경우, 인스턴스의 생성이 완전하지 않은 상태이므로 this() statement 이전에 다른 statement를 쓸 수 없음
public class Customer {
protected int customerID;
protected String customerName;
protected String customerGrade;
int bonusPoint;
double bonusRatio;
String agentID;
double saleRatio;
public Customer() {
customerGrade = "SILVER";
bonusRatio = 0.01;
System.out.println("Customer() call");
}
public int calcPrice(int price) {
bonusPoint += price * bonusRatio;
return price;
}
public int getCustomerID() {
return customerID;
}
public void setCustomerID(int customerID) {
this.customerID = customerID;
}
public String getCustomerName() {
return customerName;
}
public void setCustomerName(String customerName) {
this.customerName = customerName;
}
public String getCustomerGrade() {
return customerGrade;
}
public void setCustomerGrade(String customerGrade) {
this.customerGrade = customerGrade;
}
public String showCustomerInfo() {
return customerName + "님의 등급은 " + customerGrade +
" 이며, 보너스 포인트는 " + bonusPoint + "입니다.";
}
}public class VIPCustomer extends Customer{
double salesRatio;
private String agentID;
public VIPCustomer() {
//컴파일러가 super(); 를 넣어줌 (디폴트 생성자)
bonusRatio = 0.05;
salesRatio = 0.1;
customerGrade = "VIP";
System.out.println("VIPCustomer() call");
//customer쪽의 생성자가 먼저생성이 된다음에 VIP가 생성됨 그래서
//이름과 아이디를 만들수가있는거임
//인스턴스 변수는 인스턴스가 생성될 때 생성된다.
//그렇기 때문에 인스턴스 변수의
//값을 읽어오거나 저장하려면 인스턴스를 먼저 생성해야한다.
//인스턴스 변수는 객체가 생성될 때니까 부모생성자가 생성될때
//(객체가 생성될때)니까 제일 위에 말이 나오는거임
}
public String getAgentID() {
return agentID;
}
}