Spring Security란 ?
Spring기반의 어플리케이션의 보안(인증과 권한)을 담당하는 프레임워크이다.
Spring security는 Filter기반으로 동작한다.
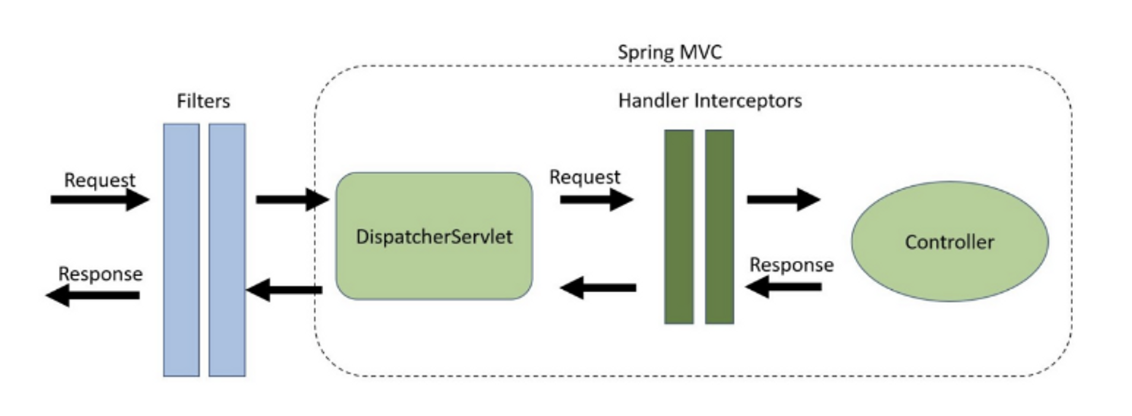
- Filter : dispatcher servlet으로 요청이 도착하기 전에 동작한다. spring에 종속적이지 않다.
- Interceptor : dispatcher servlet을 지나고 Controller 도착하기 전에 동작한다.
위 그림을 이해하고 가면 좋다. 필터와 인터셉터의 자세한 내용은 다음에 자세히 작성해보겠다.
목표
- spring security 아키텍처 기반에서 인증절차가 어떻게 진행되는가?
- 커스터마이징된 인증절차 개발시 어떤 작업을 추가로 해야하는가?
개발 환경 셋팅
build.gradle에 의존성 추가 필요
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-security'
출처:https://www.baeldung.com/spring-mvc-handlerinterceptor-vs-filter
위 이미지는 가장 많이 보이는 아키텍쳐이다. 참고하면 이해하기 좋다.
시큐리티에서 주요 컴포넌트는 아래 세가지 클래스이다.
- SecurityContextHolder
- SecurityContext
- Authentication
아이디/패스워드로 인증에 성공하면 사용자의 principal과 credential 정보를 최종적으로 SecurityContextHolder에 보관한다.
spring security는 내부에 인증절차가 이미구현되어 있다. 인증절차를 이해하고 나면, 구현체와 설정을 통해 새로운 인증 절차를 추가할 수 있다.
인증절차는 어떻게 진행되는가?
-
Client가 어플리케이션에 요청을 보내면, servlet Filter에 의해서 Security filter로 security 작업이 위임되고 여러 security filter 중에서 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter(Username and Password Authentication 방식에서 사용하는 AuthenticationFilter)에서 인증을 처리 한다.
-
AuthenticationManager가 가지고 있는 provider목록을 순회하면서 provider가 실행가능한 경우에 provider의 authenticate메소드를 호출하여 인증절차를 수행한다.
- AuthenticationManager
- AuthenticationManager는 인증을 처리하는 방법을 정의한 API이다.
- AuthenticationFilter에 의해 동작한다.
- 인증을 처리하면 SecurityContextHolder에 Authentication값이 세팅된다.
- ProviderManager
- AuthenticationManager의 가장 일반적인 구현체이다.
- AuthenticationProvider 목록을 위임받는다.
- 각 AuthenticationProvider는 인증 성공,실패,결정할 수 없음을 나타낼 수 있고, 나머지AuthenticationProvider가 결정을 할 수 있도록 전달한다.
- AuthenticationProvider
- 각각의 AuthenticationProvider는 특정 유형의 인증을 수행한다.
- id,pwd 기반의 경우 - username,pwd가 유효한지 검사
- saml 기반의 경우 - saml assertion을 수행 후 authentication 리턴
- UserDetailsService로 토큰의 사용자 아이디를 전달하여 DB에 존재하는지 확인한다. DB 회원정보를 UserDetails라는 객체로 반환한다.
- 각각의 AuthenticationProvider는 특정 유형의 인증을 수행한다.
인증 절차 Custom하기
- CustomAutenticationProvider
-
provider 내부에서 인증절차를 수행할 뿐 아니라, 추가적으로 supports메소드를 통해서 token타입에 따라서 언제 provider를 사용할지 조건을 지정할 수 있다.
-
supports메소드를 override하여 provider의 동작 여부를 결정 할 수 있다.
-
커스터마이징된 token을 사용하는 경우, provider 동작조건을 제한함으로써 다른 인증 수행하는 provider에게 영향을 주지 않는다.
@Component
@ReguiredArgsConstructor
public class CustomAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticationProvider {
private final CustomUserDetailService customUserDetailService;
private final PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
String userName = authentication.getName();
String password = (String) authentication.getCredentials();
UserDetails user = customUserDetailService.loadUserByUsername(userName);
if (user == null) {
throw new BusinessException(ResponseCode.USER_NOT_FOUND);
}
if (!this.passwordEncoder.matches(password, user.getPassword())) {
throw new BusinessException(ResponseCode.INVALID_PASSWORD_ERROR);
}
return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(user.getUsername(), password, user.getAuthorities());
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class‹?› authentication) {
return UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class.isAssignableFrom(authentication);
}
기본 인증절차
1. provider 내부에서 username을 가지고 사용자 정보 조회
2. 사용자 정보가 유효한지 판단 - pwd 일치하는지 등 커스텀 확인가능
3. AuthenticationToken에 사용자정보 세팅
(token자체가 Authentication 객체이기 때문에, 이후에 SecurityContextHolder 내부 context 객체에 token 값이 저장되어 있다.)
- CustomAuthenticationToken
- spring security는 기본적을 제공하는 token이 존재한다.
(ex) AnonymousAuthenticationToken,UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken)
기본 제공 token 외에 추가적인 필드들을 가져야하는 경우, 별도의 token 생성한다.
- WebSecurityConfig
- WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter를 상속받아 security관련 설정을 관리하는 클래스이다.
private static final String[] PERMIT_URL_ARRAY = {
"/api-docs",
"/swagger-resources",
"/swagger-resources/**",
"/configuration/ui",
"/configuration/security",
"/swagger-ui.html",
"/security/**",
"/**/swagger-*/**",
"/error"
};
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf().disable()
.exceptionHandling()
.authenticationEntryPoint(jwtAuthenticationEntryPoint)
.accessDeniedHandler(jwtAccessDeniedHandler)
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers(PERMIT_URL_ARRAY).permitAll()
.anyRequest()
.authenticated()
.and()
.apply(new JwtSecurityConfig(tokenProvider));
}
-
permitAll()은 해당 요청에 대한 접근을 모든 사용자에게 허용하는 역할을 한다.
하지만, 요청 처리 과정에서 적용되는 모든 필터들을 무시하지는 않는다.
그저 해당 요청에 대한 인증 정보가 없더라도(모든 필터를 처리한 후에도 securityContext에 인증정보가 없더라도), 접근이 허용된다는 의미이다.
-> 로그인,회원가입같은 API은 인증절차가 필요없음으로 접근을 허용한다. -
보통 JWT와 같은 인증 filter단에서는 직접에러를 던지지않으며 ,401
-> jwtAuthenticationEntryPoint & jwtAccessDeniedHandler
마침..
기본적으로 security를 적용하면서 공부했던 내용과 custom해서 사용했던 것들을 정리해보았다.
다음에는 JWT 적용하는걸 정리해보겠다.
