Spring DI( Dependency Injection )
- spring framework의 핵심.
- 2002년에 Rod Johnson이 시작한 프로젝트.
- 경량프레임워크 (가볍다 - 빠르다)
- 모듈로 개발하기 좋다. (기능을 추가하거나 제거하기 좋다. - 유연한 구조)
- 초기에는 Spring IoC(Inversion of Control)라는 이름으로 불림 > Spring DI로 변경
- Srping DI : Spring 객체(bean)들의 생명주기를 관리, 의존성주입하여 코드의 결합도를 낮출 때 사용.(테스트, 유연성 향상)
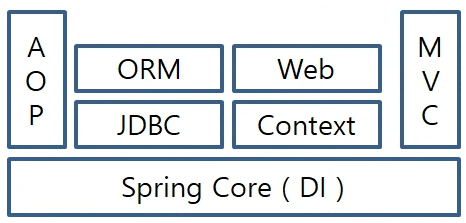
- AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming) : 관점지향 프로그래밍 (횡단관심사 처리 - 로킹,트랜잭션, 보안,,,)
- business logic과 공통코드를 분리할 수 있다.
- JDBC : JDBC의 기능개선
- ORM : DB Framework과 연동.(MyBatis, Hibernate, JPA)
- Context : JNDI를 지원
- Web : Web Framework와 연동 (Apache Struts
- MVC : MVC pattern을 손쉽게 사용.
- Spring Boot : 최소설정으로 독립실행형 애플리케이션을 개발할 때(MSA) , 내장형 서버 제공(Tomcat, Jetty)
- Spring Security : 보안 기능 제공
- 대규모 엔터프라이즈 애플리케이션을 개발할 때 사용.
Spring DI
-
강 결합( Strongly couplead )
-
약 결합( loosely couplead )를 손쉽게 사용
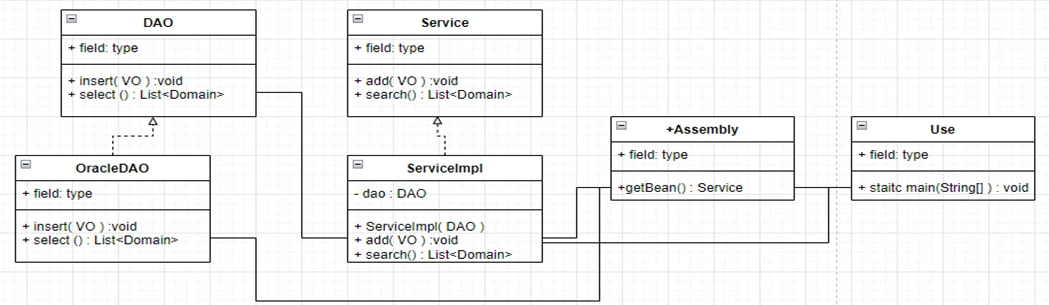
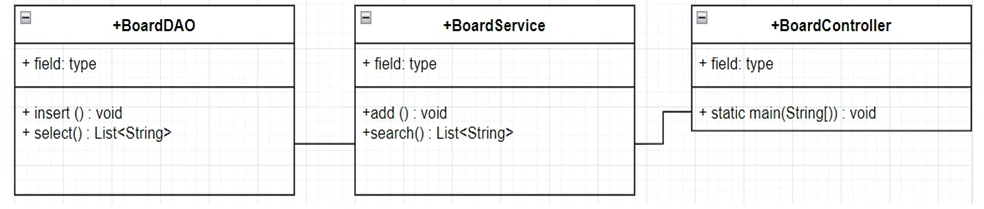
- DAO : interface에서는 DB작업 목록만 기술.(구현 클래스에서 구현)
- Service : interface에서는 업무목록만을 기술.(구현 클래스에서 구현)
- Assembly : Service에서 어떤 DAO를 사용할지를 결정하고 DAO를 생성하고 Service에 의존성 주입하는 코드를 구현
- Use : Assembly를 생성하고 의존성 주입받은 service객체를 얻어, service객체가 제공하는 기능을 사용하게된다.(Controller의 기능)
Spring DI => 약결합
- 의존성을 주입하고, 의존성을 주입받을 객체를 찾고 얻기 위해 Spring Container를 사용.
- 의존성을 주입하고, 의존성을 주입받을 객체를 찾고 얻기 : Assembly
- 실행하기 위해 별도의 Container가 필요하지 않는다.
- Container : Servlet/JSP는 실행하기위한 Container인 WAS필요
Spring Container
- Bean의 lifeCycle(생성, 사용, 소멸)을 관리, 환경설정, 의존성 주입, 환경설정파일(XML)을 로드하고 관리하는 일.
- BeanFactory, ApplicationContext, WebApplicationContext를 제공.

Bean
- Spring Container가 객체를 생성하고, 생명주기를 관리하는 대상클래스를 지칭하는 용어.
- 설정파일에 등록되거나, annotation으로 사용할 수 있다.
- bean은 Spring Container에서 singleton 방식으로 하나의 객체만 생성되고 사용.(속도향상, 메모리 절감)
- Bean을 요청 할 때마다 생성하고 싶으면 설정파일에서 scope="prototype"으로 설정하여 사용.
- 사용법
- 설정파일(applicationContext.xml)에 bean등록.(등록된 클래스는 싱글턴 객체로 생성된다.)
-
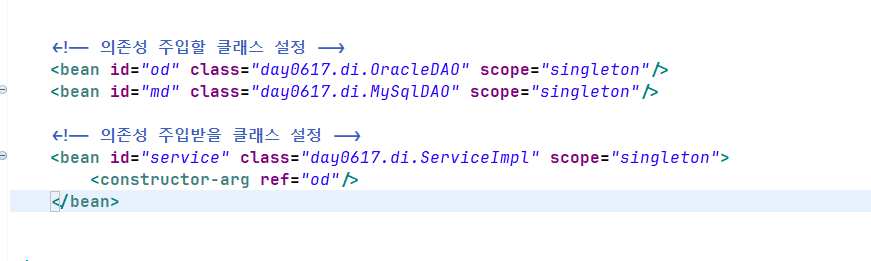
1.1 의존성 주입할 클래스를 설정
<bean id="객체명" class="패키지명.클래스명" scope = "singleton"/> <bean id="od" class="day0617.OracleDAO" scope="singleton/> -
1.2 의존성 주입받을 클래스를 설정하고, 의존성 주입.
<bean id="객체명" class="패키지명.클래스명" scope = "singleton"/> <constructor-arg ref="의존성주입할객체id"/> </bean> <bean id="service" class="day0617.ServiceImple" scope="singleton"> <constructor-arg ref="od"/> </bean>
-
- Spring Container생성 (log4j에 의존성이 있다.)
ApplicationContext ac= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("패키지명/설정파일명.xml") ApplicationContext ac= new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("절대경로/설정파일명.xml") - Spring Container로 부터 Bean을 얻는다.
Service service = ac.getBean(의존성주입받은클래스명.class);
scope = "singleton"
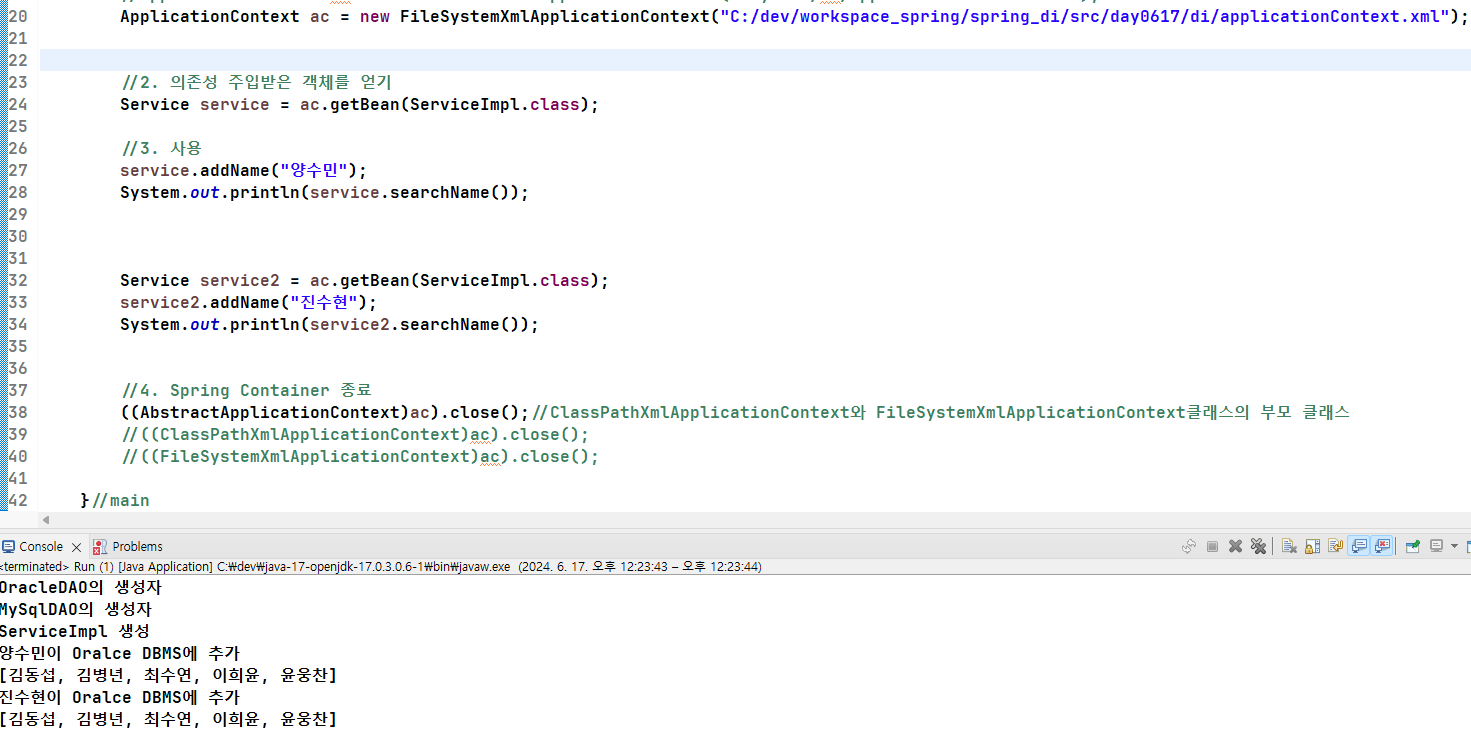
- scope이 singleton이라면 하나의 객체만 생성되고 사용된다.
scope = "prototype"

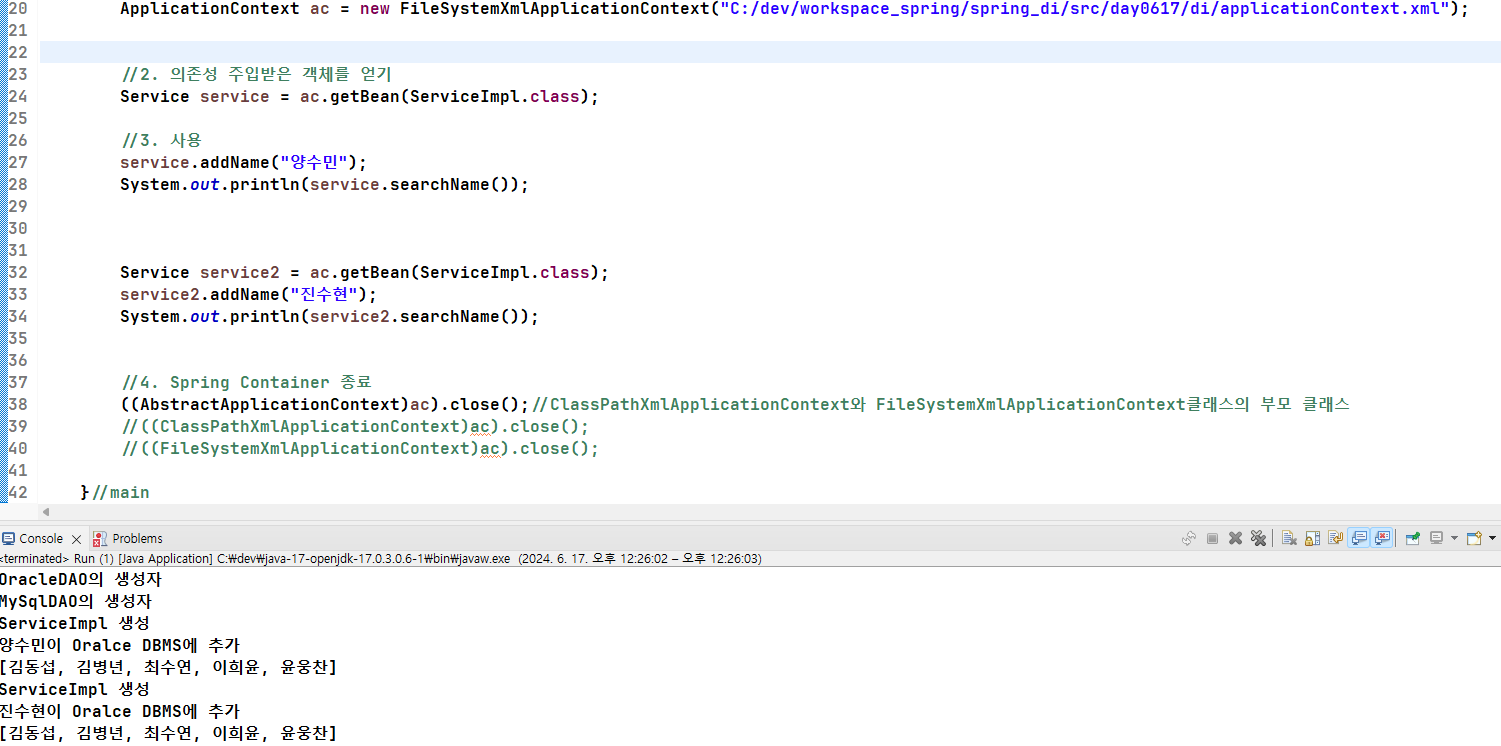
- scope이 prototype이라면 Bean을 얻어올 때 마다 객체가 만들어지고 사용된다.
Spring Container에서 bean생성
<bean id="객체명" class="패키지명.class명" scope="singleton"/>- scope속성은 getBean으로 객체를 꺼낼때 마다 생성하는 prototype 속성값과 하나의 객체만 만들고 사용하는 singleton을 사용할 수 있다.
bean으로 등록된 객체들은 Spring Container가 생성하고 찾아서 반환한다.
- 문법 )
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext({"설정파일",,,});- 설정파일이 여러개라면 배열로 처리.
- spring 2.5.3 이하 ) - 권장하지 않는다.
클래스명 객체명=(Casting)ac.getBean("찾아낼 객체의 id"); - spring 2.5.3 이상 ) -
클래스명 객체명=ac.getBean("클래스명.class");//패키지명.클래스명.class - 에러)
- 같은 이름의 클래스가 다른 id로 등록되어 있을 때 error가 발생한다.
<bean id="test1" class="day0617.Test" scope="singleton"> <bean id="test2" class="day0617.Test" scope="singleton">ac.getBean(Test.class);- 입력되는 class에 해당하는 class를 찾기 때문에 여러 개의 bean이 검색되므로 error가 발생한다.
- 같은 이름의 클래스가 다른 id로 등록되어 있을 때 error가 발생한다.
- 해결)
- 한정자 사용
ac.getBean("아이디",클래스명.class);
- 한정자 사용